The lower extremities are exposed to massive physical activity every day. When walking, running, jumping, a huge number of large and small joints are involved. But the main load falls on the ankle and knee. Together with the arches of the feet, they absorb up to 70% of the shock-absorbing load and provide protection for the hip joint and spinal column from extreme overloads. But, unfortunately, it is precisely high loads that lead to the fact that the ligamentous and tendon apparatus of the ankle and knee quickly comes to a destroyed and deformed state.
Sprained ankle ligaments often lead to instability and periodic twisting of the leg. And when the ligaments of the knee joint become separated, functional instability occurs, in which independent movement of a person becomes either difficult or impossible.
Differential diagnosis of fiber separation is necessary to exclude ruptures, bone fractures, destruction of menisci, etc. The diagnosis begins with a visit to an orthopedist. Already during the initial examination and a series of functional diagnostic tests, an experienced doctor will be able to make an accurate diagnosis. An x-ray is then ordered. It eliminates damage to bone tissue, fractures, cracks, and dislocations. When conducting an MRI examination, a verdict may be made - fiber separation of one or another ligament. In this case, diagnostic arthroscopy of the knee or ankle is prescribed. During an endoscopic abdominal examination, if ruptures are detected, an operation is performed to restore the integrity of the ligamentous and tendon apparatus. Then follows a period of rehabilitation and the patient completely restores the health of his joint.
To undergo complete rehabilitation treatment, you can contact our manual therapy clinic in Moscow. Call the administrator and make an appointment for a free appointment with an orthopedist. The doctor will review the results of the examinations completed, conduct an examination and talk about the prospects for using manual therapy methods in your individual case.
Ligament dislocation - what is it?
Let's look at the question of what it is - ligament separation and how it is dangerous for the health and mobility of the patient. First, let's take a look at the anatomy and physiology of the knee and ankle joints.
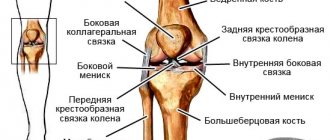
So, the knee joint is formed by connecting the condyles of the tibia and femur. They are separated from each other by dense cartilaginous menisci, which absorb shock absorbing loads when walking, running and jumping. A dense articular capsule is formed around the joint; inside it is synovial fluid, which is absorbed and secreted by the cartilage layer covering the heads of the bones. This is another shock-absorbing protective mechanism. The front of the joint is bordered by a triangular bone - the patella. It is attached to the epiphyses of the tibia and femur with the help of tendons and its own ligamentous apparatus.
The stability of the knee itself is provided by four large ligaments:
- the anterior cruciate prevents the femoral condyle from moving forward;
- the posterior cruciate restricts the posterior movement of the tibial condyle;
- 2 lateral (lateral and medial) limit mobility in the right and left lateral planes).
Most often in the practice of a traumatologist and orthopedist, swelling and disintegration of the anterior cruciate ligament occurs, since it bears the maximum physical, mechanical and shock-absorbing load. Young active people who are fond of sports and experience regular overload of the lower extremities suffer more often.
The posterior cruciate and collateral ligaments are less affected. But even with significant injuries, they are subject to destruction of the collagen fibers that form the ligament tissue.
Normally, the ligament of the ankle or knee joint consists of tightly intertwined collagen fibers. It is a strong connective tissue. Its disadvantage is a low degree of extensibility and a complete lack of its own blood supply. She can receive fluid in limited quantities only with the active work of the muscles surrounding her.
When an injury occurs, mobility is limited for natural reasons. Therefore, the damaged ligament does not receive enough diffuse nutrition. It begins to undergo ischemia and gradual degenerative dystrophic destruction. The fibers become sparser, the density of the ligamentous tissue decreases.
In this condition, there is a high probability of a complete or partial rupture, which will not heal on its own. Surgery will be required to restore its integrity. This is the biggest threat to patient mobility. In addition, when the ligaments become loose, he risks that the process of deformation of the cartilage and bone tissue of the joint will begin in the near future. Deforming osteoarthritis may require joint replacement surgery or make it impossible for a person to move independently. Therefore, if a process of ligament disintegration is detected, you should immediately contact an experienced orthopedist for restorative treatment using conservative methods of manual therapy.
Diagnosis of pathology
Additional diagnostic methods include:
- Computed tomography,
- Arthroscopy,
- Ultrasound scanning,
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI),
- X-ray of the knee joint in 2 projections.
As a rule, an X-ray examination is initially performed to rule out damage to bone tissue. It also allows you to study the nature and height of the joint space, the presence of a “joint mouse” in it, a torn fragment of bone or cartilage.
Patients for whom radiation examination is contraindicated (small children, pregnant women, patients with an artificial pacemaker) undergo ultrasonography - ultrasound of the joint. It can reveal both bone damage and changes in articular cartilage and ligaments.
MRI is the most reliable modern tomography method; it can be used to determine any changes in the tissues of the joint, their size and location with a high degree of accuracy.
Arthroscopy is a modern visual diagnostic method that allows you to completely examine the entire joint from the inside and study all its elements. Through a small incision in the skin, an optical apparatus with a video camera, a lighting and magnification system is inserted into the joint, and the image is projected onto the screen. This procedure is not only diagnostic, it also allows you to perform a number of therapeutic measures.
Sprain of the anterior cruciate ligament of the knee joint
Sprain of the cruciate ligament of the knee joint is an occupational disease of athletes, loaders, builders, painters, plasterers and representatives of other professions associated with increased physical stress exerted on the lower extremities.
In approximately 60% of cases, anterior cruciate ligament rupture of the knee joint is associated with trauma. It can develop after the first dislocation, or it can begin to form against the background of scar deformation after several sprains or bruises.
Disintegration of the cruciate ligament manifests itself as a feeling of instability in the knee when walking. Any awkward movement causes an attack of acute pain, which limits the mobility of the leg for several days. Then everything returns to relative normality again. Sooner or later, the separation of the anterior cruciate ligament leads to its complete rupture. This makes it impossible to walk independently. Surgery is required to restore integrity.
Sprain of the posterior cruciate ligament is compensated in most cases. The shock-absorbing load is absorbed due to the increased work of the surrounding muscles. Therefore, this pathology worries patients little. Even with a complete rupture of the posterior cruciate ligament, a person can walk and do squats at first. However, after 2–3 months, this will negatively affect the condition of the anterior cruciate ligament, which will also begin to become loose against the background of increased physical stress on it.
Causes of damage
The anterior cruciate ligament is subject to injury much more often due to the peculiarities of its structure; it consists of 3 bundles: medial, lateral and median, which creates conditions for fiber disintegration during injuries.
The anterior or posterior cruciate ligament can be torn for the following reasons:
- Sharp rotation (turn) of the lower leg,
- Strong direct blow to the knee,
- A strong blow to the back of the shin.
- Excessive sharp flexion of the knee joint,
- Deviation (twisting) of the shin inward, outward, posteriorly.
This mechanism of injury mainly occurs in athletes - football players, handball players, basketball players, therefore people involved in team sports are at risk for cruciate ligament injuries. It is they who are more likely to experience cross fiber disintegration due to regularly repeated excessive loads on the ligaments.
Female athletes are at greatest risk for this injury. This is due to the structural features of the knee joint in women, when the ligament is close to the thigh muscles and can rub against the bone. Hormonal levels also play a role - estrogens, progesterone, they reduce the density of the ligamentous apparatus, making it less durable.
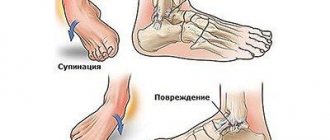
Ankle ligament sprain
When ankle ligaments sprain, symptoms appear immediately after the traumatic impact. As soon as the traumatic swelling of the soft tissues subsides, the instability of the position of the head of the tibia and fibula in the joint capsule becomes visible to the naked eye. Constant displacement occurs even with careful walking. Repeated ankle sprains occur constantly.
After a few months, the patient begins to feel a constant dull pain in the joint area. After significant physical activity, swelling and redness of the skin appears.
Unfortunately, all these are signs of deforming osteoarthritis of the ankle joint, which began to develop against the backdrop of dislocation of the ankle ligaments.
Fiber separation often occurs in the projection of the interosseous, deltoid or tibial ligaments. It is they who together provide stability to the joint and a strong connection between the heads of the tibia and femur.
Risk factors that can provoke the development of ankle ligament sprains:
- curvature of the legs and thighs due to rickets and osteomalacia;
- incorrect placement of the foot in the form of clubfoot and flat feet;
- practicing outdoor sports (football, volleyball, basketball, tennis, etc.);
- wearing high-heeled shoes;
- stretching of the Achilles tendon and its subsequent scar deformation;
- incorrect choice of shoes for everyday wear and sports;
- plantar fasciitis and heel spurs;
- excess body weight;
- diabetic foot and other types of angiopathy.
If the ankle ligaments are torn, you should seek medical help from an orthopedist or traumatologist. If the ankle ligaments are torn, you should seek medical help from an orthopedist or traumatologist. At the initial stage, treatment is carried out using conservative methods without surgery.
How to repair a torn knee ligament?
In most cases, the separation of the knee ligament is a reason for performing endoscopic plastic surgery. For reconstruction, synthetic materials or parts of ligaments taken from the ankle joint are used. They are installed using bone screws. After surgery, active rehabilitation is required.
There are techniques for restoring ligament dislocation using manual therapy methods. This can only be done in the early stages, when the risk of ligament rupture is not high. By increasing microcirculation of blood and lymphatic fluid, the scarring process can be accelerated. Reflexology allows you to start the process of natural tissue regeneration. And physical therapy in combination with kinesiotherapy allows you to enhance diffuse nutrition and strengthen the ligamentous apparatus of the knee.
Treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture of the knee joint
It is necessary to begin treatment of anterior cruciate ligament rupture of the knee joint with differential diagnosis and selection of appropriate tactics. An experienced orthopedist must evaluate the condition of the knee joint, eliminate the risk of complete rupture of the ligament, and decide whether the ligament will be treated with surgery or the patient will be placed in a cast for several months. After a period of immobilization of the lower limb, restoration of mobility begins. After surgery, rehabilitation begins 10 days later. An individual program is being developed, which includes manual therapy, therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, etc.
Complex treatment of anterior cruciate ligament dislocation is carried out over 3 to 4 months. During this time, the patient completely restores the health of the damaged joint. The usual range of mobility of the lower leg returns, serious physical activity and sports are allowed.
If you need treatment for a sprained ligament, you can make a free appointment with a podiatrist at our chiropractic clinic. The doctor will conduct an examination, make a diagnosis and develop an individual rehabilitation program depending on the type of traumatic injury to the ligamentous apparatus.
What is a torn cruciate ligament of the knee?
The cruciate ligaments are formed by dense collagen fibers that do not stretch. They rigidly connect the femur to the bones of the lower leg, preventing displacement, and this is their big advantage.
The process of disintegration of ligaments is often irreversible due to their poor blood circulation; this requires qualified, often surgical treatment.
The knee joint bears a very heavy load and is often subject to injury. In cases where the impact of force on the joint is very large, a “minus” of the cruciate ligaments appears. The lack of tensile ability leads to their partial or complete rupture, loosening and disintegration, when the bond between the fibers weakens, and in general the ligament loses its strength.