Stenosing ligamentitis is a serious dysfunction of the hand, in which a failure occurs in its tendon-ligamentous apparatus. Self-diagnosis is unacceptable, because the disease is often confused with acute arthritis, osteomyelitis, pathological dislocation and even sepsis. The diagnosis of stenosing ligamentitis is made on the basis of an x-ray of the hand (if necessary) and after analysis of the current clinical picture.
The pathogenesis of dysfunction of the tendon-ligamentous apparatus of the hand causes controversy among specialists, because no one can yet voice the exact details of the formation of the pathology.
Its most reasonable interpretation is based on an analysis of the energetic work of the fingers during the day. They carry out their activities due to the uninterrupted functioning of tendons. In the channel, consisting of connective tissue, they slide so that the finger moves in different directions.
With a provoking factor in the form of inflammation, the tendon becomes more voluminous. Its new dimensions are not designed for the size of the canal, so the usual path of the terminal structure of the striated muscles may deviate. If significant edema forms, even such a modified route cannot be performed. It should be remembered that the formation of inflammation begins initially in the ligamentous area, and then spreads to the tendon territory.
Finger dysfunction with stenosing ligamentitis has the following numerical indicators of the number of patients for each of them:
large - 25%;
index - 3%;
average - 20%;
unnamed - 44%;
little finger - 8%.
There are no age restrictions for this disease. During the development of the body, problems usually arise with the thumb. However, experts do not diagnose a child under 2 years of age. The disease may disappear on its own as people get older, but in some cases it develops into a more serious form of ligamentitis. It is better for parents to initially play it safe and visit an orthopedist with their child at the first alarming symptoms.
The disease can be combined with certain pathologies, significantly worsening the general condition of the patient:
1. Epicondylitis. We are talking about inflammatory and degenerative transformations of the elbow joint.
2. Arthrosis. If it causes damage to the small joints of the hand, then its tandem with stenosing ligamentitis is dangerous.
3. Humeroscapular periarthritis. The lesion is fixed in the same area as with epicondylitis, but covers the periarticular soft tissue.
Symptoms of rupture/damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers
Common signs of ligamentous injury include:
- Soreness.
- Limited swelling.
- Passive mobility of the joint in a non-standard direction.
In some cases, the fingers become spindle-shaped. This defect may persist for several months.
When the interphalangeal ligaments are damaged, patients complain of severe pain, weakness in the joint, discomfort when moving, and swelling. If the ligament is completely torn, the finger may become hyperextended. In case of injuries to the dorsum of the hand, the extension function of the fingers (one or more) is impaired. If the nerves are damaged, the fingers may become numb. Other sensory disturbances also occur. Hemorrhages may also occur.
Treatment of a sprained finger: what to do for ligament injuries
Most patients recover well with appropriate physical therapy. One of the key components of treatment is that the patient gets enough rest from activities that aggravate the pain. To stabilize the joint and protect it from further damage, protective tape or braces are used and must be worn for a certain period.
Rest from aggravating activities in the absence of further tissue damage allows the body to begin the healing process. Once the patient can perform these movements painlessly, provided there is no worsening of symptoms, a gradual return to normal activities is carried out.
Treating a finger sprain by reducing bleeding, swelling and inflammation in the first 48 to 72 hours is vital. This process includes avoiding aggravating activities, regular cooling, using a compression bandage, and elevating the affected limb to height. Anti-inflammatory medications are helpful in this initial phase of injury treatment. They speed up the healing process by reducing pain and swelling associated with inflammation.
It is also important to perform movement and strength exercises at the beginning of the rehabilitation process. This is to prevent stiffness and weakness and ensure that the finger functions correctly. These exercises should be used as soon as pain permits and following the instructions of the treating physical therapist. A gradual return to activity should occur in the absence of pain, provided that symptoms do not increase.
Physiotherapy for Sprained Fingers: Ensuring Optimal Treatment Results
Other means for immobilization and treatment of the hand
Despite the effectiveness of physical therapy, a small percentage of patients with finger sprains do not fully recover and undergo other treatment. Immobilization, splinting, or surgery is required to ensure optimal results. The doctor may need further testing, X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, or evaluation by a specialist who can advise on procedures appropriate to improve the condition. Sometimes surgery is required.
Therapeutic exercises for developing injured fingers
The following exercises are prescribed to patients with a sprained or dislocated finger. You should discuss their appropriateness with your physiotherapist. Provided that they do not cause worsening of the condition and symptoms, the exercises are performed 3 times a day.
- Clenching a fist. Clench and unclench your fist, straightening your fingers as far as possible without pain. Repeat 10 times.
- Spreading your fingers to the side. Fingers together and extended. Spread your fingers as far apart as possible without pain and return to the starting position. Repeat 10 times.
Diagnosis of rupture/damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers in the clinic
Diagnosis of injuries to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers begins with a simple examination and questioning of the patient. The doctor performs a visual inspection. He determines the type of damage by palpation (palpation of the hand). Additionally, instrumental examination methods are prescribed.
Our doctors have the necessary skills and knowledge for quick and high-quality diagnosis and diagnosis. We can conduct examinations using modern, high-precision, expert-class equipment from the world's leading brands. Diagnosis will take a minimum of time, and the doctor will be able to begin treatment immediately.
First aid
A finger sprain is an injury that requires medical attention. If the sprain is caused by a fall, then immediately apply ice to the sore spot. This approach will help reduce swelling and relieve pain. After applying a cold compress, it is important to wrap the injured joint with an elastic bandage to keep the arm stationary.
To reduce pain, you need to raise your hand above the level of your heart. This method will help reduce pain and relieve swelling. Then you can begin to warm up the joint. If the damage is minor, then after such physical exercise the fingers will return to normal. Taking painkillers is indicated.
Examination methods
The main examination methods include:
- Ultrasound. An ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of the hand and determine the functionality of tendons and ligaments. Examining the hand, the doctor determines damage to the nerve threads, pinching, and small bone fractures that are not visualized on x-rays.
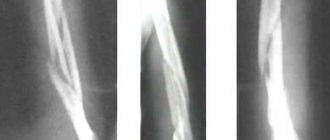
- X-ray examination in frontal and lateral projection. This examination is aimed at clarifying the type of injury. It also allows you to confirm or refute a bone fracture. Also, an x-ray can reveal the degree of injury to hard tissues that are located next to the ligamentous apparatus.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). This survey is accurate and informative. It may be prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Examination methods are chosen by the doctor.
First aid and treatment for sprained finger
The content of the article:
As paradoxical as it sounds, all it takes is to injure your hand and a person feels helpless. The fact is that we are accustomed to the fact that our strength is in our hands, and when trouble happens, for example, such as a sprained finger, it brings a lot of inconvenience, and, most importantly, loss of performance.
Tension is a partial violation of the integrity of individual fibers. A ligament is a fiber that provides adhesion to bone tissue. When certain factors occur, the ligament begins to peel off, a process called sprain. You can see what a sprained finger is in the photos provided.
Treatment of rupture/damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers in the clinic
When the ligaments of the hand apparatus are torn, treatment can be either conservative or surgical.
Usually a plaster splint is placed on the arm for 2-3 weeks. It allows you to fix the hand in a functionally and anatomically correct position. The patient is then observed. If, after removal of the cast and rehabilitation therapy, instability of the joint remains, surgical treatment is prescribed. The operation can also be performed in fresh cases with severe instability of the joint. The intervention is aimed at applying a special suture to a ligament that is torn or torn with a bone plate.
If for some reason suturing is impossible, autoplasty of the ligament is performed. As part of the operation, channels of small diameter (2-3 mm) are formed in the bones in the direction from the back to the palm. A tendon graft is taken from the palmaris longus muscle. It is performed in a figure-of-eight pattern and tightened to eliminate lateral instability but preserve the ability of the fingers to flex and extend. The ends of the graft are sutured. Rehabilitation after such an operation lasts 2-3 weeks.
Important! If the damage is not detected promptly or treated, periarthritis may develop. At the same time, the fingers increase in volume, and the pain persists for a very long time. The patient loses the ability to move his fingers normally and is forced to change his usual lifestyle.
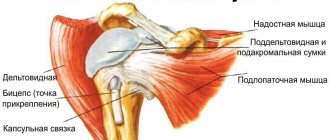
Role and functions in the body
The ability of the human hand to move at the wrist is extremely important for everyday life, as well as for professional activities and sports. The wrist joint guarantees the following capabilities for the upper limb:
- rotation, deflection back and forth, left and right, as well as fixation in each of these positions,
- complete blood exchange through the artery located in the wrist canal, as well as a network of small capillaries,
- nervous sensitivity, providing the most important function of the human body - the sense of touch.
- full participation of the wrist and finger in the exchange of lymph,
- protection against damage to the heads of bones when they come into contact with each other.
Damage to the wrist joint is a risk for the motor and tactile functions of the wrist, as well as a threat to its participation in metabolism. Therefore, maintaining the normal state of this area must be treated with the utmost care.
Prevention of rupture/damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the fingers and medical recommendations
To prevent damage you should:
- Try to reduce the risk of injury. To do this, you must always make all movements carefully. Before any physical activity, you should warm up the ligamentous apparatus and the joints themselves. It is very important to monitor the condition of your muscles.
- Visit a doctor regularly if your ligaments and joints are weak (especially if you have any chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system). An experienced specialist will not only talk about preventive measures, but will also constantly monitor the health status of his patient.
- Pay attention to proper nutrition. You should definitely include foods that are good for your ligaments in your diet. These include fatty fish, ginger, garlic, broccoli, walnuts, fresh berries and fruits. On your doctor's recommendation, you can take complex vitamins regularly.
If you want to learn everything about preventing ligamentous injuries, contact our doctor. You can also make an appointment if you have an injury. Our doctor will prescribe the necessary diagnostics and then carry out treatment. Call us or leave a request on the website!
Diagnosis of the disease
Specialists who treat the hand for this type of dysfunction are an orthopedist and a traumatologist. To make a diagnosis, multifaceted diagnostics are not needed. All the doctor needs to do is examine the patient’s hand and gently palpate it.
Such manipulations are necessary to detect the area of inflammation, which feels like a lump to the touch. If there are no assumptions about the presence of degenerative-dystrophic changes in the joints, then the specialist will refer the patient for an x-ray.
To confirm the development of a pathological process in the body, the need to undergo some laboratory tests is not excluded. Usually, the doctor needs to analyze a general blood test, which, if leukocytes and ROE are elevated, will confirm the presence of inflammation in a person.
Dislocated thumb
Dislocation of the finger joint to the outer side of the hand occurs in the case of a flexion mechanism of injury, to the inner side - in case of an extensor one. The dorsal one can cause displacement and pinching of the tendon between the proximal phalanx and the metacarpal bone, which will greatly impede its return to its previous position. The injury causes extreme pain. After a dislocation, with slight movement of the injured limb, it springs slightly, and normal movements are impossible.
Injuries are called open if the skin and soft tissue are damaged. The integrity of the skin accompanies a closed injury.
The thumb becomes deformed more often, since when falling, a person protects his chest and transfers his body weight to the extended finger.
First aid
Severe pain that accompanies injury requires immediate medical assistance. Having the knowledge of what to do in case of a dislocation, you can significantly alleviate the victim’s condition by providing first aid for a dislocation or fracture.
- First you need to free your hand from excess clothing and jewelry and fold up the sleeves.
- The limb should be in an elevated position so as not to provoke excess blood flow to the site of injury.
- Then you need to apply ice to your hand or (if you don’t have it) a towel, previously left in cold water for about 20 minutes.
- Damaged tissue covers are treated with an antiseptic.
- To prevent further displacement of the joint, it is fixed with a tight bandage until examined by a doctor.
- You can give a pain reliever.
- It is necessary to immediately transport the victim to the hospital.
The joints cannot be adjusted on their own - this can cause disastrous consequences. In addition, a splint/bandage is sometimes required.
Only a doctor should treat sprained and sprained fingers. Reduction is a painful procedure and cannot be performed without local anesthesia.
There are many treatment methods; they are selected by specialists depending on the direction in which the finger is dislocated:
- An uncomplicated dislocation is reduced by gently pulling the tip of the limb until a characteristic click is heard, which will indicate that the joint has taken the correct position. To relieve swelling and pain, pain-relieving ointments (Diclofenac, Dolobene and others) can be prescribed.
- A dislocation complicated by sprained or torn ligaments of the fingers may require surgical intervention. Surgeries are also performed in cases where more than 7 days have passed since the injury and there has been no reduction. The operation is completed by applying a plaster cast or splint for a period of 2 to 4 weeks. The need for fixation is due to the fact that a sprained or dislocated finger must heal properly.
- If the reduction is not carried out on time, the formation of a false joint may occur. Then you cannot do without surgery - you will need to not only restore the bone itself, but also the connecting apparatus.
At the discretion of the doctor, additional physical procedures are prescribed.
With timely contact with a traumatologist and his correct actions, the injury goes away and no complications are observed.