Most often, arthrosis of the hip joint is diagnosed in older people. The reason is the natural aging of the body, metabolic disorders and vital processes. In most cases, the disease is the result of injuries and microtraumas. Despite the similarity of symptoms in patients, orthopedists practice different approaches to the treatment of coxarthrosis, including both radical surgery and conservative intra-articular injections.
Coxarthrosis is more common among older people
The key to successful treatment is finding the cause
The treatment regimen depends on what caused the coxarthrosis, whether it is primary or secondary, and whether the patient has concomitant pathologies. There is no universal drug that can relieve pain and restore joint mobility. The set of therapeutic measures includes various measures and medications, the set of which is determined individually after diagnosis. Why is it so important to determine the cause?
- for injuries or an active lifestyle of the patient, treatment will be the same;
- with passive pastime, against the background of which stagnant processes develop, - others;
- if coxarthrosis was a consequence of arthritis - third;
- if it was caused by hormonal disorders, for example diabetes, the fourth, etc.
Orthopedists carefully study the patient’s medical history to rule out the primary nature of the pathology and determine the root cause of the secondary one. Knowing it, you can prevent re-damage to cartilage in the future, since otherwise the treatment of osteoarthritis will not give the desired results.
Without knowing the cause, there is no point in treating coxarthrosis
Gelatin for arthrosis of the knee joint, application
Edible gelatin is a product of animal origin, which contains many useful components:
- amino acids;
- collagen;
- iron;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- potassium;
- phosphorus;
- sodium;
- vitamins;
- starch.
Most often, professional athletes, elderly people and those engaged in mental activity need such useful elements. Gelatin helps with arthrosis as an auxiliary drug to the main method of therapy. It helps strengthen ligaments and increase joint elasticity.
Treatment of arthrosis with folk remedies
You should avoid using gelatin if you have the following pathologies:
- haemorrhoids;
- varicose veins;
- high degree of blood clotting;
- problems with the kidneys and gall bladder;
- urolithiasis disease;
- individual intolerance to product components.
Side effects include problems with the gastrointestinal tract and problems with bowel movements. In order to avoid constipation, you can take various dried fruits during treatment, for example, prunes, dried apricots, and figs.
What therapeutic methods are used at stages 1 and 2 of coxarthrosis?
The earlier treatment is started, the higher the patient's chances of taking control of the disease and maintaining freedom of movement. There are many methods, but not all of them are suitable for every patient. It is important not to overdo it, follow the specialist’s recommendations and not postpone therapy until later.
The diagram includes several points:
- short-course non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, since medications have side effects on the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system;
- vasodilators to improve blood circulation (after administration, the ability of cartilage to self-heal increases);
- muscle relaxants - drugs to relieve spasm of the thigh and leg muscles, to improve blood circulation in the joints;
- chondroprotectors to restore cartilage tissue and stop its deformation;
- intra-articular injections of a synovial fluid prosthesis, for example Noltrex, which restores the functionality of the hip joint for 12-18 months;
- hormonal drugs are relevant if the disease is accompanied by severe pain, as well as if muscles and tendons are inflamed;
- ointments and compresses are a method with low efficiency, since the product must overcome the skin, fat and muscle tissue (the effect of ointments is rather to massage the thigh, as a result of which blood circulation is activated and pain is reduced);
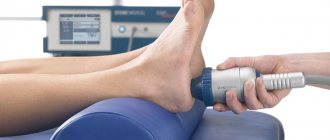
- physiotherapy - UHF therapy, laser, magnetic, cryotherapy, phototherapy (physiotherapy in combination with massage is especially effective);
- manual therapy;
- Exercise therapy to strengthen muscles and improve blood circulation.
It is very useful for patients with coxarthrosis to swim in sea water
Blog
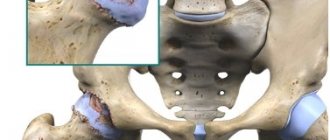
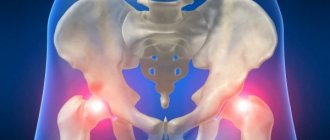
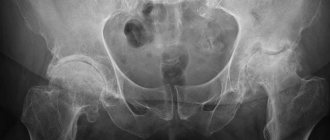
Coxarthrosis is a degenerative disease of the hip joint, characterized by a progressive course and disruption of the static-dynamic function of the musculoskeletal system. Since the hip joint is the most powerful in the human body and experiences heavy loads during life, it is not surprising that diseases of this joint take 2nd place after back pain.
There are primary coxarthrosis (idiopathic, i.e., of unknown etiology) and secondary coxarthrosis, which occurs against the background of hip dysplasia or congenital hip dislocation, as a result of injury, or an inflammatory process in the joint.
The reasons are different in all cases - the clinic is the same.
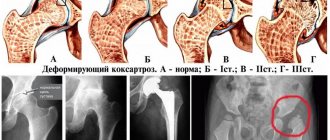
The main complaint of patients with coxarthrosis is pain. But the nature, intensity, duration and localization of this pain depend on the severity of the degenerative process in the joint, i.e. from the stage of coxarthrosis. There are three stages of coxarthrosis.
In the first stage , periodically after physical activity (long walking, running), pain occurs in the hip joint, less often in the hip or knee joint. As a rule, the pain goes away after rest. The range of motion in the joint is not limited, muscle strength is not changed, and gait is not impaired. Radiographs show minor bone growths that do not extend beyond the labrum. They are usually located around the outer or inner edge of the articular surface of the acetabulum. The head and neck of the femur are practically unchanged. The joint gap is unevenly slightly narrowed.
In the second stage , the pain is more intense, radiates to the thigh, groin area, and occurs at rest. The function of the joint is impaired. First of all, internal rotation and abduction of the hip are limited, i.e. flexion and adduction contracture is formed. The strength of the muscles that abduct and extend the hip decreases, and their hypotonia and hypotrophy are determined. Therefore, lameness begins to appear when walking. The radiograph shows significant bone growths along the outer and inner edges of the acetabulum, extending beyond the cartilaginous lip. Deformation of the femoral head, its enlargement and uneven contour are noted. Cysts can form in the most loaded part of the head and acetabulum. The neck of the femur is thickened and widened. The joint space is unevenly narrowed (up to 1/3-1/4 of the original height). A tendency to displacement of the femoral head is determined.
In the third stage , the pain is constant and occurs even at night. When walking, patients are forced to use a cane. There is a sharp limitation of all movements in the joint (flexion-adduction contracture) and hypotrophy of the gluteal muscles, as well as the muscles of the thigh and lower leg. There is a tilt of the pelvis in the frontal plane, which leads to functional shortening of the limb on the affected side. The patient is forced to step on his toes to reach the floor and tilt his torso to the affected side when walking to compensate for the tilt of the pelvis and shortening of the limb. This compensation mechanism leads to a shift in the center of gravity and overload of the joint. Radiographs reveal extensive bone growths on the side of the roof of the acetabulum and the head of the femur, and a sharp narrowing of the joint space. The neck of the femur is significantly expanded and shortened.
Unfortunately, there is still no unified theory of the pathogenesis of coxarthrosis. Most scientists believe that the trigger point is a violation of blood circulation in the joint due to both deterioration of venous outflow and disruption of arterial inflow. As a result of tissue hypoxia, underoxidized metabolic products accumulate, activating proteolytic enzymes and hyaluronidase in the synovial fluid, which destroy cartilage proteoglycans. It becomes thinner, loosens, fragments, and its shock-absorbing properties are lost. As a compensatory reaction of the articular surfaces of the hip joint, marginal bone growths are formed. Subsequently, sclerosis develops and cysts form in the articulating parts of the femoral head and acetabulum.
Treatment of coxarthrosis due to the lack of a single pathogenetic mechanism for the development of the disease is symptomatic. Its goal is to reduce pain, for which analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs are used (analgin, indomethacin, ortofen, etc.). To improve redox processes in cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors, vitamins, rumalon and other drugs are prescribed. In a clinic setting, electrophoresis of a solution of novocaine, dimexide, as well as ultrasound therapy, magnetic therapy, and laser therapy are used. After reducing the pain, manual massage of the lumbar region, hip joint, thigh and therapeutic exercises (kinesitherapy) are recommended.
Here we come to the most interesting question of this article. For us, kinesitherapists, it is obvious that therapeutic exercises in the treatment of coxarthrosis should not occupy the last, but the first, or rather, the leading place. Is it possible to consider a joint disease in isolation from its inseparable component - muscles and ligaments? After all, without their direct action, a joint is a set of bone structures, and nothing more. The ancient Greeks said: “The body is a single whole, treat the patient, not the disease.” The human body is perfect, there is nothing superfluous in it. And just as in nature the death of a mosquito leads to the death of entire populations of birds, so in the human body the loss of the quality of any muscle group, for example, hypotrophy of the adductor and abductor muscles of the thigh in coxarthrosis, leads to the loss of a large section of the vascular network feeding the joint (for reference : there are 3-4 capillaries in one muscle fiber). So what can we expect from drug therapy then? After all, anyone understands that the drug is delivered to the point of action through the bloodstream. And in our joint area there is ischemia and dystrophy. How much of the drug gets into the joint in this position? Minor...
Therefore, in the first place in the treatment of coxarthrosis, we must place physical therapy (kinesitherapy), which will allow us to influence the joint at the level of the pathogenesis of the disease, thus ensuring maximum effectiveness of the drug treatment carried out in parallel. After all, the “pumping” function of muscles cannot be replaced by any other procedures. And only by restoring the trophism of the joint can we count on regeneration processes in it. And if there are already existing defects in the structure of the joint, it is necessary to ensure the maximum level of safety for physical work with it.
For this purpose, strength training equipment with a strictly specified movement geometry is used.
Modern kinesitherapy centers use the MTB (Bubnovsky multifunctional simulator), which received a certificate in July 2011 as a means of medical rehabilitation. The main advantage of MTB is the possibility of decompression work on the affected joint under conditions of individual selection of load when performing each exercise. The treatment program for each patient is drawn up individually, based on the results of myofascial testing. During testing, the functionality of the musculoskeletal system is determined, i.e. the strength of individual muscle groups, the ability to move joints, the condition of the muscles of the upper limbs and back. In addition, the motor reaction of the muscles is determined, that is, the time spent on the ability to perform the next exercise; learning the technique of movements and diaphragmatic breathing, which is necessary to reduce intra-abdominal pressure when performing strength exercises.
The prescribed treatment program is carried out individually, under the supervision of an exercise therapy instructor. Our work experience shows that a well-trained muscular system helps to develop compensatory mechanisms even with severe disorders in the joint. But it would be better not to let them know...
Recently, a patient asked me a question that I could not answer. For several years she wandered around to different doctors (rheumatologists, surgeons, orthopedists) with one diagnosis - coxarthrosis of the second degree. Treatment was prescribed but there was no improvement in health. After studying at our center for a month, she noticed a clear positive trend and asked: “Why wasn’t I referred to you for treatment earlier? Aren’t our doctors interested in seeing the patient get better?”
No, I do not believe that our doctors do not want the best for their patients. Probably, the role of reasonable physical training for the treatment of joint diseases is simply underestimated. But in vain... After all, back in 1786, Professor N. M. Maksimovich-Ambodik said: “A body without movement is like stagnant water, which molds, deteriorates, rots .
So let's not let it come to this!
Physiotherapy and sports medicine doctor
E.I.Vlasova
What is offered to patients at stage 3 of coxarthrosis?
Traditionally, in advanced forms of coxarthrosis, patients are recommended to undergo hip replacement. This is a radical way to relieve a person from pain - expensive, lengthy, and requiring long rehabilitation. One of the surgical options is arthrodesis. The articular bones are fixed with metal staples to completely immobilize the supporting anatomical structure.
After total endoprosthetics, the patient undergoes long-term rehabilitation. During this period, it is very important to follow all recommendations, otherwise there will be a need for repeated intervention. If prosthetics are contraindicated, surgeons may recommend osteotomy - temporary fusion in the desired position of artificially broken hip bones. However, there are other, more gentle options.
Even at stage 3 of coxarthrosis, it makes sense to take a course of Noltrex intra-articular injections, which will help avoid complex surgery. The drug is injected into the joint, it expands the rubbing surfaces and restores the viscosity of the joint fluid. The hip joint is again able to absorb the load, so the pain during movement goes away. After 12-18 months, the course is repeated.
Noltrex is a good alternative to joint surgery in old age
Treatment of arthrosis with gelatin, recipes
Gelatin for the treatment and prevention of knee joint disease is used in the form of jelly, marshmallows, aspic, various tablets and drinks. There are several ways to drink gelatin for arthrosis .
Method 1:
- 1 tablespoon of the product is diluted in ½ glass of water;
- leave for 12 hours for swelling;
- then add half a glass of juice to the resulting mass;
- mix thoroughly until the granules are completely dissolved.
This medicine should be drunk in full in the morning on an empty stomach, and eaten after half an hour. The duration of therapy is 30 days.
Method 2:
- 5 grams of gelatin are stirred in 1 glass of water;
- The water should be warmed up well beforehand;
- wait until the mass thickens.
Before drinking the drink, you can stir in honey or sugar.
Method 3: dilute 10 grams of gelatin in 200 grams of any liquid and drink every morning and evening for 90 days.
If arthrosis of the joints is difficult to treat with gelatin in its pure form, it can be added to various food products: soups, drinks, yoghurts, broths, etc.
Jelly will be a very tasty medicine to treat the disease. It should be prepared like this:
- 10 grams of gelatin are diluted in 1/3 cup of preheated milk;
- add a little honey or sugar;
- do not touch until the mixture swells;
- Heat the drug over low heat until the gelatin is completely dissolved;
- cool and put in the refrigerator.
Use this jelly three times a day.
What therapeutic methods do most orthopedists prefer?
Orthopedists in different countries, with different experience and qualifications, make choices depending on the clinical picture of each patient. But there are also “favorite” treatment methods that are preferred in most cases. To quickly relieve pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are mainly used in a short course. Among chondroprotectors, the latest generation of drugs are in particular demand.
As a basic treatment method, orthopedists most often choose intra-articular injections of synovial fluid prosthesis. In the older age group, this is sometimes the only possible option, since the cardiovascular system in old age is not ready for general anesthesia, and not everyone agrees to undergo long-term rehabilitation. It is much easier, faster and safer to take a course of 2-4 injections - and get rid of pain for a year - than to undergo surgery.
Whatever therapeutic method the orthopedist chooses, he will always recommend reviewing the diet, as well as adding the right, complex carbohydrates to it, which will provide the body with energy. In the fight against chronic joint disease, it will never be superfluous!
External use of gelatin
In addition to oral administration, gelatin is also used for external treatment. For this purpose, various compresses, rubs and ointments are prepared based on the product.
The compress recipe is as follows:
- dry powder is poured onto the sore knee;
- place a wet cloth on top;
- wrap the knee with film and a warm scarf on top.
Such compresses are applied every night for 1 week.
There is another way to apply a compress:
- Soak a gauze bandage in warm water;
- Place gelatin between the layers;
- apply the bandage to the knee and wrap it with film;
- wrap your knee with a warm blanket or scarf.
Keep this product for at least a couple of hours. The course of therapy ranges from 7 to 14 days.
It does not really matter what kind of gelatin is used: in the form of granules, powder or foliage. They are the same product, but different types require different amounts of time to swell.
Traditional healers recommend using gelatin in complex therapy. At the same time, you should take the product orally, apply compresses and drink various vitamin complexes for joints.
Traditional medicine does not consider gelatin a drug, but its use should still be discussed with your doctor in order to avoid negative consequences for the entire body.