Types of ligament ruptures
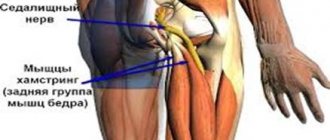
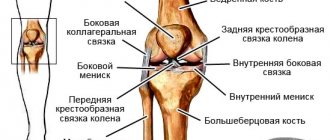
Most often, a ligament rupture is classified according to the location where it occurred - for example, a rupture of the cruciate ligament of the knee joint, ligaments of the foot and ankle, shoulder, elbow, and hip joints. Ligaments are in close proximity to joints, and their rupture usually means loss of function.
As for the degree of rupture, it can be either complete or partial. In the first case, the injury is severe; recovery from it, with proper treatment, takes from several months to six months. In the second case, the situation is a little simpler, and although complete recovery will also not occur soon and requires temporary restriction of movements in the joint.
This type of injury can also be classified based on its occurrence. There are traumatic and degenerative ruptures. With the first, everything is clear - it is a consequence of an injury, be it a blow, physical strain, or something else. As for the degenerative rupture, it is provoked not so much by injury or stress as by a violation of the elasticity and strength of the ligament. Such trauma is observed in older people, who are capable of being injured even in situations where any other person would get by with a slight fright.
Ointments for swelling and bruises
A bruise or sprain of the ankle is accompanied by damage to small capillaries, resulting in local hemorrhage, which is manifested by the appearance of bruises and hematomas. Against the background of severe inflammation, the outflow of lymphatic fluid is disrupted, and intercellular fluid enters the tissue, which manifests itself as severe swelling.
Such processes provoke increased pain, and the presence of problems with blood vessels can result in the formation of blood clots and the development of varicose veins.
Therefore, an important stage of therapy is the use of agents that improve microcirculation and vascular tone. This group includes products containing heparin.
You can use:
- Heparin ointment;
- Hepatrombin;
- Lyoton 1000;
- Heparoid Zentiva.
No less interesting are venotonics containing troxerutin such as:
- Troxevasin ointment;
- Troxerutin;
- Venolana;
- Phlebatona;
- Troxegel;
- Venohepanol;
- Troxevenol;
- Venorutinol.
Usually such products, for example heparin, troxevasin ointment, are not expensive, but quite effective. They prevent the formation of blood clots, improve local blood flow, and resolve already formed hematomas.
Signs of ligament damage or tear
There are several obvious symptoms of this type of injury that indicate the severity of the damage in the area. The most common include the following:
- Like any injury, a ligament rupture is accompanied by severe pain at the site of injury, usually the source of pain is the joint area. Therefore, an erroneous diagnosis is possible.
- Vessels are located next to and inside the ligaments, which can cause hematoma and edema to form. A ligament rupture itself is never open, but it can become part of a more complex complex injury.
- Since the ligament is the main stabilizing part of the joint, when it ruptures, the joint becomes unstable and pathological movements begin to occur in it, which should not occur normally.
- Given the damage or rupture of the ligaments, the joint may become deformed and its function may be impaired.
- There may be audible signs of ligament rupture in the form of a click, crunch or crack in the damaged joint at the time of injury.
In some cases, other symptoms are possible, including, first of all, increased body temperature and hyperemia. When a specific ligament ruptures, it is possible to experience special symptoms that are characteristic only of an injury in that particular location.
Sprained joints: symptoms and treatment
Ligaments are special formations consisting of connective tissue. Their main function is to hold the joint and at the same time ensure its mobility in certain directions. Sprained joints are not only common among professional athletes; such injuries often occur in everyday life. The ankle and shoulder joints are most often injured. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, as well as the increased load on the joints.
Symptoms of a sprain:
A sprained joint is characterized by pain and limited mobility. For example, in case of injury to the ligaments of the leg, a person cannot even lean on his foot. At the time of injury, severe acute pain is observed. As a rule, the process takes place silently. If a complete rupture of the fibers occurs, a loud pop is clearly audible. When stretched, swelling and hyperemia of the skin may form, as well as small bruises at the site of injury. Sometimes there is a subfebrile body temperature, which ranges from 37.0 – 37.2 degrees.
Causes of sprains:
Ligament damage can occur in absolutely anyone, even those who lead an inactive lifestyle. An ankle sprain can occur in the following cases:
- An unfortunate fall, for example, on ice.
- Stumbling over an obstacle.
- Tucking the legs (especially important in the winter season).
- Working with heavy weight due to profession or when playing certain sports.
The risk of such injury is significantly increased in women who prefer to wear high heels or platform shoes.
A hand sprain usually occurs due to a bad fall that results in you landing on your hand.
Athletes experience sprains much more often. Representatives of almost all sports are susceptible to this type of injury.
Note that previous injuries significantly increase the risk of re-injury. Regardless of the type of injury, it is very important to promptly and fully treat the injury, even if it is a minor sprain.
Classification:
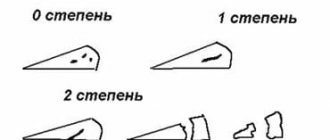
In medical practice, this joint ligament injury is usually divided into several degrees:
First degree.
The fibers are not torn, only pain is observed, which goes away within 1 - 2 weeks.
As a rule, there are no other symptoms. Second degree
.
Some of the fibers are completely torn, there is acute pain, swelling of the skin, and sometimes small subcutaneous hemorrhages are noticeable. Independent movement is difficult; in order to fully move you have to use crutches, stilts or other auxiliary attributes. Third degree.
In this case we are talking about a complete rupture of the ligaments. The pain is acute and does not subside even when standing still. There is severe swelling, extensive hematomas, lack of support and impaired motor activity. In particularly advanced cases, surgical assistance may be required.
With the first or second degree of severity, you can get by with conservative treatment: local ointments or creams, exercise therapy, massage and other manipulations. This will help quickly cope with pain and speed up the process of tissue regeneration. With the third degree of severity, the situation is more complicated; surgical assistance may be required. Recovery time is individual and depends on the characteristics of the body and the location of the injury.
Diagnostics:
It is quite difficult to independently understand that we are talking about a sprain, and not about another pathology. If no improvement is observed within several days, and the pain only intensifies, you should immediately consult a doctor. With such problems, they turn to a traumatologist or orthopedist-traumatologist.
As a rule, to determine a sprain, a specialist just needs to visually look at the injured area, palpate and take an anamnesis. But still, to definitively confirm the diagnosis, diagnostic procedures, for example, ultrasound diagnostics or computed tomography, can be prescribed. Only after this the doctor prescribes full treatment. Typically, the recovery period ranges from 1 to 4 weeks.
How to relieve pain from sprains at home?:
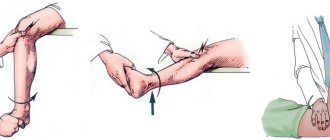
If a joint sprains, first aid measures must be taken immediately. This will help avoid complications and speed up the recovery process. Immediately after an injury, use restraints such as an elastic bandage or splint. If you don’t have anything suitable at hand, you can take regular cloth or gauze. Apply a fixative bandage to the sprained area.
1. At home, a cold compress will help reduce the intensity of pain. To cool the injured area, you can use ice or frozen food wrapped in a cloth. If there is nothing suitable nearby, place your arm or leg (depending on the location of the injury) in ice water. The compress must be applied for 10-15 minutes. This method will prevent or reduce the manifestation of edema and hematomas. 2. It is recommended to keep the damaged area at an elevated position. When the body is in a horizontal position, you should place a rolled towel, pillow, blanket, etc. under it. 3. Provide maximum rest to the damaged area. Try to limit physical activity until the pain subsides. 4.After 2 – 5 days (depending on the severity), gradually begin massaging the injured area. This will lead to improved blood circulation and speed up the process of tissue repair. 5. As soon as the pain begins to subside, begin therapeutic physical activity. Develop the ligaments gradually, start with light exercises and do not overdo it. If you experience acute pain when performing exercise therapy, postpone this activity for another couple of days. And in this case, it is advisable to see a doctor.
Diagnosis of ligament rupture
Only a qualified traumatologist with experience in treating such injuries can make a correct diagnosis. Most often, the examination begins with collecting the patient’s medical history, where the important point is the fact and nature of the injury. Then a clinical examination is performed, which always starts with a healthy joint. A number of clinical tests are performed that clearly indicate a particular intra-articular injury. In most cases, after testing, a clear picture of the damage will be obtained and a preliminary diagnosis will be made. Additional research methods are often used to confirm
- X-ray – is mandatory to have a general idea of the joint, as well as to exclude bone-traumatic injuries. It is often recommended to perform on a healthy joint;
- magnetic resonance imaging – provides a layer-by-layer image of soft tissues and intra-articular formations, which allows you to determine the nature, extent and level of damage to ligaments, muscles, cartilage, etc.
- ultrasound examination;
- CT scan;
In complex situations, when the injury is severe or old, and when clinical tests do not allow a clear clinical picture to be determined, several types of additional examination may be performed to clarify the diagnosis.
Ointments with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects
An important stage in the treatment of a sprained ankle includes reducing pain due to the inflammatory process. External agents, which include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, will help to cope with this problem.
To quickly relieve pain, you can use ointments containing:
- Diclofenac - in Diclovit, Ortofen, Diclak, Voltaren, Diclofenac;
- Ibuprofen - in Nurofen, Dolgita;
- Nimesulida - in Naiza;
- Ketoprofen - in Artrosilene, Febrofide, Ketonal, Fastum;
- Indomethacin - in Indovazin, Indomethacin-Acri;
- Piroxicam - in Finalgel.
Such drugs have a pronounced analgesic effect and can significantly reduce the inflammatory process locally. Apply up to 3 – 5 times a day. After application, the product is rubbed into the skin. No fixing bandages are required at the site where the ointment is applied.
In case of severe pain, in parallel with the external remedy, the patient is recommended to take tablets with an analgesic or NSAID. Considering that non-steroidal drugs have a number of serious contraindications and complications, preference is still given to external use.
This is especially true for patients with stomach and digestive problems, who are strictly prohibited from taking such drugs.
The duration of treatment with ointments containing non-steroidal agents does not exceed 5 - 7 days. This period is quite enough to remove painful symptoms of a sharp nature.
Important! Despite the lesser negative impact on the body of ointments with NSAIDs than tablets or injections, you should not use them for more than a week.
- Separately, it is worth highlighting ointments containing viper venom, for example, Salvisar. The peculiarity of such ointments is that they do not contain NSAIDs, which means they do not cause side effects characteristic of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments, while they have an analgesic effect for arthritis, myalgia and neuralgia.
What to do if a ligament is torn?
It is not possible to establish an accurate diagnosis on your own after an injury, but if an injury occurs that is accompanied by pain or swelling, you should immediately follow a few simple steps to provide first aid. These are the steps:
- The damaged joint must be motionless (immobilized). To do this, it is best to apply a splint - any oblong solid object will do. This is one of the most important stages, because any movement in the damaged joint, even accidental, will not only cause pain to the victim, but can also create additional complications, aggravating the injury.
- The best way to prevent swelling is to apply cold to the injured joint. The most effective is an ice pack.
- If the joints of the limbs are injured, another good way to limit the increase in swelling is to elevate the injured limb.
- Next, the victim needs to take a pain reliever. This can be a tablet drug or an intramuscular injection.
- After completing these measures, you must seek specialized medical care.
Ointments with hormonal agents
Products containing glucocorticoid hormones have gained quite controversial popularity. Treatment of sprains is usually carried out with hydrocortisone and prednisolone ointments.
Indeed, such gels are an ambulance for the most unbearable pain. In addition, they are able to quickly stop the inflammatory process. Ointments from this group cope well with such tasks, and patients note a significant improvement in the condition of the injured leg.
Therefore, having tried such therapy once, a person refuses other treatment. But it is difficult to predict what the future consequences of such therapy will be.
All hormonal agents included in the ointments are synthesized from cortisol. Long-term use of a stress hormone can provoke not only a number of negative consequences, but also addiction, as well as withdrawal syndrome. The skin and muscle tissue are at risk. Bruising, tissue thinning, and muscle damage are often observed.