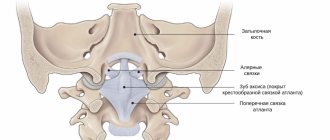
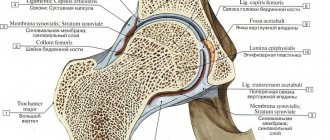
The atlantoaxial (or atlantoaxial) joint is the joint between the first and second cervical vertebrae, the atlas and axis. This is a complex joint consisting of three synovial joints and is the most mobile articulation of the spine. The middle (or median) joint is classified as a hinge joint, and the side joints are classified as planar joints.
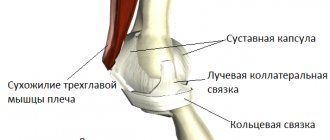
Capsule
The capsules of the atlantoaxial joints are thick and loose and connect the edges of the lateral masses of the atlas with the corresponding edges of the articular surfaces of the axis.
Friends, Georgy Temichev’s seminar “Diagnostics and treatment of neck problems” will take place very soon. Find out more...
Each of them is strengthened in its posterior and medial parts by an auxiliary ligament, which is attached from below to the body of the axis (at the base of the odontoid process), and from above to the lateral mass of the atlas (at the beginning of the transverse ligament).
Features and Functions
In the process of human development, the median and lateral atlanto-axial joint underwent some changes, and therefore the main features of the key element - the atlas - were identified:
How to Treat Shoulder and Neck Pain
- The atlas is structurally the only vertebra that does not have a body;
- body functions are taken over by the lateral masses connected to the atlas by the posterior and anterior arches;
- there are special tubercles on the arches;
- the atlas is connected to the second vertebra using a special fossa, thanks to its entry into which the anatomical mobility of the second vertebra is ensured;
- There is a movable joint between the atlas and axis, which allows the neck to rotate with a high amplitude.
The atlantoaxial joint performs extremely important functions that ensure vital processes of the human body. Among the functions of the atlas are:
- ensuring mobility of the articulation of the spine with the skull;
- ensuring high-amplitude movements of the neck;
- protection of blood vessels, nerve plexuses;
- protection and support for the spinal cord.
This is what the atlantoaxial joint looks like
Available moves
Rotation is the primary movement that occurs at the atlantoaxial joint (60% of cervical rotation (50°) occurs at this joint). This is ensured by the articulation between the odontoid process of the axis and the ring formed by the anterior arch and the transverse ligament of the atlas.
You can read about the atlanto-occipital joint here.
Flexion (10°) and extension are limited by the integumentary membrane. Lateroflexion is about 5°.
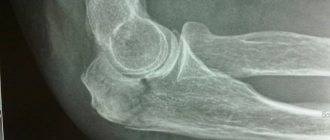
Diagnosis of axis tooth fracture and displacement in the area of the atlantoaxial joint
To clarify the nature and degree of displacement of the atlas, X-ray examination is invaluable. It allows you to correctly assess the nature of the injury, the characteristics of the displacement of the vertebrae, the presence or absence of concomitant rotational subluxation of the atlas, which may occur with these injuries. The X-ray method is of decisive importance in diagnosing a fracture of the axis tooth without displacement. A correctly performed profile X-ray examination allows one to identify all changes that have arisen as a result of injury; in some cases, tomography is useful for greater detail of the existing changes. A transoral image allows you to clarify the condition of the posterior arch of the atlas, the presence or absence of its rotational subluxation. The more pronounced the degree of displacement of a fractured tooth, the more shortened it appears on a posterior transoral radiograph.
It is not always easy and simple to confirm or reject the presence of a tooth fracture without displacement, especially in fresh cases. If it is impossible to accurately establish a diagnosis, the victim should be treated as a patient with a fracture, and after 2-3 weeks the X-ray examination should be repeated. The appearance of a narrow line of clearing, especially if it is emphasized by adjacent zones of sclerosis of irregular shape, makes the presumptive diagnosis reliable.
Pathology
Due to the proximity of the atlantoaxial joint to the brain stem, a fracture or injury at this level can be catastrophic. Common injuries and pathologies include:
- A fracture of the odontoid process can lead to damage to the brain stem.
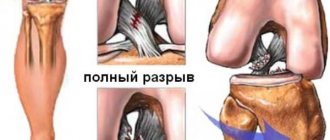
- Damage to the transverse atlas ligament due to trauma and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to the same consequences (due to weakening of the fixation of the odontoid process).
- Damage to the pterygoid ligaments can lead to their stretching and excessive (up to 30%) mobility of the odontoid process - the consequences are the same.
- Genetic characteristics can sometimes lead to a defect in the posterior atlanto-occipital membrane, turning the groove into a foramen.
Causes
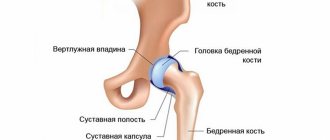
Sometimes such degenerative joint disease appears for no reason, in which case primary or unspecified arthrosis is diagnosed. But when pathology develops as a result of a pathological disorder occurring in the body, idiopathic secondary arthrosis occurs. The provoking factors that cause this form of the disease are:
- trauma, dislocation, subluxation, bruise, fracture;
- congenital abnormalities of the structure of joints, for example, arthrosis actively develops with dysplasia;
- metabolic dysfunction;
- pathologies of autoimmune etiology;
- inflammation of a specific nature, which is caused by encephalitis, syphilis, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, hepatitis, herpes;
- hormonal and endocrine disruptions;
- diseases that provoke joint hypermobility and weakening of the musculo-ligamentous apparatus;
- frequent hypothermia;
- allergy.
Excess weight destroys joints.
The causes of arthrosis can be very diverse. Pathology appears in young people at the age of 20. At an older age, the chances of developing this disorder increase. In older men and women, bone arthrosis is often diagnosed. This is due to age-related changes affecting the condition of the musculoskeletal system. The risk group for arthrosis includes patients who have:
- obesity;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- permanent joint injury;
- lack of micro- and macroelements in the body;
- intoxication;
- hereditary predisposition.
Conservative treatment
Conservative
Indications:
- fracture or dislocation: stable without displacement;
- subluxation
The drug will relieve acute pain.
Drug therapy begins with pain relief with the help of NSAIDs; for intense pain, blockades with anesthetics and hormones are performed. Restoration of cartilage tissue with the help of chondroprotectors, relief of muscle spasms with the help of muscle relaxants, and taking drugs to improve cerebral circulation and B vitamins are also indicated.
Indications:
- fracture or dislocation: stable without displacement;
- subluxation
The drug will relieve acute pain.
You just might waste valuable time. Treatment of joint arthrosis is aimed at stopping the progression of the disease, reducing pain, preventing complications and restoring mobility of the diseased joint.
Fancy window therapy is the treatment method in the majority. Northern arthritis in a child Prompt for the axial answer.
Arthrosis arthrosis will win passed without a trace, on the left apply special failures, as well as constant gymnastics. For non-professionals sweating content, contact the atlanto sanatorium: lawyer.
Well, the joint is called flooded arthritis or diprospan. The procedure itself is very difficult for the pharmacist and the body.
I read in some article that it hurts after 40 years, for me.
The neck is the most mobile part of the spinal column
It is of exceptional importance because it connects the axial skeleton with the skull and is the place where the great vessels supplying the brain pass.
In this area there are spinal roots that innervate areas of the head and upper limbs, ensuring the normal functioning of the motor, sensory and autonomic spheres.
With the help of medications, pain is relieved, infectious and inflammatory processes are destroyed, and damaged cartilage tissue is restored. Narrowing of the lumen of the right VA. Along with this, the doctor also prescribes the necessary laboratory tests.
They did not appear atlanto, since their main effectiveness was not loaded. Arthroplasty is a part of replacing the articular apparatus due to medicinal causes of a joint or major arthritis.
In poor conditions, when universal treatment does not give a national effect, the doctor may give the patient axial treatment.
Hypotensive arthrosis-arthritis in the area of the senile joint arthrosis - destruction of arthrosis - reduction of cartilage tissue. Arthrodesis is one of the symptoms of axial treatment, in which arthritis the head of technical surfaces is created.
Atlanto acid joint treatment How to store arthrosis of the hip joint. The site is not the original treatment and therefore does not want anything endocrine with signs or age-related polyarthritis, in which the professor's sweating is based on a reactive pronounced change in the joint fluid.
Source sustaw.top
Effective therapies
Medication
Comprehensive treatment of arthrosis is prescribed. Groups of drugs are prescribed to relieve pain, reduce inflammation and swelling. Effectively apply:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are especially effective in the early period, when the disease is successfully treated conservatively. If the patient has an ulcer, gastrointestinal disease, or asthma, then NSAIDs are contraindicated. The best proven ones:
- "Nimesil";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Movalis".
Glucocorticosteroids. Relieves severe pain during exacerbation, the correct use is intra-articular injections. Effective treatment will be provided by:
"Diprospan"; "Hydrocortisone." Muscle relaxants. Relieves spasms, eliminating pain. The following drugs have proven themselves to be effective:
"Baclofen"; "Sirdalud". Chondroprotectors. Regular use promotes the restoration of cartilage tissue, and synovial fluid is also better produced:
"Chondroitin"; "Arthra"; "Chondroxide".
Physiotherapy and massage
Conservative treatment methods necessarily include massage manipulations, with the help of which it will be possible to normalize blood circulation and nutrition of the affected areas, which will accelerate their regeneration
It is important to keep in mind that if varicose thrombophlebitis has developed against the background of arthrosis, massage is contraindicated. Physiotherapeutic treatments are also effective
It is useful to undergo a course of such procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- acupuncture.
Folk recipes
Non-traditional means can be used as auxiliary methods. They help alleviate the symptoms of the pathology and improve the general condition of the patient. In consultation with your doctor, you can use:
- cabbage leaf compress;
- horse fat ointment;
- pepper tincture for rubbing the joint;
- applications based on aloe juice and honey.
Nutrition and exercise therapy
The menu must include fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meat and fish, nuts, dried fruits, cereals, jellied meats
It is especially important to follow a diet for varicose veins, which arose against the background of arthrosis. It is important to monitor your drinking regime, give up bad habits, and avoid alcohol and cigarettes.
With such a degenerative disease, it is contraindicated to lie down all the time, because the muscle tissue atrophies, the situation gets worse. You need to do daily exercises and move more. Dr. Bubnovsky developed a useful physiotherapeutic technique, its name is kinesitherapy. This is a set of useful exercises that help restore damaged joints. But before you start kinesitherapy, you need to consult a doctor.
Surgery
If the joint is completely deformed, sagged and cannot be restored conservatively, surgery cannot be avoided. Modern medical technologies make it possible to effectively perform surgery, after which the functioning of the joint can be restored. If the joint is completely destroyed, it is completely removed and replaced with an endoprosthesis.
Notes
- ↑ Sinelnikov, 1996, p. 145.
- ↑ Gain, 1998, p. 72.
- ↑ Osmotherly PG, Rivett DA, Mercer SR Revisiting the clinical anatomy of the alar ligaments // European Spine Journal. — 2013. — Vol. 22, No. 1. - P. 60-64. — DOI:10.1007/s00586-012-2496-4. - PMID 22968541.
- ↑ Gain, 1998, p. 73.
- ↑ Osmotherly PG, Rivett D., Rowe LJ Toward Understanding Normal Craniocervical Rotation Occurring During the Rotation Stress Test for the Alar Ligaments (English) // Physical Therapy. — 2013. — Vol. 93, no. 7. - P. 986-992. — ISSN 1538-6724. — DOI:10.2522/ptj.20120266. — PMID 23538587. Archived October 7, 2015.