With systematic exercise, the spastic state of the muscles improves, joint mobility increases, thereby reducing increased muscle tone. This leads to feedback in the central nervous system, due to which the brain receives the correct body-head-body signals, which leads to improvement in the motor development of children with cerebral palsy.
Usually, during the training process, the order of the child’s motor development is observed, but, as practice shows, not all children go through the intermediate stages. There are children who, without learning to crawl, learned to walk. There are also children who cannot hold their heads up well, but can stand and even move independently, either crawling or on their feet. And this does not prevent the child from going back a step and learning to perform intermediate stages later, despite the fact that he has “jumped” this stage and is performing the functionality without observing the order of motor development. And the task of our specialists is to teach or prepare the child for those motor actions for which he is currently ready.
How to teach a child with cerebral palsy to hold his head
Raising the head while lying on the back is a very important element in the motor rehabilitation of children with cerebral palsy. Children who cannot hold their head up have difficulty performing other exercises. Therefore, the ability to hold your head up is very important for further motor development. There are many ways to control the head. This is lifting the head on a ball from a position lying on the back, lifting the head from a hard surface from a position lying on the back, lifting the head with the help of a cushion placed under the child’s chest and shoulders, lifting the head from a position lying on the stomach, getting the child interested in toys. It is very important to take advantage of every opportunity to place your baby on his stomach!!! Through I don’t want, through reluctance, by getting me interested in anything, even a little bit, but constantly. This is the basics! You yourself will be surprised how much stronger the child will become and will begin to lie down longer and more willingly over time. And it will be much easier for the child to move to the next level - revolutions.
Causes
In the vast majority of cases, the pathological condition is congenital in nature.
The development of pathology in a child may be associated with oligohydramnios, breech presentation, genetic connective tissue diseases, joint hypermobility and other abnormalities.
Also in childhood, a combination of recurvation with fibrous changes, dysplasia of the hip or knee joints, dislocation, and absence of the patella can be observed.
Usually recurvation has a congenital character of development
Rarely, the disease can be acquired. In this situation, the causes of recurvation of the knee joint in an adult include:
- weakened functionality of the quadriceps femoris muscle;
- anterior pelvic tilt with muscle weakness;
- limitation of range of motion in the ankle joint;
- shortened calf muscle with increased tone.
Also, pathology in an adult can be a consequence of surgical intervention to transplant part of the flexors in patients with paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle. Consequences may occur if a specialist selects incorrect muscle tissue.
There are several options for why recurvation of the knee joint develops in a child. When treating, the root cause of the pathology is of great importance, and therapy is prescribed taking it into account.
The causes of the pathology may be the following:
- weak quadriceps;
- shortening of the calf muscle, which is accompanied by increased tone;
- limited movements of the ankle joint;
- anterior pelvic tilt, which is accompanied by muscle weakness.
The development of pathology in a child may be associated with oligohydramnios and other pathologies. Recurvation is often combined with fibrous changes, dysplasia of the hip or knee joint, dislocation, and absence of the patella.
How to teach a child with cerebral palsy to roll over
If a child does not hold his head well, turning over will be much more difficult for him, so when controlling the head, you need to practice turning over as well. Rollovers from back to stomach are performed using the arms. The child’s arms are raised upward, the forearm or shoulder is compressed, and with light pressure, due to the rotation of the shoulder, the body and hip are turned over. This method is more suitable for older children. An easier way of turning over, which is relevant for young children, is turning over using the lower extremities. We squeeze the child’s knees with our hands, cross our legs, and point our upper thigh in the opposite direction, i.e. if the foot is left, the turn will be to the right. Rotation of the hip joint will entail a revolution of the body and pelvis. When a child lies on his stomach a lot and for a long time, it is easier for him to learn to roll over and enjoy it. He understands that he can move in this way, take a more comfortable position. And he is ready for the next stage - crawling .
What is tenosynovitis?
The strong formations of connective tissue that serve to attach muscle to bone are called tendons. In places most susceptible to stretching, the tendons are surrounded by a sheath, which in its functions and structure is similar to the synovial membrane of the joint. To reduce injury and ease of sliding, fluid is produced.
Under the influence of predisposing factors, inflammation appears in the cavity (tendon sheath), which leads to stenosis of the canal and a decrease in the production of synovial secretions. When the skeletal muscles are activated, friction occurs, which results in severe pain.
Training the crawling skills of children with cerebral palsy
Crawling on all fours is the basis of verticalization. Very often, children with high spasticity in their legs master the skills of crawling on their stomachs. Their entire emphasis is on the upper body and arms, and pushing off with their fingertips, the child jerks forward, falling face down, and after that freeing his arms for the next “crawl.” An easier way to move in space is to crawl on all fours. First you need to practice focusing on your hands. When the child’s arms become stronger, it will be easier for him to pull up his legs and kneel, and he can practice moving in a position on all fours with the help of an adult. By simultaneously moving the arm and the opposite leg forward, i.e. right hand - left leg, then left hand - right leg. A great help when practicing crawling are hand splints, which fix the hand in a straight position. But here it is very important to choose the right size and fix the hand correctly. This stage for a child with cerebral palsy can drag on for years, and therefore many children move on to the next stages without really learning to crawl. Moreover, a child can be “stuck” at the crawling level for a long time not due to physical reasons, but because the brain has not yet matured and needs a push, feedback from verticalization in space.
Personalities of bone infarction
Coronary vascular disease contributes to the development of pathological actions. A heart attack affects not only the tissues, but also the muscles of the skeleton. We are talking about the hip, shoulder joints and tibia. A disease without qualified help can lead to complications.
The development of pathology is stimulated by countless reasons, including impaired blood supply, embolism, and vascular spasms. Severe physical damage affects bone structure. Various diseases become a prerequisite for bone marrow infarction:
- pancreatitis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- ankylosing spondylitis syndrome;
- sickle cell anemia;
- osteoporosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
Medical studies do not provide a detailed answer as to why bone marrow infarction develops.
Balance exercises
Equilibrium, balance or maintaining a child’s pose in space is all the same. It all comes down to freely transferring body weight from foot to foot, from hand to hand, or from hand to foot and back. In every body position we must maintain balance - this is one of the most important and necessary human skills. You can develop it with many exercises and simulators. The most accessible and common exercise machine is a balancer, which is available in many options. In the form of a balancing board - on it you can, standing on all fours, swing left and right, or, turning the child, back and forth. Also on your feet. A balancer in the form of an inflatable disk - shifting from foot to foot, working with the feet, transferring body weight from toes to heels, etc. The main thing is to teach the child to work with the pelvis separately from the shoulders.
Diagnostic measures
Making an accurate diagnosis is possible through an external examination of a person. During the examination, the doctor should clarify the factors with which the patient associates the occurrence of pathological symptoms, which is especially important in the adulthood of the patient.
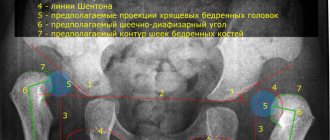
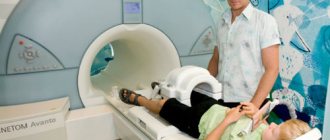
In complex clinical cases, targeted radiography or computed tomography of the knee joint is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. The methods make it possible to detect displacement of the epiphyses of the bones that form the knee, as well as accompanying degenerative processes in the joint.
Important! Only the attending physician should interpret any diagnostic data and prescribe therapy! When trying to self-medicate, the disease progresses, leading to negative consequences.
How to control the gait of children with cerebral palsy whose knees are bent backwards (recurvation)
During recurvation, the muscles of the back of the thigh are weakened (hamstring group). These muscles need to be strengthened. You can lie on your back and bend your leg so that your heel touches your buttock. Then you can also do it with a weighting agent. The same leg lift can be performed while standing, you just need to make sure that the knee is pointing down and the supporting leg does not go into recursion. Also, the child must be taught to stand and walk with his knees bent. And it is necessary to use special orthoses.
Etiology and pathogenesis
Recurvation of the knee joint is a serious disorder of the musculoskeletal system. The disease is expressed by hyperextension of the knee joint, with further deformation and dysfunction. There are 2 main etiological reasons for the development of the disease:
- Congenital recurvation. The causes of this pathology are: oligohydramnios, breech presentation or dystrophy of the quadriceps muscle. It can develop against the background of genetic connective tissue diseases: cerebral palsy, Larsen syndrome, joint hypermobility.
- Acquired. The disease occurs after surgery on the flexors. The reason is the muscle tissue chosen incorrectly by the doctor.
Training a child with cerebral palsy to stand upright
Proper execution of a standing pose is the basis for future walking and an opportunity to learn to control the hip and knee joints. The correct static position - standing - is when the legs are straightened, the body is straight, the shoulders and hips are at the same level. There is a dynamic standing pose - this is when the head, limbs and body can voluntarily carry out movements and maintain balance. There is training for standing poses with support from two hands, one hand. There is a big difference - the support is in front of the child or on the side of him. It is also necessary to train the child with support for the pelvis and gradually move the support down to the feet, i.e. Gradually move your hands down.
If a child can maintain balance, both static and dynamic, he is ready for walking exercises.
Treatment approaches
To treat recurvation of the knee joint in a child, a conservative and surgical approach is used. Therapy should be started as early as possible, preferably before the baby is eight months old.
The following methods are most effective:
- physiotherapy on the joint area;
- regular therapeutic massage;
- physiotherapy;
- up to the age of two years, it is possible to use an immobilizing plaster cast to keep the knee in a bent position;
- after two years, orthoses, individual splints at night and orthopedic shoes should be used.
If conservative methods do not show effectiveness, then treatment includes surgical procedures: reconstruction of the knee joint, changing the length of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus of the joint, various types of osteotomy and supracondylar resection of the femur. The specific type of operation is always determined only by the doctor after examining the child.
How to treat knee recurvation in adult patients? Surgical interventions are not indicated, since corrective orthoses, orthopedic shoes and exercise therapy complexes are used to correct joint hyperextension.
Motor correction of cerebral palsy
is aimed at improving and correcting existing functions, such as: incorrect grip of the hand, incorrect gait, lack of coordination when walking, hyperkinesis during tension during the implementation of any motor functionality. Correction of motor disorders in children with cerebral palsy is carried out in two ways: individually and in group classes. Exercise therapy for children with cerebral palsy is compiled individually, and massage and speech therapy sessions are also provided individually. Group classes are aimed at socializing children.
The medical clinic accepts patients from all regions of the country: Moscow, St. Petersburg, Yekaterinburg, Chelyabinsk, Novosibirsk, Ufa, Kazan and others.
Useful articles:
- Meltdown in autism and how to cope with it
- Teaching reading to children with autism
- Forms of autism
Diagnostics
Before treating a pathological disorder, a specialist conducts a thorough examination. Usually, to identify a disease, it is enough for a doctor to conduct an examination of the patient , during which complaints and characteristic symptoms of the disease are clarified.
To clarify the preliminary diagnosis, radiography may be prescribed, which will help determine the presence of displacements of the epiphyses of the bones (tibia and femur).
Etiological factor
Experts suggest two main causative factors in the development of the pathological process. According to the type of cause, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- Congenital. This form is established from the moment when the baby is diagnosed with a shortened calf muscle with the presence of hypertonicity of the muscle fibers in it, tense anterior femoral muscles, as well as a flat-valgus position of the feet. Usually this condition is combined with subluxation or dislocation of the ankle joint. In accordance with statistical data, such a pathological process is bilateral, and pathology is diagnosed with a frequency of one case per thousand children.
- Acquired. A pathological condition that develops after surgery to transplant part of the instep supports to the patella in a person who has paralysis of the fibers of the quadriceps femoris muscle. This condition is detected mainly in cases where the physician has incorrectly selected muscles for transplantation.
Etiological factor
Experts suggest two main causative factors in the development of the pathological process. According to the type of cause, the disease is divided into the following forms:
- Congenital. This form is established from the moment when the baby is diagnosed with a shortened calf muscle with the presence of hypertonicity of the muscle fibers in it, tense anterior femoral muscles, as well as a flat-valgus position of the feet. Usually this condition is combined with subluxation or dislocation of the ankle joint. In accordance with statistical data, such a pathological process is bilateral, and pathology is diagnosed with a frequency of one case per thousand children.
- Acquired. A pathological condition that develops after surgery to transplant part of the instep supports to the patella in a person who has paralysis of the fibers of the quadriceps femoris muscle. This condition is detected mainly in cases where the physician has incorrectly selected muscles for transplantation.
Symptoms
The pathological condition has a characteristic clinical picture, which can be accurately determined even at an early stage of development:
- limitation of flexion function;
- one leg is shorter than the other;
- tension of the popliteal ligaments with the formation of folds on the knees;
- bending of the lower leg backwards in a standing position;
- deformation of the knee area with a pronounced bend of the knee backward;
- the gait is similar to kangaroo jumping (with bilateral lesions).
Recurvation is characterized by characteristic symptoms that have varying degrees of severity
As the pathology progresses and in the absence of treatment, the deformity only intensifies and can lead to limitations in movement.