What is a meniscus?
Knee
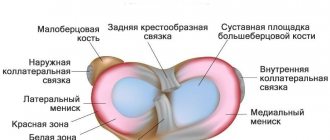
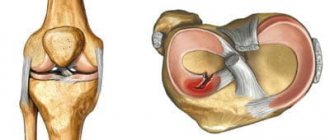
is a complex component of the musculoskeletal system, which is formed by the surfaces of 3 bones - the patella, the femoral condyles, as well as the sockets of the tibia and fibula. Since it can withstand significant loads caused by body weight, paired crescent-shaped cartilage components are located in the joint space. They are called the lateral (outer) and medial (inner) meniscus.
These components have a body (the wider part) and two horns (tapered parts that face forward and backward). Due to such anatomical features of structure and localization, these components provide shock absorption, strengthening and certain stabilization of the joint.
Mechanism
The pathogenesis of damage involves the implementation of several mechanisms, which include:
- Sudden excessive flexion, which causes stretching of the ligaments, as well as the cartilages themselves.
- Rotation (rotation) of the femur with the tibia fixed and vice versa.
- Bruise with a blunt object or a fall (quite often changes develop when falling on objects with sharp edges - the edge of a step, curb).
These damage mechanisms are more often realized in relation to the internal meniscus
. This is due to the fact that it is fixed more rigidly by ligaments, therefore, under any mechanical influence it practically does not move, which is accompanied by a violation of its integrity.
The outer cartilage is less susceptible to injury, since it has high mobility. A frequent variant of integrity violation is pathological changes in the properties of cartilage tissue, leading to a decrease in its strength.
Meniscus injury
A part of the knee joint called the meniscus is attached to the bone. A rupture can result from:
- Sudden twisting of the leg.
- Awkward movement in the presence of inflammatory processes.
- A strong blow to the knee with a hard and heavy object from above.
- Hitting your knee on a hard surface.
It is worth noting that destruction is influenced by the high loads that a person may experience in the gym. This is why you shouldn’t start with intense training right away. Otherwise, a serious injury will make you forget about classes for a long time.
Etiology
The causes of meniscal tears can be different; the most common triggers include:
- A person’s young age, as well as a life of high physical activity.
- Playing sports (amateurs or professional athletes) that are characterized by high mobility. These sports include football, volleyball, hockey, and athletics.
- Congenital defects of cartilage tissue caused by changes in certain genes that are inherited. In this case, a rupture can occur already in childhood, even in the absence of excessive physical activity.
- Acquired deterioration in the density of cartilage tissue, which is predominantly formed against the background of a decrease in its trophism and leading to degeneration. This provoking factor leads to pathological damage in elderly people after moderate loads on the legs.
- Long-term inflammation caused by specific (tuberculosis, syphilis) or nonspecific infections, as well as an autoimmune condition in which antibodies are produced to one’s own cells (rheumatoid arthritis).
Identification of provoking factors is carried out during a comprehensive examination of the person, which is required to select adequate therapy, as well as prevent changes in the future.
Knee meniscus tear
If a rupture occurs, then experts divide it into several stages according to the level of damage, for example:
- Null. A characteristic feature is the absence of damage.
- First. There is a focus of increased intensity.
- Second. A linear lesion develops that does not leave the cartilage.
- Third. At this stage, the mentioned lesion reaches the surface of the cartilage.
The degree of damage in the treatment of a tear of the medial meniscus of the knee joint without surgery is diagnosed using X-rays and MRI. With this injury, the diagnosis is never made based on external signs without a detailed examination.
Posterior horn meniscus tear
If we are talking about a rupture of the meniscus of the posterior horn, treatment of such damage, then the injury is provoked by:
- Turns on one leg without lifting off the floor.
- Insufficient development of ligaments and the knee joint.
- Jumping and running too fast.
- Injuries that can occur with a degenerative knee joint.
- Excessively fast walking.
It is worth noting that in older people, such damage often occurs due to the destruction of cartilage tissue. It is difficult to treat, as it is provoked by age-related arthrosis, which young people are not susceptible to.
Classification
The choice of treatment method, namely surgical intervention or therapy without surgery, is made by the doctor based on the research conducted, as well as determining the type of injury in accordance with the modern classification.
The severity may be:
- Incomplete meniscal rupture
- injury or changes are characterized by the formation of a pathological focus that does not extend through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, therefore its shape and general anatomical structure are not disturbed. - A complete rupture of the meniscus
is a severe violation of integrity, accompanied by the spread of changes through the entire thickness of the cartilaginous component, disruption of the shape, as well as the frequent formation of a fragment that can displace and wedge into the joint space.
MRI is used to determine the extent of damage in modern medical institutions. Using this technique, the severity of damage is assessed according to Stoller, which implies 4 degrees of severity.
Based on the location of the damage, a rupture in the anterior or posterior (horn) area, body, or a combination thereof is identified. Also, after identifying the main etiological factor that led to the corresponding injuries, a pathological or traumatic rupture is determined.
Meniscus treatment
Often, a rupture of the knee joint causes symptoms that may indicate a violation of the integrity of the meniscus , either partial or complete.
It is worth knowing that even minor damage can cause a rupture. Many people do not understand this and ignore the characteristic signs, which leads to serious consequences in the future.
Such a gap is indicated by difficulty in straightening the knee joint, accompanied by severe pain. The duration of the most acute period directly depends on the severity of the lesion, for example:
- If we are talking about incomplete, minor injuries, then the pain is considered unexpressed and disappears over the next few weeks.
- When destruction characterized by moderate severity is observed, the pain becomes acute and movements are limited. However, with such an injury, the patient can move, but not without difficulty. If the necessary treatment is carried out, the listed symptoms disappear within a few weeks. But in the absence of therapy, a chronic pathological process occurs.
- When the knee structure is severely damaged, swelling and severe pain are present. A large amount of blood accumulates in the joint, and this condition is called hemarthrosis. If such an injury is present, the patient can move independently only in exceptional cases. Most often, movement is impossible. The damage requires serious treatment - mandatory surgery.
It is worth noting that if there is a slight destruction of the meniscus of the knee joint , then when acute and subacute phenomena subside, the process becomes chronic. Its characteristic feature is constant moderate pain accompanied by impaired movement.
Clinical picture
Damage to the cartilage of the knee joint after an injury is characterized by the appearance of quite characteristic symptoms. Among them:
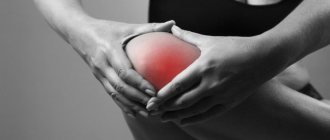
- Pain that appears immediately after exposure to a traumatic factor. It is usually pronounced, localized on the outer or inner surface of the knee, and also intensifies when trying to perform movements in it.
- Decreased range of motion in the knee, the severity of which depends on the degree of damage. In the case of the formation of a cartilage fragment, a block of movements may develop, which is accompanied by intense pain.
- Signs indicating the development of an inflammatory reaction, which always accompanies changes in cartilaginous components. These include hyperemia (redness of the skin), swelling of the soft tissues with an increase in the joint in volume, as well as a local increase in temperature, manifested by the skin becoming hot to the touch.
Pathological changes, prolonged inflammation, as well as damage due to a congenital decrease in the strength of cartilage tissue are accompanied by a longer development of clinical symptoms. At first, pain may be absent or appear only during exercise. Then it intensifies and becomes permanent. Movements in the knee are accompanied by the appearance of “crunching” or “clicking” sounds.
Application
You should know that any ointment or cream is applied to clean, dry skin without damage. The use of external preparations on open wounds is prohibited. The amount of medication and the intensity of therapy are determined by the doctor in each case individually. As a rule, a strip of ointment 3-4 cm long is applied to the knee joint area and rubbed in with light massage movements until completely absorbed. Despite the fact that such drugs have a low degree of absorption into the blood, they are prescribed with caution for use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. But in addition, each group of drugs has its own contraindications. You should not purchase it yourself, without a doctor’s recommendation.
Study
Based on clinical manifestations, it is impossible to make a reliable conclusion about the nature and severity of changes. In modern clinics, before determining treatment tactics, an objective examination is required, including several basic methods of visualizing the components of the knee:
- X-ray
is a study that allows you to identify significant changes, in particular a complete rupture. To more accurately establish the localization of changes, a study is carried out in frontal and lateral projections. - MRI
is a diagnostically informative technique that involves performing layer-by-layer scanning with tissue visualization due to the physical phenomenon of resonance of the nuclei of hydrogen atoms. They are part of the molecules of organic compounds in a strong magnetic field. This study makes it possible to assess the severity of damage according to Stoller. This is necessary to determine further therapeutic tactics. - Computed tomography is a technique for layer-by-layer visualization of tissue. X-ray radiation is used for this. The method is very accurate and informative. It allows you to detect even minor traumatic or pathological injuries.
- Ultrasound examination is a diagnostic method characterized by the absence of radiation exposure to the patient’s body. It makes it possible to detect inflammatory changes and assess the volume of intra-articular fluid.
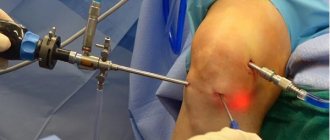
- Arthroscopy
is an innovative invasive technique characterized by direct visual examination of internal structures using an optical arthroscope equipped with a video camera and lighting.
Today arthroscopy
is not only a diagnostic research method. It has also become widespread for performing minimally invasive surgeries with minimal damage to healthy knee tissue.
First aid to a patient
The victim may experience severe pain from a couple of days to a week. If the severity of pain is moderate, you can do without contacting a traumatologist. To relieve pain and reduce suffering, you need:
- Apply ice to the sore knee. This will relieve swelling. Cold during prolonged contact causes blood vessels to constrict, thereby reducing local hyperthermia.
- You can reduce the intensity of pain with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, including ibuprofen, diclofenac, analgin.
- To reduce the risk of worsening the situation, it is important to ensure immobility of the injured limb using a splint. It is better if the knee is elevated in relation to the healthy leg.
When the acute period is over and the patient can see a traumatologist, the specialist will assess the extent of the damage and prescribe a course of treatment and care.
Principles of therapy
The choice of therapeutic tactics is made by the doctor individually for each patient. It is based on the results of a clinical examination and imaging techniques of the components and tissues of the knee. In modern medical institutions, therapeutic tactics include several main areas, which include:
- Therapy without surgery.
- Surgical intervention.
- Rehabilitation.
All stages of treatment are prescribed sequentially. Regardless of the main stage of therapeutic measures (surgery or conservative therapy), the final restoration of knee function necessarily includes rehabilitation.
Gymnastics to restore knee function
Any gymnastics is indicated only if the acute period has already ended and you can work with the knee joint without pain. As a rule, gymnastics is prescribed after wearing a plaster cast or splint for a long time. To return the knee to working capacity, you need to begin to gradually warm it up according to a certain method.
Clinics offer physical therapy sessions where, under the supervision of a specialist, patients recover from serious injuries. If a doctor has diagnosed a meniscal tear, any exercise will be postponed until the tissue has completely healed.
Exercises begin with minimal loads. First, these will be exercises for flexion and extension of the sore knee. You need to do it while sitting on a high chair. 10 lifts twice a day is enough. Gradually, the load can be increased, in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations. If you experience any pain, you should immediately report it to a specialist to adjust your rehabilitation plan.
Therapy without surgery
Any intervention involving tissue dissection is invasive, so modern traumatologists and orthopedists try to carry out treatment without surgery whenever possible. Conservative treatment is possible in certain cases:
- Diagnosed incomplete rupture with the absence of cartilaginous fragments.
- Localization of damage - due to certain anatomical features, an incomplete tear of the lateral meniscus of the knee joint is diagnosed; treatment in this case is possible without surgical intervention.
- The patient has absolute contraindications to surgery - usually conservative therapy is prescribed to elderly patients with pathological changes in the cartilaginous components.
Therapy without surgical intervention can be carried out in a hospital or on an outpatient basis, but only if the patient follows medical prescriptions in a disciplined manner.
Indications and benefits
It is possible to treat a torn meniscus of the knee joint without surgery if the patient has been examined by a doctor and, based on the results of x-rays, has come to the conclusion that conservative treatment can be done. External use should be used in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures, massage and medications. Beneficial properties of creams and gels:
- improvement of blood microcirculation;
- anesthesia;
- relieving inflammation;
- resorption of bruises;
- restoration of mobility.
Self-use of medications in case of injury without prior consultation with a doctor can aggravate the condition of the joint.
General recommendations
Following general recommendations is a prerequisite for successful treatment, these include:
- Functional rest - during the entire stage of the main course of therapy, as well as partially during rehabilitation, the knee should not be subjected to stress. To ensure rest, a special motor regimen is used for the patient, and a tight bandage is applied to the joint using an elastic bandage or plaster splint.
- Diet – Dietary recommendations include eating high-calorie, highly digestible foods with sufficient fat, protein, carbohydrates and vitamins. Also, organic compounds that are directly involved in the synthesis of the intercellular substance of cartilage tissue must enter the body with food.
- Quitting bad habits - during the main course of therapy, it is advisable to give up smoking and drinking alcohol-containing drinks, since nicotine and alcohol are vascular toxins, they significantly slow down the processes of tissue regeneration (healing).
The implementation of such general recommendations (with the exception of functional rest) is desirable at the rehabilitation stage.
Drug therapy
In almost all cases of conservative treatment without surgery, medications of various groups are used. The most widespread are:
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs based on adrenal hormones and glucocorticosteroids. They are used in the development of a pronounced inflammatory reaction in the form of intra-articular, intravenous or intramuscular injections.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - reduce the intensity of the process, the synthesis of mediators of the inflammatory reaction by cells of the immune system, thereby reducing the severity of manifestations. These drugs are mainly used in the form of injections or tablets for oral administration. Additionally, local therapy may be prescribed in the form of a cream or ointment.
- Chondroprotectors are a large group of medications, the active substance of which is the main structural component of cartilage tissue. These drugs have the ability to slow down degeneration processes, as well as restore damaged cartilage tissue.
- Vitamins are an essential component of drug therapy, helping to improve the course of metabolic (metabolic) processes in the body and accelerating healing.
Medicines are used over a long period of time, which is determined individually by the attending physician.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
Physiotherapeutic treatment involves the use of physical factors that have a therapeutic effect. Most medical clinics use procedures such as electrophoresis with topical medications, treatment with a magnet, ozokerite, and mud therapy.
They help reduce the intensity of inflammation and also accelerate the healing of damaged tissue. As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures are combined with the prescription of drug therapy.
Types of ointments
Usually, drugs in this form are supplemented with treatment with tablets.
The choice of external use should be based on the symptoms of the disease and examination results. Treatment of the meniscus is prescribed in a comprehensive manner. But the simultaneous use of ointments from different groups in the same damaged area is prohibited. The break should be at least 4-5 hours. The best option is to combine tablets and gels.
Warming
A group of drugs that is used during the rehabilitation period after surgery, a few days after an injury, or for prevention. Warming ointments have a vasodilating effect, which improves metabolism in the knee and accelerates the penetration of medicinal components into the tissue. Beneficial features:
- cessation of pain;
- improved mobility;
- normalization of blood circulation.
Warming ointments include:
- "Apizartron";
- "Espol";
- "Finalgon";
- "Viprosal";
- "Capsicam."
Chondroprotectors
Cartilage regeneration will occur faster when using Theraflex.
A group of drugs that contain the active substances glucosamine, chondroitin and collagen. They help restore cartilage tissue, normalize metabolic processes in it, improve the elasticity of cartilage and motor activity of the joint. Additionally, they relieve pain and swelling. Common representatives of this group are:
- "Structum";
- "Teraflex";
- "Alflutop";
- "Rumalon".
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NSAIDs are represented by a group of drugs that are well tolerated by the body, when used locally, practically do not cause adverse reactions and are non-hormonal drugs. Used to achieve the following therapeutic effects:
- pain relief;
- relieving inflammation;
- getting rid of puffiness and swelling;
- increase in range of motion;
- resorption of bruises and contusions.
The most commonly used:
Dolgit will eliminate the inflammatory process in the joint and its accompanying symptoms.
- Heparin ointment;
- "Dolgit";
- "Fastum gel";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Artrosilene".
Folk remedies
A popular remedy for pain relief when the knee meniscus is damaged is an ointment made from vinegar and eggs. To prepare it, take vinegar essence and 1 whole egg. It is placed in a vessel and filled with vinegar to cover the top by 1 centimeter. Next, you should put the container in the closet for 5 days. After the expiration date, add 200 ml of sunflower oil and expose to light. The product should also be infused for 5-6 days. At the end of this time, the ointment is ready for use. It should be applied to the damaged knee joint with massaging movements, then wrapped with a warm cloth.
The use of alternative medicine in the treatment of meniscus injury is agreed with the doctor.
Alternative Treatment
In modern traumatology and orthopedics, the acceleration of regeneration processes is carried out using alternative methods of non-surgical treatment. The most common of them is the introduction of platelet mass into the joint cavity. This is a suspension of platelets in a saline solution with a high content of growth factors. They are produced by formed elements of blood.
These compounds affect the functional activity of cells of cartilage, bone and connective tissue with an increase in the intensity of the process of synthesis of components of the intercellular substance. The duration, frequency of administration of biological drugs, as well as the dosage are determined by a medical specialist individually.
Treatment of meniscus without surgery
If we are talking about non-surgical treatment of a tear in the knee joint, then such damage is eliminated through the use of the following drugs:
- Analgesics.
- Vitamins.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Inflammatory agents.
It is noteworthy that the treatment of a torn meniscus of the knee joint is facilitated by a diet that involves consuming foods with a large amount of vitamins. To eliminate the consequences of destruction, ointments such as Alezan, Tentorium are well suited.
When treated, they can effectively reduce pain and eliminate swelling. As an additional procedure during treatment, specialized exercise therapy massage can be performed. For relaxation, you can use myostimulation.
Recovery
After surgical or conservative treatment, rehabilitation is carried out, which is aimed at restoring knee function. This result is achieved through the use of special exercises with a gradual increase in the load on the joint. They enable the cartilage components to fully adapt and also prevent their re-injury in the future.
The duration of such measures may vary, depending on the nature of the damage, as well as the direction of the main course of therapy. It may only last a few months. In some cases, after open surgery, the rehabilitation period may exceed 1 year.
How to identify a meniscal injury
The reasons why a meniscus injury occurs can be not only falls and other mechanical impacts. Common precursors to damage are:
- gout;
- intoxication of the body of any etiology;
- rheumatism;
- age-related changes.
In addition, minor injuries to the meniscus that do not lead to a tear, but are associated only with its stretching or thinning, will eventually cause a tear. If you do not pay attention to the thinning or gradual breakdown of cartilage tissue in time, this can lead to deformation and arthrosis, which ultimately leads to disability.
Meniscus injury is a common problem that traumatologists encounter in their practice. Men are three times more likely to suffer a torn meniscus than women. The average age at which the peak of knee ligament injury occurs is 23-25 years.
At the time of injury, the victim experiences pain not only in the knee area, but along the entire length of the limb. Only after two weeks the pain will be localized in the sore knee. The main signs of a meniscus tear are:
- acute pain;
- hyperthermia at the site of injury, meaning the knee may become hot compared to the rest of the body;
- enlargement of the knee due to severe swelling;
- a loud crunching sound during flexion and extension of the joint, including without load;
- severe weakness of the femoral muscle;
- lumbago when trying to put pressure on the leg.
Forecast
The effectiveness of therapeutic measures depends on the severity of changes in the cartilaginous components of the knee and the condition of the patient’s body as a whole. Since incomplete rupture occurs quite often, conservative therapy is preferentially prescribed.
The disciplined implementation of medical prescriptions, including general recommendations, as well as the patient’s responsible approach to rehabilitation are the basis for obtaining a favorable result of the treatment.
No comments. You can be the first to leave a comment.