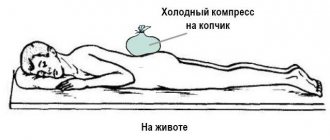
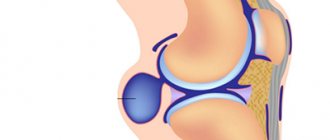
Epithelial coccygeal duct is a congenital defect in the form of a narrow canal in the soft tissues under the skin of the sacrococcygeal region. The passage is located in the fold between the buttocks, and comes out to the surface of the skin with one or more small openings (primary openings). Inside the passage there are sweat and sebaceous glands, hair follicles, and connective tissue fibers. Their waste products exit through the primary openings in the form of secretions, and infection can penetrate into the tissue through these same openings.
In the absence of inflammation, the epithelial coccygeal duct gives virtually no symptoms. Exceptions may include minor discharge from the passage, moisturizing the skin between the buttocks, and itching.
Delicate and complex problem
Coccyx cyst (epithelial coccygeal duct) is one of the most delicate and complex health problems.
Those who have dealt with her understand what we are talking about. Coccyx cyst occurs in both men and women. According to statistics, the stronger sex suffers three times more often. The delicacy lies in the localization of the pathological focus. The formation is located in a fairly intimate place (the area of the coccyx, sacrum and intergluteal fold) not far from the anus. Not everyone will easily want to share this with others, even with relatives and loved ones. Not everyone is ready to immediately show the sore spot, discuss their complaints and discomfort, even with doctors. When an epithelial cyst of the coccyx becomes complicated (abscess formation, suppuration, relapse), a person in most cases is deprived of the opportunity to maintain his usual lifestyle and quality of life. Irritating pain, excruciating discomfort, serous or purulent discharge, an unpleasant odor appear, laundry gets dirty, and additional hygiene procedures become necessary. Often it is simply impossible to sit normally. And this is not the whole list of inconveniences.
Many in this situation are forced to give up their usual activities, sports, and even intimate life. All this is depressing. Adding to the delicacy is that a coccyx cyst clinically manifests itself more often in adolescence or puberty. Teenagers are known to be especially sensitive to such problems, although they will try their best not to show it. Wise advice, understanding, help and timely consultation from a surgeon are especially important for them.
The complexity of this pathology lies in the fact that very often there are relapses (repeats) after improper preparation for surgery, an insufficiently radical operation (incomplete removal of cysts, fistulas and leaks), inattentive management in the postoperative period, failure to follow doctor’s recommendations, ignoring basic hygienic procedures and other reasons. Some people have to undergo surgery for coccyx cysts not once, not twice, but multiple times. You won’t believe it, but there are still people who suffer all their lives due to relapses. This reduces the quality of life and is certainly a tragedy. It shouldn't be like this!!!
It is necessary to initially take this disease and the initial operation very seriously. Agree, no one wants to have multiple surgeries. However, repeated surgical intervention should be taken no less seriously, and perhaps more seriously, if the clinical situation has recurred. It is very important to prevent chronicity and continuation of the sluggish process. A coccyx cyst is not a very common and not at all an ordinary problem. The choice of clinic and doctor is extremely important to minimize the risk of relapse. Consultation and surgery with a qualified surgeon who has experience in treating this pathology is necessary.
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment method directly depends on the type of lump and the reason for its appearance. First of all, the patient is recommended to rest in bed, correct nutrition, and take medications. It is impossible to try to cure the problem using traditional methods on your own, since in most cases this provokes rapid progression of the disease and the appearance of complications.
Drug therapy
First of all, the patient is prescribed a group of drugs aimed at suppressing the inflammatory process and disinfecting the area. Medicines are selected individually, depending on the stage of development of the process, the presence of severe symptoms and the test results obtained. The following medications are usually used:
- "Aspirin", "Traumel", "Ibuprofen", "Piroxicam". They are prescribed for severe pain syndrome to alleviate the condition. Additionally, some of them have anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
- "Novocaine", "Lidocaine". Pericoccygeal blockades are used infrequently, only if tablets and capsules do not cope with the task and do not eliminate severe pain.
- "Baralgin" and "Dexalgin". Used in the presence of muscle spasms.
- Nimid and Diclofenac. Prescribed for severe inflammation.
- "Dolobene." It is used in the form of a gel if the patient has suffered an injury or severe bruise to the area.
Antibiotics and immunostimulants are used for osteomyelitis and other pathological disorders. Additionally, bactericidal agents, hydrogen peroxide, sea buckthorn oil or Sophora tincture are used.
For bruises and hernias, UHF therapy is especially effective as part of complex treatment
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic techniques are prescribed as a complement to the main therapy. They are aimed at strengthening the body, as well as launching regenerative processes. The following methods of restoring damaged tissue are usually used:
- Phonophoresis.
- Paraffin therapy.
- Diadynamic therapy.
- Ultrasound therapy.
- Darsonvalization.
- UHF therapy.
All of them are effective for benign formations, bruises, and hernias. In a short period of time, they allow you to activate metabolism in the affected area, speed up the patient’s recovery, and normalize blood flow. Many techniques have immunostimulating, antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Surgical intervention
A lump on the tailbone larger than 1 cm in size, which does not resolve for a long time, can begin to compress the spinal cord. To prevent serious consequences, it is removed surgically. The same solution is used for furunculosis, which is accompanied by an abscess. The decision is made by the doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient. The operation is carried out in several stages:
- The purulent contents are removed from the cone. This is done by medical personnel using a syringe.
- The abscess is opened, the cavity is thoroughly drained.
- As the inflammation subsides, the second part of the operation is performed, which involves excision of the coccygeal tract.
Surgery is also prescribed for chondroma. The endoscopic method, stereotactic therapy or radiosurgery is used for this.
Coccyx cyst. What is this? What is the reason? Classification
Coccyx cyst (epithelial coccygeal duct, pilonidal cyst, ECC) is a closed small cavity (tube-shaped canal), which is located subcutaneously in the area of the upper part of the intergluteal fold. It does not have a direct connection with the coccyx and sacrum. The inside of the cyst cavity is covered with a special epithelial lining, which contains ordinary hair follicles, hair, sweat and sebaceous glands.
According to the main generally accepted version, a coccyx cyst is a type of congenital pathology. An unusual defect (anomaly) in the area of the intergluteal fold is formed in the prenatal period. As a result, a person has a cavity (canal or passage) with a special internal epithelial lining under the skin in the upper part of the intergluteal fold in the coccyx area. According to another version, a cyst (epithelial tract) is formed as a result of hair ingrowth into the skin due to improper inward growth with intussusception (immersion). The appearance of the formation is often associated with injury to the sacrococcygeal region or prolonged sitting (professional drivers often suffer). The cause of suppuration is most often the addition of a specific infection (present in the anus).
In childhood, a coccygeal cyst practically does not make itself felt, since there is no infection in the formation cavity, there is no active hair growth and gland secretion. Clinical manifestations of the disease usually occur between 13 and 30 years of age. As a rule, during these years of life there is increased hair growth, active secretion of sweat and sebaceous glands, including inside the cyst. The hair in the cyst grows, and the glands secrete their secretions inside the formation. It all adds up.
When the cavity becomes full, unpleasant discomfort appears, excruciating pain, weeping, itching and other symptoms may appear. Then one or more primary serous holes (serous fistulas) open between the buttocks in the coccyx area. The contents of the formation (serous discharge, tufts of hair) are released. When holes appear, microorganisms actively colonize the cavity (infection) in which they were not previously present. If for some reason the connection with the external environment is closed, there is a delay in the evacuation (removal) of the discharge from the formation. Overflow, tension, acute inflammation and abscess formation (suppuration) occur.
It so happens that this pathology has many different names. This can sometimes be confusing or misleading. If there is no inflammation, the formation is called an uncomplicated coccyx cyst, dermoid cyst, or epithelial coccygeal duct. In the English literature, a pilonidal cyst or pilonidal sinus (pilonidal cyst, pylonidal sinus, hairy or hairy cyst, “hair nest”) is more common due to the presence of hair inside. Holes or holes that occur primarily or secondary are called fistulas in the coccyx region. When acute inflammation and exacerbation of chronic inflammation occurs, suppuration occurs and abscess formation, the diagnosis sounds like an abscess, a festering coccyx cyst or a festering epithelial coccygeal tract. All these names describe different stages or features of the same process.
However, the following classification is most often used in clinical practice:
- Coccyx cyst uncomplicated by inflammation (without clinical manifestations)
- Acute or exacerbation of chronic inflammation of the coccyx cyst
- Chronic inflammation (sluggish process) of coccyx cysts
- Remission of the inflammatory process (cold period)
TYPES OF PATHOLOGY
According to the clinical classification, there are four types of the disease:
| Uncomplicated epithelial coccygeal tract | It occurs latently, without pronounced symptoms. |
| Acute form of inflammation | It has two stages - infiltration and the stage of formation of a purulent abscess. |
| Chronic form of pilonidal cyst | It is characterized by the presence of three stages - infiltration, recurrent abscess, purulent fistula. |
| Remission of the inflammatory process | It occurs with weakening or complete disappearance of negative symptoms. |
Contact a specialist on time! Only with the help of timely and high-quality medical care will it be possible to avoid the transition of the disease to an acute or chronic stage.
Basic preventive measures:
- Observe all rules of personal and intimate hygiene
- Rinse the intergluteal fold
- Wear loose, clean, eco-friendly clothing (avoid tight, tight, synthetic clothing)
- Avoid trauma to the coccyx area
- Avoid prolonged sitting
- Epilation and/or depilation in the tailbone area
- Promptly treat and sanitize primary holes, wounds and microtraumas in the coccyx area.
- Immediately contact a surgeon if the first signs of discomfort and inflammation appear
If clinical manifestations or relapse appear, then the only correct preventive measure will be surgical treatment.
WHY DOES A FISTULA APPEAR?
The pathology is associated with a malfunction that occurs during the development of the embryo. The disease also manifests itself in patients who have a genetic predisposition to a specific form of the intergluteal fold and sacrococcygeal region.
There are certain factors that can trigger the activation of the disease. A fistula on the coccyx tends to appear against the background of:
- weakened immune system;
- lower back injuries;
- inflammation of the follicles;
- presence of infections in the body;
- increased hair growth in the sacrum area.
In some cases, the pathology is associated with a sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, and poor personal hygiene. Sometimes the disease manifests itself after severe hypothermia.
What worries you about a coccyx cyst? Symptoms
If the coccyx cyst is not complicated or is in the “cold period” after inflammation, then in the vast majority of cases it does not manifest itself and is asymptomatic. From time to time there may be some discomfort in the coccyx area, serous discharge or moisture above and between the buttocks. Sometimes anal itching can be disturbing. Small points (retractions) of the skin in the area of the coccyx and intergluteal fold are visually determined.
When an infection enters the cavity, discomfort increases significantly, inflammation and pain occur in the area of the coccyx and sacrum. Primary openings (holes, fistulas) may appear from which serous, sanguineous or purulent discharge is released. With suppuration and abscess formation, secondary purulent fistulas can form.
In the absence or delay of discharge from the cyst, a painful infiltrate (swelling, edema, tumor, lump) appears through the holes with clear contours in the area of the coccyx and intergluteal fold, which interferes with movements and walking. When the contents of the cyst become infected, acute inflammation develops. Pain, swelling, and redness appear in the area of infiltration. Increased body temperature (fever). Abscess formation occurs (formation of a cavity with suppuration).
After the abscess of the coccyx cyst is drained independently or as a result of surgery (outflow of pus), relief occurs. Pain, swelling and redness disappear, inflammation subsides. The fistula gradually closes, and the postoperative incision wound heals. A period of imaginary well-being begins (the cold period). There is no point in waiting for a complete cure, since there remains a focus of dormant chronic infection (the substrate of chronic inflammation), which becomes aggravated or becomes re-inflamed under certain favorable conditions.
If radical surgery is not performed, then periods of exacerbations and remissions (the interval between exacerbations) can alternate for months and sometimes years. During remission, there is usually no edema or hyperemia. Periodic dull pain or discomfort in the tailbone area may be bothersome. Inconvenience occurs when sitting and in the presence of scanty discharge from holes or fistulas. Fistulas can function, open and close. With prolonged remission, pigmentation and scar tissue changes appear around the holes.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF THE DISEASE
A fistula under the coccyx may not appear for a long period of time. The first symptoms can occur during puberty, characterized by puberty in adolescents. In the lumen of the coccygeal passage, the hair follicles are activated, and waste from the activity of the sweat and sebaceous glands accumulates. The abundance of microflora in the area of the passage itself and in the skin fold between the buttocks is explained by the close location of the anus.
If the primary openings do not provide adequate drainage, the risk of inflammation increases. In this case, the walls of the coccygeal tract begin to collapse, the pathological process affects the fatty tissue, and a purulent abscess forms. Some ulcers reach large sizes, break through the skin and form a secondary opening (purulent fistula of the coccyx).
In patients with the acute form of a pilonidal cyst, the following symptoms are observed:
- pain, swelling of tissues in the area of pathology development;
- redness of the primary openings of the fistula;
- swelling around the tailbone;
- discharge of large volumes of pus;
- increased body temperature;
- inability to sit or lie down.
A fistula in the coccyx area can significantly worsen the patient’s general well-being. In the absence of adequate therapeutic measures, the pathology can lead to general intoxication of the body, requiring emergency medical care.
Treatment of coccyx cyst (preoperative examination, preparation, operations)
Treatment of coccyx cyst is surgical.
To clarify the diagnosis and exclude other pathologies (rectal fistulas, presacral teratoma, osteomyelitis), an examination of the rectum is necessary; in some cases, radiography, colonoscopy or irrigoscopy may be required. Before surgery, thorough depilation of the surgical field is very important and cleansing enemas are required. In case of abscess of a coccyx cyst (festering epithelial coccygeal duct), acute inflammatory phenomena or exacerbation of a chronic process, the first stage is to drain the purulent contents of the cyst (open, drain). The abscess is opened urgently with a small incision under local anesthesia. The cavity is emptied, sanitized with antiseptic solutions and drained. After the drainage of pus, relief occurs. Bandages with water-soluble ointments (levomekol) are applied. The pain goes away, the inflammation subsides, and the postoperative incision wound heals. A period of imaginary well-being begins (full recovery does not occur). A focus of dormant chronic infection remains. Without the second stage - radical surgery (complete excision or removal of the coccyx cyst), as a rule, suppuration is repeated again and again. With a long delay of radical intervention, inflammation can become chronic with the formation of new infiltrates and secondary fistulas.
Primary radical surgery (uncomplicated coccyx cyst) or the second stage of treatment after the subsidence of acute inflammatory phenomena during the period of remission (“cold period”) is carried out as planned. The operation is performed under local infiltration, spinal anesthesia or intravenous anesthesia. Surgical intervention consists of removing (excision) the pathological formation (cyst, canal, tract) along with the internal lining, the contents of the cavity, the surrounding tissues that have changed after repeated inflammatory processes to the fascia. All primary and secondary holes (holes, fistulas) are also excised. To minimize the risk of relapse, all passages and fistulas must be painted with a special dye. After excision of the coccyx cyst, the postoperative wound is usually sutured tightly. Donati sutures are applied to ensure good bleeding control and accurate alignment of the wound edges.
In a number of clinics, the postoperative wound is left open or the edges of the wound are sutured to its bottom for secondary healing (marsupilization). In our opinion, this tactic of postoperative wound management has many disadvantages:
- traumatic
- decrease in the patient's quality of life
- possible secondary infection
- high probability of relapse
- vicious postoperative scars after secondary healing
Removal methods
You can remove a coccyx cyst using 4 different methods, during which the epithelial tube is eliminated. The selected technique is directly related to the presence or absence of inflammation, the complexity of the disorder, and the general health of the patient. Before the operation begins, the surgeon indicates to the patient possible methods of surgical intervention, notes their advantages and disadvantages, and then, together with the patient, selects a treatment method that is relevant in this situation.
Possible methods for getting rid of a pilonidal cyst include the following:
- With an open wound. During the surgical intervention, the purulent secretion is opened and the pus exudate is removed - these actions are performed by attaching the edges of the wound to the bottom. They prevent the secondary implementation of the coccygeal tract, but greatly slow down the recovery process, resulting in an increase in the duration of rehabilitation. This factor contributes to the rare use of the procedure.
- With a closed wound. Due to the presence of recesses for drainage, which are used during surgery with the closed wound method, the likelihood of developing negative manifestations is reduced. The postoperative recovery period is much shorter.
- Bascom method. This technique is performed only by highly professional surgeons, since it requires suturing abnormal passages. Elimination of the primary passages occurs with the help of a needle, and in order to go through the stage of removing exudate, a well-equipped drainage system is required.
- Sinusectomy. When using this technique, there is no cutting of the skin. Blue methylene dye is injected into the created hole, after which the sinuses are excised by performing electrocoagulation, that is, current section.
If several formations are found on the coccyx, then the operation is performed using skin flap plastic surgery. This number of cysts indicates the possibility of their re-development. To avoid such an event, complete opening of the epithelial entrance is performed, and then its clearing. After this, skin flaps are transplanted to cover the incised surface.
Today, laser treatment for coccygeal cysts is becoming increasingly popular. The use of laser surgery is more aesthetically pleasing and the patient is left with no scars after recovery. During this type of surgery, anesthesia is also used, this is done in order to completely minimize the likelihood of pain.
The cost of the procedure in Moscow exceeds the price of 10 thousand rubles. In other Russian cities, the procedure may cost less.
Postoperative period. Dressings after surgery
In the postoperative period, bed rest must be observed during the first day after surgery.
You can get up and walk the day after surgery. You can sit down on days 5-6-7. Fully sit for 8-9 days. It is very important to avoid stress on the seams. It is necessary to avoid traumatizing the postoperative wound, and subsequently the scar. In the postoperative period, antibacterial therapy is prescribed if the process was accompanied by acute inflammation and abscess formation. Painkillers are used in the presence of pain. A modern breathable aseptic dressing with an absorbent pad is applied to the sutures. Dressings are done daily. On days 4-5, if there is no discharge from the wound, you can bandage it every other day. During primary healing, the sutures are removed 12-14 days after surgery. If the postoperative wound is treated openly, then secondary healing takes a fairly long period. In such a situation, it is best to use modern medical dressings and fixation means for dressing and care. In the postoperative period, the patient's quality of life should not suffer. We can select special dressings to care for an open wound, even if you had surgery in another clinic.
Diagnostic procedures
A lump in the lower back requires consultation with a doctor. He will conduct palpation and visual examination, determine the structure and degree of development of the pathological process. If there is a purulent focus, an additional test is prescribed to determine glucose in the blood. This is necessary to determine the presence of an infectious process and the degree of sterility of the biological fluid. In addition, the following types of instrumental studies are carried out:
- X-ray. It is used to determine the presence of injury or a crack in the bone structure, intervertebral hernia or osteomyelitis. It is easy to see the affected area in the image, so it is taken in several projections.
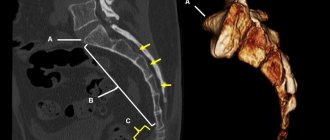
- Fistulography. Used with a contrast agent. It is one of the types of x-ray examination. The image allows you to identify the branching of the fistula and the presence of damage in neighboring organs. Before the procedure, the tract is thoroughly cleaned and washed, filled with a contrast agent based on iodine and barium. The quantity depends on its length. The procedure is prescribed primarily before surgery.
- Sigmoidoscopy. The technique is used to identify fistulas. A special device allows you to examine the rectal cavity, identify a tumor or abscess, and collect material for further research in the laboratory.
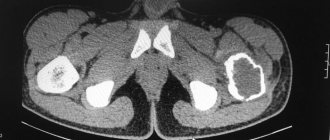
- Ultrasound. Diagnostics allows you to determine the condition of soft tissues, identify cysts or tumors. It is painless and can be used as many times as necessary to clarify the condition.
Prescribed when the picture is insufficient as an additional MRI technique. The research method is expensive, but highly informative. With its help, the condition of the pelvic bones, spinal discs, vascular damage, and spinal cord infarction is revealed.
To eliminate acute pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers
Complications and consequences
If the process is severe, the following complications may develop:
- relapse
- coccyx osteomyelitis (purulent bone lesion)
- fistulous pyoderma (purulent skin lesion)
- fungal infection
- multiple communicating purulent fistulas and pathological tracts with epithelial lining (sacrococcygeal region, perineum, scrotum, inguinal folds, anterior abdominal wall, anus)
Complications require painstaking, lengthy, often multi-stage treatment. Competent prevention, the right choice of clinic and doctor, timely treatment, radical surgery, and compliance with all recommendations will help you avoid such problems.
Causes of the disease
You will have to learn about the symptoms and treatment of coccyx cysts if problems occur at the stage of development of the tail section of the embryo. In this case, a channel lined with epithelium appears, which, under favorable conditions, becomes inflamed.
Experts believe that abundant hair in this area leads to pathology. If hair growth is disrupted, it begins to sink into the skin, which provokes inflammation. However, this is not the only factor contributing to the formation of a cyst. Also cause the disease:
- clogged pores and follicles;
- sedentary lifestyle of the patient;
- genetic predisposition;
- infections treated incorrectly or untimely;
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- damage in the buttocks area.
An experienced doctor will determine what caused the pilonidal cyst of the coccyx, and then he can prescribe treatment for you.
Exercises for the tailbone
After repositioning the tailbone or after surgery to remove a cyst, it is important to apply a certain set of measures, such as exercises for the tailbone, which will strengthen the affected area and normalize blood flow to the affected tissues
In addition, inflammation of the coccyx after surgery requires the use of antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
For several months after therapy, it is important to pay attention to the fact that for tissue healing it is necessary to reduce sudden movements of the pelvis and the load on the tailbone to a minimum
How to treat
Treatment of the disease is usually surgical. The thing is that conservative methods do not give a lasting effect - the disease appears again and again, causing great inconvenience to the patient. However, each case is assessed individually, and the doctor examines the situation from different angles and chooses the optimal treatment.
Conservative way
It is often an addition to surgery. This involves taking medications aimed at relieving inflammation, painkillers, as well as applying ointments to the affected area.
Surgical procedures
If you are worried about a coccyx cyst, the symptoms and treatment of which had to be studied in order to understand what to do next, you should also know that surgical intervention will allow you to forget about the symptoms of the disease once and for all. This operation will not be complicated; it includes:
- opening of the cystic capsule;
- cleaning the resulting cavity from the contents, thoroughly washing and disinfecting;
- removal of the epithelial tract and all its branches, which can lead to relapses.
Treatment of a cyst on the coccyx in men in this way allows you to avoid constant problems with inflammation of the fistulous tract, as well as get rid of constant trauma to the area, which is associated with the emergence of new tracts.