Complications of lumbago 2530
Coccyx subluxation is a very common pathology in people of all ages. The first injury can occur in early childhood, when the child is just learning to walk. Anterior deviation of this part of the spinal column occurs when there is a sharp fall on the buttocks area.
Subluxation can also be caused by destruction of the joint connecting the coccyx to the sacrum. This type of pathology most often occurs in middle-aged people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and are mainly engaged in sedentary work. Prolonged static position leads to disruption of blood microcirculation in the coccyx area. This negatively affects cartilage tissue. It is destroyed and the coccyx is displaced. With partial stretching of the articular capsule, subluxation is observed with displacement of the lower part of the coccyx anteriorly or posteriorly.
From the point of view of medical terminology, subluxation can be considered a condition after a traumatic impact, in which there is a change in the position of the articular part of the coccyx in the capsule relative to the lower part of the sacrum. Deviation from the physiological axis can reach 30% or more. A dislocation is diagnosed if the joint capsule is overstretched and the tailbone extends beyond its limits. In this case, the person usually loses the ability to move independently. Any movement in him provokes an acute pain attack. When the coccyx is subluxated, a person does not experience serious problems with independent movement. The condition is accompanied by mild pain. It does not restrict movement.
Any experienced vertebrologist will be able to distinguish a subluxated coccyx from a complete dislocation. By palpation, he will be able to determine the location of all vertebrae. An experienced specialist can perform a reduction procedure during the initial manual examination. Although this doesn't help anyone. In order to ensure the stability of the position of the coccyx and sacrum in the future, it is necessary to conduct a full course of restorative therapy. During this procedure, the doctor will strengthen the muscle and ligamentous apparatus and help restore normal elasticity of the joint capsule. Only in this case can we guarantee the absence of recurrence of coccyx subluxation.
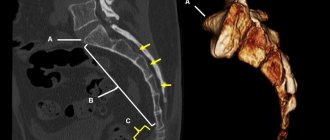
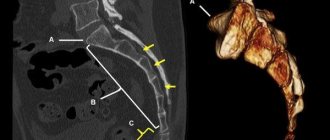
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct an X-ray examination in different projections. Quite often, subluxation is associated with a traumatic impact, such as a fall or bruise. Often this results in the formation of concomitant traumatic tissue lesions, such as a bone fracture or a compression fracture. They will also be visible on an x-ray. If it is difficult to make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor may recommend an MRI examination.
If you suspect that you or your loved ones have a subluxated coccyx, do not delay visiting a doctor. We recommend that you contact a traumatologist immediately after an injury. And then treatment must be carried out in specialized manual therapy clinics. There are specialists working there who will help not only restore the integrity of the damaged spinal column, but also create conditions to prevent recurrent subluxation in the future.
How can you get a dislocation?
The spine in the lower part ends in the sacral vertebrae, at the end of which the sacral joint is localized. The connective tissue is cartilage, which plays the role of holding the sacrococcygeal ligaments. As soon as a fracture-dislocation occurs, the vertebrae in this section are displaced.
Dislocation of the coccygeal vertebrae occurs in the following cases:
- in case of an unsuccessful fall on the gluteal region of the body or back;
- labor (large baby);
- impact on the coccygeal region;
- strenuous physical activity (for example, during sports training);
- cycling (riding on potholes and uneven roads);
- weak depreciation of the knee joints and weakness of the muscular system in the lumbar region.
In most cases, subluxation of the coccyx is diagnosed in children and adolescents, who, due to their mobility, can often fall, for example, in physical education lessons, during outdoor games, dancing, etc.).
It is very easy to get a tailbone injury
In old age, dislocation can occur due to wear and tear of the muscle tissue and an increase in its level of weakness. In addition, older people develop joint pathologies, which also affect the condition of the bones.
[node:field_similarlink]
Causes of subluxation of the coccyx anteriorly and posteriorly
Subluxation of the coccyx posteriorly is less common than displacement in the opposite direction. This is due to the fact that anatomically this section of the spine is already slightly rotated in front. The main cause of posterior subluxation is pregnancy, complicated by prolapse of the pelvic day and divergence of the pelvic bones with the formation of symphysitis. Sharp pressure on the tailbone from the inside brings it to a position where its angle of inclination changes. If you move awkwardly or carelessly sit down on a hard surface or fall on your buttocks, the tailbone may shift posteriorly. Reducing such an injury is quite difficult due to the anatomical features of the joint.
It is believed that the main cause of subluxation of the coccyx is traumatic impact - a bruise, a fall, sudden bends, etc. in fact, in a healthy person with a similar traumatic effect, such an injury may not occur. Prerequisites for subluxation may include:
- degenerative dystrophic changes in the cartilaginous tissues of the spinal column in the lumbar and thoracic region (due to disruption of depreciation processes, the main load falls on the point of traumatic impact, i.e. on the coccyx);
- deforming osteoarthritis of the iliosacral joint of the bones - this joint also absorbs most of the shock-absorbing and mechanical load exerted on the spinal column;
- cicatricial deformities of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus, designed to ensure the stability of the position of all parts of the spinal column;
- atrophy and dystrophy of the muscular frame of the body;
- changes in posture in the lumbar and thoracic spine;
- incorrect foot placement;
- excess body weight;
- metabolic disorders and lack of microelements in the diet;
- smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages leads to disruption of microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid in the coccyx area, and destruction of its joint;
- Osteoporosis and osteomalacia lead to an increased risk of compression fractures and cracks in bone tissue.
Subluxation of the coccyx anteriorly can be old, received in infancy. Throughout his life, a person may not realize that his lowermost part of the spinal column is incorrectly located. This can give unexpressed symptoms in the form of periodic tingling in the lower extremities, numbness of the legs, especially in the toes. With a detailed examination, the chiropractor will be able to detect deviation of the coccyx and put it in its physiological place.
What symptoms occur with injury?
The signs of injury to the coccyx are the same in all cases. It is possible to diagnose the exact pathology in this area only with the help of appropriate diagnostic measures, namely the X-ray method.
Symptoms of a dislocated coccyx are primarily expressed in the development of pain. It occurs during injury and is present for a long time. It differs in different intensity at different stages: at first it is acute, over time aching sensations appear.
If after injury the symptom is observed constantly, then over time pain occurs only when the position of the body changes (during standing, sitting, turning). The symptom may radiate to other parts, for example, to the anus and groin.
The intensity of discomfort increases during bowel movements and when straining. In this case, the pain has a shooting character. The syndrome intensifies upon palpation of the injured area. Visually, you can detect swelling of the coccygeal region and subcutaneous hemorrhage of varying sizes (based on the degree of injury).
Despite such pronounced clinical manifestations of the injury, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on them alone. For this purpose, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed, carried out in a hospital setting.
No ads 1
The difference between a dislocation and a subluxation
A dislocated coccyx is a severe displacement of the joint surfaces that requires immediate assistance. Specialists can diagnose a coccyx fracture. With subluxation, the disturbances are not so significant; the displacement of the articular surfaces does not occur completely.
Dislocation is always preceded by injury; subluxation can appear for no reason - a sharp turn, prolonged incorrect position of the spine. The symptoms of both pathologies are similar.
Diagnostics
If a subluxation of the coccyx is suspected, the doctor palpates the injured area. The procedure involves inserting fingers into the rectum, which allows you to determine the degree of injury and the level of joint displacement.
The diagnosis is carried out by a traumatologist. Even if the injury is minor and there is no severe pain, this is not a reason to cancel diagnostic measures.
MRI will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis
After palpation, an X-ray examination of the affected area is performed. If necessary, magnetic resonance imaging of the vertebrae and spinal cord is prescribed. Such a diagnostic event will help make an accurate diagnosis and identify complications.
Causes
Post-traumatic coccydynia develops as a result of injury to the coccyx (bruise or fracture), spine, or surgery in the sacral area. The injury occurs after a fall or direct blow to the tailbone. Moreover, the first signs of pathology may appear a long period after the episode - several weeks or even several months.
In women, post-traumatic coccydynia can develop as a result of difficult childbirth or complicated pregnancy. This condition in women requires special attention from a gynecologist. In some cases, to avoid the development of complications, a woman may be prescribed a cesarean section.
Another risk factor is undergoing surgery in this area, as well as on the spine. During the operation, some nerve tissue may be affected, which as a result provokes the occurrence of coccydynia.
People over 40 years of age are at greatest risk. In this case, the disease is most often observed in women.
First aid
If there is severe pain in the coccygeal region, it is recommended to call an ambulance or take the victim to the hospital on your own.
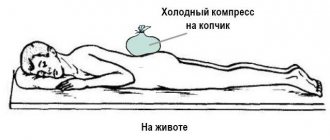
Before the doctor arrives, you need to numb the injured area. To do this, apply a cold compress (you can take any product from the refrigerator), which helps reduce the intensity of the syndrome in a few minutes. If the pain is severe, you can take a painkiller tablet.
It is prohibited to take a sitting or semi-sitting position. In this case, bone displacement becomes even more difficult. It is allowed to lie on your side and remain in this position until the ambulance arrives.
Important! Self-medication, namely bone realignment, is prohibited. Before such a procedure, it is necessary to accurately determine the location of the displacement, its angle, and associated damage, which is only possible based on the results of instrumental diagnostics.
Indications for coccyx blockade
Injections of medications into the spine are prescribed if other conservative treatment methods, such as medications and physical therapy, are ineffective. With their help, it is possible to interrupt the pathological nerve conduction of the pinched areas, thereby relieving the patient of chronic pain.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
If desired, a coccyx block can be completed at a medical clinic. The main indication for the procedure is the treatment of coccydynia.
Features of pain in this disease:
- dull, aching, bursting or pulling, in severe cases the pain is burning, sharp;
- accompanied by pressure and a feeling of heaviness in the lumbar region;
- pain radiating to the perineum, buttocks, sacrum, rectum;
- worsens in a sitting position, after rising from a chair, during physical activity, constipation, can occur during sexual intercourse, coughing, sneezing;
- decrease while walking, after defecation.
Soreness is not the only symptom of coccydynia. Due to constant pain, a person becomes more careful in his movements and tries to sit on a chair so as to experience the least discomfort. The patient sits on one buttock, thereby moving the body weight to one side. As a result, muscle overstrain occurs, curvature of the spine and joint deformation are likely.
This is how a patient with coccydynia sits
Constant severe pain provokes nervous tension, sleep problems, leads to rapid fatigue, and the development of irritable bowel syndrome. They cause deterioration in physical and psycho-emotional condition.
Relieving the patient of constant debilitating pain and returning him to normal life is the main goal of the neurologists at the SmartMed clinic. It is important to understand that coccydynia is a chronic disease, so its treatment requires a professional approach.
Treatment
Treatment of such an injury involves following the following recommendations:
Why does the tailbone hurt in women?
- realignment of displaced vertebrae using local anesthesia;
- restriction of mobility of the injured area;
- use of medications with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects;
- performing exercise therapy;
- carrying out physiotherapeutic procedures.
Among the drugs with an analgesic effect used for trauma to the tailbone, Nimesil, Diclofenac, Movalis are distinguished. Pain syndrome in pregnant women and children can be treated with drugs Ibuprofen, Papaverine, No-shpa, rectal suppositories, which contain anesthesin. If defecation is difficult, medications with a laxative effect are prescribed (for example, Duphalac, suppositories containing glycerin, etc.).
If the injury is not treated in time, pain in the tailbone can become chronic.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of dislocation and subluxation of the coccyx is carried out, which helps not only to eliminate the symptoms of damage, but also to prevent complications. This can be electrophoresis, laser and magnetic therapy. During the recovery period, physical therapy is required.
Surgical treatment of coccyx dislocation is carried out when conservative methods are ineffective and in severe cases of injury.
Why is injury dangerous?
Any injury to the spine affects the condition of the entire body, damage to the coccyx is no exception. Without timely contact with a specialist, the following consequences may occur in case of dislocation or subluxation of the coccygeal bone:
- the coccygeal bone may be deformed;
- the victim may experience intense pain caused by inflammation in the nearby nerve roots;
- for representatives of the fair sex, the process of childbirth may be disrupted;
- the functioning of the coccygeal bone is impaired;
- due to weak elasticity and resilience of the ligamentous apparatus, repeated dislocations may occur;
- chronic pain syndrome develops, it can appear even in patients who have undergone treatment.
With a timely visit to the traumatology department, you can receive adequate treatment of coccyx herbs and prevent the development of possible complications.
Complications
Any disease and any injury can have negative consequences if treatment is not started in a timely manner or if it is carried out incorrectly. A displaced coccyx fracture is no exception. Complications include:
- coccydynia – chronic pain in the sacrococcygeal region (usually occurs in the absence of treatment for the injury);
- violation of the natural shape of the bone element, which causes complications during the birth process in women.
To avoid negative consequences, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible and carry out appropriate treatment measures.
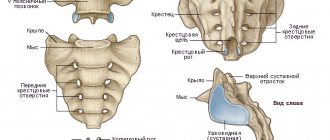
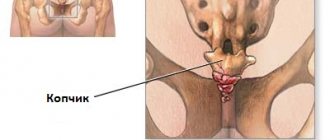
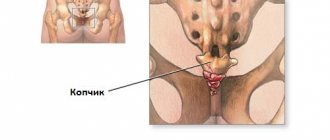
Physiology of the coccyx
The coccyx is the lowest part of the spine, completing it. It belongs to the rudiments, that is, it does not perform any vital functions, but has been preserved in the human body, combining about four vertebral units. They grow together by adolescence (sometimes much later), and in girls the one on top remains mobile. Nature has thought through this moment to facilitate the birth process.
Can the coccyx be called an extra appendage? Not at all. It is joined by ligaments, tendons and muscle fibers, including the anal sphincter, intestines, and pelvic floor.
From above, the coccyx is attached to the larger bone of the sacrum, through the holes in which the pelvic nerve fibers pass.
The merits of the coccyx in the functioning of the body are difficult to overestimate. Thanks to it, a person can move freely, sit down, stand up, bend over, and cope with physiological needs. This element also supports the spinal column and protects it.
Symptoms
The symptoms of the pathology are similar to those of other pathologies, spinal injuries in the lumbosacral region, therefore the clinical picture rarely serves as the main diagnostic sign. In pathology, the patient notes the following phenomena:
- Pain in the coccyx area that appears immediately after injury;
- Hematoma, abrasion, swelling of the injury area;
- Discomfort increases when changing position; it is minimal when the patient is standing or lying down;
- Discomfort actively erodes in the groin area and lower back;
- Worsened by defecation;
- Increases after prolonged physical inactivity (regardless of posture);
- The patient experiences minimal discomfort when walking.
The clinical picture is the same regardless of the degree of injury. With complete dislocation it is also similar.
What it is?
A bruise is a closed injury that affects soft tissues that are compressed at the moment of impact. At the same time, the bones retain their integrity. Signs sometimes do not appear immediately, but after a few days.
What is the coccyx? This is the lower region of the spine, which includes up to 5 fused vertebrae . The coccyx is considered a vestigial organ that has lost its value.
The coccyx consists of several fused vertebrae
But he still plays an important role:
- The gluteal muscles, which are involved in the work of the hip, are attached to the tailbone.
- Ligaments that control the functioning of the intestines and genitourinary system are also attached.
- The tailbone is the fulcrum when bending backwards, and also maintains the balance of the body.
In the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10), coccyx bruise is located in section 19 of the ICD - injuries.
The following codes have been assigned:
| ICD-10 S30.0 | bruise of the lower back |
| ICD-10 S32.20 | closed coccyx fracture |
| ICD-10 S32.21 | open fracture |
| ICD-10 S33.2 | dislocations of the sacrococcygeal joints |
A bruised tailbone occurs quite often and the cause can be not only a direct blow or a fall. The structure of the bones in this section is such that the slightest excess of load on the coccyx leads to damage. Even cycling can cause problems. And for people with fragile bones (osteoporosis) and excessive weight, a slight fall ends in disastrous consequences.