Magnetic resonance imaging is a diagnostic method that allows you to obtain a detailed understanding of the nature of pathological changes in any area of the human body.
MRI scan of coxofemoral joints, normal variant
In orthopedic practice, MRI of the hip joint is often performed to clarify the causes of coxalgia - pain in the joint. The research method does not involve the use of ionizing radiation, which is especially important for children and pregnant women. The process of creating clear images that can be enlarged and viewed in volumetric form is based on the use of magnetic resonance and computer technology. Contrast is used to improve visualization capabilities. The diagnostic value of photographs obtained after gadolinium administration is comparable to the results of arthroscopy - an invasive study involving penetration of surgical instruments into the joint cavity.
How is an MRI of the hip done? Scanning is carried out on devices with different magnetic field strengths. The doctor can independently choose programs depending on clinical tasks. This is relevant if it is initially unclear what causes the pain syndrome: pathology of the pelvic organs or joints. In standard situations, multiparameter sequences are used.
Hip diseases on MRI
Impingement syndrome on MR photo
Magnetic resonance scanning is performed to diagnose a number of pathological conditions. What does an MRI of the hip joint show? The pictures visualize:
- Femoroacetabular impingement syndrome.
Mechanical conflict between the femoral head/neck and the edge of the acetabulum is caused by unilateral or bilateral bone defects of congenital or acquired origin. Modified articulation components cause limb dysfunction due to impingement during movement. Pathological bone friction promotes the growth of osteophytes against the background of constant trauma to the acetabular labrum. If the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner and treatment is not started, the latter will rupture over time. The cartilage tissue of the articulating bones will be destroyed. Such a mechanical conflict often contributes to the formation of coxarthrosis and is accompanied by progressive pain syndrome.
MRI: pronounced epiphysiolysis on the left - dystrophic condition of the growth plate, a symptom of the head slipping in the area of the femoral neck
MRI of the hip joint for femoroacetabular impingement syndrome shows possible causes of the disease:
- congenital malformations;
- complications after injuries and surgical interventions;
- concomitant avascular necrosis of the femoral head;
- inflammatory processes in the synovial bursa;
- osteochondropathy (Perters disease);
- epiphysiolysis (Salter-Harris fracture);
- atrophied muscles around the joint, etc.
In severe cases of diabetes mellitus with circulatory disorders, regular physical overload, concomitant diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue (arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc.), destruction of bone and cartilaginous structures is detected.
- Osteoarthritis. A long-term pathological process leads to a complete loss of function of the hip joint due to the destruction of all components of the joint. Changes in bone tissue, ligaments, blood vessels, cartilage and surrounding muscles can be seen on an MRI with contrast. Involvement of nerve bundles causes persistent hip pain. Predisposing factors include:
- endocrine disorders;
- doing strenuous sports;
- obesity;
- concomitant arthritis, arthrosis, etc.
The disease has three degrees of severity. MRI of the hip joint shows changes at an early stage, when drug therapy can prevent/slow down the progression of the pathology.
- Avascular necrosis of the femoral head.
The appearance of the specified pathology on MRI, the changes correspond to stage 2
The development of avascular necrosis is caused by long-term malnutrition of the hip joint against the background of blood thickening, thrombus formation, compression, and twisting of blood vessels. During ischemia, voids are created in bone tissue, leading to deformation and cartilage detachment. Clinical manifestations are nonspecific, which causes difficulties in making a diagnosis. There are many provoking factors:
- injuries;
- long-term hormone therapy;
- intoxication;
- exposure to ionizing radiation, etc.
Early changes are not visible with x-rays or ultrasound. MRI of the hip joint is one of the effective ways to detect the disease at an early stage.
- Inflammatory processes.
Subacute osteomyelitis on MR scan and plain radiograph: periosteal detachment (head), purulent lesion (arrows)
Rheumatoid, septic, psoriatic, reactive, juvenile arthritis, osteomyelitis lead to modifications of the hip joint and synovium (synovitis). Determining the genesis, in addition to MRI and CT procedures, involves performing laboratory tests to assess:
- P-factor;
- uric acid level;
- C-reactive protein;
- HLA B27 antigen;
- antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptide, etc.
Arthritis of the hip joint (coxitis) can be a manifestation of ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarticular tuberculosis, and a number of metabolic disorders in the human body. There are four stages of disease progression:
- I - abrasion of tendons, reduction of space between bones, slight deposition of fluid, increased pain during exercise;
- II - development of erosions and muscle atrophy;
- III - formation of osteophytes, increase in edema, destruction of cartilage;
- IV - modification of all articulation structures.
- Synovial lesions. Diseases of the inner layer of the joint capsule or the osteofibrous canal are rarely recorded. Pigmented nodular synovitis is a tumor-like pathology of the joint with an unknown genesis. The disease is characterized by hyperplasia (excessive growth) of the membrane and deposition of hemosiderin. An MRI photo shows cartilaginous bodies formed in the inner layer of the capsule in synovial chondromatosis.
- Tumors.
MRI: femoral neck metastasis with stress fracture formation (circled)
Benign and malignant neoplasms can develop in the hip joint. An MRI photo shows the presumptive nature of the tumor. Verification of the diagnosis requires a biopsy. Pain is noted when nerve endings, border tissues, and blood vessels are compressed, which happens with any tumor, so the absence of a symptom should not delay magnetic resonance imaging. Primary bone tumors are best diagnosed using CT; MRI is more suitable for demonstrating soft tissue changes.
- Hip dysplasia. To determine congenital underdevelopment of the joint, accompanied by subluxation, ultrasound sonography is often not enough. MRI can be done on young children without harm to health, starting from the age of one month.
- Traumatic injuries.
Femoral neck stress fracture on MRI
The pathology is more often diagnosed in older people, which is associated with age-related disorders of mineral metabolism. When a tumor and infection occurs, a so-called pathological fracture of bone tissue occurs. MRI photo shows:
- dislocations, sprains and ruptures (full and partial) of ligaments;
- bruises with internal hemorrhage;
- hematomas, etc.
Contraindications
MRI is contraindicated for patients with pacemakers, metal clips on cerebral vessels, middle ear implants, artificial heart valves, ferromagnetic metal structures and prostheses, insulin pumps, tattoos using metallic inks near the diagnostic area, and is also not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy. After hip replacement, scanning depends on the material of the prosthesis. MRI with contrast is generally not performed on pregnant or breastfeeding women.
MRI of the hip joint: indications and contraindications
The endoprosthesis can cause defects in images, so X-ray diagnostic methods are preferable
MRI is performed when the results of computer scanning, radiography, and ultrasound are ambiguous. The method is suitable for dynamic observation: for medical reasons there are no restrictions on the number of MRIs. The clinical manifestations of a number of pathological processes are similar, and extensive diagnostics are required to accurately determine the genesis of symptoms. Indications for MRI of the hip include:
- prolonged pain syndrome, unexplained lameness, discomfort while walking and/or at rest, limited range of motion in the joint;
- no effect/short-term improvement during therapy;
- assessment of post-traumatic complications - in an emergency, the search begins with CT;
- primary detection of the disease - inflammation, destruction, tumor pathology, congenital malformations, infectious lesions, degenerative processes, etc.;
- examination before surgery and after surgery - endoprosthetics, etc.;
For pain associated with neuralgia, MRI of the hip joints shows normal, the study is performed to differentiate the processes.
Contraindications to MRI scanning:
- the presence of implanted devices in the body - myo-, neuro-, pacemaker, defibrillator, insulin pump, permanent hearing prosthesis, vascular clips made of metal with paramagnetic properties, Ilizarov apparatus, etc.;
- pregnancy in the first trimester;
- children up to a month old;
- obesity with body weight above 120 kg (for closed circuit scanners);
- the patient’s poor health due to an acute condition: pain syndrome due to injury, heart attack, stroke, etc.;
- inability to remain in a supine position for a long time;
- some mental and neurological pathologies - alcoholic delirium, epilepsy, claustrophobia, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease (MRI will be done in a hospital setting under sedatives).
A contrast study is not available for patients with a history of an allergic reaction to gadolinium, end-stage renal failure, or pregnant women at any stage. Permanent dental structures - veneers, pins, braces, endoprostheses made of titanium do not interfere with magnetic resonance scanning
Conducting research
Scanning the hip joint is quite simple and does not cause any pain to the patient, which is a huge advantage over other diagnostic procedures.
The patient should change into a sterile hospital gown for greater comfort, then lie down in a horizontal position on the couch. To ensure immobility, the patient's body will be secured with straps during the MRI of the hip. This is also done to ensure that any involuntary movements of the legs and arms are completely eliminated.
The medical staff will explain how you can inform your doctor about changes in your health if it suddenly worsens. It is worth noting that any deterioration in well-being can only be caused by an unstable psycho-emotional state against the background of experiences. This is why it is so important to get ready to undergo the examination, especially since the procedure does not involve any risks for the patient.
After preparation, the couch is moved into the inside of the tomograph, and the scanner begins its work. Despite the fact that during the examination the patient is alone in the office, he is not left for a minute without the close supervision of the doctor, who monitors the progress of the scan from the next office.
As soon as the device starts working, the subject may hear specific sounds. This is a normal phenomenon and should not be alarming. An MRI of the hip joint lasts approximately 30 minutes without contrast and about 1 hour with its use.
As soon as the MRI of the hip is completed, the patient can immediately change into his own clothes and go to await the decoding of the images and the conclusion.
It is important to remember that with photographs of the hip joint and interpretation, it is imperative to contact a highly specialized specialist to prescribe appropriate treatment.
How is an MRI of the hip done?
To improve the signal-to-noise ratio, the problem area should be as close to the center of the table as possible
Magnetic resonance scanning of the said joint is performed using different devices. Images taken with closed-loop equipment are more informative. The best option is to do an MRI on a closed scanner with a magnetic field strength of 1.5 Tesla. Low-power installations are used for screening diagnostics of athletes in the absence of complaints.
The patient arrives at the clinic 20 minutes before the test. After completing the paperwork and depositing items containing metal, the x-ray technician places the patient on the tomograph table.
During the diagnostic procedure, you can examine one or two hip joints, depending on the indications: systemic diseases require a comprehensive examination of several areas.
The patient is placed on his back, with the big toes brought together to ensure rotation of the hip joints. To prevent accidental movements, use a popliteal bolster and soft fixation of the limbs with belts. A coil is placed over the area of interest. When contrast is planned, a catheter is installed in the cubital vein and an automatic injector is connected: at a given time, an amplifier drug will enter the body.
After evaluating the targeted images, the radiologist selects the desired MRI sequences. The medical staff monitors the progress of the diagnosis through a window from an adjacent room, and communication is carried out via speakerphone. If the patient's health worsens, the scanning can be paused; the patient has a special button at hand. After the scan is completed, a conclusion and a disk with a recording of the diagnostic procedure are usually issued. The video can be opened using a program that supports the dicom format.
Algorithm for proper preparation
It is imperative to determine in advance whether the patient is allergic to the contrast agent. Since patients do not always know how the body will react to a previously unused drug, a preliminary allergy test should be performed. If the reaction is positive, you can try replacing the drug with an analogue, using antihistamines, or using a CT scan instead of an MRI.
Another important stage of preparation is to notify the attending physician about pregnancy, since any stage of pregnancy becomes a contraindication to the use of magnetic resonance imaging with contrast, because the contrast can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and harm the fetus. Ignoring the ban can result in severe pathologies in the development of the unborn baby.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
Young children are allowed to undergo such an analysis, with a serious outweighing of the benefits over the possible harm, when the choice is between the child’s life and conducting the study under general anesthesia.
As a rule, childhood is a relative contraindication, as are psychological disorders and uncontrolled motor syndrome. The categorical nature is explained by the fact that the victim must endure the entire procedure in complete immobility, when any movement displaces the three-dimensional image and requires repeated examination.
Other relative contraindications include diabetes mellitus, renal and liver failure.
All this is dangerous only when it is necessary to use contrast, since the elements of the drug must be eliminated naturally in a timely manner.
And with the final relative prohibition of claustrophobia, new generation devices with open side parts will help to cope. They are used both to examine the spine and to diagnose possible deviations of the hip joints.
Separately, you should take care to remove all metal elements from yourself before starting the study. We are talking about jewelry, piercings and metal elements on clothing. You need to warn the specialist in advance about the presence of any built-in electronic elements such as pacemakers and wires to support the bone skeleton.
How to prepare for an MRI of the hip joint?
Before registering for the procedure, all questions can be discussed with your doctor.
No special measures are required; it is enough to remove metal objects (keys, coins, etc.), payment cards, remove jewelry, watches, and wear loose clothing without zippers or rivets. Take with you a package of documents: passport, descriptions of the results of previous diagnostics, a doctor’s referral, medical insurance (if payment will be made through an insurance company).
The introduction of contrast into the body rarely causes clinically significant side effects, but in 8-10% of cases autonomic reactions are recorded - drooling, dizziness, nausea, etc. To prevent such phenomena, you need to have a light snack 15 minutes before leaving home.
For women during lactation, preparation for an MRI of the hip joint with contrast involves storing milk for several feedings. An increased drinking regimen after the diagnostic procedure will facilitate faster disposal of gadolinium chelates.
How is an MRI of the hip joints performed if you also need to look at the internal organs? If you suspect a possible pathology of the uterus, appendages, prostate, seminal vesicles that support pain, preparation for the study involves cleansing the intestines and eliminating flatulence. The bladder is assessed in a full state.
Preparatory activities
Preparation for tomography of the hip joint is directly related to how the MRI will be performed: in the classic version or using a contrast agent.
If contrast is not used, then no fundamental restrictions will have to be observed. The patient does not need to change his usual lifestyle or observe any strict restrictions on food intake.
But if the doctor ordered an MRI of the hip using a contrast enhancer, then you will have to make sure that there is no allergic reaction. To do this, a sensitivity test is performed at the medical center: a small amount of contrast is injected subcutaneously, and after 20-30 minutes the result is assessed.
If a rash, irritation, redness, itching or other allergy symptoms appear on the skin, the administration of contrast for scanning the hip joint to the patient will be strictly prohibited for safety reasons.
Such manifestations occur in people in exceptional cases, since contrast rarely causes such a reaction. It is advisable to carry out such a test once, and all subsequent diagnostics using contrast can be carried out with confidence without the need for a repeat test.
Every patient should remember that they must come for a study using contrast on an empty stomach. Otherwise, nausea and discomfort in the intestines may occur.
The radiologist should also conduct a conversation with the patient before starting the study in order to identify contraindications, which may include:
- pregnancy in women;
- the presence of a number of chronic diseases;
- existing metal objects in the body.
It is very important not to hide any important facts from the radiologist, as this will be the key to safety during the scan.
Immediately before starting the MRI, you will need to remove any jewelry. Personal belongings will have to be left outside the office. Gadgets and metal objects can interfere with the operation of the device, cause malfunctions and have a negative impact on the quality of pictures.
Interpretation of MRI of the hip joints
A radiologist interprets the images. Normally, traumatic changes are not detected on a series of tomograms:
- the structure of the bone tissue is homogeneous, without degenerative signs;
- there is no subchondral sclerosis of the articular surfaces;
- the joint capsule is not thickened, there is a small amount of synovial fluid in the cavity with a homogeneous MR signal;
- the bony roofs of the acetabulum are formed correctly, the joint spaces are uniform, the congruence (comparability, coherence) of the surfaces is preserved;
- the integrity of the ligamentous apparatus is not compromised;
- the signal of the cartilaginous component is without features, there are no areas of thinning;
- there are no marginal sharpenings of the articular surfaces of the acetabulum;
- surrounding soft tissues without visible pathology;
- femur and pelvic bones in the scanning area without focal changes.
Anatomy of the hip joint
Providing this joint with a wide range of movements in several planes and significant physical activity lead to the development of various diseases
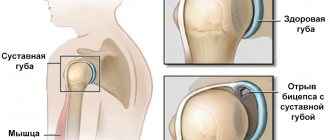
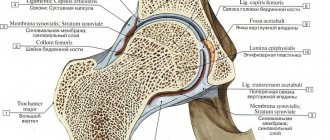
The coxofemoral joint is formed by the proximal end (head) of the femur and the acetabulum. The latter consists of the ilium, ischium and pubis, and has a rounded shape. The acetabulum is divided into an articular surface, an acetabular fossa, or a recess. The articular capsule is formed by multiple ligaments. The head of the femur, like the acetabulum, is partially covered with hyaline cartilage, the rest is made up of synovium, which produces fluid to reduce friction. Ligaments and joint capsule serve to limit the range of motion (prevent dislocations, hyperextension of the limb).
Which is better: CT, MRI or X-ray of the hip joint?
Epiphysiolysis of the femurs on MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging and computer scanning are complementary diagnostic methods, since it is often necessary to evaluate both the soft tissue structures and bones that form the joint. In emergency situations, CT has the advantage of providing results within a few minutes. Long-term consequences of injuries, tumors, and avascular necrosis are better demonstrated by MRI. In modern traumatology, radiography is used to search for gross injuries or advanced processes emanating from bone tissue; if possible, it is better to do a multispiral computer scan. Of the listed imaging methods, MRI is the safest, since X-ray diagnostics involve radiation exposure to the body.
At the Magnit clinic in St. Petersburg, an MRI of the hip joint can be done using Siemens expert-class equipment with a field strength of 1.5 Tesla. There are discounts at night; a conversation with a doctor is included in the total cost of the procedure. Sign up by calling +7 and come - we will be happy to help!
How the procedure is performed
The patient takes off his metal accessories, takes out his phone and plastic cards from his pockets, enters the office with the device and lies down on the couch. Our center has open-type MRI scanners, so there is no need to stay in a confined space. To prevent random movements from interfering with the images, the person being examined needs to lie still. During the procedure, the patient hears tapping or humming of the device; if these sounds cause irritation, you can use earplugs or headphones. During the examination, the patient can communicate with the doctor. The MRI procedure is performed without pain or adverse reactions.