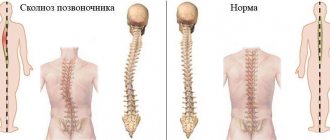
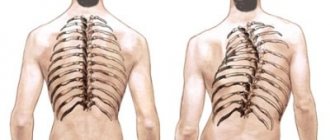
Main groups of scoliosis according to Cobb (1958)
According to the Cobb classification, there are five groups of scoliosis.
- Group I. This includes scoliosis of muscular (myopathic) origin. The basis of such curvatures is insufficient development of muscles and ligaments. The group may also include rachitic scoliosis - these scoliosis appear as a result of a dystrophic process not only in the skeleton, but also in the neuromuscular tissue.
- Group II. It includes scoliosis of neurogenic origin (causes: poliomyelitis, spastic paralysis, neurofibromatosis, syringomyelia). This can also include scoliosis caused by radiculitis, lower back pain, changes in the intervertebral discs that lead to compression of the roots.
- III group. These are scoliosis due to abnormal development of the ribs and vertebrae and ribs. It includes all congenital scoliosis that occurs due to bone developmental disorders.
- IV group. These are scoliosis due to diseases of the chest (for example, due to burns or plastic surgery on the chest).
- V group. This includes idiopathic scoliosis, the origin of which currently remains unexplored.
Determining the severity of scoliosis
The severity of scoliosis is determined by the size of the S-shaped curvature of the spine. To obtain a numerical characteristic of the curvature, an x-ray is taken. Then, in the upper section of the curvature, two lines are drawn perpendicular to the spine - at the upper and lower vertebrae, between which the curvature is contained. Next, two lines are constructed perpendicular to these. The angle between the second lines in degrees is a measure of the degree of curvature. If the spine is absolutely straight, then the first two lines will be horizontal, and the second two will be vertical (and therefore parallel to each other). If the spine is curved, then the first two lines will form an angle, and therefore the second two lines will also form an angle with each other.
According to the John Cobb method, in the normal case, the angle between parallel straight lines is considered equal to 0 degrees, and therefore in weak scoliosis the number of degrees is close to 0, and the stronger the degree of scoliosis, the further this number is from 0. According to V.D. Chaklin’s method, the angle between parallel straight lines is considered equal to 180 degrees, and therefore in weak scoliosis the number of degrees is close to 180, and the stronger the scoliosis, the further this number is from 180.
For the lower section, measurements are carried out in exactly the same way.
The next section provides a classification of severity levels in accordance with the Cobb method.
Thoracolumbar corsets
Buy thoracolumbar corsets
The use of corsets can be both preventive and therapeutic. Many centuries have passed since the invention of the first corset. In the 18th century, during the heyday of “corset” fashion, this piece of clothing was used not only to create a wasp waist, but also to create a regal posture. Already in those days, corsets had shoulder straps, like on modern orthopedic reclinators, which turned the shoulders, giving a slender posture and a fuller bust.
The main purpose of modern thoracolumbar corsets is not aesthetic, but medical. Our spine is a complex and fragile system. Any violation of the correct bending or geometry of the joints threatens global health problems. Even such a common disease as scoliosis is not as harmless as many people think. Curvature of the spine leads to incorrect relative positions of the vertebrae, atrophy of the intervertebral discs, and pinched nerve endings. As a result, we get osteochondrosis - a disease of the 21st century, which now affects even many young people. Osteochondrosis cannot be cured “suddenly”; many diverse measures are required, from reducing sedentary loads to the use of medications. One of the preventive measures is to prevent hypothermia of the back. Therefore, thoracolumbar corsets of this profile have a warming effect.
Thoracolumbar corsets fix the spine from the waist to the shoulder blades. For complex postural disorders and compression fractures of the spine, thoracolumbosacral corsets are recommended. They fix the entire back to the tailbone.
The main elements of the corset are stiffening ribs, which are made of metal or polymer plates. It is also important that the shoulder straps are positioned comfortably, do not put pressure on the shoulders, and do not compress the vessels in the armpit area.
Corsets can serve as the only corrective means in treatment, or be part of a complex therapy, including massage, manual therapy, water treatments, and more. For spinal injuries, corsets of a more rigid design are used. They not only limit the overall mobility of the spine, but also protect against rotational movements, support the body in the desired position, and have a warming effect.
It is advisable to combine the use of a corset to correct spinal curvatures with other preventive measures. Sleeping on an orthopedic mattress promotes effective muscle relaxation. Its elastic elements support the natural deflection of the spine. The corset partially relieves the load on some muscle groups. Therefore, in order to avoid muscle atrophy, they perform sets of physical exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back and shoulder girdle. To improve blood circulation, it is useful to use orthopedic massagers. They improve blood flow to the affected area, relieve discomfort from prolonged static tension, and tone the muscles.
The choice and wearing of a corset should be agreed upon with a doctor. Self-medication and improper use can lead to muscle atrophy and aggravate spinal pathologies.
Division of scoliosis by severity
- Scoliosis 1st degree. The lateral deviation is small (up to 10 degrees). The degree of twisting is also small (twisting is determined by the deviation of the spinous processes from the midline and the asymmetry of the roots of the arches).
- Scoliosis 2 degrees. The primary arc of curvature is 10-25 degrees. The twisting is noticeable. X-rays show deformation of the vertebral bodies in the upper part of the curvature. Due to the twisting of the spine, a muscle roll can be clinically identified.
- Scoliosis 3 degrees. The primary arc of curvature is 25-40 degrees. The deformity is even more pronounced; there is a large rib hump and severe deformation of the chest. The X-ray shows that there are wedge-shaped vertebrae in the upper part of the curvature and adjacent areas.
- Scoliosis 4 degrees. The angle of the main curvature is 40-90 degrees. Severe disfigurement of the torso. Posterior and anterior costal hump, deformation of the pelvis and chest, kyphoscoliosis of the thoracic region, desaturation of the ligamentous apparatus. Radiographs show severe wedge-shaped deformation of the thoracic vertebral bodies.
Causes of scoliosis of the lumbar spine
There are many causes of the disease. These may include the presence of thoracic scoliosis, which is accompanied by the occurrence of a similar pathology in the lower back. In addition, scoliosis in the lumbar spine can be provoked by:
- unequal pressure on the discs between the vertebrae;
- lack of movement and physical activity;
- back injury;
- excess weight, leading to additional stress on the lower back;
- congenital causes of the disease;
- rickets, tuberculosis and infections;
- cerebral palsy (in childhood);
- rheumatism;
- woman's pregnancy;
- clubfoot, flat feet;
- tight clothes;
- tumor diseases;
- hernias;
- metabolic disorders.
In addition, the lack of prevention is essential in the formation of scoliosis in this part of the spine.
Types of spinal curvature in scoliosis
Upper thoracic (cervicothoracic) scoliosis
This is a rather rare form of scoliosis, in which a short primary curve and a long and flat secondary curve are formed. Affects the cervical spine, and sometimes even the facial bones. A crooked neck, asymmetry of the eyes, a slanted nose, and so on may be detected. Deformation of the upper chest and shoulder girdle. It is difficult to correct, especially if the process is neglected and treatment is started late.
Thoracic scoliosis
With this type of scoliosis, the curvature involves 6-7 vertebrae. Deformations of the spine and chest are pronounced, often with the formation of a large muscular hump. In addition to the steep primary arc, two secondary arcs are formed - above and below the main curvature. Due to twisting, the plane of the pelvis does not coincide with the plane of the chest. On the convex side the scapula protrudes, on the concave side the chest flattens. Thoracic scoliosis appears on average at 9-10 years of age. They need to be treated at an early age because once the spinal column is fully formed, treatment becomes difficult or even impossible.
Combined scoliosis
This type is characterized by the simultaneous manifestation of both curves - the thoracic and lumbar, that is, the curvature of the spine takes the form of the letter S. It is more common in girls, and in the thoracic region the curvature usually goes to the right side, and in the lumbar region - to the left. It is difficult to treat, and in advanced cases it is practically untreatable.
Thoracolumbar scoliosis
Characteristic is the protrusion of the vertebral bone crest on the side of the concavity of the curvature. It also occurs more often in girls. The usual age of detection is 9-10 years. It can be treated well, especially at an early stage.
Lumbar scoliosis
Five vertebrae are usually affected. When the torso is tilted, twisting is noticeable - in the form of a muscle roll. The costal hump is missing. The chest deformity is weak. Internal organs are little affected. Scoliosis of this type is not prone to progression. Therefore, its course is relatively favorable and it is relatively easy to treat.
Remember that before using any treatment methods and medications, you should consult a specialist to know about possible contraindications and the applicability of these treatments and medications for you personally!
Right-sided scoliosis in the lumbar and thoracic spine
Scoliosis is a disease that occurs due to lateral changes in the form of deviations that occur in the vertebrae. When talking about the vertebral part of the chest affected by scoliosis, they mean the constancy of the manifestations of such a disease with a diagnosis of scoliosis on the right side.
This disease mainly poses a threat to adolescent children, when the moment of rapid growth occurs. Since it is during this period of time that various deviations from correct development may occur, which leads to right-sided scoliosis of the thoracic region. The main thing is that only this age makes it possible to completely cure the disease, since the spine has not undergone final formation and can be corrected.
Classification of scoliosis
The varieties that classify the disease are determined by different criteria. In first place is the criterion with the localization of spinal lesions. It contains cervicothoracic, lumbosacral and thoracolumbar diseases. There is also double curvature scoliosis, when two parts of the spine are affected at once.
In second place is a fairly common criterion, depending on vertebral curvatures. Here, curvatures with one, two and three arcs are distinguished. The degree of the disease depends on the angle of vertebral curvature. For example, scoliosis, which is right-sided of the first and second degrees, can be cured conservatively. The main condition will be the timely detection of the emerging disease and the beginning of the fastest treatment. According to medical data, scoliosis on the right side of the lower back is a fairly rare disease; it is more typical for the vertebrae of the thoracic region.
Neck and scoliosis
It would be extremely rare to acquire scoliosis in the cervical spine. But still, this situation can arise in a child who was injured at birth. Although this is a fairly rare problem, it contains very dangerous and unpleasant forms of diseases that serve as a direct cause of headaches, feelings of dizziness or motion sickness during transport trips. After all, such scoliosis causes deformation of the bones of the skull and curvature of the vertebrae of the neck.
Scoliosis on the right side of the thoracic spine
This form of spinal disease causes deformation of the vertebrae in the form of a single arch - the so-called C-shaped scoliosis, i.e. the letter turns out to be turned to the right, which is why we speak of right-sided scoliosis. In the case of thoracic scoliosis, severe deformation of the figure occurs, which causes the appearance of a rib hump, depending on the deformation of the thoracic cage.
There is also a disease on the right side of the thoracic region in the form of dysplastic right-sided scoliosis. It is very dangerous, as it can progress due to loss of time to start treatment. And if the disease has been advanced, then you can expect serious deformation of the sternum, and, as a result, the inability to breathe freely, leading to problems in the cardiovascular system. All these symptoms correspond to another diagnosis of right thoracolumbar scoliosis.
According to the observations of specialists, the appearance of right-sided scoliosis of the spine in the lower back is a very rare occurrence. More often you can find left-sided scoliosis in the lumbar region. It cannot be detected without consulting a doctor, since such scoliosis has absolutely no visual manifestations. But this does not reduce the risk of pain in the lower back later, at the age of twenty to thirty. In this case, it will be difficult to cure such a disease, so the only way out is to fight its progression.
Diagnosticians insist on timely examination and detection of the disease, since it is easier to determine first-degree thoracolumbar scoliosis compared to second-degree lumbar scoliosis.
scoliosis treatment
Scoliosis is treated with therapeutic exercises.
Therapeutic physical education with gymnastic exercises restores the muscular state of the entire corset and ligament apparatus, thanks to which the body gains the right to correct the problem itself. This treatment procedure is effective for scoliosis that occurs on the right side of the spine in childhood and adolescence. But this treatment must include massage courses that perform similar physical activities. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms
The most important symptom of lumbar scoliosis is that the hip girdle is asymmetrical. In this case, the lower limbs visually have different lengths. But at the same time, the symptoms will depend on what type of scoliosis the person has. The types of lumbar scoliosis are:
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- S-shaped.
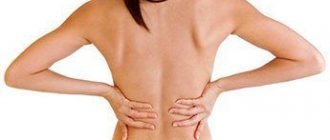
The most important symptom is the presence of pain in the lower back, the person stoops, there is pain in the sternum, severe weakness, and changes in gait may also be observed. A person with lumbar scoliosis becomes less mobile due to pain, and his limbs are not as sensitive as before. Neck pain, foot pain, swelling in the lower back, and numbness in the arms and legs may occur. Often the picture is complemented by disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Treatment
Spinal deformities are treated only in a complex manner. During the treatment process the following are used:
- medicines;
- exercise therapy;
- operations.
The treatment method is determined individually.
Drug therapy
To relieve inflammation caused by scoliosis in the lumbosacral region, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. You may also need to use painkillers and muscle relaxants that help relieve muscle spasms.
Exercise therapy
Treatment of scoliosis of the lumbar spine also necessarily involves taking a course of professional massage, visiting a chiropractor, using acupuncture and physiotherapy. It will not be superfluous to follow a special diet during the treatment process. The first degree of scoliosis is often treated with corsets and exercises, which are selected by a neurologist
individually.
Surgery
Scoliosis of 1st or 2nd degree of the lumbar region, as a rule, is not treated with surgery. However, if the disease progresses, unbearable pain, neurological manifestations, cardiac or pulmonary failure, etc. occur, surgical intervention is inevitable.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of lumbar scoliosis of 1st degree is carried out only by an experienced neurologist
. Of course, you can look at your back yourself and determine how straight the spine is, but when you contact a specialist, in addition to examination and questioning, you will be referred to diagnostic procedures, which will allow you to be sure of the presence or absence of scoliosis, as well as associated abnormalities. Diagnostics may include:
- Blood and urine tests.
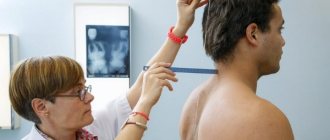
- Measuring height while standing, sitting, determining body weight.
- X-ray
or
MRI
of the lower back. - Fluorography
. - Muscle tone study.
- Ultrasound of organs
. - Cardiography
, etc.
Based on the results of such studies, the doctor will determine whether you have grade 1 or 2 scoliosis of the lumbar spine, and if it is present, he will select the optimal treatment method.