Back pain is an unpleasant, but quite common symptom that indicates the development of serious health problems in a person.
Pain in the back can be associated both with problems of the musculoskeletal system and with disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
It is very important to make a correct diagnosis at an early stage of the disease and begin timely treatment, which will help you return to a full life and prevent the progression of diseases dangerous to health and life.
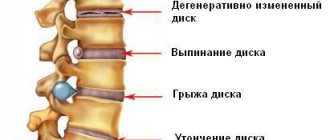
If you feel back pain below the lower back , then this may indicate the onset of the development of progressive osteochondrosis, which, in the absence of timely and adequate treatment, leads to protrusion of the intervertebral disc in the lumbar region.
Protrusion is a complex and insidious pathology, which is characterized by a violation of the stability of the cartilage tissue of the fibrous ring, which leads to infringement of the substance of the spinal cord. This is a borderline condition before the development of an intervertebral disc herniation.
After the formation of a hernia, prolapse of the fibrous ring occurs; the nucleus pulposus can enter the cavity between the vertebrae, which, when compressed, pinches the nerve roots and causes severe, almost unbearable pain in the lower back.
Pain below the lower back in men and women
In addition to osteochondrosis, back pain below the lower back may also indicate problems with internal organs.
In women, this symptom may indicate inflammatory processes in the pelvic cavity, where the organs of the reproductive system are located: the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes. This is also where the bladder is located. Therefore, when contacting the clinic, first of all adnexitis, adhesive disease, cystitis and tumor processes are excluded.
In men, back pain below the waist may indicate prostate adenoma or chronic prostatitis.
Treatment methods
When the causes of pain are determined, the treatment method for each patient is selected individually. Vertebrologists prefer to use conservative treatment, but in some patients the disease is so advanced that the only way to solve the problem is surgery.
A conservative form of treatment for lumboischialgia is carried out taking into account the identified deviations. All patients will have their own personal treatment program. The main stages here are: individually developed drug therapy, specialized massage, multi-stage physiotherapy, often manual therapy, sometimes osteopathy, as well as personal sessions with a specialist in the rehabilitation program.
Drug therapy
Most patients are prescribed medications in combination to quickly relieve pain and solve several problems at the same time. They are selected personally, based on the main diagnosis and taking into account other existing diseases. A number of medications have contraindications for use in diseases of internal organs.
The main components of drug therapy for spinal diseases are:
- NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are a number of medications that relieve inflammation and reduce pain. These are medications produced in many forms that have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties and are available in many dosage forms (from tablets, injections and suppositories to creams, ointments, etc.);
- Corticosteroids are popular drugs with powerful anti-inflammatory effects, which are used when NSAIDs are poorly effective;
- Muscle relaxants are a number of medications that eliminate muscle spasms, which reduces the severity of combat and plays an important role in processes such as the treatment of the back and spine;
- Chondroprotectors are drugs that accelerate recovery processes in intervertebral discs. They are often used when treating the spine and joints;
- B vitamins are substances that improve neural connections in the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy procedures are used to improve blood circulation, metabolism, regenerate damaged tissues, more accelerated restoration of impaired or lost mobility, reduce inflammation and swelling at the site of pain. Typically, patients receive courses of physiotherapy consisting of 8-15 sessions. Typically this includes:
- laser therapy;
- electrophoresis sessions;
- ultrasound therapy;
- exercise therapy;
- UHF.
When treating lumbar ischialgia, physical therapy should not be neglected. Exercises are developed individually for all patients. They start from the diagnosis, take into account age, take into account the level of physical fitness, collect anamnesis of concomitant diseases, etc. This approach helps to choose the level of load and the most effective and non-harmful exercises.
Lower back hurts and radiates to the leg: causes
Sometimes pain in the lower back is accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lower extremities. Pain from the back, as a rule, radiates to the leg, reaching the heel, and sometimes involves part of the foot.
Most often, the cause of such pain is radiculitis, ischalgia or lumbago. All these diseases are associated with damage to nervous tissue. Changes in cartilage tissue, deformation of the vertebrae and the appearance of so-called osteophytes (bone spurs) lead to pinched nerve roots, which cause attacks of pain radiating to the leg.
After injury, the nerves become inflamed and swelling forms around them, which further aggravates the pressure.
The pain in the lower back is felt as sharp, burning and constraining movement. If measures are not taken, then with a prolonged inflammatory process, atrophy of the gluteal, thigh and calf muscles is possible. vertebrology diseases of the legs diseases of the spine low back pain
Causes of pain syndrome
Why does the lower back hurt? The doctor will not be able to answer this question immediately. This symptom is characteristic of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, urinary and reproductive systems.
Pain may be associated with spinal diseases, including:
- radiculitis;
- osteochondrosis;
- spina bifida;
- rheumatism.
The distinctive features of these pathologies are increased pain during movement; the pain can radiate to the buttock or leg. As a rule, health improves at rest.
Sharp pain in the lower back is characteristic of kidney pathology. Severe discomfort in the lower back can be observed with the following diseases:
- inflammatory process in kidney tissues (pyelitis, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, hydronephrosis);
- urolithiasis (pain caused by the movement of stones through the urinary system);
- oncological changes in tissues (kidney cancer, tumors of the pelvis and ureter, bladder cancer);
- injury to the kidney or ureter.
If the cause of lower back pain is the genitourinary system, the condition will be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent urination;
- pain when urinating;
- change in urine color;
- hematuria;
- increased body temperature;
- chills and sweating;
- general intoxication;
- vomiting, nausea;
- fatigue and general weakness;
- headache.
An important difference from diseases of the musculoskeletal system is the fact that to alleviate the condition, painful areas cannot be heated. This can provoke an inflammatory process and worsen the overall picture.
Discomfort can be caused by pathologies of the reproductive system. Why does the lower back hurt in women? A gynecologist can answer this question. The causes of discomfort are the following conditions:
- menstrual irregularities;
- painful or heavy periods;
- pregnancy;
- menopausal changes in the body;
- inflammatory process in the reproductive system.
In some cases, a urologist-andrologist will help you find out why lower back pain occurs in men. Lumbar syndrome can be caused by the following disorders:
- pathological process in the prostate gland (prostatitis, adenoma, prostate cancer);
- epididymitis (inflammatory process in the epididymis);
- tumor processes, such as testicular cancer.
Pathology requires different medical care and in some cases it must be urgent. That is why, when the lower back hurts, a comprehensive examination is necessary. You can get it at the State Urological Center. Competent specialists from various fields work here. They will help determine the cause of the pathology and provide qualified assistance.
Which doctor should I contact?
When a doctor diagnoses a patient in order to identify the cause of pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, he first needs to understand the degree of intensity of the pain and its nature. In women, it is important to determine whether there is a connection with pregnancy or menstruation. For diagnosis, it is important to establish the nature of the pain and the frequency of its occurrence, since different characteristics may indicate different diseases.
If the nature of the disease is acute, then the patient may experience cramping pain that gradually increases; complications include chills, nausea, and elevated body temperature. Such pain indicates that the inflammatory process is rapidly developing. When pain of this nature is observed for a long time, some kind of chronic disease may well develop, therefore it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
To diagnose pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, clinical laboratory and hardware-instrumental research methods are used:
- laboratory tests for herpes infection, which affects the development of pelvic ganglioneuritis;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (ultrasound) - to exclude organic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- X-ray of the spine and pelvic bones;
- absorption densitometry to exclude osteoporosis;
- X-ray studies (irrigoscopy), endoscopic (sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, cystoscopy) of the gastrointestinal tract and bladder;
- laparoscopy.
Causes of nagging pain
Painful spasms vary in intensity. When internal organs rupture, the pain is unbearable due to perforation and bleeding inside. Chronic pathologies are characterized by nagging pain, and in the case of intracavitary pressure - pulsating pain. Let's take a closer look at the reasons for pulling in the lower back and lower abdomen:
- Inflammation of the appendix
. Discomfort is accompanied by vomiting and fever. The pain is usually sharp, sometimes aching. If appendicitis is not dealt with in time, it can rupture and lead to a fatal condition - peritonitis of the peritoneum. - Infectious lesions in the genitourinary system, inflammation - urethritis, cystitis
. In addition to pain, blood clots in the urine are possible. - Various infections in the intestines
. The pain is usually in the lower abdomen, but radiates to the lumbar region. Sometimes mucous and bloody discharge appears in the stool. You need to urgently consult a doctor, since the condition is fraught with sepsis. Sharp, cramping spasms signal that the pathological process has begun. - Colitis
. In addition to aching pain, a person may experience hyperthermia and bloating. Initially, the pain is acute, gradually becoming dull when the malaise becomes chronic. - Urolithiasis disease
. The discomfort is repeated often, is dull in nature, but can also be acute. Localization is noted in the lower abdomen and lower back.
Sometimes the lower back hurts and radiates to the groin due to a stroke. In this case, emergency medical assistance is needed.
Adenoma is the most common and dangerous disease of the pituitary gland, which is accompanied by pathological growth of glandular tissue and concomitant compression of vital areas of the brain - the optic nerves and blood vessels. Read more in the article: “Pituitary adenoma: symptoms and treatment in women.”
Types of back pain in men
| Strong pain | Spinal fractures, radicular syndrome due to hernias and protrusions, pinched spinal nerves, tumors and metastases in the spine |
| Sharp pain | Osteochondrosis of the spine, sprained or torn muscles, vertebral hernias and protrusions, compression fractures and other injuries |
| Nagging pain | Radicular syndrome, osteophytes, radiculitis, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system (STDs) |
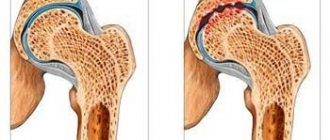
| It's a dull pain | Arthrosis of the hip joint, sprained muscles and tendons, inflammation of the joints of the spine, spondylosis, spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis, STDs |