General information
As the body ages, the structures of the spine wear out. Joints, ligaments, and intervertebral discs are especially susceptible to negative changes. All changes that occur in the spinal column are purely individual and depend on many factors.
For some people, this disease is not age-related; its development can be triggered by other reasons. The symptoms of the disease are also highly individual. In some people, the clinical manifestations of degenerative changes are more pronounced, in others they are moderate. Also, the appearance of pain is directly influenced by the location of the pathology, its effect on the spinal cord or spinal roots.
Spondylosis deformans can develop in all parts of the spinal column. And the symptoms are determined by the localization of the pathological process. Doctors often diagnose osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis.
Which structures are subject to negative changes?
Degenerative age-related changes are most often observed in the following structures:
- intervertebral discs;
- facet joints;
- bone apparatus and ligaments.
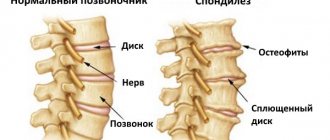
Over time, as the body ages, gradual wear and tear of all body tissues occurs. The annulus fibrosus and nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral discs also undergo changes. They weaken, the fibrous ring wears out, and the amount of fluid in the nucleus pulposus decreases.
This negatively affects the shock-absorbing properties of the intervertebral discs. The result is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, increasing the risk of hernia formation and deforming spondylosis.
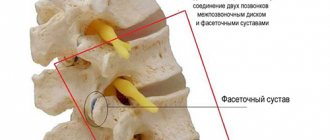
Facet joints, which are present in each vertebral body. Thanks to these structures, flexion, rotation and extension of the spine occur. The shell of these joints is cartilage tissue. This is a connective type of tissue that contains lubricant and also has a sliding surface.
When age-related degenerative changes occur in the facet joints, the cartilage tissue gradually decreases in size and bone growths called osteophytes are formed. These degenerative changes can lead to osteoarthritis and osteoarthrosis, which are characterized by joint hypertrophy.
Bone spurs form near the edges of the intervertebral disc plates. As a result, the following negative changes are observed:
- deterioration of blood microcirculation in vertebral structures;
- compaction of the end plates due to sclerotic processes;
- thickening or compaction of bone structures under the end plates.
Ligaments consist of fibrous tissue fibers, which are the connecting link for the vertebrae. Thanks to them, the spinal column is protected from excessive load. With pathological changes in this area, a loss of ligament strength occurs, and this is fraught with a direct negative effect on the spinal structures.
What is spondyloarthrosis
Spondyloarthrosis, also called simply arthrosis of the spine, belongs to the category of degenerative pathologies. With this disease, the so-called facet joints are damaged, followed by destruction of cartilage tissue. Typically, joints begin to deteriorate in the lumbar and sacrum areas. Interestingly, the disease is also called facet arthropathy.
Most often, the disease develops in people who have reached old age (approximately 70% of cases). This occurs as a result of ongoing age-related changes in the body. Unfortunately, recently the disease has become increasingly common among young people of working age. This is due to a number of features of the rhythm of life of a modern person - for example, low mobility and improper unbalanced nutrition.
To understand the mechanism of development of spondyloarthrosis, you should familiarize yourself with the processes that occur during the disease. Thus, the spinal column consists of individual bone elements - vertebrae, as well as intervertebral discs, all of which are connected into a single, fairly mobile system through various tendons and other elements. Almost every vertebra has processes and arches, between which there are small joints, which are called facet joints. The bone arches and processes themselves are thin and covered with so-called hyaline cartilage.
If the spine is affected by a number of negative factors (and there can be a whole set of them under modern living conditions and an irresponsible attitude towards one’s own health), then first of all it is the cartilage tissue that begins to suffer and collapse, precisely in the area of the facet joints. As a result, inflammatory processes are launched, the person experiences discomfort and pain. This also affects the condition of the tissues surrounding the affected element, including blood vessels, nerve endings, etc.
Symptoms of spondylosis in various parts
The clinical symptoms of spondylosis deformans are directly determined by the specific part of the spine in which degenerative changes develop.
The cervical spine is the most mobile, which makes it vulnerable to various disorders. Pain in the neck is very common if cervical spondylosis develops.
Painful symptoms can radiate to the shoulder girdle, to the elbow joint, and even down to the wrist joint and phalanges of the fingers. In the presence of osteophytes, compression of the nerve roots occurs, which transmit nerve signals to the limbs. In addition to pain, the disease manifests itself as weakness in the arms.
Sometimes it happens that osteophytes grow in the front part of this section, so it becomes difficult for a person to swallow. Common symptoms of cervical spondylosis deformans are:
- intermittent pain;
- pain radiates to the shoulder girdle, arm, hands and phalanges of the fingers;
- stiffness occurs in the neck or shoulder, it is observed most often in the morning after waking up, and the joints also become limited in movement;
- numbness in the shoulder or neck;
- muscle weakness, tingling in all parts of the upper limb;
- the appearance of a headache in the occipital lobe;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- difficulty swallowing.
If spondylosis deformans develops in the thoracic region, pain occurs. Most often, this symptom appears when a person bends his torso forward. Hyperkinesthesia also occurs.
Common manifestations of thoracic spondylosis deformans include:
- the appearance of pain in the top or middle of the back;
- pain during flexion and extension movements;
- the appearance of stiffness in the morning after waking up.
Lumbar spondylosis deformans is most often diagnosed in people over 40-45 years of age. Morning stiffness in the lower back occurs, and severe aching pain appears. Most often, several segments in this department undergo degenerative changes.
If a person remains in a sitting position for a long period of time (for example, during work), pain occurs due to compression of the lumbar vertebrae. But the intensity of painful sensations increases when lifting and carrying heavy objects, or when the body is sharply tilted.
Common symptoms include:
- recurrent lower back pain;
- the presence of stiffness in the morning after a person gets out of bed;
- numbness in the lower back;
- stiffness or limited movement in the lower extremities;
- muscle weakness or tingling in the lower leg, foot, or buttocks;
- difficulty walking;
- in advanced situations, with serious degenerative processes, bowel or bladder functions may be impaired.
The severity of symptoms directly depends on what stage the disease is at and how much the vertebrae have become deformed and worn out. Also, a person’s lifestyle is closely related to the occurrence of pain.
Consequences
Since the initial development of the disease is difficult to notice, if you have any pain in the spine, you should consult a doctor for examination. The earlier treatment begins, the higher the likelihood of normalization of processes in the spine.
Cervical spondylosis deformans can cause glenohumeral periarthritis. Spondylosis deformans occurring in the cervical region can trigger the occurrence of glenohumeral periarthritis. In this case, there may be a significant limitation in the mobility of the shoulder joints, as well as pain in the shoulders.
Spondylosis deformans must be treated, since a strong proliferation of osteophytes can affect the spinal cord, which can lead to paralysis . If in the first stages of the development of the disease there is a chance to avoid serious complications, then in an advanced form the process is irreversible.
In addition, as the disease develops, pain in the legs appears, lameness , which occurs due to pain in the calves, and loss of sensitivity in the skin of the gluteal muscles may develop.
Causes of spondylosis deformans
The key reason for the development of this pathology is the aging of the body, the gradual wear and tear of various segments of the spinal column. The human body experiences daily stress for many years, during which time dystrophic changes occur in different structures of the spine. Soreness and stiffness are a consequence of these changes. Moreover, if pathological changes occur in one segment, this invariably entails negative changes in neighboring segments.
Initially, the intervertebral discs are affected. The result is the development of osteochondrosis. This disease can be diagnosed even at a young age for various reasons. Those changes that develop in the discs cannot but affect other motor segments of the spine. The fibrous ring, the basis of which is collagen, becomes deformed, and the amount of fluid in the disc decreases. This impairs its shock-absorbing capabilities and the load is not distributed evenly. The disc becomes thinner and denser, and this is already fraught with pathological processes in the articular system, since the joints try to take on part of the load that falls on the spine.
When the disc becomes thinner, the cartilage tissue in the joints quickly wears out, this provokes an increase in the mobility of the spinal column, and these are favorable conditions for the nerve roots that are located nearby to be constantly irritated.
As a result, a compensatory reaction of the body develops - excessive growth of the bone structures of the periarticular capsules appears. Doctors call these bone growths osteophytes. As osteophytes continue to grow, compression on the nerve endings of the spinal cord increases. This is accompanied by severe symptoms.
The immediate causes that can cause the rapid development of spondylosis deformans include:
- hereditary predisposition. If at least one of the parents has disorders in the musculoskeletal system, if early osteochondrosis develops, this can be passed on to children at the genetic level;
- the presence of bad habits that negatively affect blood microcirculation - smoking, alcohol abuse;
- constant lifting and carrying heavy loads;
- maintaining a sedentary, sedentary lifestyle.
Prevention
Treatment of cervical spondylosis is a long and complex process . It is easier to prevent a disease than to figure out in the future how to normalize the condition.
Basic methods of prevention:
- use of orthopedic mattresses for sleep and rest;
- yoga classes;
- swimming;
- maintaining correct posture.
It is important to walk more, while keeping your back and head straight. People working at a computer should warm up their neck and shoulders at least once every 1-2 hours: make circular movements with their shoulders, tilt their heads in different directions.
Diagnostics
If a person has pain or stiffness in one part of the spine, doctors will need additional diagnostics in order to make the correct diagnosis. As a rule, this disease develops gradually as the body tissues age. A correct differential diagnosis should also be carried out, since the symptoms may be similar to other diseases of the musculoskeletal system, for example, osteochondrosis may develop.
First you need to contact a neurologist. He evaluates complaints and collects anamnesis. The following nuances are important for a specialist:
- when did the first unpleasant symptoms appear?
- what type of activity a person is engaged in, because this could also provoke the development of pathological processes;
- what exactly did the person do to reduce the severity of the pain, what medications did he take and which medications helped him get rid of the intensity of the symptoms;
- whether the pain radiates to other areas, joints or parts of the body;
- what exactly causes an increase in pain or after which the pain becomes less pronounced.
A neurologist performs an external examination of the spine, assesses the correctness of posture, how well movements are preserved, and whether there is spasm in the muscles. An assessment of the joints is carried out - hip, sacral.
Instrumental research techniques are key in making the correct diagnosis:
- radiography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
Using these methods, the doctor determines how severe the changes are in the ligaments, discs, muscles and nerves. If there are foci of an infectious process, scintigraphy may be additionally prescribed. Only after a comprehensive examination does the doctor make a diagnosis and prescribe subsequent therapy. The sooner treatment is started, the faster you can get rid of discomfort and stop the progression of the disease for a while.
Treatment of spondylosis deformans
In most situations, the course of the disease is slow, the person does not carry out any measures. But with the active development of deforming spondylosis, it is imperative to carry out conservative treatment or even radical surgery (in advanced, severe cases).
Conservative therapy is most often used using complex measures:
1. Acupuncture. Using this method, you can reduce the severity of pain in any part of the spine.
2. If the pain syndrome is severe, it is difficult for the patient to move; during the period of exacerbation, bed rest is recommended. Its duration is no more than three days.
3. Traction method. Spinal traction using various equipment (for example, Evminov's prophylactic) is rarely performed; after such treatment, it is possible to reduce the severity of pain and stiffness.
4. Massage. Thanks to manual influence on all segments of the spinal column, it is possible to improve blood microcirculation, reduce compression of the vertebrae by breaking up salt deposits, and eliminate muscle tension.
Drug therapy is mandatory in the treatment of spondylosis deformans. The doctor prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which can help relieve pain and stiffness. They are given either orally or by injection.
Drugs such as Mydocalm, Dicloberl, Dexalgin, Movalis, Revmoxicam, Remesulide, Nimesil and others are often used. The doctor also prescribes muscle relaxants, which help get rid of muscle spasms within a short period of time.
Remember that independent use of any medications is unacceptable, since many of them can provoke the development of adverse reactions in the body. Also, when using such medications, it is necessary to take into account possible contraindications. If there are chronic diseases of the digestive system, it is necessary to take gastroprotectors in parallel.
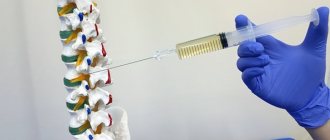
Administration of steroid drugs by the epidural route. This treatment is indicated in the presence of severe pain symptoms. This treatment is especially effective if there is swelling or an inflammatory process in one of the affected segments.
Typically, the steroid drug is administered together with a local anesthetic, for example, Novocaine. Such injections act almost immediately after administration, but the effect of their use usually lasts no more than three days. This makes it possible to quickly relieve the severity of pain and connect other methods of therapy.
Exercise therapy
According to most experts, this method has the greatest effect in the complex treatment of spondylosis deformans. By systematically applying moderate physical activity to the spine, you can maintain muscle tone.
Due to this, pain is reduced, the stability of the spinal column increases, and the condition of the ligaments improves. Degenerative processes stop developing. But a method such as physical therapy should be used only after the acute inflammatory process has been stopped and the pain from deforming spondylosis has been eliminated.
Physiotherapy
This includes:
- ultrasound treatment;
- electrical stimulation;
- ozokerite applications;
- electrophoresis;
- balneotherapy;
- cryotherapy.
Thanks to such procedures, you can get rid of stiffness in the joints and vertebrae and stop pathological changes in them. An important aspect of complex therapy is body weight control.
When there is a lot of weight, significant pressure is placed on the spine and all joints. Therefore, doctors recommend taking measures to correct weight. Additionally, you should eat a balanced diet and give up bad habits.
Degrees of the disease
It is necessary to clearly understand that spondylosis cannot form overnight, even if trauma contributed to this condition. It develops quite slowly, since bones need a certain period of time to grow. It is for this reason that the disease has certain stages of development:
- Primary or first degree. This is the very first stage, during which the disease only begins to manifest itself in terms of its development, but without expressing itself in any way externally. That is, there are practically no symptoms. Stage 1 spondylosis is characterized by small growths on the bone bodies of the vertebrae.
- The second stage of the disease is also called moderate spondylosis. The bone processes begin to increase in size, causing damage to tendons, muscle structures and nerve fibers. As a result, the patient begins to experience mild or insignificant pain. His movements become more constrained and it becomes more difficult for him to move. Stage 2 spondylosis deformans most often signals problems in the body, so it is at this stage that patients begin to see a doctor, skipping the initial stage of development of the disease.
- And the severe stage is degree 3. When a person’s condition is so advanced that the disease enters the very last phase of its development, then most often the bone growths on the vertebrae grow so much that they fuse almost all the mobility in the affected area of the back. This causes the muscle tissue to become tense. As a result, so-called spasms occur. They lead to an even more severe course of the disease, because in this case the body does not receive the normal level of blood flow, and, therefore, does not receive the full complex and volume of nutrients that are carried by the blood.