The ligamentous apparatus of the spine, like the spine itself, does not have its own vessels, and in order for it to maintain its elasticity and youth, the muscles around it must work well and pump blood. The neck, as one of the most mobile and unprotected parts of the spine, undergoes various age-related changes. The result is decreased mobility and soreness in the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle.
If there is instability of the cervical spine, strengthening the neck muscles helps to at least reduce it.
Simple exercises, the effectiveness of which has been proven in practice, are an excellent way to strengthen the neck muscles. Doing the exercises will not take you much time, and the results will exceed all expectations.
To enhance the effectiveness of the exercises, it is recommended to undergo 2-3 massage sessions with an experienced specialist who can identify and eliminate spasms of the deep muscles of the neck.
Start doing these exercises when the pain in your neck and shoulders calms down. Important: any exercises that increase pain and worsen the general condition must be stopped. You can return to them after some time.
Clothes should be loose, it is advisable to remove shoes. Perform all exercises (especially the first days) smoothly and gradually. Remember the important principle: “Endure mild pain, do not allow severe pain.”
Do these exercises daily for at least 2 weeks.
Active lateral neck tilt
While sitting on a chair, keep your back and neck straight. Slowly tilt your head to the side so that your right ear is as close as possible to your right shoulder, the movement should be smooth until you feel pain in the muscles, and then return to the starting position. Relax and repeat the movement in the other direction. Make sure that you do not twist your head or raise your shoulder while doing the exercise. Repeat this exercise 10 times in each direction.
About exercises after neck surgery
After surgery, you may still have stiffness and weakness in your neck and shoulder on the side you had surgery on. The exercises described in this material will help strengthen the muscles of the neck and shoulder and make them more flexible. This will help you regain range of motion and function in your neck and shoulder.
It is important for your recovery to start doing these exercises when your doctor prescribes them. It will also determine how well your shoulder and neck will function in the future.
If you experience pain, nausea, dizziness, swelling, or discomfort while doing these exercises, stop the exercises and call your doctor.
to come back to the beginning
Prevention of cervical osteochondrosis
Despite sedentary work and the prevalence of osteochondrosis, one should not assume that the disease cannot be prevented. Can! Will exercise be effective for osteochondrosis? Definitely yes! You just need to follow some recommendations:
- Control your posture in the office, at your desk, in front of the computer;
- Visit an orthopedist regularly and have your spine corrected;
- Avoid accumulating excess weight;
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress and a low pillow;
- Do yoga, swimming;
- Avoid sudden head movements;
- Eat more vegetables, fruits, dairy products, nuts; give up cigarettes and alcohol.
Follow these tips, introduce therapeutic exercises and regular physical activity into your life. Exercise for spinal osteochondrosis is useful both for preventing the development of the disease and for its treatment. But don't forget to consult your doctor. Only he will be able to select individual exercises based on the analyzes and research performed.
Dear readers, that’s all for today, leave your opinion about this article in the comments, does neck exercises help you with osteochondrosis?
Is it possible to perform these movements with various back diseases?
A common cause of spinal diseases is weakness and underdevelopment of the muscles of the spinal column. It is necessary to perform the complex for back diseases This is a good way to treat and prevent exacerbations of musculoskeletal diseases.
In this case, it is necessary to follow certain recommendations:
- When the acute process subsides, you need to perform exercises, but at a very slow pace, gradually stretching the muscles. Gradually you can move on to performing the entire set of exercises.
- From this system you need to choose those movements that suit you most. They need to be performed smoothly and measuredly, at a slow pace. After performing each movement, give the back muscles time to relax to prevent spasm.
- For hernias and scoliosis, you should consult with a physical therapy doctor who will be able to select the most effective exercises from this complex for you.
- For hernias and varying degrees of scoliosis, different training sessions with different loads may be recommended. Properly selected exercises for each patient individually evenly distribute the load on the spine, relieve muscle spasm and release the compressed nerve root.
- “Child’s Pose” and “Cat” are included in all systems of physical therapy, since their daily use gives a very good effect - it relieves pain and relieves muscle spasms.
- A set of 6 exercises for the back with dumbbells.
- Training the back muscles with an expander.
- The legendary Japanese method with a roller for spinal health.
- We have compiled a ranking of the 10 best workouts for losing weight on your back.
- Of the individual exercises you need, “Deadlift” and “Dumbbell Row”.
This system, despite its apparent lightness and simplicity, provides a good workout of the main muscle groups and charges the body with energy! By doing these exercises regularly in the morning, you will feel a positive effect on the body and, once you get used to it, you will no longer be able to refuse them.
A complex of 7 exercises for the spine
Completing this set of exercises will help improve or even restore the health of the spine. The charging system is focused on gentle stretching and strengthening of the muscles of the back, spine and neck. An important part of it is relaxation of the back and relaxation of the body, which has a beneficial effect on the health and general condition of the human body.
The relaxation stage cannot be neglected - it is better to do fewer exercises, but with complete relaxation in accordance with the technique! Correctly performed workouts can improve blood supply to the spinal muscles, correct posture, reduce the curvature of the spinal column, and lose weight in the lower back and shoulder blades. This therapeutic exercise in the morning has no age restrictions - even older people can do it.
It is highly recommended for sedentary work. Carefully! Performing the complex during the acute stage of any spinal diseases is strictly prohibited. First of all, consult a doctor.
"Cat"
We stretch the muscles of the back and neck. It is recommended to include muscle stretching training as one of the first in your morning exercise routine. “Cat” makes it possible to awaken the body and perform other exercises with pleasure. It allows you to stretch the muscles of the spine and prepare them for stress, eliminating slouching.
About 4 different types of “Cats” and their effect on the spine, see here.
“Cat” can also be done in the middle of the day after performing some monotonous work - it helps relieve fatigue and improve blood circulation in the back muscles.
- We get down on all fours, kneel and lean on our hands.
- As you exhale, bend your back up as much as possible and lower your head.
- As you inhale, bend down and raise your head up.
- The movements are leisurely and smooth, like those of a cat.
We perform from ten to twelve times, two to three approaches.
Detailed technique in the photo. “Cat” is suitable for any age; it is an excellent exercise for the back muscles for children. Helpful advice! You need to start a set of morning classes with “Cat”, as it gently stretches the muscles after sleep, and end with the “Child’s Pose” asana, as it promotes rest and relaxation.
"Downward Facing Dog"
Promotes good stretching of the neck muscles, a straight back, back of the thigh and lower leg, and improves cerebral circulation. Helps to wake up and invigorate after sleep.
About 12 useful properties of Downward-Facing Dog, as well as lightweight movement options, see here.
- We get down on all fours and both palms. Feet shoulder width apart.
- As you inhale, lift your buttocks, straightening your legs. Feet should be firmly on the floor.
- The exercise at the end point is represented by a triangle, the vertex of which is the buttocks. This position should be held for about a minute, while breathing freely and measuredly.
We rest, completely relaxing the muscles, for one minute. We repeat three times. This pose is an excellent back exercise for pregnant women, even in the 8th month.
"Upward Facing Dog"
Morning exercises that include this movement promote good stretching of the muscles, back, hips and abdomen. Activates the work of internal organs.
About the detailed technique and 9 useful properties of “Upward Facing Dog” here.
- We lie on our stomach, bend our arms at the elbows and place them under our shoulders, palms down, and straighten our legs.
- As you exhale, move your shoulders back, straightening your chest.
- Raise your head, then, bending your back, lift your upper body up. in this position for about one minute. Then we slowly lie down on the floor.
Rest for one minute, repeat three times.
"Crocodile"
This exercise is extremely effective for spinal health and pain relief. It can be learned and performed at any age. Classic complex “Crocodile” from Dr. E.A. Antipko consists of 12 steps and can be used as an independent back health system. Let's look at one of the movements.
- We lie with our backs on the floor, with our arms at our sides. The palms should be turned up.
- Next you need to spirally rotate the spine - head to the right, hips and feet to the left
- Repeat the movement for the other side
- It is very important to move symmetrically
You need to perform 10 such twists in both directions.
"Boat"
Forms a muscle corset, reduces waist size, and works the latissimus dorsi muscles. Loads the gluteus maximus, thighs and calves. The “boat” can be performed while lying on your back, as well as lying on your stomach. The option “lying on your stomach” is suitable for us.
See more about the effect of the “Boat” on the spine here.
- We lie on the floor on our stomach, legs together, arms extended forward.
- As we exhale, we bend, trying to raise our straightened arms and legs as high as possible.
- We stay in this position, lie down on our stomach and relax our muscles, breathing freely.
We repeat three times. The rest time between sets is one minute.
"Bridge"
This movement, performed in the morning, strengthens the lower and upper back, works the back extensors, and increases the flexibility of the spine. Promotes the formation of a “royal” posture.” The “bridge” loads the small muscles of the body, which is not possible for all exercises. You can perform a bridge while lying on a ball (fitball), resting your lower back on it.
- We lie with our backs on the floor, arms extended up.
- Leaning on your hands and feet, we begin to smoothly lift your body, lifting it off the floor.
- When you get into a bridge position, your back should be an arch and your buttocks should be higher than your head. Not everyone can achieve such a perfect bridge the first time. But with persistence and some effort, you can master it by developing stretching and flexibility.
- while performing the movement .
We repeat three times. The rest time between sets is one minute.
"Child's Pose"
This morning exercise stretches the muscles of the thighs and legs, relieves back fatigue after sleeping in an uncomfortable position, and relaxes the muscles of the back and neck. Relieves tension, promotes the development of mobility of the hip, knee and shoulder joints.
Technique:
- We get down on our knees, feet together.
- We place the buttocks on the heels.
- As you exhale, bend forward and stretch your arms along your body, palms up. We rest our foreheads on the floor.
- We focus on how the spine stretches.
- You can stay in this relaxed position from one minute to three minutes.
An option for performing the exercise is to stretch your arms forward.
This allows you to stretch your back muscles even more. Attention! “Child’s Pose” is recommended to be performed last in the morning exercise system, as it promotes rest and relaxation.
Anatomy
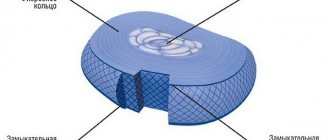
This article is not intended to describe the anatomy of the cervical spine in detail, but rather provides a brief overview to help you understand the recommendations and risk factors presented. The cervical spine (neck) typically includes seven mobile vertebrae and six intervertebral discs, with the most distal disc between the seventh cervical and first thoracic vertebrae. Each intervertebral disc consists externally of a fibrocartilaginous ring with a gel-like material (nucleus pulposus) in the center (Figure 1A) (1). The main functions of the intervertebral disc are to provide shock absorption, movement, and stability in the spinal column (31, 49). The disc provides shock absorption, allowing the nucleus pulposus (NP) to migrate within the annulus fibrosus. In mature adults, the PN contains water (75% by weight) and hydrophilic (water-absorbing) molecules called proteoglycan aggrecans (20% of dry weight) (49). The high water content of a normal PU helps to evenly distribute the compressive load in the disc (31).
Rice. 1.
A) Lateral view of the cervical spine in a neutral position, showing the red intervertebral disc, blue annulus fibrosus, and yellow nucleus pulposus; B) Lateral view of the cervical spine showing posterior migration of the nucleus pulposus during flexion; C) Lateral view of the cervical spine showing forward migration of the nucleus pulposus during extension.
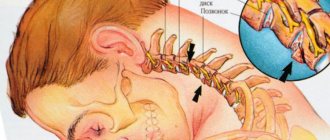
Movement of the cervical spine is usually considered in three planes with six directions of movement. It is customary to distinguish between flexion (movement of the chin to the chest), extension (look up), rotation (turning the head from side to side) and lateral flexion (movement of the ear to the shoulder). Although the disc allows movement, it is also responsible for maintaining stability. In cases of disc degeneration, there may be a lack of spinal stability. As the disc degenerates, the proteoglycan and water content decreases (49). This disc degeneration (shrinkage) causes instability (excessive movement) in the spine, which leads to painful compression or stretching of spinal connective tissues such as ligaments or nerves (31). Disc herniations can occur independently of degeneration, as a result of overuse of activity or posture.
The position of the PU in the ring during neck movements can be predicted based on an understanding of normal biomechanics, as well as in vitro and in vivo laboratory studies. Research has shown that when the neck is flexed, the PU tends to move posteriorly (due to anterior compression), whereas when the neck is extended, the PU tends to migrate anteriorly (Figures 1B and 1C) (5, 52). The biomechanical behavior of the disc is important to consider when treating and preventing hernias in the cervical spine. Prolonged neck flexion causes and aggravates compression of the nerve roots with compression and loading of the disc, displacing the PU posteriorly (18, 52, 56). The hydrostatic pressure created by the PJ leads to the formation of cracks through which the PJ can escape (56). PJ protrusion mechanically compresses or irritates the nerve root, leading to neck pain and radiculopathy (1). For patients with a herniated disc, evidence suggests that positions or repetitive movements that require excessive neck flexion should be avoided or minimized. It is necessary to adhere to a specific neutral position that preserves the natural cervical lordosis. Normal cervical lordosis is an anterior convex curve resulting from the wedge-shaped intervertebral discs, with greater thickness in the anterior portion compared to the posterior portion (55). Maintaining a natural lordosis when performing exercises minimizes asymmetries or loading predominantly on the anterior part of the disc, which can lead to a herniated disc.
conclusions
Given changes in the cost of health care, as well as restrictions on the number of visits, people are likely to discontinue a formal rehabilitation program before reaching premorbid levels of fitness and activity. Despite the usual stability of patients, impairments persist at the time of discharge. In the presence of impairments and limitations of function, SSCTs may find opportunities to work with clients who wish to improve function; in this case, they need knowledge about appropriate post-rehabilitation care. The training program should consist of recommendations for maintaining correct posture, improving muscle performance and returning to a high level of fitness if necessary. More importantly, the SSCT involved in post-rehabilitation needs to recognize the occurrence of unexpected symptoms (pain lasting more than a few days or migrating to the shoulder or arm) to determine the need for urgent referral to a qualified specialist. Finally, the likelihood of neck pain reoccurring is high, so improvement should be gradual with careful monitoring of the client's response to training. Collaborating with your healthcare provider before developing a program is helpful in understanding the prognosis and appropriate precautions. SSCTs can have a significant impact on clients' post-rehabilitation; however, this appears to depend on the development of safe and effective training programs that promote return to sports and recreational activities.
Original:
https://journals.lww.com/nsca-scj/Fulltext/2017/06000/Post_Rehabilitation_Considerations_for_Clients.7.aspx
Advantages and benefits of this complex
Advantages:
- This complex of exercise therapy for the back includes movements borrowed from the practice of yoga. They are an excellent way to bring all body systems into a state of harmony.
- It is not recommended to include active exercises in morning exercises, since the body has not yet fully woken up. This complex provides a gentle load and at the same time promotes thorough muscle development and stretching.
- To overcome a sedentary lifestyle, it is recommended to follow this system. It does not take much time, is performed without significant stress, and at the same time heals the body and charges you with a good mood.
- Selection of movements. From the entire morning complex, you can choose from three to five exercises that are most suitable for you and perform them. After doing morning exercises, you feel cheerful and pleasant sensations in your muscles and throughout your body.
An indicator that you have correctly followed the technique of performing morning exercises will be a pleasant sensation in your muscles and vigor. Morning exercises are necessary for everyone - both those who have active physical work and those who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Without physical activity, unfavorable changes occur in the body: this concerns the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, the musculoskeletal system, and the functioning of internal organs.
Don't forget that in addition to training, there are 7 more reliable methods for getting rid of cellulite on your back.
Attention! If for some reason you did not have time to complete the complex in the morning, you can perform it in the evening. The only condition is that two and a half hours must pass after eating.
Diagnostic Imaging
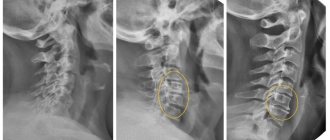
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive evaluation option for diagnosing intervertebral disc pathology in the cervical spine (40, 44). Traditional X-ray is not suitable for diagnosing acute discogenic pathology due to low sensitivity for soft tissue analysis. Low sensitivity typically results in an excessive number of false negatives (the condition of interest is not detected). As the pathology becomes chronic and degenerative changes occur, x-rays can be used to evaluate the decrease in intervertebral disc height, which indicates the process of degeneration. MRI also correlates well with surgical findings in the diagnosis of cervical radiculopathy (27). SSCT is not involved in diagnosis; however, based on the information provided above, many clients with a herniated disc will likely be diagnosed using an MRI.
Electrodiagnostic evaluation, particularly needle electromyography (EMG), is an important tool in the evaluation of people with cervical spine pain with associated radicular symptoms in the upper extremity (pain, paresthesia, sensory changes, weakness of movement, and decreased tendon reflexes). Electrodiagnostic tools, including EMG, nerve conduction assessment, somatosensory evoked potentials, and response latency, provide objective evidence of neural dysfunction. Needle EMG studies are widely used to diagnose radiculopathy because the test is able to localize the level of damage to a specific nerve and provide information about the severity of the condition (24). From a SSCT perspective, knowledge of this test indicates a neurological cause of weakness. People with weakness due to nerve compression will take longer for their muscles to respond to exercise compared to people who are weak from a sedentary lifestyle.