- Three-stage pain correction system
- How to relieve pain: a description of the stages of a three-step scheme
- How often does cancer pain occur?
- What is the reason for failure in pain treatment?
- Technologies for managing chronic pain syndromes
- Painkillers for stomach cancer
- Painkillers for lung cancer
Often the first and only symptom of cancer is pain. It causes suffering to the patient, reduces the quality of life, leads to depressive disorders, suicidal intentions and actions.
The fight against pain is a pressing problem in oncology. In order to effectively cope with pain, the doctor must correctly assess its causes, nature, and intensity.
At Euroonko, the area of pain medicine is very well developed. Our doctors use all available methods, including innovative ones.
Pain relief by injection
The peculiarity of all painkillers is that they do not affect the cause of pain, but only eliminate it. Therefore, they are used for symptomatic auxiliary treatment. Usually, painkillers in tablets or ointments are used at home, but severe pain can only be relieved with injections. This method of pain relief has advantages:
- the drug begins to act quickly, alleviating the patient’s condition;
- fewer side effects;
- easier to dose.
Medicines are usually administered intramuscularly - into the gluteal muscle, less often injections are given intravenously or intraarticularly. As a last resort, you can give an injection in the leg or shoulder.
Painkillers for lung cancer
The cause of chest pain due to lung cancer can be the tumor itself or a surgical procedure. Other possible reasons:
- Metastases in the brain lead to headaches.
- Metastases of the abdominal organs lead to abdominal pain.
- Metastases in the bones lead to bone pain and pathological fractures.
- Paraneoplastic syndrome leads to neuropathic pain in different parts of the body.
- Pain is one of the side effects of chemotherapy.
In addition to pain-relieving injections for lung cancer with NSAIDs and narcotic analgesics, other drugs, nerve blocks, radiation therapy, and palliative surgical interventions help.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
What painkillers are used for injections?
Despite the fact that these are symptomatic drugs, their use is necessary for the treatment of many pathologies. If the patient experiences discomfort, his recovery will slow down. With chronic pain syndrome, performance decreases and depression develops. Therefore, painkillers are used in the following cases:
Advertising:
- after injuries, surgical interventions;
- during dental treatment, tooth extraction;
- severe migraine;
- renal, biliary or hepatic colic;
- arthritis, bursitis, arthrosis and other joint pathologies;
- osteochondrosis, spondylosis, intervertebral hernia;
- oncological diseases;
- painful periods.
Painkillers in tablets are usually used on their own. But if the pain is severe and oral medications do not help, injections should be used.
Medicines from several groups are used for this: analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, local anesthetics, antispasmodics.
The list of such drugs is large, it is difficult to figure out which one is better on your own. But there are several remedies that are used most often. According to doctors and reviews from patients, these are the best painkillers.
Hypertension is a pathology that can lead to crisis and stroke, so blood pressure needs to be controlled with medications. Read more in the article: “how to quickly and effectively reduce blood pressure with pills.”
| LS group | Active substance | Drug names | Indications for use | How long does it last? |
| Narcotic analgesics | morphine | Morphine, Diamorphine, Skenan, Omnopon | operations, fractures, malignant tumors, heart attack, | effect in 10 minutes, lasts 8-12 hours |
| Narcotic analgesics | codeine | Codeine, Codelmixt, Sedal-M, Caffetin, Solpadeine | operations, neuralgic, muscle and joint pain, dysmenorrhea, migraine | effective in 10-20 minutes, for 4 hours |
| Narcotic analgesics | trimeperidrine | Promedol, Naloxone | operations, heart attack, pericarditis, renal colic, neuritis, peptic ulcer, oncology, radiculitis, | in 10-20 minutes, 3-4 hours |
| Non-narcotic analgesics | metamizole sodium | Analgin, Baralgin, Optalgin, Spazmalgon, Tempalgin, Bral | neuralgia, operations, biliary colic, radiculitis | in 30 minutes, 3-4 hours |
| Non-narcotic analgesics | tramadol | Tramadol, Tramal, | trauma, neuralgia, oncology | in 15 minutes, 6 hours |
| Non-narcotic analgesics | butorphanol | Butorphanol, Moradol, Stadol, Naloxone | pain relief during childbirth, surgery, oncology | immediately, lasts 3-4 hours |
| NSAIDs | ketorolac | Ketanov, Ketorol, Dolak | injuries, radiculitis, neuralgia | 30 minutes, 6 hours |
| NSAIDs | dexketoprofen | Dexalgin, Dexonal, Ketodexal | operations, renal colic, arthritis, osteochondrosis | 20 minutes, 2-3 hours |
| NSAIDs | diclofenac | Diclofenac, Voltaren, Ortofen | arthritis, radiculitis, trauma, migraine, algodismenorrhea | 20 minutes, 2-3 hours |
| NSAIDs | ketoprofen | Ketoprofen, Ketonal | arthritis, sciatica, sciatica, trauma, surgery | 15 minutes, 6 hours |
| Steroid hormones | hydrocortisone | Hydrocortisone | pain in joints and spine | after 6-20 hours, several days |
| Steroid hormones | dexamethasone | Dexamethasone, Dexasone | oncology, trauma, joint pathologies | 6 hours, several weeks |
| antispasmodics | drotaverine | Drotaverine, No-Shpa | colic, spasms, peptic ulcer, algomenorrhea | 3-5 minutes, 6-8 hours |
| antispasmodics | papaverine | Papaverine, | intestinal spasms, renal colic, angina pectoris, cholecystitis | 15-30 minutes, 4 hours |
To choose the right medicine, you need to take into account the patient’s age, the intensity of the pain and its cause. The strongest narcotic analgesics, Butorphanol, Ketanov, should not be used for ordinary headaches or toothaches. Joint pathologies and radiculitis are treated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. And for spasms and colic, antispasmodics are needed.
Heartburn is an unpleasant sensation accompanied by a burning sensation in the chest and heart area. The condition is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms; changing eating habits, following a diet and traditional recipes will help get rid of it. Read more in the article: “remedy for heartburn at home.”
Technologies for managing chronic pain syndromes
Euroonko is equipped with all the necessary equipment, including individual wearable pumps and devices for dosed administration. The clinic has the licenses and permits required by the legislation of the Russian Federation. We have a well-equipped pain therapy department staffed by physicians who specialize in pain medicine.
Use the quick links to find out about the pain relief method you are interested in:
- Pain relieving patches
- Spinal anesthesia
- Epidural anesthesia
- Catheterization techniques
- Neurolysis through the gastrointestinal tract using endosonography
- Injection of drugs into myofascial trigger points
- Fascial blocks and nerve and plexus blocks
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Neurosurgical interventions
- Patient controlled analgesia (PCA)
Pain relief for stage 4 cancer can significantly improve the patient’s quality of life, reduce, and in most cases prevent suffering. This helps to give the terminally ill patient additional time during which he can actively communicate with family and friends and spend the last days of his life without painful symptoms.
Pain relieving patches
This is a method of transdermal administration of the drug. The patch contains four layers: a protective polyester film, a reservoir with the active substance (for example, fentanyl), a membrane that adjusts the release intensity and an adhesive layer. The patch can be applied anywhere. Fentanyl is released gradually over 3 days. The effect begins within 12 hours; after removal, the concentration of the drug in the blood slowly decreases. The dosage may be different, it is selected individually. The patch is prescribed, as a rule, at the very beginning of the third stage of pain relief for oncology.
Spinal anesthesia
During spinal anesthesia, the medicine is injected into the spinal canal, subarachnoidally. This leads to a temporary “switching off” of tactile and pain sensitivity. The introduction requires a certain amount of experience from the doctor. Local anesthetics and opioid analgesics are used as pain relievers. The effect is long lasting and pronounced. Mainly used for surgical interventions, for acute, unbearable pain, it has a number of side effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Sign up for a consultation now
Epidural anesthesia
A more gentle method compared to the previous one. The medicine is injected into the space where the spinal nerves form. The drugs are similar to spinal anesthesia. Epidural anesthesia is used for long-term pain relief when oral and parenteral methods of administration no longer provide results.
Catheterization techniques
Catheterization techniques allow for long-term, high-quality pain relief. The introduction of port systems into the epidural and subarachnoid space with the use of local, narcotic and adjuvant drugs allows for long-term relief from pain and reduces the use of other analgesics that have their own side effects.
Neurolysis through the gastrointestinal tract using endosonography
Neurolysis (neurolysis) is the process of destruction of the nociceptive (pain) nerve pathway.
One of the most effective methods is neurolysis of the celiac (solar) plexus
, which is located in the retroperitoneal space in the upper abdomen and innervates the abdominal organs: stomach, liver, biliary tract, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, adrenal glands, large and small intestines to the splenic flexure.
The analgesic is administered transgastrically - through the gastrointestinal tract; accuracy is ensured by endoscopic ultrasound control. Such methods of local anesthesia are used, for example, for pancreatic cancer with an effectiveness of up to 90%
. The analgesic effect can last for more than several months, while narcotic analgesics would have to be administered continuously using the classical method.
Injection of drugs into myofascial trigger points
Myofascial pain syndrome is expressed in muscle spasm and the appearance of painful lumps in tense muscles. These are called trigger points and are painful when pressed. Injections into the trigger zone relieve pain and improve mobility of the body area. The purpose of trigger point injections is to “break” the pain cycle of pain-spasm-pain. They successfully treat spasms of many muscle groups, especially in the arms, legs, lumbar region and neck, and head. Often used as adjunctive therapy for fibromyalgia and tension headaches.
Fascial blocks and nerve and plexus blocks
The same qualitative effect is provided by fascial blockades and blockades of nerves and plexuses.
A nerve or plexus block involves injecting a drug near the nerve that connects to the affected organ and causes pain. Peripheral blockade procedures are performed by experienced specialists using ultrasound navigation, which allows for more precise administration of the analgesic drug to the required location without affecting or damaging the nerve structures.
The use of hormonal drugs during blockade can eliminate pain for a long time, and repeated blockade can eliminate pain for several months
. Depending on the type of anesthetic, the procedure is carried out once a year, once every six months or every week. Another plus is the minimal number of negative consequences.
Radiofrequency ablation
This technology is based on selective thermocoagulation of certain nerves with special electrodes. The affected area is carefully controlled, allowing very small areas to be treated without damaging nearby motor and sensory nerves. Recovery after the procedure occurs very quickly and with almost no consequences, which allows the patient to return to normal life.
The procedure can be performed without hospitalization. Radiofrequency destruction gives a long-lasting effect that can last up to a year or more
.
The incidence of complications and side effects is very low. If the pain returns, treatment may be repeated.
Write to an oncologist
Patients with obvious mental disorders, with secondary pain or drug addiction are an unsuitable population for neurodestructive manipulations. Such patients may continue to complain of pain even if the procedure is successful. The patient must have a realistic view of the outcome of treatment. He must understand that the goal is to reduce pain, not completely eliminate it.
a diagnostic blockade is required.
. A good effect of a diagnostic blockade can predict a satisfactory result of neurodestruction. However, the same diagnostic block must be repeated at least one more time, even if the pain relief was significant, to negate the placebo effect.
If the result is not entirely clear, differential blocking should be used. In patients with widespread or multilocal pain, the outcome of treatment usually does not meet expectations. The patient should be aware that targeting one area may not achieve the desired effect and may require additional destruction to achieve maximum pain relief.
Euroonco doctors talk about radiofrequency ablation:
The procedure should be avoided on mixed nerves as it may result in loss of skin sensation and muscle weakness. Deafferentation pain can be aggravated by destruction of the damaged nerve. When pain is of central origin (spinal or higher), peripheral nerve destruction may cause an increase in pain perception due to the elimination of incoming stimulus. The best alternative in this case is neuroaugmentation with TENS or spinal cord stimulation.
Neurosurgical interventions
During the procedure, the neurosurgeon cuts the spinal or cranial nerve roots through which the nerve fibers pass. Thus, the brain is deprived of the ability to receive pain signals. Cutting the roots does not lead to loss of motor ability, but may complicate it.
Patient controlled analgesia (PCA)
This type of pain relief is based on a simple rule: the patient receives analgesics when he wants it. The scheme is based on individual perception of pain and the need to take analgesics. In European countries, RSA has been accepted as the standard for postoperative pain management. The method is simple and relatively safe
. However, patients must be thoroughly instructed.
PCA is most effective when using catheter methods (epidural, spinal anesthesia, nerve plexus block with catheter installation), as well as port systems, both venous and epidural and intrathecal.
Analgesics for injection
Advertising:
The main effect of these drugs is pain relief. Therefore, they are most often used to relieve pain. These are symptomatic remedies; they do not cure, but only alleviate the patient’s condition. According to the characteristics of their action, analgesics are divided into narcotic and non-narcotic.
Narcotic analgesics
These are drugs based on morphine, opioids and their derivatives. Able to relieve severe pain. They affect the central nervous system and block nerve impulses. Lead to drowsiness, euphoria, and impaired concentration.
The disadvantage of such analgesics is that they are addictive and dependent, which is why they are called narcotic.
There are several of the most popular drugs in this group.
- Diamorphine
- an effective analgesic based on morphine. Quickly and effectively relieves pain, reduces the excitability of pain centers, has a hypnotic effect, and relaxes. Used only in hospitals, usually when treating cancer patients. Effective after operations, in case of heart attack. May cause breathing problems, spasms and severe dependence. - Codeine
— stimulates opiate receptors, therefore quickly relieves pain. But its main effect is the normalization of the central nervous system, an antitussive effect. It also causes drowsiness and addiction, but not as strong as morphine. - Promedol
with the active ingredient trimeperidrine. Affects nerve cells and the passage of impulses, has a slight antispasmodic effect. Due to this, it quickly reduces pain. Used in surgery, oncology, after injuries, during childbirth. It is also effective for pulmonary edema, fever, poisoning, and shock. Suitable for use by children from 2 years of age. The downside is that it is addictive and slows down your reaction speed. Therefore, it is used only in hospitals or for outpatient treatment with a doctor’s prescription. - Omnopon
is a complex pain reliever based on morphine and codeine. The composition also contains antispasmodics: papaverine, noscapine, thebaine. Used as injections to relieve severe pain. Has an antitussive and hypnotic effect. Causes drug addiction and can depress respiratory function.
Narcotic analgesics are used in hospitals for short-term relief of acute pain. They can be purchased at a pharmacy only with a doctor's prescription.
Advertising:
Non-narcotic analgesics
This group of drugs does not have the disadvantages of narcotic analgesics, but their analgesic effect is weaker. Use only for pain of mild or moderate intensity.
- Analgin
- the most famous painkiller. The active ingredient is metamizole sodium. Injections are given intramuscularly and intravenously. Effective for moderate pain. Helps with osteochondrosis, neuralgia, pain in muscles, joints, internal organs, after injuries. You can use no more than 1 ampoule at a time. Intravenous injection is more effective. It must be administered slowly, over at least 5 minutes. When injected into the buttock, the effect occurs only after half an hour. No more than 3 injections per day are allowed. - Tramadol
belong to the group of non-narcotic analgesics. But it affects nerve impulses, and the features of action are similar to morphine. It also causes addiction, drowsiness, and decreased reaction. Sold only by prescription, most often injections are made in a hospital. Tramadol is effective for severe pain, has a quick effect, and the results last a long time. It is used after injuries, operations, neuralgic and oncological pathologies. Does not depress breathing, reduces cough reflex. - Butorphanol
- refers to opioid non-narcotic analgesics. The active ingredient is butorphanol. Considered more effective than morphine. Relieves severe pain, the result lasts 4 hours. It is used to relieve pain after injuries and operations, and for cancer. Has a hypnotic and antitussive effect. Sold only with a doctor's prescription, may depress breathing. - Bral
is a complex drug containing metamizole sodium and two substances with an antispasmodic effect. Relieves pain, inflammation, relaxes smooth muscles. Therefore, it is especially effective for spasms, neurological pathologies, and after operations. The drug is well tolerated and can be used by children from 3 months. Contraindications include pregnancy, liver pathologies, and bronchial asthma. May cause allergic reactions. Cannot be used for a long time.
From this group, only Analgin, Bral and other medications containing metamizole sodium can be purchased without a doctor's prescription. It is necessary to take into account the presence of contraindications.
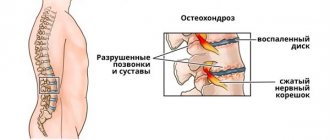
Chondroprotectors for back pain
Chondroprotectors are drugs that have the ability to stimulate metabolism in cartilage and protect it from damage and premature wear. The mechanism of action of chondroprotectors is the ability to trigger the synthesis of collagen - the main protein of connective tissue, responsible for the strength, elasticity and flexibility of joints, bone tissue, intervertebral discs, ligaments and tendons. Taking chondroprotectors allows you to slow down the destruction of cartilage, reverse degenerative processes, and restore the structure of connective tissue. Thanks to these effects, chondroprotective drugs relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve spinal mobility.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Most often, chondroprotectors are prescribed orally in the form of tablets and capsules. There are injectable forms of this group of drugs that are administered intramuscularly for back pain caused by degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis of the spine, intervertebral hernia, spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis, spondylosis). Chondroprotectors are usually well tolerated by patients, do not have significant side effects, and are etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. The disadvantage is that to obtain any significant effect, long and expensive repeated courses of treatment are required.
Chondroprotective drugs for the treatment of back pain:
- Chondroitin sulfate (Chondrolone);
- Alflutop.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
This group of drugs has a complex effect: relieves pain, inflammation, swelling and fever. Their action is based on the ability to block the production of prostaglandins. These hormone-like substances are responsible for the appearance of pain and are involved in the development of inflammation. Therefore, NSAIDs are effective for moderate pain.
Advertising:
- Ketanov
- the most common painkiller from the NSAID group. The active ingredient is ketorolac tromethamine. The result is noticeable within 15 minutes. Helps with severe and moderate pain. It is used in dentistry, oncology, renal colic, pain in the lower back, joints, after injuries, operations. It is prescribed to women during the postpartum period. Causes serious side effects: nausea, decreased performance, tachycardia. Contraindicated in pregnancy, peptic ulcers, asthma, and children under 16 years of age. Use no more than 1 ampoule intramuscularly, up to 3 times a day. - Dexalgin
— active ingredient dexketoprofen. Helps with mild to moderate pain, relieves inflammation, and has a slight antipyretic effect. Affects receptors and reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins. Effective for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, toothache, after injuries. Well tolerated, results are felt for up to 6 hours. But it cannot be used to relieve chronic pain. There are also contraindications: pregnancy, bronchial asthma, liver and kidney pathologies. - Diclofenac
effective for mild to moderate pain. It also relieves inflammation and swelling. It is used to alleviate the condition after injuries, tooth extraction, operations, migraines, joint pathologies, painful periods. Often causes allergic reactions, dizziness, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, exacerbation of pancreatitis. It has many contraindications and is prescribed with caution to elderly patients. You can use 1 ampoule intramuscularly, no more than 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is 2-3 days. - Ketonal
with the active ingredient ketoprofen. Capable of relieving severe pain. Most often used for pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, but it helps with headaches and toothaches, after operations. Prescribed 1 ampoule 2 times a day for no longer than 3-5 days. It is advisable to use the shortest course. If you take into account contraindications, Ketonal is able to quickly alleviate the patient’s condition. - Movalis
is a modern medicine from the group of NSAIDs based on meloxicam. Quickly relieves discomfort in the back and joints, reduces inflammation, is effective for migraines and algodismenorrhea. One intramuscular injection per day is sufficient. The drug is easily tolerated and rarely causes side effects.
Almost all NSAIDs are contraindicated during pregnancy, bronchial asthma, and during breastfeeding. They should be used with caution in children, the elderly, in the presence of aspirin-induced asthma, liver pathologies, and heart failure. Often cause allergic reactions, impaired renal and liver function, decreased concentration, and bradycardia. There may be swelling and a painful lump at the injection site.
How to relieve pain: a description of the stages of a three-step scheme
Low pain therapy
The patient is prescribed non-opioid analgesics: NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, etc.), Paracetamol. When choosing a drug, the toxicity to the liver and kidneys inherent in all non-opioid analgesics, as well as the gastric toxicity of non-selective NSAIDs, and the risks from the cardiovascular system when using selective NSAIDs are taken into account. It is advisable to accompany the use of first-line drugs with adjuvant and symptomatic therapy: ion pump blockers, corticosteroids, antispasmodics, benzodiazepines, antihistamines, etc.
Therapy for “moderate” pain
The oral route of drug administration is preferred if the patient can take the drugs by mouth. For patients with mild to moderate pain in whom adequate pain control is not achieved by regular oral paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the addition of an opioid analgesic may provide effective pain relief without adverse side effects. As an alternative, low-dose opioid analgesics (eg, morphine, TTC fentanyl) may be used.
Therapy for “severe” pain
If the pain is intense and an opioid analgesic in combination with NSAIDs or Paracetamol is ineffective, therapy with strong opioid analgesics should be started. If they were prescribed for moderate pain, you need to increase the dose of the drug until it is effective. Registered prolonged forms of strong opioid analgesics in our country and used in our clinic are: morphine in capsules and tablets, TTC fentanyl.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Glucocorticoids for pain relief
Advertising:
Synthetic analogues of adrenal steroid hormones have been used in medicine for a long time. They have anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, anti-shock effects. For pain relief, such drugs are used in the form of intra-articular injections and blockades. Injections are given in the knee, shoulder and hip joints, and elbows.
Steroid hormones should be used in this way as a last resort, as they destroy cartilage tissue.
It is recommended to do no more than 1 injection every 2-3 months. Contraindications include infectious arthritis, osteoporosis, and joint instability.
- Hydrocortisone acetate
- a synthetic hormonal agent. It is most often used topically to block joints and the spine. Helps with bursitis, arthritis, rheumatism. Accumulates in tissues, the result is felt no earlier than after 6 hours. After injection into the joint, it can damage the cartilage tissue, so such injections are made once every 1-2 weeks, no more than 5 times. - Dexamethasone
is the most powerful glucocorticosteroid. It has a pronounced analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antihistamine, desensitizing effect. The effect develops quickly and lasts for several weeks. It is easily tolerated and rarely causes side effects. Helps with rheumatoid arthritis, after injuries. Usually one injection is enough. Repeated administration is allowed after a month.
After injection, necrosis and necrosis of muscle tissue may develop. To avoid complications, do not put stress on the joint. Alcohol consumption is contraindicated during treatment.
When are antispasmodics needed?
Pain can be caused by spasm of smooth muscles. This happens with migraine, renal or biliary colic, spastic colitis, algodismenorrhea. Antispasmodics help cope with such painful sensations. They block the flow of calcium into muscle cells, promoting their relaxation.
Advertising:
- Papaverine hydrochloride
- this antispasmodic has been used for a long time for various spasms and colic. Relieves pain from angina pectoris, cholecystitis. It is administered intramuscularly, intravenously or subcutaneously. May cause drowsiness, decreased blood pressure, and heart rhythm disturbances. - No-Shpa
- active ingredient - drotaverine. Acts as a vasodilator and antispasmodic. Helps with colic, migraine, algodismenorrhea. It is used intramuscularly, intravenously. You need to introduce it slowly.
A patient with hypotension when antispasmodics are administered should lie down for some time after this. These drugs lower blood pressure and may cause dizziness.
Local anesthetics
For local anesthesia, anesthetics are used - agents that relieve pain in one place. They are used for anesthesia during dental treatment, joint pathologies, and simple operations.
- Novocaine
- a product based on procaine that has been popular for a long time. It acts locally, is used for blockades of the spine or joints, relieves pain in dentistry, and for diagnostic procedures. The peculiarity is that it turns off the sensitivity of nerve endings. You can inject the product into 3-4 points, then the anesthesia will be more effective. It is easily tolerated and quickly excreted by the kidneys. - Lidocaine
is a stronger anesthetic, with the active ingredient lidocaine hydrochloride. Blocks the conduction of nerve impulses, dilates blood vessels and relaxes muscles. Used in dentistry, traumatology, surgery. Injections are made into the gums, joints, and soft tissues.
These are the most common anesthetics, despite the fact that they cause many side effects. Especially often these are allergic reactions, heart rhythm disturbances, decreased or increased blood pressure.
How to choose the right pain reliever?
Injectable pain relievers help with severe pain. They are usually used in hospitals as prescribed by a doctor. But sometimes you need quick relief. To do this, you need to choose a good painkiller so that it is as effective as possible.
To relieve a regular migraine, non-narcotic analgesics are sufficient; for pain in the back, NSAIDs are more effective, and No-Shpa is better for relieving renal colic. Correct use of such injections will help alleviate the patient's condition.