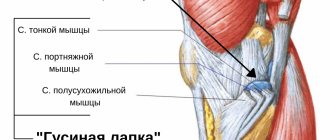
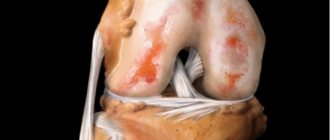
The knee joint is one of the most complex structures of the musculoskeletal system. It is formed by the tibia, fibula and femur.
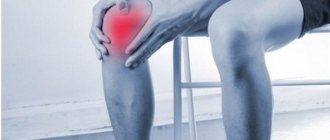
Since this joint experiences quite heavy loads, it is strengthened with connective tissue cords (ligaments) to increase stability. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) serves to strengthen and increase stability of the knee joint and prevents posterior and inward displacement of the tibia. The ACL is damaged quite often; the injury is characterized by partial or complete rupture of connective tissue fibers.
Causes
The main cause of knee ACL rupture is excessive force on the knee in the form of rotation on the supporting leg, in which the body and femur rotate outward while the lower leg and foot remain in one place. This mechanism of damage to the anterior cruciate ligament occurs when running, when you need to turn sharply, as well as during jumping, when the body continues to move by inertia. Most often, this type of injury occurs in athletes who engage in running, athletics, basketball, volleyball, handball, and skiing.
Also, a rupture of one ACL of the knee joint can develop when excessive mechanical force (impact) is directly applied to the anterior region of the knee. More severe damage to the anterior cruciate ligament is provoked by several factors, which include:
Prevention
In order to exclude the possibility of disease, it is necessary to use knee pads when playing sports, avoid injuries and overloads of the knee, and at the slightest symptoms of pathology of the knee joint, immediately consult a doctor. After suffering from ligamentosis and completing a course of treatment, it is necessary to observe a work and rest regime appropriate to the disease, engage in physical therapy, and observe safety precautions when playing sports.
It should be remembered that advanced ligamentosis is irreversible, and the sooner it is detected, the greater the chance of recovery without surgery. For this reason, in the early stages of this disease, it is appropriate to use shock wave therapy, which can be a worthy alternative to surgery.
Causes
Causes
- Congenital decrease in the strength of connective tissue fibers of various structures of the musculoskeletal system, including the ACL.
- Engaging in active or contact sports.
- Anatomical features of the knee joint, in particular the width of the joint space (a wider gap is a factor in which the likelihood of ligament damage increases).
- Human age – in older people, the strength and elasticity of various structures of the musculoskeletal system significantly decreases.
- Gender – in women, the likelihood of ligament damage is higher than in men, which is associated with lower strength of the structures of the ligamentous apparatus, caused by the hormones estrogen and progesterone (female sex hormones).
- Any knee injuries suffered in the past in which the anatomical relationship of its structures is disrupted.
Finding out the cause of ACL rupture, as well as provoking factors, will allow the doctor to select the most effective treatment, as well as preventive measures.
Treatment
When diagnosed with ligamentosis, treatment should always be comprehensive. First of all, it is necessary to fix the joint at rest, interrupt sports activities and eliminate physical activity. In the acute phase of the disease, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, or otherwise NSAIDs) are prescribed to relieve pain.
In advanced cases, surgical intervention is required, as a result of which the irrevocably ossified ligaments are replaced with special fiberglass prostheses. If there was an early diagnosis of ligamentosis of the knee joint, treatment may be less radical.
After removing acute inflammation in the primary stages of ligamentosis, it is possible to restore normal blood circulation, destroy deposits of calcium salts and excess cartilage tissue, and increase the elasticity of ligaments using shock wave therapy (SWT).
Kinds
For ease of diagnosis and prescribing adequate therapeutic tactics, all ACL ruptures are divided into several types. According to the severity of the damage, they are distinguished:
- Microdamage (1st degree) – only single connective tissue fibers are torn.
- Partial rupture (2nd degree) - the overall integrity of the ligament is not compromised, but a portion of the connective tissue fibers rupture.
- Complete rupture (grade 3) – the integrity of the entire ligament is disrupted with a pronounced impairment of the functional state of the knee.
Also, the rupture can be isolated (only the cruciate ligament is damaged) and combined with the involvement of other structures of the knee - rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament, lateral (lateral) ligaments, meniscus tear.
What is patellar tendinopathy and why does it occur?
Patellar tendinopathy
(patellar apex syndrome, jumper's knee, patellar tendinopathy) is characterized by pain around the patella. The condition occurs after unusual or excessive stress on the patellar ligament. Examples of such loads are intense jumping (basketball, volleyball), and activities accompanied by a large number of sudden movements and stops (tennis, badminton) or rapid changes in direction of movement (football).
The disease is also common among runners. Hence another name - runner's knee
1.
Definition
Symptoms and causes
Therapy and exercise
medi products
Symptoms of an ACL tear
Symptoms of an ACL tear
- Pain in the area of injury, the intensity of which depends on the severity of the rupture.
- Increased pain when trying to perform passive and active movements in the knee.
- Swelling of the soft tissues of the knee area, provoked by the development of an inflammatory reaction and the release of blood plasma from the blood vessels into the intercellular substance.
- Limitation of passive and active movements in the knee joint due to its instability and pain.
- Instability of the knee joint, accompanied by posterior displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur.
The severity of these manifestations depends on the degree of violation of the integrity of the ligament, as well as in combination with damage to other structures of the knee. The maximum severity of clinical symptoms is determined at grade 3 rupture.
Ligamentosis of the knee joint. Causes of occurrence and risk groups. Treatment
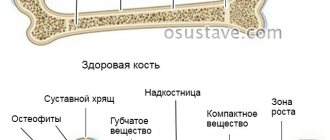
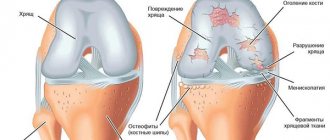
In the knees, the bones are attached to the joints by ligaments. If instead of them cartilage tissue is formed or ossification occurs, this is a sign of their deformation. Ligamentosis is a disease of the ankle joint.
The bones of the knee joint are mobile with healthy muscles and ligaments. As soon as they cease to be elastic, or bone growths of various sizes protrude in the knee joint, then such deformation signals an illness in this area - the leg loses the ability to move smoothly.
Causes of inflammation
Ligamentous fibers weave around the knee joint in a special way, which ensures its mobility or staticity in a certain position, preventing the joint from moving to the sides under load.
Injury to the cruciate ligaments in the knee joint is common. The reason is various injuries in which the ligaments and tendons become inflamed, and as a result - ligamentitis.
If the inflammatory process is left unattended (at this time the body's immune defense decreases), this will lead to changes in the ligamentous tissue.
Knee injury occurs when:
- excessive physical activity;
- falling to your knees;
- sudden turns (movements);
- stretch marks, dislocations;
- cross-country or running with jumping on hard surfaces.
The capsular-ligamentous apparatus is the first to take the blow. The ligaments are stretched and torn, which leads to their damage.
The risk group includes:
- Track and field athletes and athletes who lift weights or play with a ball.
- Old people. They should be wary of this disease, because... Due to age-related changes, expressed in a slowdown in metabolism, tissue nutrition deteriorates.
- People with diabetes mellitus, which can provoke ligamentous transformation.
- Patients with deforming osteoarthritis, autoimmune diseases, rheumatoid arthritis.
All changes negatively affect joints and ligaments, and recovery will take a lot of time.
How to determine the onset of the inflammatory process
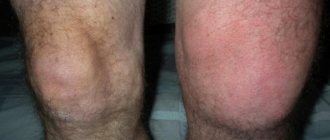
bruised joints
accompanied by pain - this is how the cruciate ligaments react to external influences
.
- After active physical activity, pain appears. She has a whining character.
- The unpleasant sensations do not go away even when the leg is in a calm position.
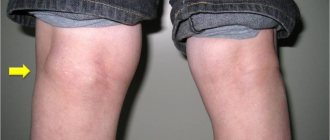
- Redness, bruising, and hematoma appear.
- The motor ability of the knee joint is significantly weakened.
The person has difficulty moving, lameness appears
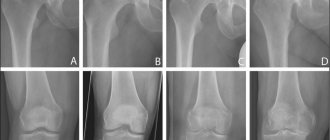
Don't put off visiting your doctor. Using diagnostic methods (X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, CT), a specialist will determine the stage of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What does diagnostics provide? During the examination, disruptions in the knee structure are visible, osteophytes (bone growths) are detected. Is there an excess of calcium salts?
Main methods of treatment
For chronic symptoms, the patient is prescribed complete rest without any physical activity. To completely immobilize the area, wrap it with an elastic wide belt.
During course therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed that relieve puffiness, redness and pain. In case of severe exacerbation, injections are prescribed into the joint area.
Do not self-medicate. See a therapist!
To consolidate success, a physiotherapist can subject the patient to procedures: direct electric current, laser radiation and a magnetic field, massage, and therapeutic exercises.
The best treatment is prevention!
Preventive measures are the basis for not provoking deterioration of the joints in the knees and sprains.
If you have ligamentosis, you should not overexert your legs - the load should be moderate. In case of exacerbation, it is recommended to use knee pads and a bandage.
There is no need to completely give up physical education. Exercises using a certain method improve blood circulation and help restore metabolic reactions in the human body.
To improve the functioning of the ligamentous apparatus, perform simple gymnastic movements:
- straighten and bend the feet;
- slowly, slowly, bend our knees;
- standing straight, we perform rotational circles with our feet one at a time;
- lying on your back imitate walking"
- We grab small objects with our toes or roll a small ball.
Each workout should be performed up to 10 times.
People's Councils
Ligamentosis is afraid of heat. Under the influence of heat, damaged ligaments are restored and healed faster. For the procedure you will need:
- 2 tbsp. Steam spoons of rolled oatmeal flakes in boiling water, without cooking. Apply to the painful area. Wrap with a warm scarf. Keep the compress for 30 minutes.
- Natural honey (no more than 1 tsp), pre-grated horseradish + 2-3 drops of pine essential oil. After mixing, apply the mixture to the affected joint area. Keep warm by covering with a warm scarf.
- Gauze or any cotton fabric is immersed in melted paraffin (white, yellow). Fix. The paraffin mixture retains heat for a long time. Because of this, a special film is created on the skin. Toxic substances are eliminated along with sweat. Blood supply improves, pain goes away, muscle and ligament mobility is restored.
Type of heat therapy
The procedure includes an application, i.e.
application of molten paraffin and ozokerite (natural mountain resin, which contains minerals and natural antibiotics). The wax-like mixture and ozokerite heated to a molten state are poured into a mold and wait until it cools to a soft state. The warm mass is ready, all you have to do is apply it to the sore knee. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Diagnostics
Diagnostics
- Arthroscopy is a diagnostic technique in which a special optical device, an arthroscope with a camera and lighting, is inserted into the joint cavity, allowing the doctor to conduct a thorough examination of its internal walls.
- Ultrasound examination of the knee.
- Radiography is a visualization technique that makes it possible to determine gross damage.
- Computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, which are high-resolution techniques that allow visualization of even small violations of the integrity of the knee structures.
Using diagnostic arthroscopy using microinstruments, the doctor can perform minor surgical procedures aimed at restoring the integrity of the connective tissue fibers of the ligaments.
physiotherapy
physiotherapy
Additional treatment methods:
- physiotherapy – many methods are used that can improve blood circulation in the joint, accelerate the elimination of swelling, and normalize regenerative processes;
- physical therapy - static gymnastics is prescribed from the third day, in the recovery period (after removing the cast) they move on to dynamic exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the limb;
- arthrotherapy - injections of hyaluronate and platelet-rich plasma into the joint, accelerate tissue regeneration and prevent cartilage degeneration.