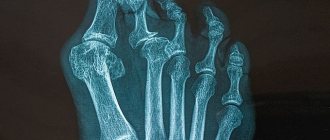
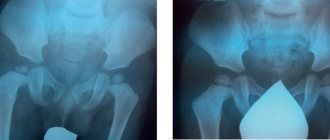
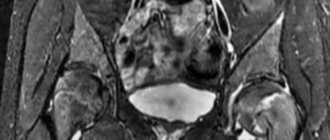
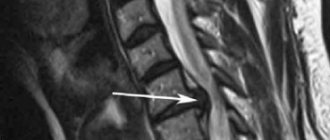
Scintigraphy is an advanced imaging technique used to evaluate certain skeletal abnormalities. It uses radioactive tracers to identify changes in bone metabolism before they become visible on x-rays - for example, to detect fractures in bone structures.
The procedure can identify problems in any part of the skeleton, but is particularly useful in areas where clinical examination, including diagnostic analgesia, is often difficult, such as the pelvis and back.
Indications for osteoscintigraphy
Which doctor prescribes the procedure and why?
Scintigraphy of skeletal bones is performed to identify various pathological processes in bone tissue.
A referral for the procedure is usually prescribed by a rheumatologist in the following cases:
- establishing the cause of long-term pain in the bones;
- clarification of the results of x-ray examination for fractures;
- determination of the degree of complexity of fractures (detection of fragments in soft tissues);
- identification of bone metabolism disorders (metabolism) - foci of necrosis, Paget's disease;
- diagnosis of osteomyelitis (in adults), rickets (in children);
- suspicion of bone cancer or the presence of metastases in them;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of malignant diseases of the bone skeleton.
Indications
The main advantage of scintigraphy is early detection of diseases. Thanks to this method, it has become possible to find the problem before clinical signs appear and avoid serious health consequences.
Main indications for osteoscintigraphy:
- chronic pain, the cause of which could not be identified after other examinations;
- complex and minor bone injuries that are difficult to diagnose using x-rays;
- inflammatory lesions of the osteoarticular system (rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthropathy, osteomyelitis and others);
- suspicion of metastatic bone lesions (often with prostate cancer in men, breast cancer in women, lymphoma);
- monitoring the effectiveness of polychemotherapy and radiation treatment for oncology;
- primary bone tumors (Ewing's osteosarcoma, myeloma);
- determination of inflammation in the area of joint prostheses.
Indications for three-phase scintigraphy:
- injuries;
- assessment of the condition of the bone graft;
- inflammatory diseases of the osteoarticular system.
Contraindications
In connection with the use of radiopharmaceuticals, experts do not recommend performing osteoscintigraphy:
- for pregnant women - the procedure is not prescribed as planned, only for emergency indications;
- lactating women - during the removal of radiopharmaceuticals from the body (2-3 days), the baby cannot be fed with breast milk. Radionuclides enter the secretions of the mammary glands, such milk must be expressed without giving it to the baby;
- tendency to allergic reactions - you must warn the doctor about this even before the examination, since allergies of varying severity may develop to radiopharmaceuticals;
- diagnostic procedures with barium - undergoing, for example, an X-ray of the stomach with a barium suspension a day before osteoscintigraphy can significantly affect the quality of the image.
Side effects of osteoscintigraphy
A bone scan involves the use of a radiotracer, most commonly technetium −99m, which is injected into the blood. The radiation level of the radioactive tracer is very low, much lower than that of a CT scan. The radiopharmaceutical is quickly eliminated from the body: after 1-2 days it completely leaves the body. Therefore, there are no radiation-related side effects.
There is a small risk of an adverse reaction caused by technetium-99m. After administration of the drug, the patient may experience:
- soreness or redness at the injection site;
- feeling of a strange taste in the mouth;
- chest pain or discomfort;
- cardiopalmus;
- change in odor perception.
These side effects occur in only 1% of patients. In most cases, they soon go away on their own without treatment.
Methodology
The radiopharmaceutical is administered intravenously. After the injection, the patient is allowed to go home for 3 hours or is asked to wait on the territory of the medical center. During this time, it is advisable to drink 1-1.5 liters of water to speed up the removal of radionuclides that are not absorbed by bone tissue. Immediately before the procedure, you need to empty your bladder.
Bone scintigraphy is performed in a sitting or lying position. The patient must remain completely still and cannot talk during the entire procedure (from 30 minutes to 1 hour). The medical staff of the diagnostic room is located in an adjacent room, from where they monitor the process and condition of the patient through a special window.
The gamma camera used for scanning is a large (50 cm in diameter) crystal that captures and records radiation across the entire surface of the patient’s body. The obtained data is processed by a special program and displayed on the radiologist’s computer monitor.
Where is scintigraphy done?
It is better to undergo scintigraphy at a medical center that specializes in radiodiagnostics.
3.How is the examination carried out?
Skeletal scintigraphy is performed and interpreted by a nuclear medicine specialist or a radiologist.
Before osteoscintigraphy, you must remove all jewelry and undress.
A special substance is injected into a vein in the arm to allow the bones to appear in photographs. The substance takes 2 to 5 hours to reach the bones. During this time, you will be asked to drink several glasses of water to flush out the substance. You will need to empty your bladder immediately before taking pictures.
To take pictures, you will be asked to lie down on a table. A special camera scans your bones. The camera does not emit radiation.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
results
Photo: Pharm-sintez CJSC
The radiologist issues a conclusion the next day after the examination.
The photographs visualize the entire human skeleton. This is very important for identifying metastases, which are often located in the bones of the skull, ribs and spine.
Bone scintigraphy makes it possible to determine the exact location of the lesion (in bones or soft tissues), as well as to distinguish a malignant formation from a benign or other pathological process (inflammation, infection, mechanical damage).
How is recovery after the procedure?
The examination is carried out in a gamma camera, which illuminates the human body with radioactive rays, detecting radiopharmaceuticals in the bones and joints. Despite the apparent complexity, the procedure does not produce any harmful consequences and immediately after diagnosis the patient can return to their normal lifestyle. Recommendations for the rehabilitation period include monitoring sufficient fluid intake on the first day (the more, the better), as well as observing good personal hygiene measures - thorough bathing, washing all things.
OSG Security
After osteoscintigraphy, it is recommended to take a warm shower using soap or gel, wash your hair with shampoo, and wash the clothes you wore during the procedure.
Cotton balls after radiopharmaceutical injection, bandages or adhesive plasters (if used) must be disposed of in radioactive waste bins located in the clinic. Hazardous medical waste should not be brought home.
Also, to speed up the process of removing radiopharmaceuticals from the body, you need to drink more fluid. For the day after the examination, it is advisable to exclude or limit as much as possible contact with pregnant women or small children.
Osteoscintigraphy is the only highly informative method for diagnosing malignant diseases of bone tissue, absolutely painless and safe for the patient. Minimal radiation exposure allows for monthly examinations. Compared to traditional radiography, the radiation dose during scintigraphy of skeletal bones, performed with modern equipment, is tens of times less.
What is a bone scan
Skeletal scintigraphy is a special type of diagnostic that uses small amounts of radioactive material to assess the severity of various diseases and bone conditions, including fractures, infections and cancer.
Content:
- What is a bone scan
- Indications and contraindications for the procedure
- Preparing for bone scintigraphy
- Algorithm for the procedure
- Safety of diagnostics
The diagnostic procedure is non-invasive and, with the exception of intravenous injections, usually painless. The device uses radioactive materials combined with bone tissue (tropic), called radiopharmaceuticals or radioisotopes. Due to them, visualization of bones is carried out, based on their introduction into the patient’s body and subsequent observation of their distribution and interaction with the environment. The skeleton becomes visible on a special device by capturing gamma radiation from isotopes included in the preparation.
The radioactive energy is detected by a special camera or imaging device that creates a picture of the bones, called a scintigram. The bone abnormality appears as a darkening on the image.
Since the procedure is able to depict the body's functions at the molecular level, it makes it possible to identify the disease at the earliest stages, and therefore select the most effective treatment.
In fact, skeletal scintigraphy, or bone scanning, can often detect bone abnormalities much earlier than conventional x-rays.
Preparing for the procedure. Results Evaluation Criteria
The decision to perform scintigraphy is made by the attending physician, based on the amount of information obtained during other studies of the patient. The procedure itself is carried out in several stages, each of which requires adherence to a clear sequence. The beginning of the procedure involves the introduction into the patient’s body of a special drug, which includes special indicators, which are radioactive elements. After a certain period of time, depending on the type of study, a nuclear scan of the patient is performed using special equipment. Bone scintigraphy
in some cases, it is carried out using radioactive strontium injected into the patient’s body. Less commonly, the isotope of technetium is used as the main component of indicators. The scanning time is 40-50 minutes, depending on the scanning area and the quality of the resulting images. If the images are not sharp enough, scanning is repeated once or twice.
Evaluating bone scintigraphy
, it is necessary to note the criteria for assessing the results of diagnostics carried out in this way. The scan results are evaluated as follows:
- comparison of the number of bone tissue impulses against the background of the general activity of the indicator;
- comparison of the number of impulses in the affected area with the behavior of healthy tissues;
- assessment of the number of metastases.
Moving on to the scintigraphy procedure itself, doctors carefully determine the patient’s condition regarding the body’s existing allergic reactions to certain medications. In general, bone scintigraphy is safe for the patient and does not have a negative effect on the body being studied. The high rate of removal of radioactive elements from the body is also important.
The research results are transferred to the attending physician for subsequent thorough analysis of the patient’s condition, the stage of development of the pathology, in order to select subsequent treatment for the patient. In the normal condition of the patient, the radioactive tracer distributes evenly in the bone tissue without revealing any visible activity. Each area of the human body contains a certain amount of the indicator. As a result of the presence of pathological changes, as a reaction, the concentration of radioactive isotopes in tissues either decreases or increases. The accumulation of a radioactive tracer in a certain area accurately indicates the source of pathology or inflammation. By examining the image, the number and expressiveness of the spots, one can determine the presence of fractures, a malignant tumor, osteomyelitis, and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
In some cases, on the contrary, a lack of a radioactive substance indicates the presence of a certain type of cancer or a disorder in the body’s circulatory system.
Bone
scintigraphy is an accurate diagnostic method, but the accuracy of the data obtained may be negatively affected by the following factors:
- the presence in the patient’s body of high concentrations of barium and bismuth components, elements that distort image quality;
- the patient’s condition does not allow him to remain in one position for a long period of time;
- a full bladder, making it difficult to examine the bones of the pelvic area.
Pregnancy may be a factor preventing scintigraphy. The danger of exposure to radioactive elements on the fetus excludes the possibility of using this technique for diagnosis. When assessing the capabilities of this technique, one should remember some significant disadvantages of this method. Particular attention should be paid to the fact that the scan itself does not separate tissue into normal and affected areas. The results obtained during the research and the analysis process are interpreted simultaneously with the existing symptoms of the disease, the results of other studies, based on personal observations of physicians and patient complaints.
In modern medicine, bone scintigraphy
carried out during complex diagnostics, along with traditional diagnostic methods.
The data obtained during the research confirm or deny the information obtained as a result of x-ray examination, the use of MRI and CT, a number of blood tests and biopsy material. Considering the specificity of many oncological diseases, it should be recognized that bone scintigraphy
in some cases does not allow identifying the presence of pathology, and therefore is not effective as a research method.
4.What are the risks and what can interfere with the examination?
What are the risks of bone scintigraphy?
Allergic reactions to the radioactive substance are very rare. Your body will get rid of it throughout the day through urine and feces. The dose of radioactive radiation received during skeletal scintigraphy is extremely small and therefore has no risk.
What can interfere with osteoscintigraphy?
Skeletal scintigraphy may be interfered with by:
- Pregnancy;
- Barium is in your body;
- Inability to maintain a calm position;
- Full bladder.
Carrying out a scan
The patient is injected with a solution containing radiomarkers, then the patient is placed on the equipment table. The liquid spreads throughout the body and lingers in the bone tissue for only a few hours. While this process is happening, the patient needs to drink about a liter of water, then lie down again. After the solution has spread, pictures are taken with a gamma camera. The duration of the scan is about 60 minutes. During this period, the patient cannot move.
Depending on the expected pathology, one of the OSG methods is selected:
- Three-phase imaging (mainly used for bone inflammation and implant monitoring).
- A full skeletal scan (Whole) is done to identify the location and growth of metastases and monitor the patient’s condition during remission.
- Projection-sighting photographs are taken if additional data about certain areas is needed.
- Single photon emission CT (or SPECT) (primarily performed as an additional test for large areas of bone involvement).
After the examination, you must immediately change into different clothes. Therefore, it is best to take things with you to the examination that you don’t mind throwing away. Even very thorough washing will not give a 100 percent guarantee that radiation from clothing will then be completely removed. Items used during the scan remain in the office. Such clothing is placed in special waste containers.
After the examination, you need to drink a lot of liquid daily - still water, compotes, slightly sweet fruit drink or rosehip decoction. This contributes to the rapid removal of radiation nuclides from the body. Immediately upon arriving home, the patient should wash thoroughly. Enhanced hygiene continues for another week. On the first day after the examination, you should not have contact with women carrying a child or children.