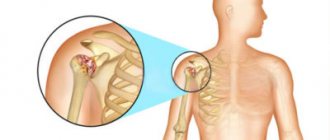
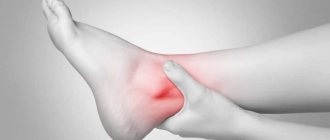
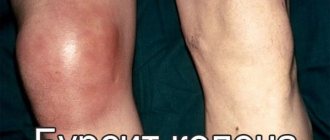
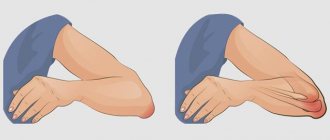
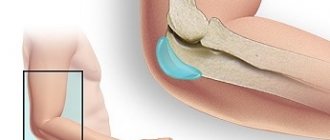
Injuries, heavy loads and many other reasons can make it painful to move your arm. The shoulder becomes swollen and even such familiar and simple actions as washing, brushing teeth, and getting dressed are difficult. These symptoms may indicate bursitis of the shoulder joint - inflammation of the joint capsule (bursa). Treatment is necessary, and not self-medication with traditional methods, but an effective therapy program based on eliminating the cause of inflammation.
Doctors at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center have all the necessary resources at their disposal to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate individual treatment. Do not delay your appointment so as not to encounter complications and prevent bursitis from becoming chronic or recurrent.
Symptoms
There are a number of symptoms that indicate the appearance of inflammation in the shoulder area. They include:
Severe pain syndrome;
Redness of the skin in the area of inflammation;
A sharp increase in body temperature;
General malaise;
Intoxication in the form of vomiting, nausea and diarrhea.
Such symptoms indicate the appearance of an acute form of the disease with the formation of a large number of salt compounds. In the presence of a chronic form of the pathology, frequent manifestations of pain are noted, which appear in the morning hours.
If a patient is diagnosed with tendobursitis, then he experiences a dull pain that forms in the forearm area. During the diagnostic process, the patient can accurately indicate the location of the combat area. Upon external examination, no characteristic changes are observed. This form of bursitis can only be detected using radiography.
Subacromial bursitis has pronounced symptoms:
Acute pain that occurs not only during physical activity, but also in a state of complete rest;
Weakness when moving the arm;
Touching the affected area causes discomfort to the patient;
The liquid contains impurities from blood and pus.
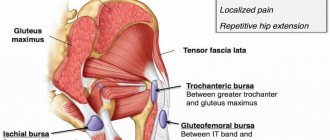
Types of shoulder bursitis
Quite a few types of bursitis are diagnosed, depending on their location, but the main ones are:
- subacromial: occurs when the inflammatory process occurs under the acromial process of the clavicle;
- subcoracoid: appears as a result of dislocation of the joint and affects its outer area;
- subdeltoid - inflammation of the bursa located under the deltoid muscle and thickening of the synovial membrane.
Also, bursitis of the shoulder joint can be: calcareous (calcium salts are deposited and turn into lime), calculous (calcium is already located very deep), subacromial (manifested by pain in the joint, especially when raising the arms to a level above the head), in the form of tendobursitis (inflammatory process combined with thinning of the tendon structure). There are also several forms of this disease: acute, subacute, chronic and infectious.
Diagnosis of pathology
An experienced doctor is able to quickly diagnose this pathology. Diagnostics includes the following steps:
Inspect the affected area for redness and swelling;
Questioning the patient. This manipulation allows you to accurately determine the cause of the disease and the duration of its course;
Radiography. This will allow us to identify the location of the inflamed lesion and its size;
Puncture of fluid from the joint capsule. Such a study makes it possible to study its composition and the presence of purulent contents;
Ultrasound diagnostics. It is carried out to determine the exact location of the inflamed area;
Magnetic resonance imaging of the shoulder.
Symptoms: Shoulder pain when raising your arm up
Symptoms:
- Pain when raising your arm up
- Pain when pressing on the shoulder and increased sensitivity
- Stitching pain upon final extension of the arm
- Night pain when lying down
- Weakened muscle strength
- Swelling, redness, hyperthermia
- Pain radiating from shoulder to arm
The pain caused by bursitis of the shoulder joint begins gradually and increases depending on the nature of the movements. As a rule, at the beginning of bursitis, patients complain of discomfort when raising their arms to the top.
If the patient does not attach much importance to his complaints and continues to lead his usual lifestyle, the pain gradually becomes stronger. If the shoulder joint begins to hurt suddenly, the cause is most likely not bursitis. Specialists who treat the shoulder joint strongly recommend not to put stress on the shoulder. Otherwise, the pain will become more and more powerful and will bring you discomfort even during rest. The shoulder's increased sensitivity to pressure can lead to severe pain at night. If the patient sleeps on an unhealthy shoulder, then the shooting pain can wake him up.
Shoulder pain due to bursitis is often accompanied by increased sensitivity on the outside of the shoulder.
When the shoulder joint's range of motion is completely exhausted, patients feel an unpleasant tingling sensation in the shoulder. Such sensations are observed when a person raises his hand above his head in order, for example, to dry his hair, comb his hair, or put on a jacket. People who constantly sleep on their sides also feel the negative effects of bursitis, since while sleeping on the sore shoulder, pressure is exerted on the inflamed mucous bursa. That is why shoulder bursitis is an unpleasant disease.
Repeated monotonous movements of the shoulder only increase the pain. Due to bursitis, pain may radiate towards the outside of the shoulder towards the elbow.
Unlike bursitis of the knee or elbow joint, inflammation of the bursa in the shoulder rarely causes external swelling or changes in the shape of the shoulder itself.
However, with extremely severe inflammation of the mucous bursa, the patient may experience redness of the shoulder joint. These not immediately noticeable signs are primarily concomitant phenomena of bacterial bursitis. Sometimes during bursitis a person's body temperature rises. Bacterial bursitis is also medically called “septic bursitis.”
Treatment of the disease
The treatment process for shoulder bursitis involves the use of several techniques. These include:
Drug therapy;
Ethnoscience;
Physiotherapy;
Surgical intervention.
Surgeries are used for the following forms of shoulder bursitis:
Stone. In this case, drug therapy does not have the desired effect. You can get rid of limescale deposits through surgery;
Calculous. In the presence of this form of the disease, salt deposits are located very deep. Their untimely removal provokes disruption of the functionality of the joint. In simple terms, the shoulder girdle is not capable of bending and straightening the limbs;
Tendobursitis. It can be cured with medication and surgery. The rehabilitation process after such treatment ranges from 1 to 5 months. At a late stage of the disease, surgical intervention is used, which allows to normalize the patient’s general well-being and restore the functionality of the shoulder region;
Purulent bursitis. Surgery allows you to get rid of purulent contents in the synovial bursa of the joint. In some cases, a blood transfusion may be needed. This manipulation is used in the later stages of the disease, when the patient begins to develop blood sepsis.
Traditional medicine offers several options for treating the disease. These include the use of the following components:
Cabbage leaf. It helps relieve inflammation and prevent the recurrence of pain;
Kalanchoe. It is used to treat purulent processes;
Salt. Dissolve it in warm water. Next, the cotton fabric is placed in the resulting solution. After this, it is applied to the affected area.
However, experts do not recommend self-medication. Incorrectly selected therapy can aggravate the situation.
Physiotherapy is carried out to normalize blood circulation in the affected area. The electrodes are applied slightly higher than the location of the inflamed area. The course of treatment is 5-10 days from the moment of diagnosis.
Drug therapy includes the use of anti-inflammatory compounds that block the proliferation of pathogenic microflora inside the synovial bursa. If the patient has purulent fluid, he is prescribed antibacterial therapy. It allows you to destroy the main pathogen and make the patient feel better.
To restore the functionality of the shoulder region, therapeutic massage and physical exercise are used. For the entire duration of treatment, the patient must wear a special bandage or bandage that will prevent movement of the arm.
To alleviate the condition, ointments are used. They quickly penetrate the bloodstream and provide temporary relief. However, it should be borne in mind that such therapy does not always have the desired effect. It slightly reduces the unpleasant sensation during the movement of the shoulder girdle.
Shoulder injuries cause damage to the joint
Severe rotator cuff injury, the most common serious injury, involves dysfunction of the muscles that allow rotation of the joint. It occurs due to improper load during complex athletic exercises, as well as in the presence of muscle tissue dystrophy, which, according to reviews from qualified specialists, is typical for people over 40. It is this type of damage that is characterized by severe pain, low joint mobility and is most acutely felt at an advanced stage when several days pass after the injury. Any injury to the rotator cuff of the shoulder joint is sensitive to timely diagnosis; limited mobility of the joint and severe pain, especially after exercise and when rotating the joint, require immediate medical attention.
Damage and sprain of the shoulder joint ligaments is another type of injury that is common in the modern world, where the concept of physical inactivity, incorrect or absent, as well as abnormal physical activity is familiar to everyone. A sprain occurs when a joint is subjected to severe and unrestrained stress that is simply not compatible with its integrity. Stretching requires urgent therapeutic and sometimes surgical measures, as it can cause complete loss of joint mobility in a neglected state.
A critical Bankart injury to the shoulder joint is a serious rupture of the labrum, which is caused by trauma and congenital abnormalities of the joint. This type of damage requires complex and radical measures, such as surgery on the shoulder joint, since the articular labrum is directly responsible for the mobility of the joint and when it is damaged, motor function is lost, inflammation and pain occur in the joint capsule and nearby muscles, especially when atmospheric pressure changes and under loads.
Slap injuries to the shoulder joint are a variation of the previous ones and occur due to frequently repeated microtraumas that are typical for shot throwing, spear throwing, serving in volleyball, etc. This type of dislocation is characterized by chronic pain and impaired joint mobility, as well as discomfort, which is often attributed to sports fatigue, ignored and treated in an advanced stage.
How to prevent bursitis?
In order to prevent the occurrence of bursitis, it is recommended to follow the advice of experienced specialists:
Reducing physical activity, which is aimed at the area of the shoulder girdle and collarbone;
Rejection of bad habits. In this case, you need to stop drinking alcoholic beverages and stop smoking tobacco products. They contain carcinogenic substances that quickly penetrate the bloodstream and contribute to abnormal changes in the body;
Proper nutrition. The diet should contain natural products, animal and plant proteins, as well as a high level of fiber. These components help normalize metabolic reactions and promote the elimination of toxic substances;
Timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment make it possible to prevent serious pathologies in the body in time;
Active lifestyle. Regular movement helps prevent salt deposits in the joints and bone mass. It has been scientifically proven that professional athletes are less likely to suffer from this pathology.
Why might this disease occur?
This disease can be caused by:
- professional activity: people who do heavy physical work often suffer from bursitis: painters, loaders, lumberjacks, and builders;
- sports training: with repeated movements combined with increased regular and monotonous load, the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process in the bursa is much higher, so athletes (tennis players, badminton players) are susceptible to the disease;
- tissue damage: bursitis can occur as a result of injury, cut or even an injection;
- injuries: a blow to the shoulder or a fall often causes hemorrhage into the periarticular bursa followed by inflammation;
- disease of the musculoskeletal system: sometimes gout or chronic arthritis can become the basis for the development of the disease;
- infectious process in the body: a bacterial or viral infection that enters the bursa through the blood vessels can cause bursitis;
- autoimmune disease: in this case, the aseptic process in the periarticular bursa is a reflection of a similar condition of the joints;
- genetic factor: in some cases the disease is inherited.
With age, the likelihood of developing shoulder bursitis increases, because this joint has the greatest range of motion of all others.
Poor posture is another cause of inflammation. When the body bends strongly forward, the space under the acromion narrows. If this area is narrowed long enough, the pressure on the subacromial bursa, as well as the tendons near it, increases, which leads to the development of inflammation.
Which joints are punctured?
Puncture is performed on almost all joints: phalangeal, hip, knee, shoulder, elbow, etc.
The puncture technique is almost the same for all joints, the only difference is the injection site. This manipulation requires the professionalism of a doctor, since it is important not to damage the surrounding tissues or touch the bone. The puncture site is treated with an antiseptic, anesthesia is given, and then a puncture is performed.
A diagnostic puncture of the shoulder joint is performed if inflammation of the joints is suspected.
The purpose of puncture of the elbow joint is to diagnose rheumatic lesions and joint injuries. A puncture of the wrist joint is performed to determine inflammation of the joints caused by connective tissue diseases. The puncture area is the back of the hand, between the tendons of the index finger and the thumb and forefinger.
The purpose of a knee is to confirm or refute the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnostic puncture of the hip joints can detect gout.
small joints of the hand will help diagnose connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus) .
Punctures of the ankle joint and small joints of the foot are performed if connective tissue diseases that cause inflammation of the joints are suspected.