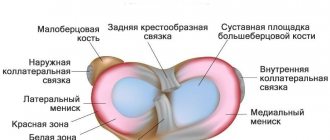
Structure: The anterior portion of the meniscus is the anterior horn, the posterior portion is the posterior horn, and the middle portion is the body. Laceration of the posterior horn is the most common injury. In addition to this, the meniscus is divided into three parts - external, middle and internal. Outer third tears have the greatest chance of healing due to active blood circulation in this area, which promotes repair and healing through the active delivery of nutrients.
Symptoms of a knee meniscal injury include pain, knee swelling, throbbing
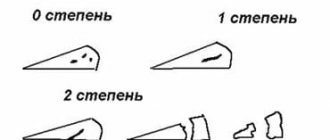
Fracture pattern: The fracture can have a variety of shapes, including horizontal, vertical and radial. In complex cases, the rupture may involve multiple structures.
A meniscus tear can be classified as complete or incomplete. A complete tear means that it passes through the entire meniscus and parts of the tissue are separated from its main mass. If the severed portion remains attached to the main mass, the rupture is considered incomplete.
Trauma or degenerative injury: Classification of a tear may also be based on the cause of the injury—trauma or a degenerative condition. If a person suddenly puts a large load on the knee (for example, lifts a lot of weight) and it can’t stand it, they talk about the traumatic nature of a meniscus tear. Degenerative damage is much more common among people over 65, with about 60 percent of the population at this age experiencing some kind of symptoms. These injuries are the result of minor injuries to the knee that occur during sports or everyday activities. These injuries weaken the meniscus and make it less elastic, and symptoms may not appear for a long time.
What is meniscus
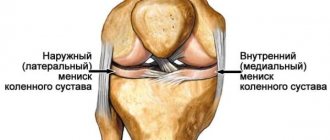
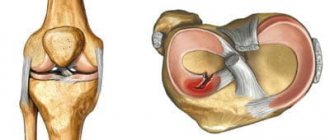
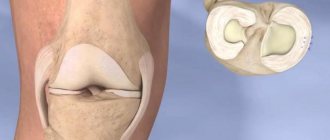
The meniscus is a dense semicircular spacer between the condyles of the tibia and femur. The menisci in the knee provide adherence to the articular surfaces and fill the lateral cavities of the joint. They act as a kind of seal, soften the pressure on the cartilage and stabilize the movement of the joint under heavy loads.
The menisci are made up of collagen and complex proteins and have a tendon-like consistency. They are highly elastic and wear-resistant, and take part in the nutrition and lubrication of the joint.
Conservative therapy
To eliminate the inflammatory process and to prevent the disease from becoming chronic, it is necessary to take treatment measures in a timely manner and comply with them for the prescribed period.
In some cases, when the meniscus has been slightly damaged, a course is prescribed that allows you to quickly get back on your feet and restore mobility to the joint. This course includes taking anti-inflammatory medications, which are taken orally or rubbed into the knee in the form of gels and ointments.
In addition, when there is a significant improvement in the condition and tests show that there is no longer inflammation, the treatment does not end there. A long period of rest greatly weakens the muscles, and it is necessary to restore their tone, as well as develop the joint. To do this, the patient must attend physiotherapy procedures that improve blood circulation in the affected area and metabolism. Thus, food products containing useful and strengthening elements bring more benefits, and these same vitamins are absorbed better and faster.
Therapeutic gymnastics is a separate point in the course of human treatment. This is a set of exercises that is prescribed for each case individually and requires responsibility from the patient himself. At first, the exercises do not carry much load, so as not to damage the joint. For example, a patient can simply move a foot or hip, and at the same time improve blood flow and maintain muscle tone. Then the complex becomes more complex, requiring movement in the joint itself. Training is carried out lying or sitting. At the final stage of treatment, full loads are recommended.
What are the dangers of meniscus injuries?
During training or at home, a person falls on his kneecap or the knee is subjected to a strong blow, for example in football. The meniscus ruptures or tears. If the body already has disorders, for example, the endocrine system suffers, or there is a history of gout or rheumatoid arthritis, recovery will not occur. A damaged meniscus ceases to perform its functions and does not alleviate pressure on the joint. This creates the preconditions for knee arthrosis.
With an injured meniscus, the cartilage layer is not able to smooth out dynamic loads on the knee joint. The joints begin to deform, friction of the cartilage causes pain. The situation is aggravated if a person is overweight.
Meniscus injury is the first step to knee arthrosis
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation
Carrying out rehabilitation measures is no less important than the main course of treatment. It involves resting the knee immediately after surgery or conservative therapy, followed by special activities that involve certain movements.
As the tissues recover, the range of motion and load gradually increase. This makes it possible for the cartilage tissue to adapt to loads and subsequently restore the functional state of the knee.
How to recognize a meniscal injury
The blow to the knee is very painful, but after a few hours the pain subsides. Alarming symptoms indicating a meniscus tear appear later, when a person has long forgotten about the injury. Pay attention to these signs:
- acute pain in the knee that spreads to the outside of the kneecap;
- local increase in body temperature - redness of the skin in the knee area;
- swelling and swelling of the knee joint;
- difficulty going down stairs;
- pain during dynamic movements - when jumping or running;
- a specific click when bending the knee.
The above symptoms are characteristic of various diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including bruises and subluxations of the ankle or knee. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself: go to an orthopedist and get diagnosed.
What is a meniscus tear and what does it mean? Answers to all questions are in the video:
Development mechanism
Development mechanism
Stability, strength, shock absorption of the knee, as well as a fairly high range of motion in it, are provided by cartilages located in the gap between the femoral condyles and the recesses of the tibia. They are paired. There are two menisci – the outer (lateral) and the inner (medial). These cartilages are characterized by a crescent-shaped shape. The wide part is called the body. Narrow areas face anteriorly and posteriorly. These are called the anterior and posterior horns.
The internal cartilage has a more rigid fixation by ligaments, so it is more likely to undergo changes. Violation of integrity is realized due to several basic mechanisms, which include a pronounced bruise, a fall on a bent limb (the cartilage is especially often injured when falling on a hard surface with a sharp edge - a step, a curb), as well as tucking (rotation of the lower leg with a fixed thigh or vice versa) . The damage is primarily localized in the area of the posterior horn, since it has the least strength.
How is a meniscus injury treated?
Injuries to the meniscus can be different: the tendon can be partially torn or completely torn, separated from the joint capsule longitudinally or transversely. The problem can be eliminated conservatively or surgically, but only after the inflammation has subsided.
After a severe knee injury, it is important to rest the leg, cool the affected area and secure the joint with an elastic bandage. If the patient is transported to the hospital in a horizontal position, the leg is placed above the chest to prevent swelling of the knee.
To make a diagnosis, MRI or CT is prescribed, sometimes together with arthroscopy. If the meniscus is displaced, a cast is applied for 20 days, and a course of restorative therapy is also prescribed.
For meniscus injuries, the following is prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors to stimulate cartilage tissue and improve the structure of synovial fluid;
- rubbing agents with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects;
- collagen, for example in food (strengthens tissue trophism and nourishes the meniscus).
Most often, meniscal injuries are treated with medication.
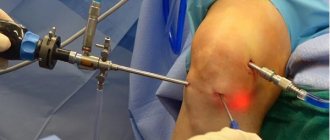
Arthroscopic technique
Arthroscopic technique
Thanks to the introduction of arthroscopic surgery into clinical practice, it was possible to achieve a significant reduction in the morbidity of surgical treatment and reduce the length of time required for:
- tissue regeneration and restoration of mobility;
- the entire course of treatment and a person’s stay in a medical institution.
Postoperative recovery
After surgical procedures, regardless of the method of their implementation, the patient remains in the hospital of a medical institution for a certain period of time. A set of measures is prescribed aimed at speedy tissue regeneration of the postoperative wound area and prevention of complications:
- Limitation of leg mobility.
- Periodic treatment of surgical suture materials with special antiseptics, which are usually used in the form of a solution.
- Prescribing antibacterial agents to prevent infection.
- The use of hemostatic medications to prevent bleeding, especially after open surgery.
The average postoperative period is determined by the method of performing the operation. It varies from 3-5 to 10 days.
Does physiotherapy help with meniscus injuries?
If the clinical picture allows the injury to be treated conservatively, drug therapy is supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures. Laser, shock wave, ultrasound and magnetic therapy help speed up recovery.
If the patient is not allergic to bee products, he may be offered bee stinging under the supervision of a specialist. The principle is this: on the first day, one bee is planted on the sore spot, on the second - three, on the third - 5. The maximum number of bees is 9. Many patients say that after just one or two stings the healing effect is impressive.
For meniscus injuries, compresses of honey and alcohol are often made
Treatment at home
Carrying out therapeutic measures at home is only possible if non-surgical treatment is prescribed. If there is a need for parenteral (intramuscular, subcutaneous or intravenous) administration of drugs, the patient receives treatment on an outpatient basis. To do this, he visits the manipulation room of a medical institution, where he undergoes the necessary manipulations.
An attempt to independently treat damage to the internal cartilage without undergoing the necessary set of diagnostic tests can cause the development of various complications, including pinching of part of the damaged meniscus with its wedging into the joint space. Such complications lead to the need for subsequent surgery.
In what cases is surgery necessary?
Unfortunately, conservative treatment does not always help. If, after several weeks after a knee injury, the pain does not go away, the joint bends with difficulty, the doctor suggests surgery. Surgical intervention is also indicated in the following conditions:
- if the result of a meniscus injury is hemorrhage inside the articular cavity;
- if the meniscus is severely deformed - torn or radically displaced;
- if the meniscus has separated from the joint capsule.
Most often, damaged menisci are sutured; in severe cases, they are replaced with artificial analogues. The operation is as complex as joint replacement for gonarthrosis, and requires a long recovery - at least four months. After meniscus replacement, the pain goes away almost immediately. Training on an exercise bike, swimming in the pool, proper nutrition and therapeutic exercises help speed up recovery.
A meniscus injury can cause no less discomfort than arthrosis of the knee joint. Moreover, it often leads to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the knee joint. Therefore, be especially careful if you are injured. Don’t let the situation take its course: see a specialist.
Principles of treatment
The main goal of therapeutic measures is to correct disorders of the cartilage of the knee, as well as its functional state. They are complex and aimed at all parts of the pathogenetic mechanism, and may include several areas:
- Conservative (non-surgical) measures.
- Operation.
- Recovery.
The scope of treatment is determined by the treating specialist based on the results of a clinical subjective examination and additional instrumental diagnostics.
Treatment without surgery
If, based on a comprehensive diagnosis, a mild injury to the internal meniscus of the knee joint has been identified, treatment may only include conservative measures without surgery. These include:
- Providing rest, which is achieved through the use of tight bandages with an elastic bandage or the application of a plaster splint.
- Prescription of medications of various groups - anti-inflammatory (glucocorticosteroids or non-steroidal drugs) medications to reduce the intensity of inflammation, chondroprotectors that promote the restoration of cartilage tissue, as well as preventing its further destruction, vitamins to improve the course of metabolic processes.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, which are of particular importance in the gradual chronic development of disorders. They include magnetic therapy, electrophoresis with medications, ozokerite.
A set of conservative treatment measures allows one to achieve a good therapeutic effect and avoid surgery, but only in the case of incomplete rupture of the internal cartilage.
Operation
If there is a complete tear that involves the entire medial meniscus of the knee, treatment usually involves surgery. Its main purpose is plastic surgery of altered structures or removal of part of the cartilage if it cannot be restored. Modern surgery is performed using 2 main methods:
First aid
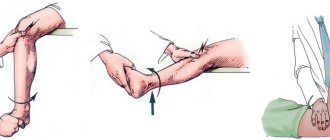
When a meniscus ruptures, the pain is so severe that the victim cannot put weight on his foot. He needs help getting to bed, laying him down, raising the injured leg by placing a bolster or pillow under his shin. You should not try to straighten a blocked joint, as this can cause even greater damage. It is necessary to fix the joint with a splint, a removable splint, or apply an elastic bandage that does not compress the skin too much.
To relieve inflammatory swelling and eliminate pain, apply an ice pack wrapped in thick cloth to your knee every hour for 10 minutes. Any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) can be used as analgesics - Ketorol, Nise, Diclofenac, Nurofen tablets.