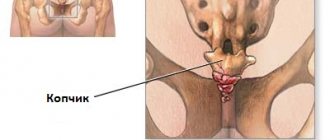
to unequivocally answer the question why the tailbone hurts . Pain in the tailbone can be caused by various reasons, and we recommend not to ignore pain in this area, since they almost always indicate serious illness.
As a rule, the most common causes of pain in the tailbone are:
- Injury
- Degenerative changes in the spinal column
- Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
- Problems with reproductive organs
Pain in the tailbone due to injury
The first thing you should do when visiting a doctor with pain in your tailbone is to undergo an X-ray examination. This procedure will help detect injuries to the spine as a whole and the coccyx area, including old ones. Usually, after an incident (fall, bruise, accident, etc.), a person experiences acute pain, which disappears over time. However, pathological changes in the form of cracks and hematomas of the periosteum may remain in the area of the spine and coccyx. Over time, calcifications and osteophytes can form in this place, which pinch the nerve endings and the person experiences periodic pain, especially after awkward and sudden movements.
Causes
An abnormal pathology forms in the sacrococcygeal region - a passage under the skin that opens outward with one or more small holes in the midline between the buttocks. The length of the epithelial coccygeal tract is about 3 centimeters. The epithelial coccygeal tract may not manifest clinical signs throughout life; the patient may become aware of the presence of an anomaly during the development of an inflammatory process, the development of a purulent cyst of the coccygeal tract. The cause of the development of suppuration of the coccyx cyst is various injuries, hypothermia, infections, and failure to comply with hygiene rules. The epithelium lining the cavity of the pilonidal cyst of the coccyx has the same properties as human skin - it secretes waste products and sweat.
Waste products are excreted through pinpoint openings in the epithelial tract. If injury or infection occurs, the primary epithelial tract is blocked, and an acute process begins, which leads to the development of complications. The walls of the epithelial coccygeal duct are destroyed, and inflammation spreads to the surrounding tissue. As a result of the inflammatory process in the coccygeal passage, phlegmon, purulent fistulas, and an abscess of the sacrococcygeal region can develop. A dermoid cyst of the coccyx is a congenital pathology that is formed in utero when elements of the germ layers are displaced under the skin, in the superficial layers of the skin. A dermoid cyst differs from the epithelial coccygeal duct in that it has a clear capsule; the epithelial coccygeal duct, unlike a dermoid cyst, has a point exit on the surface of the skin.
This type of cyst may not bother the patient for a long time, manifesting itself only in discomfort and pain when sitting for a long time. The development of the inflammatory process leads to cyst breakthrough, fistula formation, increased temperature, and severe pain when changing body position.
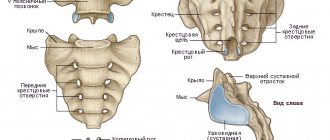
Degenerative changes in the spine
Another common reason for back pain in the coccyx area is osteochondrosis. This fairly common disease tends to develop progressively and can lead to health problems and even disability.
Osteochondrosis is especially dangerous due to its complications in the form of radiculitis, cauda equina syndrome, protrusion and herniated disc.
If the tailbone hurts due to degenerative changes in the spine, then other characteristic symptoms appear. This may include stiffness of movement, spreading of burning pain and tingling to the perineum, inner and outer thighs.
Diagnosis of coccydynia
To make an accurate diagnosis, NEARMEDIC specialists thoroughly examine the patient in order to exclude diseases that may also cause pain in this area. Most often used:
- palpation of the rectum;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity;
- radiography of the sacrococcygeal spine;
- orthopedic, urological, gynecological examinations;
- sigmoidoscopy - examination of the rectal mucosa using special equipment.
Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract
The reason why the tailbone hurts may also be pathologies of the rectum and large intestine:
- Proctitis . They are usually accompanied by disturbances in bowel movements, in which constipation alternates with diarrhea, and during an exacerbation, mucus and pus are released from the anus
- Hemorrhoids . Manifested by periodic discharge of scarlet blood after defecation and causes discomfort when sitting and walking
- Rectal fissures . Characterized by a disturbance in general health, the appearance of itching in the anus
Survey
Initially, patients usually turn to a traumatologist, orthopedist or rheumatologist. Depending on the nature of the pain syndrome, the circumstances of its occurrence and the data obtained during the examination, the doctor may refer the patient for consultation or examination and treatment to an oncologist, gynecologist, urologist or proctologist. The list of diagnostic techniques for pain in the tailbone usually includes the following procedures:
- General inspection.
The specialist detects crepitus in fractures, signs of inflammation (edema, hyperthermia and hyperemia), fluctuation indicating fluid accumulation, space-occupying formations and fistula tracts. The doctor determines the exact location of the pain, specifies which structures it is associated with - the tailbone itself or the soft tissues. - Rectal examination
. It is performed in the absence of intense pain caused by suppuration in the area of the rectum and nearby tissues. During a rectal examination, tumors and infiltrates in inflammatory diseases are identified, the location and structure of the coccyx is assessed, and compacted ligaments in coccydynia are determined. - X-ray examination.
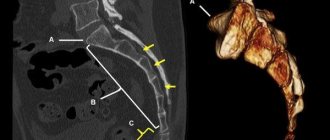
X-ray of the coccyx is a basic diagnostic technique and is recommended for all patients with pain of characteristic localization. To improve visualization, images are taken after colon cleansing. In the presence of fistulas, contrast fistulography is indicated. - Ultrasonography
. Ultrasound of the soft tissues of the coccygeal region is an inexpensive, accessible diagnostic method that allows one to assess the condition of soft tissues, identify areas with altered structure, cysts, abscess cavities and inflammatory infiltrates. - CT and MRI
. In case of uncertain radiographic data, to clarify the condition of solid structures, patients with suspected traumatic injury, neoplasm or degenerative process undergo a CT scan of the coccyx. For an in-depth study of soft tissues in inflammatory processes and tumors, MRI is performed.
The list of other methods varies significantly. The diagnostic search may include sigmoidoscopy, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and pelvis, irrigoscopy, proctodedecography and electrophysiological studies. If tumors are detected, a biopsy is required. According to indications, general blood and urine tests, blood biochemistry and other studies are prescribed.
CT coccyx
Problems with reproductive organs
In women, pain in the tailbone may indicate prolapse of the uterus and vaginal walls. Also, pain in the tailbone can appear after pregnancy and difficult childbirth. These processes cause deviation of the coccyx and incorrect position of the coccygeal horns, which injure the surrounding soft tissues.
In men, pain in the coccyx may indicate benign prostatic dysplasia, prostate adenoma or chronic indolent prostatitis.
vertebrology diseases of the spine low back pain
Clinic, diagnostics, treatment in Moscow
If an acute process develops in the sacrococcygeal region, you should immediately consult a doctor. The Yusupov Hospital offers patients cozy inpatient rooms. Patients will be able to receive consultations from multidisciplinary doctors, undergo examinations using modern diagnostic equipment, take tests and receive effective treatment. Operations in the coloproctology department are carried out as planned and urgent; after the operation, patients are cared for by attentive and experienced medical staff. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the hospital.
Treatment of coccydynia
The doctor determines how to treat coccydynia based on the reasons for its formation. But there are also some general principles of conservative treatment, which include many measures:
- electrotherapy by inserting an electrode into the rectum;
- ultrasound with a special anesthetic mixture or hormones;
- paraffin application;
- ozokerite;
- therapeutic mud;
- underwater traction;
- novocaine, lidocaine and other blockades - for severe pain;
- rectal muscle massage;
- reflexology;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- post-isometric relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles;
- physiotherapy;
- neuropsychotropic drugs - to reduce the negative emotional background, etc.
Surgical treatment at NEARMEDIC is prescribed only in extreme cases, for example, in case of a fracture or dislocation of the coccyx.
Our doctors strongly recommend that you seek professional medical help immediately after the first sensation of pain appears. Timely identification of the cause and treatment of the disease guarantees a quick recovery without consequences.
Postoperative period. Dressings after surgery
In the postoperative period, bed rest must be observed during the first day after surgery.
You can get up and walk the day after surgery. You can sit down on days 5-6-7. Fully sit for 8-9 days. It is very important to avoid stress on the seams. It is necessary to avoid traumatizing the postoperative wound, and subsequently the scar. In the postoperative period, antibacterial therapy is prescribed if the process was accompanied by acute inflammation and abscess formation. Painkillers are used in the presence of pain. A modern breathable aseptic dressing with an absorbent pad is applied to the sutures. Dressings are done daily. On days 4-5, if there is no discharge from the wound, you can bandage it every other day. During primary healing, the sutures are removed 12-14 days after surgery. If the postoperative wound is treated openly, then secondary healing takes a fairly long period. In such a situation, it is best to use modern medical dressings and fixation means for dressing and care. In the postoperative period, the patient's quality of life should not suffer. We can select special dressings to care for an open wound, even if you had surgery in another clinic.
Clinical symptoms of inflammation in the coccyx area
If the tailbone hurts, it is not always inflammation; so-called idiopathic (with an unknown cause) pain is often recorded, which is episodic or constant. Only an experienced doctor can exclude idiopathic coccydynia. Self-diagnosis of your condition can lead to the fact that, as a result of incorrect conclusions, the patient develops a serious pathology, which may require serious surgical intervention for treatment in the future. It’s better not to let your situation get to this point. You need to seek medical help when the first signs of trouble appear.
Clinical symptoms of inflammation of the coccyx:
- pain in the lower spinal column, which intensifies with any movement;
- it is difficult to move the leg on the affected side to the side;
- pain appears and radiates along the outer and inner surface of the thigh;
- palpation of the coccyx area is sharply painful;
- the outer skin is hyperemic, hot and dry to the touch;
- general well-being may suffer and performance may be impaired, but there is no increase in body temperature (if there is hyperthermia, then it is necessary to suspect inflammation of the internal organs and urgently consult a therapist in a city clinic).
Chronic inflammation in the coccyx area during remission does not give any clinical manifestations. Signs appear during periods of exacerbation.
For diagnosis, an x-ray is used, which allows us to exclude traumatic and degenerative lesions of bone tissue. Also, in patients over 50 years of age, osteomalacia and osteoporosis must be excluded. These two diseases often provoke inflammation of the bone tissue in the tailbone area. For this purpose, diagnostic scintigraphy is performed. If it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, an MRI examination is prescribed. A consultation with a proctologist, gynecologist (for women), andrologist (for men), and endocrinologist is indicated.