Malignant tumors often lead to bone damage. As a rule, we are talking about metastases - the elimination of tumor cells from the site of primary localization and their spread throughout the body with the emergence of new foci.
- Bisphosphonates for bone damage
- Classification of bisphosphonates
- Use of bisphosphonates for bone metastases
- Use of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis
- Hypercalcemia and bisphosphonates
- Side effects from the use of bisphosphonates
Most often, breast and prostate cancer metastasizes to the bones. Also, bone metastases can occur with kidney cancer, thyroid cancer and malignant tumors of the lung. The greatest destruction is observed in myeloma. In order to understand how metastases affect bones, let's first talk about healthy bone tissue.
Bone tissue is a type of connective tissue. Throughout life, it undergoes cyclical changes - bone formation is replaced by resorption (destruction of bone tissue). This process is called remodeling. It takes place in several stages:
- Resorption. Bone tissue contains special cells called osteoclasts. Their main role is to secrete substances that destroy the mineral skeleton of the bone, leading to erosion. During normal times, these cells are in a “dormant” state, but during the resorption phase they are activated by special molecules produced by osteoblast precursors and begin to do their job.
- Inversion. During this phase, mononuclear cells remove all destroyed tissue, preparing the site for reconstruction.
- Recovery. Restoration of the mineral matrix of the bone occurs due to the action of other cells - osteoblasts, which synthesize organic substances that make up the matrix of bone tissue.
- State of rest. At rest, bone tissue does not exhibit cellular activity or exhibits it minimally. Basic biochemical processes are “waiting” for a new round of the remodeling cycle.
The main point in the formation of bone metastases is the disruption of the remodeling process. Cancer cells secrete substances that stimulate both osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Thus, resorption occurs and, at the same time, abnormal growth of bone tissue occurs. The main manifestations of bone metastases are:
- Pain.
- Pathological fractures that occur without serious mechanical stress.
- Compression of the spinal cord, which can be caused by compression of the nerve roots by tumor masses or bone fragments resulting from a pathological fracture.
- Hypercalcemia is an increase in the level of calcium in the blood, in which a complex of pathological symptoms develops, for example, intoxication or a violation of the blood coagulation system. In some cases, hypercalcemia can be fatal.
To treat bone metastases, a comprehensive approach is used, including antitumor methods, for example, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, and palliative surgery. As part of pathogenetic treatment, bisphosphonates are used.
Bisphosphonates for bone damage
Bisphosphonates are drugs that affect bone metabolism. Their chemical structure is similar to natural inorganic phosphates. They have a high affinity for calcium ions, due to which they penetrate deep into bone tissue.
The mechanism of their action is based on the inhibition of the development and vital activity of osteoclasts, which is realized in several ways:
- Direct effect on osteoclasts, due to which they lose their ability to resorb bone tissue, or even die.
- They act on osteoclast precursor cells, preventing their development and differentiation.
- They have an effect on osteoblasts, which reduces the production of osteoclast-stimulating factor.
In addition, there is evidence that bisphosphonates reduce tumor volume. Why this happens is not entirely clear. It is assumed that due to decreased resorption, the tumor does not receive enough growth factors and cytokines that are contained in bone tissue.
The drug Denosumab
Denosumab is a drug consisting entirely of human antibodies (lgG2), which replaces bisphosphonates. The mechanism of action of this substance includes the ability to inhibit the functionality of osteoclasts that destroy the old bone structure.
Denosumab-based drugs:
- It makes the skeleton stronger, increases density, thereby protecting bones from fractures. Produced under the name Prolia in the state of Puerto Rico, the cost of the drug in Russia averages 15,580 rubles.
- Treatment is carried out by injecting a solution under the skin in the area of the thigh and abdomen, the course is once every six months.
- It is used at high risk of fractures , in cases where the use of other means is impossible.
Prolia
Classification of bisphosphonates
In medical practice, 8 bisphosphonate compounds are used, which, depending on their chemical structure, are divided into three groups:
- Nitrogen-free bisphosphonates. These are first generation drugs. These include clodronate, tiludronate and etidronate.
- Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. These are second generation drugs. These include pamidronate, risedronate, and alendronate.
- And finally, drugs of the latest, third generation. They are amine-containing bisphosphonates. These include zoledronic acid and ibandronate.
Clodronate
Clodronate is a first generation bisphosphonate. It is available in a form for oral use as well as for intravenous infusion. The disadvantage of oral administration is poor absorption from the stomach.
Pamidronate
Pamidronate is a second generation bisphosphonate drug. It differs from the first one in that it has one nitrogen atom in the formula. Due to this, it can suppress the process of protein rearrangement in osteoclasts, which ultimately leads to their death through apoptosis. This drug is used to treat osteolytic metastases, which are characteristic of multiple myeloma and breast cancer.
The problem with its use is that maximum effectiveness in the treatment of hypercalcemia requires the administration of high doses of the drug. However, this is accompanied by a high risk of toxic effects from the digestive system. In addition, the effectiveness of pamindronate is reduced in patients with circulating PTHrP (a protein that is formed during osteolysis)
Pamidronate is administered by intravenous infusion. A single dose is 60-90 mg. The duration of the infusion is 4 hours. The drug is used once every three weeks.
Ibandronate
Ibandronate belongs to the third generation of bisphosphonates and already contains 2 nitrogen molecules. It is more effective in patients with elevated PTHrP levels, causes fewer complications, and is not nephrotoxic. It is used once every 4 weeks in the form of 15-minute intravenous infusions.
Zoledronic acid
Zoledronic acid is a third generation drug. It contains 2 nitrogen atoms located in opposite positions. This structural feature allows it to have not only an anti-osteolytic effect, but also a negative effect on the malignant tumor itself. In particular, zoledronic acid has an antiangiogenic effect, preventing the growth of endothelial cells, thereby disrupting the blood supply to the tumor, which leads to inhibition of its growth.
The drug is prescribed intravenously at a dose of 4 mg. The infusion lasts 15 minutes. Frequency of application: once every 3-4 weeks. During the treatment period, it is necessary to take vitamin D and calcium, due to the risk of transient hypocalcemia.
How to use
Bisphosphonates have their own specific guidelines for proper administration that must be followed.
- Drink the medicine only on an empty stomach, in the morning, with plenty of water.
- The first meal after taking the drug is possible no less than an hour later.
- To prevent the effect of the medicine from being inhibited, you should drink it with plain water.
- You should be in an upright position for 1-1.5 hours.
- Together with a course of bisphosphonates, you need to take vitamin D or calcium.
Use of bisphosphonates for bone metastases
The use of bisphosphonates for bone metastases has become the gold standard of treatment. Such drugs are effective for about 2-3 years, and after the development of resistance they are changed to targeted therapy with denosumab.
Treatment begins after bone metastases are determined using x-ray studies. Scintigraphy is not suitable for detecting osteolytic metastases.
Definition of Biophosphates
Biophosphates are modern medications of synthetic origin that help block cells that destroy bone tissue in the body. In addition, over time, these medications can restore bone structure.
Today they are actively used to treat osteoporosis and other pathologies that cause bone fragility. Many experts also claim that biophosphates can have a beneficial effect on the body during cancer complications that provoke tumors in the bones, as they prevent the spread of metastases and reduce pain.
Use of bisphosphonates for osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a chronic disease characterized by loss of bone mass. As a result, bone density decreases and the risk of pathological fractures increases. This pathology is more typical for women during menopause, but it also occurs in older men.
To treat the disease, an integrated approach is used, including a special diet and physical therapy. Pharmacotherapy is also used in individuals at high risk of developing pathological fractures. The drugs prevent bone loss in clinical trials. The most effective in this regard are alendronate, zoledronic acid and risedronic acid.
Effectiveness studies
Studies have shown that long-term use of bisphosphonates strengthens bones and reduces the risk of fractures.
This table compares the clinical effectiveness of bisphosphonates in preventing osteoporosis-related fractures.
| Clinical study | Number of patients | Bisphosphonate and duration of use | Reducing the risk of spinal injuries | Reduces the likelihood of damage to other bones |
| VERT-NA (16) | 2458 | Risedronate (5 mg/day) 3 years | 41 | 39 |
| VERT-MN (27) | 1226 | Risedronate (5 mg/day) 3 years | 49 | 33 |
| FIT I (4) | 2027 | Alendronate (5 mg/day) 2 years, (10 mg/day) 1 year | 47 | 20 |
| FIT II (10) | 4272 | Alendronate (5 mg/day) 2 years, (10 mg/day) 1 year | 44 | 12 |
| BONE (8, 26) | 2946 | Ibandronate , 3 years | 62 | 60 |
Hypercalcemia and bisphosphonates
Until relatively recently, hypercalcemia (increased calcium levels in the blood) was one of the most common life-threatening complications of bone metastases. At the end of the twentieth century, about 20% of patients with metastatic breast cancer developed this condition. However, thanks to the use of bisphosphonates, the incidence of such complications has decreased significantly.
There are two mechanisms for the development of hypercalcemia:
- The first is based on the fact that bone metastases lead to osteolysis, in which calcium from destroyed bone tissue enters the blood. This pathway is implemented in myeloma and breast cancer metastases.
- The second mechanism is not associated with bone metastases, but is realized by stimulating calcium resorption under the influence of parathyroid hormone-like proteins, which can be secreted by extraosseous tumor foci.
Hypercalcemia leads to impaired kidney function, causing a lot of fluid to be excreted in the urine. As a result, dehydration occurs, kidney function deteriorates even more, calcium is not excreted, and the situation closes in a vicious circle.
The clinical picture shows the following symptoms:
- Cardiovascular system disorders - decreased blood pressure, arrhythmias and other heart disorders.
- Gastrointestinal disorders - nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, pancreatitis.
- Impaired consciousness, lethargy, stupor and even coma.
The main points in the treatment of hypercalcemia are fluid replacement, increased calcium excretion and blocking tumor-induced bone resorption. It is at this last moment that the action of bisphosphonates is directed. Currently, they are recommended to be prescribed to all patients with identified bone metastases.
A little history
It turns out that bisphosphonates were discovered by scientists quite a long time ago, back in the 19th century. For the first time, the synthesis of the first BFs was carried out in Germany. The surprising thing is that initially these substances were used only in various industrial sectors (in the production of mineral fertilizers, textile production, oil refining, etc.) and had nothing to do with medicine.
For medical purposes - for the treatment of bone tissue - bisphosphonates began to be used only in the middle of the twentieth century, when their amazing ability to influence the processes of both calcification and decalcification was discovered. Since then, bisphosphonates for osteoporosis have been widely used throughout the world.
Side effects from the use of bisphosphonates
The following side effects may occur during treatment with bisphosphonates:
- Dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence.
- Increased body temperature, accompanied by muscle aches.
- Transient hypocalcemia is a decrease in calcium levels in the blood.
- Headache.
- Itchy skin.
- Rash.
- The appearance of blood in the urine.
A rather rare, but at the same time serious complication is aseptic osteonecrosis of the jaw. Most often it occurs after dental procedures. In this regard, it is recommended to delay the start of treatment with bisphosphonates until the oral cavity is sanitized and its mucosa is healed.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Acute phase reactions
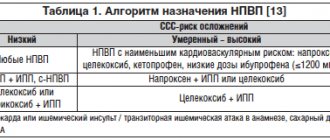
From 10 to 30% of patients after the first infusion of BP experience manifestations of acute phase reactions (APR): fever, general malaise, myalgia, arthralgia, bone pain [1, 2]. The cause of the development of OPD is a transient increase in the level of pyrogenic cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α, due to the activation of γδ-T lymphocytes and the development of a Th1 immune response [3, 4]. These phenomena occur 1–3 days after administration of the drug and can last up to 7–14 days, but their frequency and severity decrease sharply with subsequent infusions. Manifestations of OPD can be controlled by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or paracetamol. When using oral BP, such reactions occur much less frequently and their manifestations are less pronounced.


![Table 1. Main risk factors for AP and bone fractures [2]](https://shoes-clinic.ru/wp-content/uploads/tablica-1-osnovnye-faktory-riska-op-i-perelomov-kostej-2-330x140.jpg)