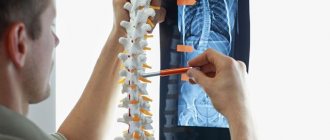
Atlas is the first vertebra in the cervical spine. It controls the movement of the spine and ensures a stable position of the skull. The atlas is attached to the occipital part of the skull and is connected to the second vertebra - the axis. Together they form the atlantoaxial joint. In the set of injuries involving the cervical vertebrae in children, cases of atlantoaxial subluxations predominate. This is explained by the physiological and anatomical characteristics of child development. This pathology can be either congenital or acquired.
Causes of atlantoaxial subluxation
A common cause is birth trauma. Vertebral subluxations in children often occur as a result of cesarean section or malpositioning of the baby.
Other reasons include:
- Careless handling of the baby; the head was held incorrectly until the child was able to hold it himself.
- Mechanical injury due to a car accident, fall, somersault over the head.
- A sharp turn of the head to a sudden sound or call.
- Sleeping on a pillow that is too high.
- Muscle hypertonicity, cerebral palsy.
Subluxation of a cervical vertebra in a child affects future lifestyle and well-being. If atlantoaxial subluxation is suspected, the baby should be scheduled for examination.
Subluxation of the cervical vertebrae in children
The spinal column is a column of overlapping vertebrae. With subluxations, a person experiences limitations in mobility, which are usually acute. It is not possible to perform any movements; the sensations are painful, but not severe.
Attitude to the problem
Very often people do not pay attention to the symptoms, considering their condition to be some kind of norm. Here are the most common reasons for this attitude:
- The person is not aware of the presence of damage;
- The long-term existence of trauma has very negative consequences, many do not understand this;
- You don’t want to go to the doctor and the person is even ready to come to terms with his existing disorders;
- “It will go away on its own” - constant internal complacency;
- Many people think that this problem is very frivolous and not worth much attention.
Very often, doctors are faced with advanced cases when there are already significant circulatory disorders, because the decisive factor for the person was one of the reasons listed above.
Pediatric subluxation
In children under five years of age, such disorders appear very rarely. But at the age of 8-12 years, when physical activity increases, the number of such injuries increases many times.
Today, adults are much more likely to suffer from various joint displacements than children. 9/10 of the total number of this pathology occurs in adults and only 1/10 in children. They have features in the skeleton, as well as in the musculoskeletal system, and it is because of them that this ratio develops.
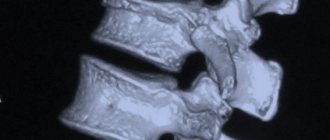
The condition of a joint when the joint surfaces lag behind each other, but the points of contact are preserved, is called subluxation. The entire joint stops functioning normally. Objective methods, x-rays and computed tomography diagnose this disease.
Today, when talking about such a violation, they do not mean complete dislocation. Movement of articulated surfaces without contact between them, accompanied by a serious disorder in the functioning of the body, is a complete dislocation.
Causes
These pathologies occur very often and in many people, even in newly born children. Let's consider the parameters that influence the frequency of occurrence of the considered deviations:
- Position of ligaments, tendons and joints;
- Do the joint characteristics correspond to the normal purposes of the body part.
In adults, bones, joints, ligaments and tendons are fully formed, so the above reasons apply more to them. About 85% of all cases of injuries, both in adults and in children, occur in the joints of the shoulder, collarbone and elbow.
Subluxations can be present from birth and acquired later. The intrauterine development of the child is disrupted, and a rounded head of the articular joint and a shallow articular notch are formed. This is the main cause of congenital disorders. Injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system are the main factors of acquired pathologies.
Symptoms of pathology
Common expressions for subluxations include:
- severe cutting pain is felt at the site of the damaged joint;
- the external appearance of the joint is different from normal;
- you feel hot inside, swelling has appeared and the skin turns red;
- limited movement in the joint.
In children, the ligaments and tendons that strengthen the joint are very stretched, making the fixation of the joint very fragile. A large number of uncontrolled movements appear that would normally be impossible. That is, the child’s joint is not fully secured, which is why violations occur. The musculoskeletal system becomes similar to that of an adult when a child becomes a teenager.
Children have a very high rate of development of degenerative processes at the site of the damaged joint. Therefore, in order not to reduce the situation to the point of inevitability and the necessity of performing an operation, it is necessary to identify the injury and correct it very quickly.
cervical subluxation in children
If the integrity of the second cervical vertebra is damaged, subluxation of the first vertebra may occur. Such pathologies in medicine are called “Kienböck’s subluxations.” When they occur, there is a disruption in the functioning of the spinal cord, nerves and blood vessels. This provokes the development of serious clinical signs. Symptoms:
- there is severe pain in the back of the head and neck;
- pain in temples;
- noticeable forward tilt of the head;
- the neck is convex;
- impossible to move your head.
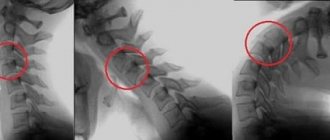
Based on the medical examination and x-ray, the type of subluxation is determined. The exact degree of displacement is determined by x-ray examination.
Principles of treatment of childhood cervical subluxation
Conservative methods of treating cervical subluxations in children are focused on completely restoring the correct structure of the joint for the entire anatomy. The child should not be left unattended after the disorder has been corrected. It is necessary to carry out rehabilitation, joint restoration measures, as well as preventive measures.
If you feel like you have a subluxation, you need to use a tight splint or collar to secure the child’s neck. Take the child to the hospital very carefully and quickly. Only a doctor can perform the reduction. They are adjusted using the traction method, when the anatomical structures return to their usual place with a sharp, one-step movement. For the child, everything passes imperceptibly and without pain.
After this, for a whole month the child will wear a special supporting cervical frame and undergo physiotherapeutic procedures (thermal, massage).
Observation by a traumatologist is mandatory during the treatment period. In special cases, special medications are prescribed. They will improve blood circulation in the body and the general condition of the child. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms and consequences
There are several signs of pathology that are worth paying attention to:
- restless behavior;
- poor sleep;
- constant moodiness, tearfulness;
- poor appetite;
- apathy towards surrounding objects;
- no weight gain;
- tilting the head to one side;
- tension in the neck muscles;
- The skin in the neck area may be hot to the touch.
At a later date, with subluxation of the vertebrae, children develop rhinitis. A runny nose does not go away for a long time and is not infectious. In this case, vasoconstrictor drugs are useless, and the otolaryngologist does not find any pathology.
Consequences that childhood pathology leads to:
- scoliosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- flat feet;
- strabismus;
- mental retardation;
- hyperactivity;
- memory problems;
- fast fatiguability.
Palpation in the cervical region at the base of the skull usually reveals a small bony protrusion on one side, painful when pressed; with functional tests we can detect limited head rotation, a slight tilt of the head. Types of atlas displacement:
According to the literature, injuries to the upper cervical spine account for up to 20% of all injuries; cervical region. Damage to the I and II cervical vertebrae in children ranges from 1.9 to 6.7%. In the literature, applicable to childhood, the following injuries are mainly described: - rotational subluxation of the atlas - transligamentous subluxation - fracture of the odontoid process - dislocation of the head.
Rotational subluxations of the atlas occur as a result of direct or indirect violence, or active uncoordinated contraction of the neck muscles. According to M.N. Nikitin (1966), they amounted to 31.5% of all injuries of the cervical spine and 8.8% of all spinal injuries.
Symptoms and frequency of manifestations:
- headaches (in 80%) - muscle tightening (mainly under the neck in 90%) - tension in the neck (70%) - pain in the neck (60%) - dizziness or loss of consciousness (50%) - tinnitus ( 35%) - trembling fingers and shaking head (40%) - vision problems (30%) - nosebleeds (20%)
Until 1996, almost 60% of children in the CIS countries received rotational subluxations of the atlas during childbirth. Insufficient qualifications of obstetricians of those years, the lack of standards for childbirth management and a weak instrumental and diagnostic base contributed to accidental spinal injuries. There has been a significant improvement since 2000, although the problem is still common.
Vascular consequences:
Subluxation of the first cervical vertebra has a significant impact on the blood circulation of the brain. Depending on the severity of the patient’s condition, the following may occur: - Vertebral artery syndrome (VAS) - Cerebral angio-dystonia with hyperfusion in the middle cerebral arteries - Hemodynamic disturbances in the vertebrobasilar region - During rotational tests, the blood flow reserve is reduced - The adaptive capabilities of the cerebral blood flow autoregulation apparatus are reduced — Venous dysgemenia, impaired venous outflow — Discirculation in the ophthalmic, vertebral veins, jugular vein, straight sinus — Signs of intracranial hypertension, with symptoms of venous stagnation
Contraindications for Atlanta correction:
Age over 60 years Weight 30 kg more than the physiological norm Pain in the neck, cervicalgia, chronic myelopathy, severe inflammation of the lymph nodes of the neck, skin burns, sudden loss of vision Dysplasia of the craniocirvical zone (congenital) Fresh trauma to the cervical spine, fractures, ligament ruptures and muscles Severe muscle spasm in the neck (myofibrosis, acute myalgia, myositis, fibromyalgia, ligamentosis) Arthrosis of the atlanto-occipital, atlanto-axial and atlanto-dental joints (Cruvilier's joint) above grade 2 Cervical spondyloarthrosis grade 3-4 Listhesis of the cervical vertebrae above 4 mm Instability of the atlanto-axial and atlanto-occipital joint Subluxation according to Kovacs in more than 3 PDS Kimerli or Arnold-Chiari anomaly (except for DDP variants) Assimilation of the atlas (fusion of the atlas with the occipital bone) Non-fusion of the atlas (spina bifida atlantis) Osteoporosis, cervical osteomelitis department Bekhterov's disease (ankylosis of the cervical vertebrae) Parkinson's disease, cerebral palsy, schizophrenia, autism, epileptic seizures
Mental illnesses (neurosis, anxiety disorder, depression, somatoform disorders, schizophrenia) Multiple sclerosis Barre-Lieu syndrome in the acute period Cervical hernias over 4 mm
Diagnostic features
To determine the cause of the pathological condition, the patient must undergo a diagnostic examination, which usually begins with an initial examination and medical history. After this, the neurologist palpates the affected area.
Diagnosis of cervical subluxation
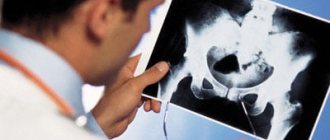
But these measures are not always sufficient to make an accurate diagnosis, so the child may be prescribed several types of x-ray examination, including an x-ray of the mouth, oblique x-rays (carried out to study all articular processes) and spondylography - a common diagnostic method for subluxation, allowing to assess the condition intervertebral discs and joints. Based on the results of the measures taken, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
X-ray of the neck
Causes of injury in newborns
Damage to parts of the spine usually occurs during difficult births. There are several causes of this injury, conventionally divided into internal and external. On the part of the mother’s body, it can be caused by the following:
- age – too mature or early;
- prolonged exposure to harmful substances as a result of living or working in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- postmaturity of the child;
- narrow pelvis;
- damage to the birth canal by infections;
- intense toxicosis;
- various diseases of the genitals;
- pathologies of the endocrine or cardiovascular system;
- complications during pregnancy.
Also, the cause of dislocation of the cervical vertebra can be disorders from the fetus, namely:
- premature birth;
- large dimensions;
- incorrect position;
- lack of amniotic fluid;
- asphyxia (suffocation), affecting the position of the cervical vertebrae;
- hypoxia (low oxygen content in the body);
- asynclitism (incorrect insertion of the fetal head during childbirth).
In addition, damage may be caused by the actions of doctors and obstetricians:
- extraction of the fetus using vacuum extraction;
- using forceps;
- turning the child by the lower limb.
Important!
Natal spinal injuries sustained during childbirth are often caused simultaneously by several factors listed above.
Rotary
In some cases, to be born, the baby needs help moving through the birth canal. This happens when it is necessary to speed up the birth process due to a threat to the health of the child or mother. To help the child, the obstetrician uses his hands or uses obstetric forceps.
To pass the head, perform rotational movements, carefully turning clockwise. Such a load can lead to displacement of the cervical vertebra or its dislocation, which often entails compression of the spinal cord and narrowing of the spinal canal.
Flexion-compression or compression
In this case, the cause of injury is excessive compression of the cervical spine. As a rule, this happens when labor is too fast, when the fetal body intensively moves forward and puts pressure on the head stuck in the birth canal. Rapid labor can occur naturally or as a result of stimulation.
The cause of compression injuries may be the desire of obstetricians to maintain the integrity of the perineum. As a result of the obstacle, the fetus is compressed at the exit, which often leads to damage to the cervical vertebra.
Distraction
Such injuries are caused by excessive stretching of the cervical spine, which is possible in two situations:
- The shoulders of a large fetus do not pass through the birth canal and it is pulled up by the head.
- Due to the breech presentation and its large size, the fetus does not pass through the birth canal, and obstetricians have to pull it out by the pelvic end. With such a sprain, ligaments often rupture and vertebral tissue is torn from the intervertebral discs, which often leads to damage to the spinal cord.
Will a caesarean section help with an injury?
During births performed by cesarean section, damage to the spine is very rare. However, surgical birth does not guarantee complete absence of trauma for the following reasons:
- Since caesarean section is not used for women who are able to give birth on their own, the indications for this surgical intervention pose a threat to the fetus.
- During the operation, the fetus is subjected to mechanical stress, increasing the risk of possible damage.
- In an artificially extracted fetus, the functions of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are triggered using special methods that often cause harm to the central nervous system.
Attention!
According to statistics, the birth process using a cesarean section is no less dangerous than a natural one: newborns are often diagnosed with displacement of the vertebrae in the cervical spine, injuries to the skull, and hemorrhage in the retina.