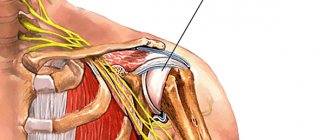
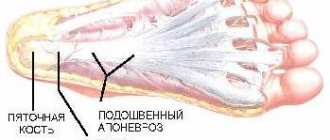
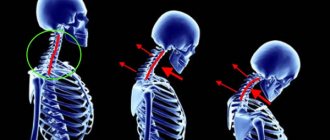
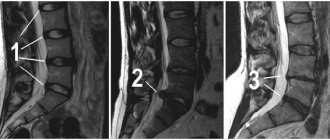
Spinal cancer is an abnormal growth of cells in the spinal cord. May occur with different symptoms. It manifests itself depending on the type and stage of development.
Stages
Spinal cancer can be either primary (appears in the spine itself) or secondary (moves from other internal organs). The second option is characterized by the presence of metastases in the spinal column. These metastases are a projection of tumors from other organs (lungs, stomach, chest, etc.). Penetration of secondary cancer into the spinal cord occurs through the blood.
There are 4 main stages. They differ:
- according to the size of the primary tumor;
- degree of lymph node damage;
- the presence or absence of metastases in internal organs.
The most severe is grade 4.
It is important to diagnose cancer early. However, we should not forget that this is a rapidly progressing cancer. Treatment in the early stages of spinal cancer allows you to completely get rid of the disease.
Symptoms and signs
Spinal cancer has its own symptoms and signs. But diagnosing this disease is quite difficult, since its symptoms resemble a number of other ailments. Therefore, the patient often mistakes the pain that appears in the spine for rheumatism and osteochondrosis. But this disease should be identified in time in order to begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Considering that the symptoms of spinal cancer are identical to other common diseases, for preventive purposes you should undergo a full examination if back pain occurs. Especially when discomfort and unpleasant sensations are present regularly or constantly.
Typically, with spinal cancer, the following symptoms appear:
- general weakness;
- frequent numbness of the upper and lower extremities;
- difficulty moving;
- frequent muscle spasms that spread throughout the body.
You should immediately consult a doctor if taking painkillers when these symptoms appear does not help, and you feel very severe pain while lying down.
But there are other signs of spinal cancer:
- the appearance of severe pain at night and early in the morning;
- even minor changes in the shape of the spine are noticeable;
- neurological signs are present (sensitivity of the limbs is impaired, as well as their movement partially or completely). With spinal cancer, respiratory disorders and heart problems may appear.
All these signs are a clear signal that a full examination should be carried out in a specialized clinic.
What's happened
This type of cancer is a malignant tumor that comes from cartilage tissue. This may be a tumor degenerated from a benign formation or a tumor that develops on bones that do not undergo changes. It is the second most common disease among skeletal cancers.
The age at which this disease usually appears is forty to sixty years. Moreover, men suffer from this type of cancer more often than women.
One of the signs of this disease is swelling of the skin in the area of the cancer site and increasing pain. There may also be an increase in the venous network over the malignant tumor, a slight increase in temperature, and limited movement in the joint.
Chondrosarcoma most often requires surgical intervention, and the tumor is removed along with adjacent tissues.
Localization of tumors in the spine
Experts distinguish six main types of spinal cancer.
- Chondrosarcoma. This is cancer of the lumbar spine. It often affects the cartilage in the sacrum. A distinctive feature is that it develops quickly and aggressively and has no symptoms. When this type of spinal cancer is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed immediately.
- Chordoma. One of the most common types. Belongs to the primary type. This is cancer of the cervical spine, which is formed from bone tissue and affects the nerves and muscles of individual locations. This type of disease is characterized by a high probability of relapses, as well as metastases of spinal cancer.
- Ewing's sarcoma. The sacral and lumbar spine are affected. Often occurs in childhood or adolescence.
- Osteosarcoma. This is one of the rarest species. Most often, this tumor affects men under 30 years of age. This spinal bone cancer is aggressive and quickly spreads to adjacent tissues.
- Multiple myeloma. In this case, damage occurs to plasma cells of the blood and bone marrow. This leads to destruction of the vertebrae. This is cancer of the thoracic spine. It is indicated for people over 45 years of age.
- Plasmacytoma is solitary. This type is similar to the previous type of spinal cancer, but the prognosis is more optimistic. More often appears in men over 40 years of age. A characteristic feature is spontaneous and sudden fractures of the vertebrae with minor impact on them.
2.Chemotherapy
The goal of chemotherapy is to shrink the tumor of the spine by treating it with special medications that are administered intravenously. Chemotherapy is given in cases where the tumor is considered inoperable. After reducing the size to an operable size, surgical removal of the tumor is performed. Chemotherapy is carried out in courses; for different patients, one course or several may be sufficient. One course of treatment is from 5 to 15 sessions of drug administration.
Visit our Neurosurgery page
Causes
Many people are interested not only in the signs of spinal cancer, but also in the main causes of the tumor. The most common include:
- genetic predisposition;
- work in production related to hazardous substances;
- blood cancer;
- HIV infection;
- AIDS;
- exposure to a radiation source (this also includes the effect of carcinogens);
- various types of spinal injuries that led to local disruption of the blood supply.
How are spinal cord and spinal cord tumors diagnosed?
Tumors of the spinal cord and spinal cord may sometimes not be diagnosed immediately because they are rare and because their symptoms resemble the most common diseases (trauma, hernia). It is especially important for your doctor to know your entire medical history and suspect that they plan to perform diagnostic tests that can confirm the diagnosis and note the location of the tumor. MRI is the study of choice because it is the only factor that produces the highest resolution images of all anatomical structures of the spine and spinal cord. Sometimes it is necessary to determine the degree of infiltration of bone structures (vertebrae) and program interventions. Lumbar puncture and special examination of nasopharyngeal fluid are often required, especially if demyelinating disease or myelitis is suspected. A bone scan can identify dispersion, usually metastatic tumors. In some cases, biopsy using axial tomography is suggested, since this is the only diagnostic test that provides histological identification of tumors, especially vertebral tumors. Not suitable for intramedullary tumors.
When to see a doctor
You must understand that pain from spinal cancer can be very different. And if you are worried about even minor discomfort in your back, you should consult a doctor.
You should be especially wary of pain that clearly manifests itself at night and in the morning (while lying down). If taking painkillers and using special ointments for a long time does not help, then you cannot postpone visiting a specialist until “later.”
If you go to the oncology department, which is located near the Mayakovskaya, Belorusskaya, and Novoslobodskaya metro stations, you can count on a whole range of diagnostic measures. If necessary, the oncologist will conduct a thorough examination of all internal organs.
Classification
Origin
According to its origin, chondrosarcoma is of two types:
- Primary;
- Secondary.
Primary
This type of chondrosarcoma is detected in 90% of cases and is divided into two more subtypes:
- Periosteal (this subtype of chondrosarcoma grows outside the bone surface);
- Central (this subtype of chondrosarcoma forms inside the bone).
Secondary
It is detected in 10% of cases and is formed from the following types of tumors:
- Chondroblastomas;
- Chondromas;
- Fibromas of chondromyxoid nature;
- Exostoses of an osteochondral nature;
- Tumors in Ollier-Maffucci disease.
Structural features
If you look at the structure of chondrosarcoma, the following subtypes are distinguished:
- Undifferentiated;
- Anaplastic;
- Clear cell;
- Typical.
Malignancy grade
Based on this criterion, the results of histological studies are taken into account, on the basis of which the degree of malignancy of chondrosarcoma is determined:
- I degree of malignancy: absence of mitotic figures, a small number of multinucleated cells, dense small-nucleated chondrocytes are present in the chondroid tissue;
- II degree of malignancy: there are cellular accumulations along the lobar periphery, an increase in nuclei is observed, there are zones of destruction and some mitotic figures, the intercellular substance is thus myxoid in nature;
- III degree of malignancy: also a myxoid intercellular substance with cells arranged in groups and cords, a large number of irregularly shaped cells, there are a large number of multinucleated and enlarged cells, there is mitosis and extensive areas of destruction.
Ewing's sarcoma
The degree of malignancy of this type of cancer directly determines how quickly metastases will form during the course of the disease, and whether relapse is possible if the pathological tumor is removed.
Diagnosis of spinal cancer
Regardless of the symptoms of spinal bone cancer, it must be diagnosed. And for this there are several methods: from laboratory studies using tumor markers to computed tomography (CT). But for spinal cancer, MRI gives the best results. The thing is that with CT it is impossible to determine the first stage of cancer development, but in the case of magnetic resonance imaging this is quite possible. A biopsy will help distinguish a benign tumor from a malignant one.
You can diagnose spinal cancer in the area of the Mayakovskaya metro station by contacting the oncology department.
Discussion
Achieving local control of highly malignant tumors such as neurogenic sarcoma is usually associated with a large number of complications, but partial tumor removal leads to a large number of local relapses and can negatively affect the quality of life of patients [10]. Neurofibroma of a plexiform structure in neurofibromatosis type 10 has almost 100% potential for malignant transformation into PVD. Angiomatous and epithelioid neurofibromas, as well as simple noncellular schwannomas, degenerate less frequently [11]. Partial removal of malignant neurogenic tumors increases the possibility of transformation with increasing grade of malignancy and leads to rapid local recurrence and spread. In this regard, the primary biopsy is of no small importance for determining the treatment tactics for a neurogenic tumor of the sacrum, and en-bloc resection should be the obvious choice of the surgeon in most cases when identifying potentially aggressive neurogenic tumors [2, 6, 12-15]. At the same time, the results obtained in this study indicate that sacrectomy is associated with a number of disabling complications [6, 9].
Over the past decade, it has become possible to reduce surgical aggression in patients with malignant tumors through the use of radiation therapy. Stereotactic radiation therapy has become an effective method of local control for PVD [17].
Stereotactic radiation therapy (SRT) involves a single or fractional high-precision delivery of a large dose of ionizing radiation to a target in order to achieve the desired biological effect in the irradiated volume with minimal impact on surrounding tissue. Local impact is achieved through the use of a large number of beams, high conformity and a sharp reduction in dose outside the target [18].
A system that is capable of performing SLT is CyberKnife. This system, combining a small linear electron accelerator with an energy of 6 MV, fixed on a robotic manipulator with six degrees of freedom, and an X-ray navigation system, appeared as a result of a number of works carried out in the 90s of the XX century [5, 7, 10, 20] .
Radiotherapy is an integral part of the complex treatment of high-grade sarcomas. Although sarcomas of bone and cartilage tissue are considered completely resistant to ionizing radiation, radiotherapy as an adjuvant to surgical treatment improves local tumor control rates and affects overall survival [5].
The overall survival of patients in the analyzed group of neurogenic sarcomas was less than 50%. This is quite consistent with the data of the world literature and is explained by the high degree of malignancy of PVD. Therefore, the most important thing for patients with signs of this disease is the optimization of the treatment approach strategy and the choice of optimal tactics. For patients with locally aggressive tumors, local tumor control is more important. However, the results of the analysis of the relapse-free survival period of patients with aggressive neurogenic tumors are not entirely reliable due to the small volume of material.
Publications in recent years indicate the need for chemotherapy as a treatment option for patients with aggressive tumors during the period of generalization of the process [19, 20]. However, according to publications, 2-year survival is observed in only 50% of patients.
Treatment
If you are diagnosed with cervical spine cancer or your body is affected by a tumor in another location, then it is important to start treatment on time. An integrated approach will help deal with the problem much more effectively. But there are different treatment methods:
- Surgery is the most important step in cancer treatment. This method allows you to remove a tumor from the human body. But often this method is complemented by other types of treatment (radiation and chemotherapy);
- Radiation therapy is prescribed if the tumor was not completely removed during surgery or if there are no other methods to get to the malignant formation. Destroys abnormal cells and prevents “surviving” cells from spreading. This method is considered the most effective;
- Chemotherapy can slow the growth of cancerous tumors. It is used both before and after surgery. Treatment is based on the introduction of potent drugs into the body;
- symptomatic treatment. It involves the introduction of painkillers into the patient’s body. For intense pain, narcotic drugs are prescribed.
Types of spinal cancers
Cancer can develop in various parts of the spine, and depending on the location of the tumor, malignant tumors are divided into 4 types:
- Intradural. With this type, the formation cuts into hard tissues, such as bones and cartilage. The spinal cord suffers, which is compressed under the influence of tumors and loses some of its functions.
- Intramedullary cancer develops within the spinal cord. This is the most dangerous type, which in a short time limits the body’s performance, the function of nerve cells and the speed of reaction to nerve signals.
- An extradural tumor forms beyond the boundaries of the spinal cord, including metastases to parts of the brain.
- Metastases from other organs not related to the spine.
The 4 stages of cancer give different external symptoms.
- At stage 1 there are no metastases, the tumor is small and does not affect neighboring organs.
- This phase is characterized by tumor growth into neighboring sections and tissues.
- The third is considered incurable. Only a small percentage of patients achieved remission. It is characterized by tumor enlargement and the appearance of the first, weak metastases.
- Terminal stage. Metastases are multiple, the tumor reaches its maximum size and covers several neighboring organs at once.
Be sure to read: Recurrence of anal cancer
Prognosis for cure for spinal cancer
Even a doctor cannot give accurate forecasts. This is due to the fact that spinal cancer is often confused with other, more common diseases, and therefore people turn to an oncologist too late. Unfortunately, this is a type of cancer that progresses quickly and can only be treated in the early stages. Therefore, if you have minor back pain, feel muscle weakness, or have musculoskeletal disorders, you should urgently seek help from a specialist.
Cancer intoxication
Having considered each point, we can derive general patterns. Firstly, it becomes difficult for a person to move. In the final stages there may be complete paralysis. Secondly, a person constantly experiences fatigue, even if he did not work and got enough sleep. It is worth paying attention to sweating: if it is cold (and sticky), then this fact indicates a cancerous disease. The number of urges to go to the toilet increases. An upset stomach is diagnosed: frequent diarrhea.
Cancer Risk Factors
The causes of spinal cord tumors are still largely unknown. Although there are specific genetics for the development of this disease, it is also possible to identify common causes that lead to healthy cells turning into abnormal ones.
Risk factors for developing cancer are:
- weakened immune system;
- Hereditary diseases: Hippel-Lindau disease and neurofibromatosis type 2;
- Side effects: Exposure to radiation therapy or industrial chemicals may increase your chance of developing spinal cancer.
People with AIDS are more likely to become infected with malignant cells in the spine. It is known that this disease completely suppresses the immune system, so the number of cancerous tumors increases.