A vertebral hernia is a rather dangerous disease, often leading to serious consequences with the end result being complete or partial disability. Registration of disability after surgery to remove a herniated disc, as a rule, is possible without any special problems only in the most difficult cases; in other cases, deciding on the issue of obtaining the status of a disabled person involves collecting the necessary package of documents and mandatory completion of the medical examination. Undoubtedly, every patient who has undergone surgery to remove an intervertebral hernia should know his rights and conditions for registering disability.
What is an intervertebral hernia?
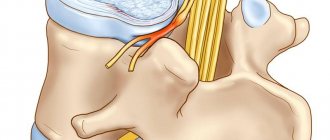
Intervertebral hernia refers to diseases of the spinal column in which inflammation and destruction of the intervertebral disc occurs. In this case, destructive processes are accompanied by destruction of the fibrous ring and displacement of the vertebrae from the main axis of the spine . Most often, intervertebral hernia appears in the lumbar region. It can occur in the cervical and chest, but this phenomenon is less common.
Intervertebral hernia is the most popular spinal disease for which surgical intervention is performed. The most common reason for surgery is severe back pain, as well as exacerbations even with minimal physical exertion.
When sent to a commission
The patient should be referred for medical examination in the following cases:
- systematic, severe pain;
- constant inflammatory processes;
- long period of use of sick leave;
- problems with the musculoskeletal system;
- especially pronounced fatigue;
- vestibulopathy syndrome;
- headaches in the form of cephalgia.
All these factors caused by a herniated disc are a significant reason for undergoing a medical examination for a disability group.
Stages of hernia
The course of the disease can occur with different symptoms depending on its stage.
Stages of development of a spinal hernia
There are the following stages of intervertebral hernia::
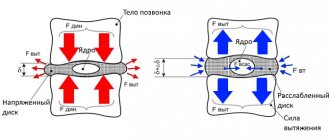
- vertebral disc protrusion . Accompanied by incomplete rupture of the fibrous ring, in which part of the nucleus can come out. At this stage, the pain is mild, there are lumbago, which intensify after physical exertion;
- partial prolapse of the intervertebral disc . Protrusion of the nucleus pulposus is most pronounced. The pain becomes chronic and localized in the affected area. The blood supply to the intervertebral disc is disrupted;
- complete prolapse of a vertebral disc . The nucleus almost completely leaves the annulus fibrosus and extends beyond it. With constant pain, limited mobility occurs due to severe pain. Shooting may occur in the leg or thigh. With a cervical hernia at this stage, a severe headache appears, the scapular area goes numb;
- flow of the nucleus beyond the ring (sequestration) . The intervertebral disc is displaced, causing pinching of the nerve endings of the spine. The syndrome is accompanied by severe and constant pain, leading to limited mobility of the spine in the area of pathology.
When the pain syndrome does not respond to conservative treatment, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Important! The effectiveness of treatment for intervertebral hernia depends on the stage of detection of the pathology and the start of treatment.
The earlier the disease is detected, the greater the chances of recovery.
Possible complications
Disability in a person is associated not with the hernial protrusion on the spine itself, but with damage to the tissues adjacent to it. The spinal cord is located above the lumbar region, but nerve fibers extend from it below. They intertwine and form complex plexuses, for which they received the name ponytail. Complications that lead to disability are associated with damage to the nerve fibers or vessels that are located around the hernial protrusion.
Among the complications that lead to disability are the following:
- When the spinal cord is compressed, the lower limbs lose sensitivity and the person becomes immobile. Compression is caused by a hernia, which is located in the area of the lower vertebrae of the thoracic region.
- Damage to nerve fibers from the cauda equina plexus can cause loss of sensation in the legs and pelvis. The person cannot move, and urinary and fecal incontinence appears. Caused by a hernia in the lumbar spine.
- Death of nerve endings and loss of sensation in any part of the body due to a pinched artery. A complication can be caused by a hernia in any part of the spine. The fibrous tissue of nerve endings needs constant nutrition and saturation with oxygen. When the nutrient artery is compressed, even for a short time, the tissue dies.
Modern surgical techniques make it possible to prevent such complications. But if a person develops one of the pathologies, then he is entitled to disability. But even after the highest quality surgery, a person needs a recovery period and should not work with weights weighing more than 3 kg. This should be taken into account when choosing a place to work.
At what stage of intervertebral herniation do people become disabled?
Intervertebral herniation can lead to disability even at the stage of intervertebral disc protrusion . Despite the fact that protrusion can be successfully treated, if the disease limits motor function, disability may be prescribed.
Disability for a herniated disc is assigned depending on the symptoms of the disease:
| First disability group | Assigned when it is impossible to recover at the main place of work due to partial or complete paralysis. Most often this occurs at the sequestration stage. |
| Second disability group | It is prescribed for prolapse of the vertebral disc core in the postoperative period, with persistent pain syndromes, limited mobility of the spine, when combined therapy and surgery do not bring results. |
| Third disability group | This category includes patients who experience mild pain in the presence of an intervertebral hernia, which worsens systematically. This condition is observed with disc protrusion. In such a situation, the patient is transferred to light labor. When adapting to new working conditions, disability can be removed. |
Please note in what cases in case of a herniated disc you can apply for disability. Indications for obtaining disability in case of intervertebral herniation may be:
- severe, constant, often with acute periods of back pain;
- frequent requests from the patient for a certificate of incapacity for work;
- ineffectiveness of continuous conservative treatment for more than four months;
- impaired coordination of the limbs, which negatively affects the quality of life;
- complications that disrupt the functioning of internal organs (genitourinary, cardiac, respiratory systems).
Important! Disability due to intervertebral hernia is assigned based on the results of a multi-stage examination, which is carried out by specialists in the field of spinal diseases.
The medical examination provides for several provisions that must be met in order to assign a disability.
Indications for passing the ITU
Experts advise applying for confirmation of disability in cases where:
- severe pain periodically worsens;
— conditions often occur that interfere with work, etc.;
- signs of the disease have become more pronounced;
- diseases of internal organs have developed;
- it became difficult to control movements.
In other words, the pain should not be controlled by medications (they no longer work). It is also necessary that the symptoms and discomfort last up to 4 months. Lack of motor control (for example, arms or legs) and problems with coordination in combination with other conditions (for example, problems with the heart, kidneys, etc.) are an indisputable reason for undergoing an examination.
It is worth keeping in mind: to assign a disability, the presence of a clear clinical picture is not at all necessary; the absence of a good result from the therapy is sufficient.
What examinations are needed to obtain disability?
Did you know that...
Next fact
In order for a medical commission to assign a disability to a patient, a whole range of measures must be completed , the results of which can confirm the need for disability. In addition, you should collect a package of necessary documents.
Medical measures include:
- examination of the spine using magnetic resonance imaging;
Intervertebral hernias are clearly visible on MRI
- X-ray examination of the spine;
- if there are circulatory disorders due to protrusion of the nucleus of the annulus fibrosus, it is necessary to conduct electromyography (study of the cerebrospinal fluid channels of the spinal cord);
- rheovasography (study of blood circulation in the pathological part of the spine), in the presence of a cervical hernia - rheoencephalography (study of the vascular system of the brain);
- lumbar puncture (extraction of cerebrospinal fluid for examination).
If an operation is performed, a neurosurgeon's report must be provided. In addition, you must provide the results of urine tests and a general blood test.
In addition to the conclusions of a medical examination of the spine for a hernia, in order to obtain disability, you must collect a package of documents:
- referral for medical and social examination;
- a certificate from a doctor confirming incapacity for work;
- patient's medical record;
- an extract from the medical record if there is no medical record.
If the patient confirms his disability or re-passes the commission, he should provide:
- certificate of disability;
- conclusion on the process of the rehabilitation period;
- examination results;
- passport, pension certificate, insurance policy.
Important! The presence of all documents does not guarantee the assignment of disability. This is especially true in cases where the patient refused to carry out procedures prescribed by the doctor or from inpatient treatment. In this case, the application for disability will most likely be denied due to the patient’s refusal of the recommended treatment.
Video: “Treatment of spinal hernia: opinion and personal experience”
Find out how therapy is carried out for a herniated disc:
- How much does surgery to remove a herniated disc cost?
- The surgical treatment of cervical hernia is described in the following article
- How to remove a hernia of the lumbar spine can be read here
- Drugs for the treatment of hernia in the lower back are described on the page pozvonochnik/drugie-zabolevaniya/mezhpozvonochnaya-gryzha/medicamentoznoe-lechenie-gryzhi-poyasnichnogo-otdela-pozvonochnika.html
- Physiotherapy, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis for spinal hernia
How are open surgeries performed?
An incision is made at the level of the hernia, at least 3-4 cm (up to length), the skin is cut, the muscles are separated, access to the spine is freed. Then the yellow ligament is opened: for this, the arches of the underlying and overlying vertebra are removed with pliers so that the structures in the vertebral column can be seen canal.The nerve root is pulled aside with a special hook, and the hernia is cut out.
to length), the skin is cut, the muscles are separated, access to the spine is freed. Then the yellow ligament is opened: for this, the arches of the underlying and overlying vertebra are removed with pliers so that the structures in the vertebral column can be seen canal.The nerve root is pulled aside with a special hook, and the hernia is cut out.
Schematic illustration of hernia removal during open surgery
If the operation is performed for stenosis, everything proceeds in a similar way, but part of the ligaments and bone tissue of the vertebra is removed, sufficient to achieve decompression of the pinched nerve roots - in other words, to give them additional space.
Open surgery for spinal stenosis
The main difficulty of most open operations with resection of bone structures is that after the removal of parts of the vertebrae, destabilization of the spinal column occurs: the overlying vertebrae no longer have anything to rely on. To correct the situation, transpedicular fixators are installed - 4 to 6 screws are tightened to maintain the spine in the correct condition. Implanting any hardware looks cool only in comics, but in real life it is a risky undertaking.
Titanium screws providing stability to the damaged spine
Full recovery after open surgery takes 4-6 months, the patient cannot sit for a long time and has difficulty moving, and needs rehabilitation with the help of physiotherapy, massage, and medications.
Let's consider possible complications during open surgery.
- Irreversible damage to the nerve roots. To open the ligamentum flavum or resect part of an overlying/underlying vertebra, you need to press hard on the pliers. And even an experienced surgeon will not give a 100% guarantee that at this moment the instrument or bone fragment will not damage the nerve.
- Durotomy. Damage to the dura mater around the spinal cord. This is not such a rare event during spinal manipulation, which can lead to damage to nerve tissue and leakage of cerebrospinal fluid - liquorrhea. And this again means compression of the roots and spinal cord, pain and impaired movement, and the risk of developing meningitis.
- Formation of scars and adhesions. Contact of nerve roots with air provokes excessive scar formation. And even if the operation was successful, replacement of the nerve tissue in the root with connective tissue of the scar will neutralize the results of the operation and will lead to a repeated deterioration of the patient’s condition.
Despite the complexity and risks of open surgery, it is still performed regularly around the world. The main reason for such adherence to tradition is that open operations are undemanding to the hospital’s technological equipment. They do not need to buy expensive equipment and improve the qualifications of surgeons and medical staff.
Endoscopic operations require the acquisition of new equipment and training of doctors - and these are serious expenses.
An experienced neurosurgeon will understand the technology of endoscopic interventions in a week, but for this he needs to get training from German or American colleagues, and then perform at least 30 operations himself using Joimax or similar equipment. In Russia, such equipment is almost impossible to find: it costs 20,000,000 rubles - an adequate price for complex high-tech technologies, but an unrealistically huge amount of money for domestic hospitals.
Therefore, at the international clinic Medica24, patients regularly come with hernia, stenosis, and radicular symptoms: pain, impaired reflexes, movements - who have not received adequate help for years. Although our neurosurgeons could have long ago relieved them of the problem in a low-traumatic way, quickly and completely.
The sequence of the procedure for obtaining disability for a herniated disc
The main basis for obtaining disability due to a hernia is an entry on the patient’s chart about the presence of an intervertebral hernia . This indicates that the patient has undergone surgery, and conservative treatment does not bring the result necessary for normal functioning and ability to work.
In order to obtain disability, you must go through all stages of this process. This process involves studying the physiological state of a patient with a herniated disc, as well as studying aspects of his life.
Sequence of actions in the presence of a hernia to confirm disability and obtain disability:
- obtaining a certificate from the attending physician, which confirms the patient’s disability, from a neurosurgeon, neurologist;
- undergoing all medical measures to obtain both pictures of the disease;
- providing members of the medical and social examination with the necessary certificates, documents and examination results.
Read more about the procedure for obtaining disability in case of spinal hernia. In addition, the commission staff studies the social status of the patient. This is necessary in order to understand what kind of social assistance the patient received if he had the disease, as well as the patient’s income before the disease. The severity of the disease, the cause of its occurrence, and adherence to the doctor’s recommendations for treating the disease are considered.
The financial condition of the patient is significant for the commission's decision to assign the patient a disability . If there are additional incomes (dividends, other profits), then they will be forced to refuse to receive a disability subsidy.
The commission staff conducts a survey of the patient about his relatives, work activity, the ability to do simple work, life satisfaction and the ability to lead a limited lifestyle.
After going through all the procedures, the decision remains with the commission. You should know that disability must be confirmed annually . If there is progress in treating the disease, then the person can be recognized as legally competent.
Types of groups: conditions for assignment
There are three types of groups: first, second, third. They differ in the amount of monthly social benefits. The first and second prohibit working officially. You can increase or decrease your group by undergoing re-examination.
So you can go back to work. It is rare to be disabled for the rest of your life. Which group the patient will receive depends on the severity of the disease and the information provided. The commission may not give group 1 or 2 if there is not enough research done. The patient has the right to request the necessary referrals for examinations.
When issuing a group, the main condition is how complicated a person’s life is by the disease. Will he be able to live a full life and work?