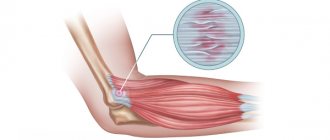
Epicondylitis of the shoulder is an inflammatory lesion of tissue in the shoulder area, which is expressed by pain in the area of the elbow joint on the outer surface.
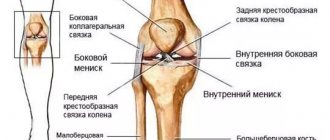
The bones of the shoulder have condyles at the edges - thickenings; on their surface there are epicondyles, they are intended for attaching muscles.
Systematic overstrain of the forearm muscles is the main factor in this disease. According to statistics, brachial epicondylitis accounts for 21% of arm diseases that arise as a result of professional activities - for example, the second name for epicondylitis is “tennis elbow.”
Treatment
Most often, treatment involves restricting arm movements. In acute epicondylitis, the limb must be secured with a bandage.
The disease is highly treatable. The treatment regimen is determined by the attending physician. As a rule, a set of procedures is recommended - drug therapy:
- Use of ointments and gels;
- Injections into the area of inflammation (hydrocortisone or methylprednisolone);
- Vitamin B injections.
As well as folk remedies and physiotherapy:
- Shock wave therapy;
- Acupuncture;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Phonophoresis and electrophoresis;
- Laser therapy;
- Currents Bernard;
- Paraffin treatment;
- Cryotherapy.
After an exacerbation of the disease, therapeutic exercises help restore the functionality of the joint.
Epicondylitis
Epicondylitis
is a degenerative inflammation of the musculoskeletal system. The disease is accompanied by pain in the elbow joint. Pathology begins to develop in the area where the tendons attach to the forearm. Appears on the inner and outer sides of the joints. Epicondylitis appears after grueling physical training on the forearms. Minor tendon injuries occur in the elbow joint.
Kinds
There are two types of epicondylitis:
- External (lateral). The pathology affects the tendons that attach to the lateral epicondyle. Occurs against the background of monotonous actions, for example, among plasterers and painters. The muscles become overstrained, and pain appears when straightening the forearm or turning the hand.
- Internal (medial). The tendons located along the internal epicondyle are susceptible to inflammation. It has a chronic course and can affect the ulnar nerve
Traumatic and post-traumatic epicondylitis can also be diagnosed. The first is typical for people over 40 years old. Manifests itself as a result of arthrosis or osteochondrosis. Post-traumatic epicondylitis occurs during the rehabilitation period when doctor's instructions are not followed.
Causes
The causes of the pathology are monotonous actions repeated on a constant basis. Frequent rotation and extension of the forearm leads to epicondylitis. The disease is typical for tennis players, massage therapists, painters, carpenters, tractor drivers, milkmaids, laborers and people in other professional fields associated with standard activities.
The provoking factors of pathology are:
- standard elbow movements repeated over and over again;
- injuries to this area;
- muscle strain;
- impaired blood circulation in the elbow;
- bone pathologies.
Symptoms and signs
Literal epicondylitis has the following symptoms:
- localized pain in the external elbow joint;
- weakened muscles when rotating the hand;
- obvious pain when lifting small weights;
- sensitivity when pressing on the affected area.
Medial epicondylitis manifests itself:
- weakening of muscles during the grasping reflex;
- pain syndrome when pronating at a right angle and when flexing the forearm;
- pain when palpating;
- compaction in the affected area.
Which doctor treats epicondylitis?
If you suspect a pathology or to diagnose this disease, you can contact an orthopedist or traumatologist. After completing complex treatment, physiotherapists and rehabilitation specialists participate in the rehabilitation process.
Diagnostic methods
First, the patient is examined and a painful point in the elbow joint is identified. The patient should then undergo a series of resistance tests while actively abducting the shoulder. It is necessary to bend and straighten the hand several times. Suspicion of a chronic course is checked by radiography.
To identify excess fluid in the humerus, an ultrasound of the joint and soft tissues is performed. MRI helps evaluate the condition of the ligaments and bone structure in the affected area.
Our clinic has its own diagnostic facilities (CT, ultrasound, MRI). Without leaving the clinic, you can make a diagnosis, see all the necessary doctors and immediately receive appropriate treatment.
Treatment methods for epicondylitis
For therapy use:
- Immobilization. A light plaster cast is applied for 10 days and the arm is suspended in a sling.
- Physiotherapy. Cold is applied to the sore joint.
- Medicines. Ointments and gels.
- Medical blockades. Methylprendisolone and hydrocortisone are used.
- Surgery. Under general anesthesia or anesthesia, the affected areas of the tendon are excised.
results
After timely manipulations, pain in the affected area decreases and blood circulation normalizes. The patient can flex and extend the elbow joint without problems. The overall condition improves, inflammatory processes go away. By following a daily routine and gentle exercises, it is possible to achieve positive results within a few months.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
During the rehabilitation and recovery period, nutrition should be adjusted and fatty and chemical foods should be removed from the diet. You should give up alcohol and smoking. Do physical exercise without effort, walk in the fresh air more often. The same type of movements that affect the joint should be avoided. At first, wear an elastic bandage.
Lifestyle with epicondylitis
The following rules should be followed:
- take a comfortable position during monotonous work, changing it periodically;
- avoid stereotypical actions that create stress on the elbow;
- eat in such a way that there is a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the diet;
- take massage courses from time to time;
- take mineral complexes.
Track.
article Prev. article
Prevention
- It is possible to avoid the development of epicondylitis of the shoulder if you load your arms moderately and protect the joints from injury or hypothermia.
- Before physical activity, you need to do a warm-up.
- You should consume foods containing calcium and vitamins more often.
- It is important to get rid of bad habits, since drinking alcohol and smoking contribute to poor absorption and excretion of calcium from the body.
At the first signs of epicondylitis, you should immediately consult a doctor.
What is epicondylitis of the shoulder joint?
Epicondylitis of the shoulder is a degenerative-inflammatory lesion of the tissues in the shoulder joint: the epicondyles and the tendons attached to them.
The humerus has at its ends so-called condyles - bone thickenings, on the surface of which there are other protrusions - epicondyles, which serve to attach muscles.
The main cause of epicondylitis is chronic overstrain of the forearm muscles, in most cases during professional activities.
Brachial epicondylitis accounts for 21% of occupational hand diseases.
Types of shoulder epicondylitis
There are two main types of epicondylitis:
- External (lateral), in which the tendons extending from the external epicondyle of the humerus are affected;
- Internal (medial), when the attachment point of the muscle tendons to the internal epicondyle of the humerus is affected.
The muscles coming from the external epicondyle extend the elbow, hand and fingers, and are responsible for supination (outward rotation) of the hand and forearm. The tendons of the flexor muscles of the elbow, wrist and fingers are attached to the internal epicondyle. These muscles provide pronation of the forearm and hand.
Causes of shoulder epicondylitis
The main cause of epicondylitis of the shoulder joint is regular trauma to the tendons under light but systematic loads. Constant continuous work of muscles and tendons causes ruptures of individual tendon fibers, in place of which scar tissue subsequently forms. This gradually leads to degenerative changes in the joint area, against the background of which an inflammatory process begins to develop.
Risk factors that provoke the disease include:
- Specifics of professional activity;
- Participation in certain sports;
- Presence of concomitant diseases.
Epicondylitis of the shoulder is often diagnosed in people whose main activity is associated with repetitive hand movements: drivers of various vehicles, surgeons, massage therapists, plasterers, painters, milkmaids, hairdressers, typists, musicians, etc.
Among athletes, tennis players and golfers are most prone to this disease. It is not for nothing that lateral epicondylitis is also called “tennis elbow,” and medial epicondylitis is also called “golfer’s elbow.”
Among other diseases, epicondylitis is often accompanied by cervical and thoracic osteochondrosis, glenohumeral periarthritis, and osteoporosis.
causes
causes
The most common provoking factor leading to the formation of microdamages in the tissues of the external meniscus area, as well as the development of inflammation, is playing sports associated with a fairly high functional load on the muscles of the forearm and hand. External epicondylitis is called “tennis elbow” because the disease is most common in tennis players.
Also, the development of epicondylitis may be associated with exposure to provoking causative factors not related to sports, these include:
- Professional human activity associated with constant high dynamic and static loads on the forearm and hand (painters, mechanics, artists, carpenters).
- Age - the older the person, the higher the likelihood of developing degenerative-dystrophic processes in the tissues and structures of the area of the external epicondyle, leading to their destruction and the development of the inflammatory process. In this case, the pathological process mainly develops against the background of normal functional loads.
- Previous injuries leading to the formation of scars in the area of the tendons and bone base, which can then become inflamed.
- A long-term inflammatory process in the area of the structures of the elbow joint, caused by a specific infectious or autoimmune (formation of antibodies to the body’s own tissues) process.
- A congenital change in the properties and strength of connective and bone tissue, caused by disturbances in the genome, while the inflammatory process in the area of the external epicondyle develops already in childhood.
During the diagnosis, the reasons that led to the development of the disease are necessarily clarified. This is necessary to select the most optimal therapeutic tactics, as well as to prevent the recurrence of a pathology such as external epicondylitis of the shoulder.
How does development occur?
The elbow joint is formed by the interaction of nerve endings with the lower part of the forearm. The humerus consists of a lateral and medial epicondyle (peculiar protrusions). The external epicondyle is firmly connected to the tendons, which is consequently responsible for the proper functioning of the hand as a whole.
With great physical activity, such protrusions wear out and minor damage to the bone tissue appears. All these effects provoke an inflammatory process, which will subsequently lead to the formation of external epicondylitis.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made based on complaints and external examination. X-rays for epicondylitis are informative only in the case of a long-term chronic course, when structural changes become noticeable in the affected joint: a decrease in bone density (osteoporosis), pathological growths (osteophytes).
MRI and biochemical blood tests are performed when it is necessary to differentiate epicondylitis from other diseases or injuries (fracture, carpal tunnel syndrome or GHS).