15.09.2020
640
36421
31031
Save
Many people think that if you have a herniated disc, you will have to forget about physical activity. But that's not true. We tell you how to train for a hernia, which loads and exercises will be beneficial and which will be harmful.
Many people think that if you have a herniated disc, you will have to forget about physical activity. But that's not true. We tell you how to train for a hernia, which loads and exercises will be beneficial and which will be harmful.
General rules
After relief of pain, aseptic inflammation, and elimination of pinched spinal roots, the patient is referred to a physical therapy doctor. He will engage in further rehabilitation of the patient with the help of physical education or gymnastics. And with a quick recovery, the exercise therapy doctor will decide on the possibility of returning to classes.
People who have previously been actively involved in sports have already formed a strong muscle corset. Therefore, the goal of the classes is to improve blood circulation and microcirculation. But at the same time, serious stress on the area of the hernial protrusion should be avoided. Exercise therapy doctors recommend following the following rules during training:
- begin training upon reaching the stage of stable remission under the guidance of an instructor who will control the distribution of loads;
- During cardio training, walking rather than running is beneficial. An exception to this rule is hernial protrusion at the initial stage;
- Before training, do warm-up and stretching exercises;
- If any discomfort occurs, stop training and take a break for a couple of hours;
- exclude any exercise with axial load, such as lunges or squats;
- perform several approaches for 5-10 minutes with breaks, and do not train non-stop;
- perform exercises slowly, without jerking, avoid strong muscle tension.
It is necessary to use orthopedic devices - soft bandages or elastic corsets with rigid inserts made of plastic or metal. They prevent the displacement of discs and vertebrae, and contribute to the correct redistribution of loads on the parts of the spine.
Orthopedic corset for the back.
What not to do, or “red flags”
In conclusion, we list the “red flags”, or risk factors, the impact of which on the appearance of a hernia can be critical:
- excess body weight;
- improper lifting of weights, for example, on the shoulder and moving the load with a tilted spinal column. This results in very strong pressure on one edge of the intervertebral disc;
- constant wearing of corsets, leading to wasting of the back muscles;
- prolonged dehydration and fragility of cartilage, especially in the elderly;
- long period of immobility;
- an attempt to ignorantly repair a hernia on your own. Intervertebral hernias cannot be repaired; only surgery can help.
Finally, it should be recalled that even in a person with widespread osteochondrosis, properly organized physical activity will help better than a diligent attempt to avoid movement. If a person has a sedentary job, then the time spent with low activity must be compensated with proper increased exercise, for example, Norwegian walking and visiting the pool. Regular adherence to these simple, inexpensive and effective measures will lead to a significant improvement in the quality of life of a patient with back pain syndrome, the presence of a protrusion or hernia, and an increase in range of motion.
Exercise equipment
Many rehabilitation centers are equipped with special simulators to accelerate the recovery of patients with pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Particularly popular are the devices developed by Dr. Bubnovsky, who has long been involved in the rehabilitation of people with hernias, arthrosis, and osteochondrosis. Exercises are also allowed in a regular gym, but during training the patient must follow all the recommendations of the physical therapy doctor. Even those parts of the spine that do not have protrusions or hernias should not be subjected to excessive loads. Crunches, leg presses and other exercises that involve slow and smooth movements are prohibited.
Hyperextension
Hyperextension is a physical exercise for developing the spinal erectors, which are located most superficially among the deep muscles. Typically, during training, a “Roman chair” is used, which is a special bench with supports for the legs or hips. It is designed for performing strength exercises with your own weight as a weight.
Correct execution of hyperextension exercises contributes to the rapid formation of a strong muscular corset of the back, including the cervical spine.
The first training sessions are supervised by an instructor. He makes sure that the patient moves slowly, without jerking, with a low range of motion. If training is not carried out in a gentle manner, then the pathology progresses quickly.
Evminov's board
This is an orthopedic simulator designed for both treatment and prevention of all spinal diseases, including hernia. The Evminov board is a wide, durable board with a crossbar and a stop. Exercises selected by the physical therapy doctor are performed on the simulator. During training, dosed traction of the spine is combined with simultaneous strengthening of the deep spinal muscles. You can increase the effectiveness of exercises on the Evminov board by simply changing the angle of inclination of the simulator.
Evminov's board.
Features of the disease
The main manifestation of a spinal hernia, regardless of its location, is pain.
Signs of a spinal hernia always manifest themselves in pain
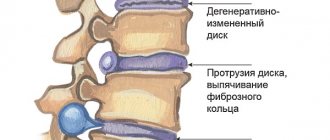
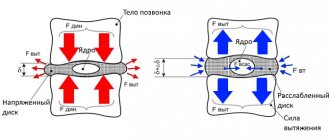
The intensity of pain depends not only on the size of the hernial protrusion and the degree of compression (squeezing) of the nerve roots, but also on external factors, for example, nutrition. If the patient does not receive enough proteins (collagen), minerals (calcium, phosphorus, iron), vitamins, the nutrition of the cartilage plates is disrupted. They are located between two adjacent vertebrae, and the space between them is filled with gelatinous pulp - a viscous liquid containing a small number of cartilage cells. The pulp is surrounded by a fibrous membrane (annulus fibrosus), which holds the nucleus in the center of the intervertebral disc and prevents it from leaking into the spinal canal.
Spinal motion segment
When the nutrition of the cartilage is disrupted, it begins to “dry out,” which leads to deformation of the intervertebral disc. Over time, the spine contracts and the nucleus pulposus moves beyond the annulus fibrosus. The displaced pulp compresses the spinal roots, which causes acute pain and severely limits the patient’s mobility, and swelling and muscle spasm in the area of the affected segment of the spine allow partial compensation of the compressive load. If measures are not taken in time to correct the pathology, a complete rupture of the connective tissue membrane may occur and the pulp may escape into the space of the spinal canal.
Intervertebral hernia. Stages
For conservative treatment of pathology, medications (chondroprotectors, glucocorticosteroids, NSAIDs, vitamin complexes), traction therapy (spinal traction), and drug blockades using analgesics are used.
Note! Therapeutic and recreational physical education is an effective method for the prevention of intervertebral hernias and the treatment of small hernial protrusions without signs of compression of the spinal roots. In more severe cases, exercise therapy is used as an auxiliary method during a period of stable remission, provided it is combined with other treatment methods: massage, high-protein and fortified diet, alternative medicine techniques (manual therapy, hirudotherapy, etc.).
Is it possible to play sports?
Before answering this question, it is necessary to understand what exactly is meant by this term. If we are talking about therapeutic physical education (physical therapy), which is used as one of the methods of conservative treatment of intervertebral hernia, then there are practically no restrictions for exercise (with the exception of an acute period of illness, severe pain, inflammatory and infectious diseases in the spine).
Exercise therapy classes have a minimal number of contraindications and proven effectiveness
Exercise therapy is a set of exercises aimed at preventing a specific disease, as well as the recovery and rehabilitation of patients after suffering pathologies (including diseases with the use of surgical treatment methods).
Exercise therapy is indicated for the treatment of hernias, as well as during the rehabilitation period after spinal surgery
Simultaneously with physical training, methods of psychological influence are developed that are necessary to develop a clear understanding of the goals of the classes and their importance in shaping the future prognosis of life and health.
Therapeutic physical culture is even used for the rehabilitation of patients who have suffered severe pathologies, for example, myocardial infarction. All complexes are developed taking into account the characteristics of a specific disease, and the exercises included in them are fully adapted for a specific group of patients, taking into account possible risks and consequences. In most cases, classes are conducted in medical institutions or sanatoriums under the guidance of a medical professional.
A set of exercises is selected by the attending physician
Sports have several fundamental differences from therapeutic and recreational methods, so the question of the possibility of continuing active training is always decided individually. The main differences between sports activities and exercise therapy:
- lack of an instructor with a medical education (most trainers in sports clubs do not have the appropriate education and necessary skills);
- discrepancy between the load and the level of individual mobility of the patient;
- high risk of injuries and damage that can lead to complete rupture of the fibrous ring and displacement of the disc nucleus pulposus into the spinal canal;
- unadapted techniques that do not take into account the characteristics of a particular disease.
Any physical activity must be appropriate to the condition of the patient with a hernia.
Note! Patients who were involved in sports before being diagnosed with a vertebral hernia are recommended to continue training according to an individual program, which will take into account the main diagnosis, concomitant pathologies and the degree of risk when exposed to a certain type of load.
Dumbbells