Shoulder bursitis is an acute or chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the joint capsule, severe pain when moving the arm, and swelling. The onset of the disease can be determined by the characteristic numbness from the shoulder joint to the hand, and the appearance of a small ball in this area. There are many reasons for the development of pathology. If the inflammation was caused by deposits of calcium and its salts, calcareous or calcified bursitis develops. This form of the disease takes a long time to develop and usually depends on external factors - nutrition, lifestyle, mechanical damage. In this article we will look at what stone bursitis of the shoulder is and how it can be avoided.
What is stone or calcareous bursitis of the shoulder, disease code according to ICD-10
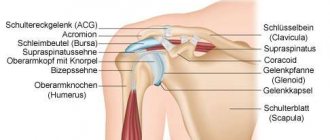
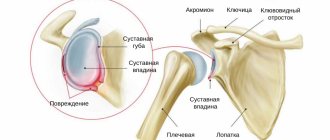
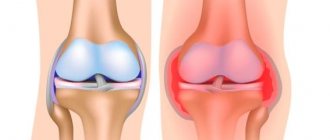
The shoulder joint is one of the movable bone joints of the skeleton and is the loosest among them. In its structure, like all such compounds, it has a synovial membrane lining the entire surface of the cavity.
This inner layer serves as its additional shock absorption and is responsible for the production of synovial fluid. The liquid is a thick mass that fills the joint cavity (from the Latin bursa - bag). Its main function is to lubricate the joint during movement, thus protecting it from friction and wear. This fluid also promotes the mobility of the joint joint and performs a shock-absorbing function. Frequent inflammation in the mucous membrane of the shoulder joint can lead to a disease called stone or calcareous bursitis of the shoulder. During the development of this disease, qualitative and quantitative changes in the joint fluid occur.
In a chronic course, such an imbalance causes calcification or the formation of calcareous deposits and stones in the tissues of the articular joint.
Causes
Many external and internal factors can provoke the development of inflammation.
Calcareous bursitis is caused by various reasons that have a negative effect on the human body.
This type of disease develops due to the accumulation of too much calcium. The inflammatory process should be blamed for this. It is this that converts beneficial calcium salts into limescale, which prevents the shoulder structures from performing their main functions.
Dense accumulations of calcium can be seen in the synovial bursa during both acute and chronic course of the pathological process.
The following unfavorable factors lead to the development of calcareous bursitis:
- Prolonged loads on the shoulder joint;
- Short-term shoulder overload;
- Injuries of various types;
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Hereditary predisposition.
Any of these reasons can cause the development of calcareous bursitis. If a person has such disorders, it is necessary to regularly prevent the formation of calcium deposits in the joint capsule.
Who is at risk
The following people are most at risk of one day encountering an unpleasant disease:
- Professional athletes;
- Workers whose permanent activities involve carrying heavy loads;
- Elderly people who suffer from arthrosis or arthritis;
- People with a genetic predisposition to this disease.
Men and women who are at risk should carefully monitor their own health. They should avoid serious overload, as this will only accelerate the onset of shoulder disease.
At risk are athletes and loaders - people whose profession requires constant stress on their shoulders.
Causes of inflammation of the bursa of the shoulder joint
Men are most often susceptible to the development of inflammation of the bursa of the shoulder joint; women encounter this disease much less often . Systematic loads on this articular joint lead to microtraumas of the synovial bursa, which results in changes in the composition of the protective lubricant. This provokes the development of an inflammatory process - bursitis.
The main causes of inflammation of the bursa of the shoulder joint:
- great physical activity;
- injuries and bruises;
- endocrine system disorders;
- allergic reaction, including diathesis;
- autoimmune diseases;
- various infections;
- rheumatoid inflammatory processes.
Often such diseases affect athletes who have been subjecting their shoulder joints to heavy loads for years. Injuries and heavy lifting also have a detrimental effect on the condition of this part of the human skeleton. This disease is also common for older people, which is caused by a decrease in muscle tone over the years.
Inflammation of the joints may indicate the presence of serious diseases in the body such as tuberculosis, brucellosis, gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.
You can learn about the treatment of prepatellar bursitis by clicking on this link.
Before there, how to treat calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint
There are several ways to treat calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint, but generally they have little effect on the patient’s condition. Pharmacological drugs help to achieve only temporary remission and reduce the severity of pain. Surgery does not completely restore the shock-absorbing capacity of the bursa of the shoulder joint. The result of this is instability of the joint, the appearance of habitual shoulder dislocations, regular exacerbations with a strong process of inflammation.
Before treating calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint, it is important to determine the etiology of the disease. To do this, it is enough to order an x-ray. It will show that the walls of the synovial joint capsule are covered with a layer of calcium salt deposits. To clarify the diagnosis, puncture, arthroscopy or MRI examination may be indicated. An experienced doctor will be able to make an accurate and correct diagnosis through examination, functional tests and x-rays.
Do not engage in self-treatment and diagnosis. If characteristic symptoms appear, consult a specialist as soon as possible.
Features of the disease in acute and chronic form
There are acute, subacute and chronic forms of the disease. The clinical course of each of them has its own characteristics. The acute form is characterized by severe pain in the shoulder joint, the intensity of which becomes even stronger when you try to move your arm up or to the side. The appearance of shoulder pain, which intensifies at night, indicates that calcium salts are being deposited. Over time, this can lead to limited mobility of the shoulder joint.
The chronic form of the disease occurs after repeated inflammation or systematic injury to a given joint. The pain in this form is less intense, but with increasing load on the shoulder joint it still intensifies. The long course of a chronic disease can eventually lead to complete limitation of joint mobility and muscle atrophy.
Causes of stone bursitis
Stone bursitis is a consequence of improper treatment of various diseases and injuries of the shoulder joint. At the initial stage, the inflammatory reaction is of great importance. It can be triggered by the following negative factors:
- hemorrhage into the synovial joint capsule due to injury to the shoulder area (bruise, sprained ligaments and tendons, bone fracture or crack);
- exposure to low temperatures and impaired trophism against the background of compensatory narrowing of small blood vessels;
- disruption of the innervation process with plegitis or cervical osteochondrosis with radicular syndrome;
- aseptic neurosis of bone and cartilage tissue of ischemic origin;
- rheumatoid or reactive arthritis of the shoulder joint;
- humeroscapular periarthritis;
- deforming osteoarthritis.
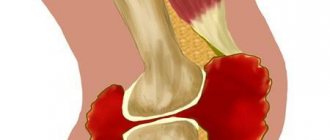
All of these diseases are potential risk factors for the development of calcareous or calcareous bursitis. But the mechanism of development of the pathology should be considered further. After the initial inflammation, tissue scarring begins. At this moment, a large number of fibrin fibers are pulled into the joint cavity. In those places where there was no direct inflammation, calcium salts begin to precipitate, which are first formed by osteophytes, and then completely penetrate deep into the physiological structure of the cartilage tissue. calcifications fill all cavities that are formed as a result of inflammatory melting of tissues.
Of no small importance is the disruption of the outflow of synovial fluid, which contains large amounts of calcium. As a result of stagnation, calcium is deposited on the inner walls of the bag and forms the primary layer of liming. The compaction of the bursa wall leads to the fact that it loses its elasticity and shock-absorbing ability. This entails further accumulation of stagnant synovial fluid and an intensification of the calcification process.
Predisposing factors of negative influence are the following aspects:
- excessive physical activity;
- exceeding the physiological amplitude of mobility of the upper limb in the shoulder joint, which entails inevitable microscopic injury to tendon, ligament and muscle tissue;
- genetic predisposition in familial cases of the disease;
- an incorrectly developed daily diet with an excessive amount of calcium and a lack of phosphorus (in the absence of this microelement, calcium is not able to be deposited in bone tissue and begins to penetrate into soft tissues);
- fractures of the upper limb;
- curvature of posture;
- various tunnel syndromes.
These factors should be eliminated from your life before starting treatment. Otherwise, the positive effect of the therapy will be short-lived. Please note that in most cases, calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint develops in professional athletes, loaders, builders, painters and finishers, cooks and sellers, and teachers. Elderly people leading a sedentary lifestyle often suffer. In them, stone shoulder bursitis is often associated with deforming osteoarthritis and leads to disability.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of the disease is individual in each case. The main symptoms of calcareous bursitis of the shoulder:
- swelling of soft tissues;
- pain that gets worse with movement;
- increased body temperature;
- decreased joint mobility;
- redness of the skin in the area of inflammation;
- decreased sensitivity.
Most signs of the disease are subjective; in order to accurately determine the degree and severity of symptoms, special instrumental medical scales have been developed . Features of the course of stone bursitis depend on age, region of residence, lifestyle and other parameters.
Diagnostic methods
Puncture for shoulder bursitis.
Only a doctor can correctly diagnose shoulder bursitis. Therefore, at the first manifestations of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor, who, based on the patient’s complaints and diagnostic procedures, will prescribe timely treatment. The set of measures to make a diagnosis consists of the following:
- examining the affected area for redness and swelling.
- establishing the cause of the disease by collecting anamnesis.
- An x-ray will indicate the form of the disease and the presence of salt deposits.
- puncture of the affected joint will help determine the presence of blood or pus in the synovial fluid. This will give an answer about the cause of the disease: in case of injury it will contain blood, and in case of infection it will contain pus.
- MRI of the shoulder joint.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, the use of several diagnostic methods is required, this is necessary to exclude synovitis of the shoulder joint. They are usually prescribed at a certain interval to assess the dynamics of the disease.
Treatment methods
Bursitis of the shoulder joint does not go away on its own. If left untreated, the disease will continue to progress and cause serious complications.
Treatment of the pathological condition must be comprehensive. Taking medication alone is unlikely to be enough. To achieve recovery, the patient should additionally undergo physiotherapeutic procedures, perform special exercises and, in addition, use proven folk remedies that eliminate inflammatory processes in the human body.
It is strictly forbidden to self-medicate for stone bursitis. Wrong actions will lead to a deterioration in human health and contribute to the development of complications.
Taking medications
The basis of treatment for calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint is taking medications. They should be prescribed by a competent specialist based on the patient’s current health indicators.
At the initial stage of development of the disease, the patient will be able to manage exclusively with conservative treatment methods. He will be prescribed a special bandage for the damaged joint and permanent rest for the injured limb. If the disease is advanced, then more radical methods will have to be used.
For calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint, the following medications are prescribed in the form of tablets and ointments:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Vitamin complexes;
- Analgesics;
- Antibacterial medications;
- Immunomodulators;
- Chondroprotectors.
Only a specialist can decide which medications to take and in what dosage.
The basis of treatment is drug therapy
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods of treatment help reduce pain and inflammation. For this diagnosis, the following procedures are recommended:
- Massage;
- UHF therapy;
- Iontophoresis;
- Electrophoresis.
Such types of treatment are prescribed only if the patient has no contraindications to such manipulations.
Surgical intervention
In particularly difficult situations, patients have to agree to surgical intervention. Advanced forms of the disease cannot be cured with medications and physiotherapeutic procedures.
During the operation, the specialist removes purulent formations and dead tissue particles in the affected area.
The decision regarding the advisability of surgical intervention is made based on the patient’s current health indicators and the individual characteristics of the development of the disease state.
Treatment strategy
Features of treatment for stone bursitis depend on the patient’s age, the stage of development of the disease and the general condition of the body. In the early stages, traditional treatment for shoulder bursitis is recommended, which includes medication and physical therapy. For the treatment of advanced forms, surgical intervention is indicated.
Medications
Treatment of bursitis involves eliminating pain, relieving inflammation and swelling, and restoring the necessary mobility to the shoulder joint. During an exacerbation, anti-inflammatory drugs are first prescribed. If the cause of inflammation is an infection, then broad-spectrum antibiotics or corticosteroid pharmaceuticals are used for treatment. During this time, it is necessary to limit the load on the shoulder joint if possible; you can use a special shoulder bandage. In addition, to reduce pain, it is recommended to take painkillers (Analgin, Ketorol, Nise).
For bursitis caused by injury, injections of Novocaine and Hydrocortisone are prescribed. Also, to relieve pain symptoms during purulent inflammation, a bactericidal patch or bandages with hydrogen peroxide are used. If there is no desired effect after treatment, the pus is removed surgically (opening the bursa or puncture). The operation is performed under local anesthesia, the rehabilitation period is up to 12 days.
Corticosteroids are steroid hormones that are produced by the adrenal cortex, not the gonads. Therefore, they do not have estrogenic activity.
You can read about the symptoms of bunion of the little toe in this article.
Physiotherapy
After eliminating pain and relieving inflammation, the patient is often prescribed various physical procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- ampipulse
A therapeutic massage will have a positive effect on a sore joint; it will help restore blood circulation. Massage should only be performed by a specialized specialist; it is always a complex of procedures, since single manipulations do not have a positive effect.
Massage is one of the key methods of treatment and rehabilitation.
Traditional methods
Calcareous bursitis of the shoulder is a chronic, complicated form of inflammation, since there are already fossilized calcareous deposits in the joint. To remove them, you can use various methods for treating shoulder bursitis at home. They should be used as an auxiliary treatment to the main one prescribed by the doctor. It is worth remembering that some medicinal plants also have contraindications. Before self-medicating, ask your doctor for advice. Several effective recipes:
- A compress of Kalanchoe juice will help relieve inflammation. To do this, after beating off the leaves of the plant, apply them to the joint for 4 hours. After this time, take a new sheet and do the same. The course of treatment is 7 days.
- Cabbage juice and vegetable oil will also help relieve symptoms of the disease. At night, lubricate the affected area of skin with vegetable oil and cover with a cabbage leaf. This procedure must be repeated for a month.
Taking pine baths is also used to alleviate the general condition. The needles have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic and strengthening effects.
Treatment of calcareous (stone) bursitis of the shoulder joint
To treat calcareous bursitis in the city clinic, mainly conservative pharmacological methods are used. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to help eliminate pain. the patient actually feels relatively healthy and ready to return to his professional duties.
But, unfortunately, such treatment of stone bursitis does not lead to the elimination of calcium salts from the synovial joint capsule. Therefore, against the background of general well-being, further progression of pathological changes occurs.
In advanced cases, treatment of calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint is carried out using surgery. Currently, endoscopic intervention is used for this using arthroscopy under local anesthesia or epidural anesthesia. During the operation, the doctor, under the control of an X-ray machine, cleans the internal contents of the synovial joint capsule. This gives a certain positive effect. Unfortunately, as practice shows, over the next 2-3 years, operated patients experience a relapse of the disease.
There is a more effective and safer treatment for stone bursitis of the shoulder joint using manual therapy methods. To do this, the following methods of influence are used:
- physical therapy increases blood supply to the surrounding muscle tissue, which entails the removal of calcium salts from the affected area;
- osteopathy and massage accelerate the process of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the area of the affected tissues - this starts the process of natural leaching of calcium salts from the affected tissues;
- kinesiotherapy helps to get rid of pain;
- reflexology starts the process of tissue regeneration;
- physiotherapy and laser treatments speed up recovery.
If you need comprehensive, effective treatment for calcareous bursitis of the shoulder joint, contact a free consultation with an orthopedist at our manual therapy clinic. Here you will be given an accurate diagnosis and told about how you can achieve a complete restoration of the damaged shoulder joint.
Prevention
To prevent shoulder joint bursitis, it is necessary to avoid excessive physical stress on this part of the shoulder. At the same time, engage in physical exercise to maintain the overall tone of the body. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes giving up smoking and drinking alcohol, also plays an important role in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system and the body as a whole.
The daily diet should contain all the necessary vitamins and elements, which will help strengthen the immune system. Eat fatty fish at least three times a week: herring, mackerel, salmon. Eating jellied meat will replenish collagen reserves in the body, the amount of which decreases significantly with age. Flaxseed oil will saturate your body with omega-3 acids; 1-2 teaspoons during the day will be enough.
conclusions
- Inflammation of the shoulder joint is a fairly common disease that needs to be treated promptly.
- Calcareous bursitis of the bony joint of the shoulder is a chronic form complicated by the formation of calcareous deposits.
- Treatment consists of a complex of various measures.
- In advanced cases of the disease, when traditional treatment does not work, surgery is prescribed.
We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with the symptoms of heel bursitis in this material.