What it is?
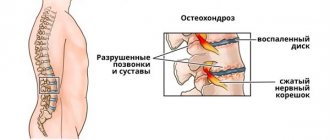
Spinal chondrosis is one of the most common diseases. This is a complex of degenerative-destructive changes, as a result of which the intervertebral discs are destroyed , and the cartilage loses its previous shape and elasticity.
Clinical picture
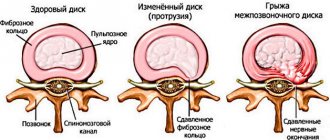
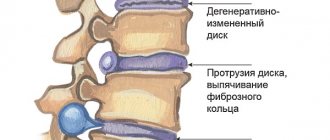
The intervertebral disc is a cartilage pad that provides flexibility and mobility to the spine. It consists of a nucleus pulposus surrounded by an annulus fibrosus. Since the disc does not have its own circulatory system, it must receive nutrients from surrounding tissues.
When the nutrition of intervertebral structures is disrupted, they can no longer fully perform their functions . When exposed to static and dynamic loads, the fibrous ring is destroyed and covered with cracks, which leads to the appearance of symptoms of chondrosis.
Subsequently, the nucleus pulposus is flattened and squeezed out.
Acute spinal chondrosis can lead to destruction of the intervertebral disc and the formation of a hernia
Do you need an X-ray of the spine?
X-ray of the spine or spondylography is one of the mandatory examinations for osteochondrosis, with the help of which structural disorders of the spine can be identified. Spondylography allows you to find pathological changes, for example, thinning of the intervertebral disc. Typically, for the cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral spine, x-rays are taken in two (and sometimes three) projections for greater detail.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible to identify pathologies associated with osteochondrosis: disc herniation and reduction of the lumen of the spinal canal, protrusion of the intervertebral disc into the spinal canal and compression of the spinal cord.
Risk factors and causes
The causes of acute chondrosis can be divided into three main groups:
| Dynamic | intense stress on the spine (for example, lifting weights) injures the discs and causes the development of degenerative changes. |
| Dysmetabolic | impaired nutrition and blood supply to the intervertebral discs provokes the development of dystrophic processes. |
| Gravitational | a long stay in an anatomically incorrect position leads to a shift in the center of gravity of the body, an increase in the load on the spine, and the occurrence of pathological processes. |
There are also factors that create a favorable background for the development of the disease .
These include:
- pathologies that are accompanied by malnutrition of the intervertebral discs (vascular pathologies, diseases of the endocrine system, metabolic disorders);
- prolonged stay in uncomfortable positions (for example, while working at a computer or driving a car);
- prolonged tension of one muscle group, leading to the appearance of muscle tension (during sleep);
- heavy physical labor (such work increases the load on the spine and leads to the development of “lumbar” chondrosis);
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of physical activity;
- presence of excess fat mass;
- state of chronic stress;
- hypothermia;
- acquired and congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system.
Note! The combination of several factors and/or causes significantly increases the risk of damage to intervertebral structures.
How is osteochondrosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis is based on a survey, physical examination and instrumental examination methods. Specific examination methods are determined during consultation.
The doctor begins the diagnosis by collecting an anamnesis: identifying the probable causes of back pain, establishing the location of the pain and its duration, identifying the presence of concomitant pathologies, for example, allergies, congenital diseases and drug intolerance. Next he moves on to inspection. The physical examination is performed standing or sitting. The doctor can identify the curvature of the spine, evaluate muscle strength and reflexes, and look at the color of the skin. To detail the picture of the disease, you need to consult with related specialists: a neurologist, neurosurgeon, oncologist, rheumatologist and phthisiatrician.
A neurologist makes a diagnosis of “osteochondrosis” if:
- regular aching back pain;
- increased pain when lifting weights, sneezing, coughing;
- numbness and a feeling of aching in the joints;
- decreased range of motion in joints;
- muscle spasm;
- damage to the nerve roots;
- changes on an x-ray of the spine.
Symptoms and diagnostic methods
The first sign of the disease is pain, the localization of which depends on the area of damage to the spinal column (thoracic region, neck, lower back).
In addition, chondrosis is accompanied by other symptoms characteristic of different parts of the spine:
accompanied by headache, weakness of the upper limbs, numbness of the fingers, pain in the shoulders, arms and throat. Sometimes patients diagnosed with chondrosis of the cervical spine complain of dizziness, toothache, loss of consciousness, hearing problems, weakened voice, and snoring during sleep.
Symptoms of degenerative changes in the intervertebral disc depend on the location Cervical chondrosis- Thoracic chondrosis can be asymptomatic or accompanied by characteristic symptoms such as weakness, intercostal neuralgia, chest pain, numbness of the fingers, pain in the heart and shoulder girdle.
- Lumbar chondrosis can be recognized by pain in the lower back (can radiate to the back, buttocks and legs), increased fatigue, irritability, insomnia, back stiffness, pain when sneezing and coughing. In advanced stages of the disease, dysfunction of the genitourinary system may occur.
When visiting a doctor, the patient must describe the nature of the pain, its characteristics and duration. The specialist’s task is to collect anamnesis, conduct a visual examination and palpation of the spine, and give directions for examination. The most effective way to diagnose chondrosis is MRI.
With the help of tomographs, you can see changes in any part of the spine, assess the nature of these changes and the complexity of the pathology. If desired, MRI can be replaced with X-rays or computed tomography. After receiving the images, the specialist will prescribe competent therapy, which is usually complex and long-lasting.
Where can osteochondrosis lead to?
Pain due to osteochondrosis is localized not only in the back. They spread to the upper and lower extremities. To your feet:
- buttocks;
- back and sides of the thighs;
- lower leg and inner ankle;
- back of the feet;
- toes;
- heels.
Pain can also spread into the arms to:
- deltoid muscle;
- the outer edge of the hand, down to the fingers;
- back of the hand;
- three middle fingers;
- ring finger and little finger (rare).
Treatment
Treatment for chondrosis is aimed at achieving the following results:
- strengthening the muscle corset;
- improving blood supply in the area of inflammation;
- elimination of pain syndrome;
- restoration of altered intervertebral discs;
- preventing further development of the disease.
First aid
When chondrosis worsens, a number of measures need to be taken so as not to aggravate the situation.:
- if pain in the neck occurs, put on an orthopedic collar; if pain in the lower back occurs, wear a corset;
- limit the load on the spine: do not lift heavy objects or sit at the computer;
- sleep on a hard bed;
- use an orthopedic pillow that supports the cervical spine in an anatomically correct position.
Drugs
Did you know that...
Next fact
For acute chondrosis, different dosage forms are used : tablets and ointments (for moderate pain), as well as injections (for intense pain).
Ointments prescribed for exacerbation of chondrosis have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and warming properties (Nurofen, Voltaren, Ketonal, Fastum gel, Indomethacin, etc.). After achieving remission, you need to consult a doctor to draw up a new treatment regimen.
Pay attention to the list of drugs used for acute chondrosis. Drug treatment of chondrosis involves the use of the following drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- painkillers;
- chondroprotectors;
- muscle relaxants;
- sedatives;
- Dietary supplements and vitamin complexes to improve metabolic processes.
With cervical chondrosis, it is important to prevent the development of cerebral circulatory disorders.
For this purpose they use:
- warming ointments (applied to the affected area of the neck, can be used during a massage);
- antispasmodics;
- vasodilators.
Note! The last 2 groups of drugs are used in the form of injections or tablets.
Surgery
If conservative therapy is ineffective, the doctor may recommend surgery to the patient. The scope of treatment in this case is determined by the severity of the disease and its clinical manifestations. During the operation, it becomes possible to remove the affected tissue, and therefore relieve pain and inflammation .
Exercise therapy
Gymnastics are not performed during the acute period of the disease, however, after entering the remission stage, you can begin to perform exercises. Gymnastics for cervical, thoracic and lumbar chondrosis are best done during the period of remission. However, each case is individual, so you should consult your doctor on this topic.
Special exercises will help strengthen your back muscles and remove muscle blocks, which will reduce the amount of medications used.
Since one of the reasons for the development of chondrosis is the weakness of the muscular corset of the back, physical therapy to strengthen the muscles becomes an important component of therapy.
The treatment complex should be compiled by an experienced specialist and should not cause pain, excessive muscle tension or fatigue.
In most cases, exercises are selected individually.
You can achieve lasting positive results with regular training.
Gymnastics will allow:
- strengthen muscles, reduce stress on the spine;
- eliminate muscle spasms in the affected area;
- increase the distance between adjacent vertebrae and prevent pinching of nerve roots;
- improve blood circulation;
- restore normal nutrition to the brain (if the lesion is located in the neck);
- normalize metabolic processes.
| The treatment complex for cervical chondrosis includes: | For thoracic chondrosis they do: | For lumbar chondrosis, the emphasis is on: |
|
|
|
If coordination of movements is impaired, it is better to perform exercises sitting.
Video: “Exercises for osteochondrosis”
Massage
Massage sessions are recommended in the subacute stage of the disease, but in some cases (with the doctor's permission) they are also carried out in the acute phase . During the first procedures, the specialist acts extremely carefully in order to prevent excessive muscle tension and increased pain. To do this, traditional techniques are used: squeezing, stroking, kneading (double ring, single, forceps).
Treatment at home
To reduce the symptoms of chondrosis at home, you can use traditional medicine:
- Take 120 grams of garlic and 3 large lemons. Grind it all in a meat grinder, put it in a two-liter jar, and pour boiling water over it. After 2.5 hours, the mixture will infuse and be ready for use. You need to take it in the morning (single serving - 100 ml), and store it in the refrigerator.
- Apply cottage cheese with a small amount of vinegar (literally a couple of drops) to a piece of cloth. Wrap the cloth around the lower back or neck (depending on the location of the affected area), hold for 2-3 hours.
- Take red capsicum, chop it finely, add 200 grams of liquid honey, a glass of alcohol and 100 ml of aloe juice. Infuse the mixture for four or five days. Soak a gauze bandage folded in four layers with the prepared infusion and apply it to the sore area. When a burning sensation appears, remove the compress, wipe your back dry and wrap it in a woolen scarf.
- Grind flowers, leaves and twigs of yellow acacia and pour in alcohol/vodka so that 3 tablespoons of plant material contain 500 ml of alcohol. When the product has been infused for a week, it can be used to prepare medicinal ointments and rub the affected areas of the back.
Pay attention to these articles:
- What drugs for spinal chondrosis are used to eliminate the symptoms of the disease?
- More information about the use of injections in the treatment of chondrosis can be found here
- Descriptions and names of effective ointments for back chondrosis are on the page
Prevention
A person is not able to influence the true cause of the disease (upright posture), but it is quite possible to prevent the premature development of chondrosis. All that needs to be done for this is to reduce the pathological impact of predisposing factors. Maintaining an active lifestyle, proper nutrition, eliminating excess fat mass, correcting body position during the working day, wearing high-quality shoes - all this will delay the development of the disease until old age.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
With cervical osteochondrosis of the spine, two main symptoms appear - cervicago and cervicalgia. Cervicago is an acute painful cervical lumbago that appears when moving the head and due to tension in the muscles of the cervical spine. Cervicalgia is aching and severe pain in the neck. Cervicalgia is accompanied by paresthesia - a disturbance of sensitivity in the form of numbness and a sensation of crawling on the skin.
If damage to the nuclei of the intervertebral discs of the neck progresses, cervical radiculitis appears - painful sensations in the back of the head. The pain is characterized by regularity; in addition, it intensifies occasionally, especially when moving the head.
This triad - cervicalgia, cervical radiculitis and cervicago - can be complicated by the syndrome of nocturnal hand dysesthesia, in which sensitivity is distorted. For example, a warm object may feel cold to your fingers, but if you shake your hands, sensitivity is restored.
Prevention
After successful treatment of cervical chondrosis, every person should know that only a change in lifestyle can prevent the recurrence of unpleasant symptoms. In the future, for preventive purposes, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- rejection of bad habits;
- proper nutrition: oxalic acid must be present in the diet;
- physical exercise: even with a sedentary lifestyle, it is necessary to do warm-ups and not give up morning exercises;
- comfortable sleep and rest: the mattress should be smooth and semi-hard;
- load control: do not lift heavy objects and follow a work-rest schedule.
To avoid having to repeat treatment for cervical chondrosis, do not neglect prevention and pay attention to the first symptoms, which may be a sign of relapse.
How to treat osteochondrosis at home?
It is not recommended to treat osteochondrosis at home. There are several reasons for this:
- at home it is impossible to accurately diagnose “osteochondrosis”, since back pain has different origins: neurogenic, vascular, viscerogenic (due to diseases of the internal organs) and psychogenic. That is, a person is treating osteochondrosis, but in fact, back pain arose, for example, due to kidney diseases;
- it is impossible to objectively assess the effectiveness of treatment without control diagnostics;
- the patient cannot adequately select treatment for himself, and folk remedies do not have an evidence base, and therefore, most likely, they are ineffective and may have side effects.
In one case, you can be treated at home - only after consulting a doctor who will correctly diagnose, prescribe adequate treatment and periodically monitor the effectiveness of therapy using X-rays, CT or MRI.
How to distinguish between heart pain or osteochondrosis?
Pectalgic syndrome is pain in the anterior chest wall, which may resemble pain in the heart. Pectalgia can be a sign of both osteochondrosis and heart problems.
However, pain during angina and heart attack differs from pectalgic syndrome due to osteochondrosis. The peculiarity of pain during angina pectoris and myocardial infarction is that it is of a compressive nature and spreads to the left shoulder blade, arm and jaw.
Pectalgic syndrome in osteochondrosis does not spread beyond the boundaries of the anterior chest wall, does not radiate to the arm and shoulder blade, and is not accompanied by fear of death. However, these are only subjective feelings. Therefore, to rule out cardiac pathology, you need to see a doctor and have an electrocardiogram done, which will reveal rhythm disturbances or signs of myocardial infarction.
If the pain begins to spread to the left shoulder blade, arm, jaw, is accompanied by a feeling of fear, is not eliminated by taking nitroglycerin and lasts more than 10–15 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.