- home
- /
- Services
- /
- Ultrasound examinations
- /
- Ultrasound of the hip joints in children
The family medical office offers to do an ultrasound of the child’s hip joints. Our clinic uses the latest diagnostic equipment, which allows us to most accurately and safely identify various abnormalities or developmental defects in newborns, toddlers and primary school children. Qualified doctors in the field of orthopedics and surgery, if necessary, will prescribe a full course of examination and therapeutic measures to eliminate possible pathologies in the future.
Why is ultrasound of the hip joints performed in newborns?
Ultrasound scanning of the TSB allows us to identify any abnormalities in newborns. It is a highly informative method that provides accurate results and allows you to identify such a serious deviation that can have a negative impact on the child’s quality of life, such as TBD dysplasia. This is a disease that is characterized by incorrect orientation of the femoral head in relation to the acetabulum. The result may be a violation of the supporting function of the leg. In order to eliminate the risk of such pathologies, ultrasound of the hip joints in infants is mandatory. It is carried out as part of a routine examination, highlighting the following stages of the disease:
| Stage | How is it manifested? |
| First (pre-dislocation) | It is characterized by insufficient development of the femoral head, in which displacement of the femoral head is not observed relative to the acetabulum. |
| Second (subluxation) | It is characterized by insufficient development of the femoral head, in which the head of the femur is partially displaced. |
| Third (dislocation) | It is characterized by insufficient development of the femoral head, in which the head of the femur is completely displaced. |
Ultrasound diagnostics allows you to promptly identify any of the abnormalities and carry out the necessary treatment to prevent the child from lameness in the future. The attending physician prescribes special exercises, selecting them individually based on the stage of deviation.
It is important for parents to know that correct and timely diagnosis allows an accurate diagnosis and treatment to begin when it produces the desired results. Lack of treatment will lead to the development of serious complications in the form of lameness and arthrosis.
Other types of ultrasound for children and adults in our center
- Ultrasound of a child's brain (Neurosonography) in children under one year of age is usually performed through the fontanelle, and after it closes, through the temporal bones. This procedure is harmless to the health of the baby and at the same time allows you to obtain a significant amount of valuable information - for example, to identify a dangerous neurological disease that requires treatment at the earliest stages of its occurrence.
- Ultrasound of the child’s heart (ECHO CG)
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed in children in the same way as in adults, and provides a lot of valuable information. For example, in the case of urolithiasis, a specialist diagnostician can identify stones of any chemical composition that usually cannot be detected using x-rays. If the baby is a newborn or infant, then an ultrasound of the child’s abdominal cavity can be done 3-4 hours after eating (that is, immediately before the next feeding).
- Ultrasound of the kidneys in children, as well as the adrenal glands and bladder, requires careful preparation. It is carried out with a full bladder, but it is important not to “overdo it”: if the bladder is too full, then the child will have residual urine and pyeloectasia. The optimal amount of water (strictly without gas!) is from 200 to 800 ml, and it should be drunk 30–40 minutes before the procedure. It is recommended that infants be fed or watered 15–20 minutes before the test.
- An ultrasound of the child’s thyroid gland allows you to monitor the condition of this important organ and the lymph nodes surrounding it and promptly notice alarming changes in their condition and functioning. This is especially important for residents of such environmentally unfavorable places as Moscow and the Moscow region. Timely prescribed therapy can save your child from serious health problems.
- Ultrasound of the mammary glands helps to identify inflammatory processes and pathologies in the formation of the mammary glands in a timely manner.
- Ultrasound of the genital organs. Ultrasound of the scrotum in boys does not require preparation, but for ultrasound of the prostate gland you need to come with a full bladder. Ultrasound of the uterus and appendages in girls is performed only transabdominally (through the abdominal wall) and also with a full bladder. To do this, half an hour to an hour before the procedure, invite the child to drink 200–800 ml of non-carbonated liquid. In infants, this study is performed 15–20 minutes after eating.
- Ultrasound of the liver in children is performed on an empty stomach. It is recommended that a few days before the planned test, exclude from the child’s diet foods that cause increased gas formation (cabbage, legumes, fiber-rich vegetables and fruits, brown bread, whole milk, carbonated drinks). To prevent constipation, you can give your child enzyme preparations and enterosorbents - activated carbon, festal, mezim-forte, espumizan (1 tablet 3 times a day) for several days.
- Ultrasound of lymph nodes.
- Ultrasound of soft tissues.
- Ultrasound of the thymus is a study of the thymus gland, an organ located behind the sternum on either side of the trachea and responsible for protecting the body. Enlargement of the thymus gland is a dangerous symptom, indicating the inability of the small body to resist infections. Such children need a special regime, care and treatment.
You can make an appointment with a doctor at the Center through:
online appointment form
or by calling the Center in Moscow:
+7,, +7 (962) 947-38-08
during the working hours of the Center (daily, seven days a week and holidays, from 9.00 to 21.00)
PRICE LIST for medical services of the Center | |
| TYPES OF MEDICAL SERVICES | Cost, rub. |
| Ultrasound of the hip joints (for children under 1 year of age) | 2000 |
Our experienced pediatric ultrasound diagnostic doctors , with whom you can make an appointment:
Indications for ultrasound of the hip joints in newborns
As already mentioned, an ultrasound of a child’s legs is performed between the ages of one and three months as part of a routine examination. Outside diagnosis is prescribed if the baby shows signs indicating the presence of dysplasia:
- Asymmetry of the gluteal folds and buttocks, differences in depth;
- Clicking and crunching of joints when bending the baby’s lower extremities at the knees and TZB;
- Different lengths of the lower limbs;
- The presence of an additional fold on the thigh;
- Increased muscle tone in the legs;
- Inability to completely move the baby’s legs to the sides, bent at the knees;
- Presence of signs of embryonic development disorder.
In addition, the study is prescribed in the following cases:
- The child was born premature;
- The baby has neurological abnormalities;
- At the birth of twins or triplets.
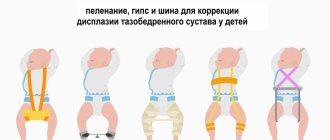
Preparation and performance of ultrasound of the hip joints in newborns
Ultrasound examination of TBD in children does not require any specific preparation. It is important that the baby is fed and calm, since excessive activity will not allow accurate results to be obtained. It is best if feeding is carried out half an hour before the start of manipulations. They provide the following:
- The baby is placed on the medical couch on his side, with the lower limbs bent in the lateral position;
- The diagnostician applies medical gel to the area under study, places the ultrasound scanner sensor on it and carefully moves it, tilting it at different angles;
- During the process, he observes the image that is displayed on the screen of the ultrasound machine.
After the procedure is completed, parents need to wipe off the gel and dress the baby. The results of the study are made available immediately.
Carrying out a diagnostic procedure
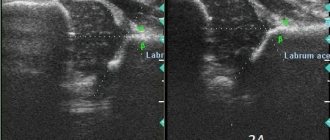
During an ultrasound, the child is placed on his side so that the examined joint is on top and bent at an angle of 20°. A gel is applied to the hip joint to facilitate the sliding of the sensor and improve the conductivity of acoustic waves. During manipulations, all articular and periarticular structures are displayed on the screen. The doctor takes pictures in the positions necessary to assess the condition of the tissues. Usually there are five of them: in the initial position, when bending and extending the leg, when abducting and bringing it to the body.
To prevent the procedure from being interrupted, pediatricians who prescribe a referral for sonography recommend not feeding the baby immediately before the examination. The child must be well-fed so as not to be capricious, but the process of regurgitation can interfere with diagnosis.
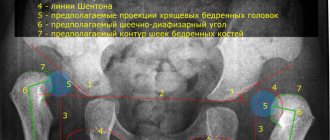
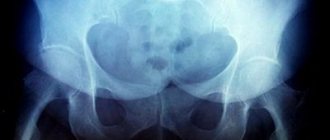
Classification of normal angles and interpretation of ultrasound results of TSB in newborns
The doctor compares the average normal values and the results obtained for a number of parameters, determining the absence or presence of pathology and its stage. One of the evaluation criteria is the echogenicity of the structures. Thus, if there is hyperechogenicity of the femur and the dome of the acetabulum, the formation of the TSB occurs correctly. In this case, the femoral head and cartilage plate will be hypoechoic.
Another criterion by which the assessment is made is the angle of the femoral head in relation to the acetabulum. In this case, the following classification has been adopted, the indicators of which are the norm for children aged two to three months:
- Angle α (“Alpha”) – is more than 60° and determines the level of elevation of the acetabulum;
- Angle “β” (“Beta”) is less than 55° and determines the development of the cartilaginous space of the acetabulum.
Experts distinguish 4 types of hip joints and 3 degrees of dysplasia:
| Types of hip joints and degrees of dysplasia | Alpha | Beta |
| Norm | No violations were found. | The cartilaginous plate is wide and short. |
| Formation delay | Delay up to three months. | Delay of more than three months. |
| Subluxation | Characterized by changes in the structure of the cartilaginous protrusion. | There are violations in the structure. |
| Dislocation | The joint is not formed correctly. | The head of the femur is not covered with a cartilaginous protrusion. |
What pathologies can be identified
Most often, during an ultrasound examination of the hip joints, the following diseases are detected:
- Arthrosis (it develops as a result of congenital dislocation of the hip, a disturbance in the circulatory system, or as a result of a fracture of the femoral neck);
- Arthritis (may occur due to infection of joint joints by pathogens);
- Synovitis, which is characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation inside the joint;
- Necrosis of bone tissue (can occur due to frequent fractures, dislocations, bruises);
- Tears and spasms of muscle fibers;
- Swelling of the joint.
The hip joints are most susceptible to various pathological processes. Diseases can be either congenital or acquired. If you visit a medical facility as soon as the first symptoms appear, you can hope for a favorable outcome and complete recovery. Otherwise, your doctor may recommend surgery.
Advantages of performing an ultrasound of the hip joints in children at the Doctor Nearby clinic
Specialists from the Doctor Nearby clinic network know better than anyone else that the accuracy of a TZD study depends on how calmly the baby behaves. They make considerable efforts to create the most comfortable conditions during ultrasound diagnostics: both for the baby and for the parents.
Appointments are by appointment only, so there are no queues. The research is carried out carefully and using modern equipment, which allows it to be as accurate as possible. The results are available immediately.
Our pricing policy is loyal to patients. You can verify this by reading our price list below. You can make an appointment by phone.
How does an ultrasound machine work?
Ultrasound is powerful sound waves. The human hearing organs can perceive frequencies from 16 to 20 kHz, so ultrasonic vibrations (from 20 kHz) are beyond our acoustic perception. However, some groups of animals (whales, dolphins, bats and others) communicate using ultrasound. Each wave is characterized by an oscillation period, frequency and length. They all depend on the elasticity/density of the medium through which this wave propagates. Any environment, including the tissues of the human body, prevents the propagation of sound vibrations. This is called acoustic impedance. The speed and density of sound waves depend on the magnitude of acoustic resistance.
As soon as a sound wave reaches the boundary of two media with different acoustic resistance (for example, soft and hard tissue), one part of it propagates in the new medium and is absorbed by it, and the other is reflected. The intensity of reflection depends on the magnitude of the acoustic impedance. The higher the indicator, the brighter and lighter the signal that the ultrasonic equipment receives. Additionally, the technique records the distance to the separation boundary, the travel time of the wave, the speed of movement, the difference in densities, and so on.
Human skin reflects 99.99% of sound vibrations, making ultrasound examination impossible. That is why the scanned area is lubricated with a special aqueous jelly, which acts as a transition medium.
The reflected sound wave enters an amplifier and special reconstruction systems. They process the information received and transform it into sections of the body part being studied. The picture is painted in black and white, which uses no less than 64 different gradients of the black and white scale. The maximum intensity of sound vibrations is recorded in white, and the minimum - in black.
There are three operating modes of ultrasound - A, B, M. A-mode provides a one-dimensional image, B-mode provides a two-dimensional image of anatomical structures in real time. M-mode is a one-dimensional image with a time coordinate. It is used to diagnose the functionality of the heart.
To make the image as informative and accurate as possible, contrast agents (echo contrast) are used. The contrast agent contains free gas microbubbles (less than 5 microns in diameter). They improve visualization of blood flow or individual organs, increase contrast between tissues and increase diagnostic accuracy.