One day hospital 3rd KO
Malykhin
Sergey Aleksandrovich
11 years of experience
First qualification category
Make an appointment
Cervical lordosis is not exactly a diagnosis, but rather a designation of the normal position of the cervical spine. Normally, it should have a certain bend. But in the case when such a bend is too smooth or, on the contrary, exceeds permissible limits, they speak of diseases. These are hypolordosis and hyperlordosis. That is, when we talk about cervical lordosis in the context of a disease, we mean one of these conditions - as a rule, they have their own reasons that you need to know about.
Causes of hypolordosis
Smooth lordosis of the cervical spine can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Osteochondrosis. This is a disease associated with the gradual destruction of vertebral discs. It is quite common and may have no symptoms at first. Subsequently, osteochondrosis manifests itself as pain, the inability to turn the head in one direction or another, a feeling of “pins and needles” and numbness in the hands and fingertips.
- Injuries of the cervical spine (cervical spine). If during an injury one of the vertebrae moves forward, then a smoothing of the lordosis of the neck will be observed. This cannot be ignored, because the problem is accompanied by acute pain and severe discomfort. It is more difficult in cases where the injury produces delayed symptoms. For example, after a fall, blow or other injury, the neck may become sore only after five to seven days.
- Spondylolisthesis (vertebral displacement) of a non-traumatic nature. The cause of this problem is various factors: heredity, weak muscles, abnormalities in the structure of the spine, etc.
What exactly causes the straightening of the lordosis of the cervical spine cannot always be determined. But comprehensive diagnostics allows us to choose the right treatment for each patient. If you have any pain or discomfort in your neck, you should immediately contact a neurologist for help.
Normal limits
Smoothed lordosis often causes compression of nerve endings, constant pain, a feeling of numbness, and the appearance of a number of other symptoms. To identify a pathological condition, specialists have determined the normal range of neck movement in the absence of disease:
- Tilt to the right and left – 45 degrees.
- Rotation in each direction is 90 degrees, with the chin parallel to the shoulders.
- Bend the neck forward to the sternum - 45 degrees, the chin touches the chest.
- Tilt of the head back to back – 40 degrees.
If there are deviations from these values or restrictions in movement, a specialist may suspect a pathological process. It may be accompanied by an increase in lordosis or its smoothing. Both conditions are dangerous for humans and require clarification of the diagnosis and the prescription of correct treatment.
Causes of hyperlordosis
If the smoothed lordosis of the cervical spine suggests that the natural curve decreases, then in this case it, on the contrary, increases - as a result, the patient also experiences pain and various types of discomfort. The reasons for this problem may be:
- Ankylosing spondylitis. This is a very complex disease in which the spine fuses into one whole, that is, the intervertebral joints, which should be mobile, become overgrown. The person twists, bends and cannot move freely. This disease progresses with age, and therefore most often occurs at its peak in older people.
- Instability of the SHOP. If you turn your attention to hyperlordosis in time for this reason, then the changes that have occurred can be corrected and the person can be returned to a comfortable life. Most often, cervical instability occurs in people with injuries, weak muscle tone, and in old age or childhood. Occupation is also of serious importance; people who either constantly bow their heads or constantly raise their heads suffer from this problem. Dentists and, for example, painters are equally at risk.
- Psoriatic arthritis. This is an autoimmune disease that is not easy to diagnose. As the disease develops, it can affect any part of the spine.
Obviously, for the treatment of cervical lordosis of this type, not only the fact of the problem with the cervical spine is important. Not least of all will be the reasons, because some of them are very serious and require additional treatment.
Possible consequences
If urgent measures are not taken, pathological processes will start in the body, leading to serious consequences. External defect and pain will significantly reduce the quality of life.
Manifestation of complications of cervical lordosis:
- Intracranial pressure increases.
- Hands are partially immobilized.
- Decreased hearing and vision.
- The entire spine is curved.
- The spinal cord is compressed.
- Metabolism is disrupted.
Unfortunately, medical research statistics indicate a steady increase in such complications.
Diagnostics
To make the diagnosis itself, the doctor does not need a lot of data. As is correct, after a visual examination and x-ray, a specialist - in this case a vertebrologist (neurologist or therapist) - will be able to determine what exactly is wrong. But diagnosis is necessary in order to understand the cause of the disease and not to miss a dangerous condition if it exists, but is hidden. For these purposes the following are used:
- clinical blood test;
- MRI;
- ;
- electromyography;
- C-reactive protein (CRP) test;
- determination of HLA-B27.
Depending on the results of the examination, it will become clear what treatment for cervical lordosis is indicated for a particular patient.
Diagnostic tests
To identify the cause of hyperlordosis, during the examination the doctor examines the medical history and palpates the spine. The diagnosis is made after examining the patient by a surgeon or traumatologist and after performing instrumental studies. The patient's complaints are identified, and the depth of the spinal curvature is measured using rulers. Physiological lordosis - with a curvature depth of up to 4 cm. Curvature of more than 5 cm indicates the development of hyperlordosis.
In order to determine the degree of curvature and identify possible causes of pathological changes, the following types of studies may be prescribed:
- radiography in lateral and direct projection - in order to determine how much the biomechanics of the spine and the angle of curvature have changed;
- CT (computed tomography) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - if neurological symptoms are present (in order to detect changes in the intervertebral discs, nerve roots, to detect protrusions and herniations of the intervertebral discs);
- spondylometry – to assess the angle of curvature;
- electromyography – to determine the functionality of muscle tissue and strength level;
In order to exclude or confirm the cause of the development of pathology, laboratory tests are prescribed if infectious diseases, inflammatory processes, or tumors are suspected.
Treatment
It is carried out comprehensively and includes the following:
- Selection of a specific motor mode. It all depends on the situation: sometimes (for example, after injuries) the patient is severely limited in activity. In other situations, on the contrary, he is shown special therapeutic exercises, which are selected individually.
- The use of different medications - most often for cervical lordosis these are painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs and vitamins.
- Massage. It is recommended to avoid massage options that are aimed at changing the position of the vertebrae - especially in inept hands, this can lead to injury. If a patient agrees to such an intervention, he must be sure that he is dealing with a high-class specialist. It is best to opt for a massage, which is aimed at maintaining muscle tone and improving blood circulation in the neck area.
- Surgical intervention. This treatment option for cervical lordosis is quite rare, since the operation has considerable risks. It is prescribed only if a person has a very severe injury or has such pain that it does not allow him to live a normal life.
The sooner a patient with lordosis of the cervical spine or hyperlordosis seeks help, the higher the chances that he will be able to restore the functionality of the cervical spine and get rid of discomfort.
Symptoms
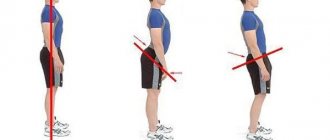
With hyperlordosis, changes occur in a person’s posture, and they can be quite pronounced. During a visual examination, a characteristic appearance is noted with the chest tilted back, the pelvis retracted posteriorly, the abdomen protruding forward, formed by a significant deflection of the back in the area between the thoracic and lumbar regions. A person's gait changes - to make walking easier, he will spread his knees and swing his arms. The head is tilted forward. Uneven load on the parts of the spinal column can cause the formation of a hump. Pathological lordosis is characterized not only by visual signs of back deformation.
Hyperlordosis of the lumbar spine is characterized by the following symptoms:
- back pain that becomes more intense during movement,
- impaired sensitivity of the lower extremities - their numbness, tingling,
- loss of sensation in the buttocks,
- dysfunction in the pelvic organs,
- dysfunction of the digestive system,
- heart disorders,
- difficulties while walking.
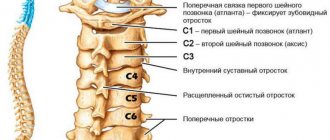
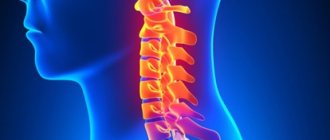
What is cervical lordosis
The normal shape of the spine in the cervical region is referred to as “lordosis.” This is a small arched protrusion anteriorly, which is formed by 5 vertebrae (the remaining two are necessary solely to ensure head movements). At the moment, there are no generally accepted methods for measuring cervical lordosis of the spine and the degree of its severity. As a rule, doctors determine his condition according to the following criteria:
- Change in appearance;
- X-ray examination.
Also, a simple test can be used to detect pathology. The person stands with his back to the wall so that his heels, thoracic spine and the back of his head are in contact with the surface. Normally, between the neck and the wall there should be a distance corresponding to the diameter of the palm of the person being examined. If this distance is greater or less, it is necessary to look for the reason for this change.
What does the term straightened cervical lordosis mean? As a rule, we are talking about changing the normal shape of the bend and smoothing it out. Doctors refer to this condition as hypolordosis. Hyperlordosis is the opposite situation, when the arch-shaped bend increases.
Prevention
Preventive measures should include the necessary changes in lifestyle and the development of new habits:
- use of an orthopedic mattress;
- maintaining correct posture while working, walking, resting;
- it is necessary to sit on a chair, leaning on the back of the chair with your entire back, without loading the lumbar region;
- stand on two legs with an even distribution of body weight;
- you should lift the load without jerking, bending your legs at the knee joints and squatting slightly;
- normalization of the diet - it should be balanced;
- Regular swimming and gymnastics classes are required.
A timely visit to a doctor at the first signs of the disease and a course of treatment selected individually for each patient, taking into account the degree of pathological changes, will help restore a full quality of life and avoid the dire consequences of spinal pathology - limitation of motor activity.
Sign up for consultation and treatment at the “YES Medical Center!” You can fill out the form on the website or by calling 8(812)323-15-03.
Our licenses for medical activities
All rights reserved by copyright law. No part of the contents of the site may be used, reproduced, transmitted by any electronic, copying or other means without the prior written permission of the copyright owner.