A purulent coccyx cyst is an inflammatory process under the skin in the sacrococcygeal region, most often found in young men. A cyst in the sacrococcygeal region appears as a result of exposure to various factors:
- A congenital anomaly that occurs when embryonic development is disrupted in the early stages of pregnancy.
- The anomaly is formed during growing up due to improper escalation of hair.
- It can develop with a sedentary lifestyle.
- Weak immunity can cause illness.
- Hereditary predisposition, trauma and other factors.
Treatment of pathologies of the sacrococcygeal region is carried out in the coloproctology department of the Yusupov Hospital. Yusupov Hospital is a multidisciplinary medical center, which includes several clinics, a clinical laboratory, diagnostic and rehabilitation centers, and a hospital. The hospital performs surgical operations in operating rooms equipped with innovative equipment. The latest world developments in the field of medicine and medications certified in Russia are used to treat patients. Consultations and treatment of patients are carried out by experienced doctors: doctors of science, professors, highly qualified doctors, patients are provided with various types of medical care.
Cyst prevention
Prevention consists of preventing embryonic formation in the coccyx area, although, of course, it is quite difficult to prevent pathology. The main thing is to observe safety and personal hygiene measures after surgery to remove a cystic tumor:
- avoid a sedentary lifestyle, walk more in the first month;
- restriction on heavy lifting in the postoperative period;
- constantly wash the intergluteal fold with solutions and antiseptics after removing the sutures;
- observe general hygiene rules;
- monitor the postoperative area until it heals.
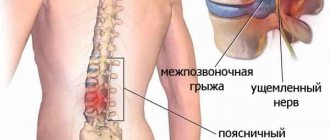
A cyst in the lumbar area is a serious pathology and patients are not recommended to use painkillers or conservative treatment methods. There is nothing terrible, but the formation must be cut out surgically, otherwise complications, relapses, and secondary infection are inevitable.
An active lifestyle will help prevent complications
A coccyx cyst is considered a congenital pathology. If not eliminated in time, then a progressive course and adverse consequences for patients are guaranteed. Only timely adoption of measures and surgical intervention to excise the tumor will allow:
- will increase the chances of a full recovery,
- minimize the risk of relapse,
- contribute to full recovery.
If unpleasant symptoms of a cyst in the coccygeal region appear in the form of pain when sitting, swelling, redness of the area, the presence of discomfort, the sensation of a foreign object, patients should not hesitate to contact a proctologist. Otherwise, to treat the anomaly, you will have to resort to coccygectomy.
Interesting and useful information about the problem can be found in the video:
You can learn about the operation to excise the formation from the following video:
How to prevent cysts from appearing?
To prevent tumors from appearing on the tailbone, it is necessary to maintain personal hygiene, regularly remove hairs from this area, and avoid injuries and damage to the spine. But if a woman has an anomaly in the development of the sacral zone, one day the tumor will make itself known.
To avoid recurrent tumors after surgery, the doctor must follow a number of rules during surgical removal:
- All elements of the cyst are removed. To make them clearly visible, a blue dye is first injected into the epithelial tract.
- Premature healing of the wound is not allowed to prevent the formation of a too thick scar.
- When applying a bandage, the doctor checks for any residual cavities.
We advise you to study - Electrophoresis for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Also, for another 6 months after the operation, the woman should regularly remove hair using depilatory creams. You cannot use a razor - it can cause ingrown hairs.
The cyst itself is not dangerous and may not bother the patient for a long time. But if ulcers, pain and discomfort suddenly appear, you should urgently consult a doctor. Otherwise, serious complications are possible.
Features and types of the disease
Depending on the characteristics and stage of development of the cyst, the disease has its name:
- epithelial course;
- coccygeal fistula;
- dermoid cyst of the coccyx;
- pilonidal sinus.
Each of these types of illness has its own structure and location. The epithelial tract forms and develops under the epidermis. A dermoid cyst appears on the skin. The pilonidal sinus is formed with the development of abnormal hair growth. The coccygeal fistula is an already mature form of the cyst with all its inflammatory processes and abscesses. All these varieties of the disease are nothing more than its forms, manifestations and stages, which form and develop one after another.
An epithelial cyst is found in people under thirty years of age, and most often it develops in men. It does not occur by itself, as it is an abnormal congenital manifestation. Experts believe that the main reason for the formation of cysts is various defects that occurred during the development of the embryo during pregnancy.
It is impossible to detect a cyst at a young age or at birth, since its symptoms do not manifest themselves for a long period until inflammatory reactions occur. The only way to treat a cyst on the tailbone is surgery.
Main manifestations of pathology
For many years, a person with a developing coccyx cyst lives quite carefree, since there are no obvious signs and characteristic symptoms of the disease. When the development of the disease reaches a certain stage, painful sensations and inflammatory processes appear in the coccyx area.
Such symptoms indicate the acute development of a cyst. The impetus for the development and formation of a cyst is various ailments and injuries of a mechanical nature. Inflammation of the coccyx cyst affects the natural subcutaneous fat layer, provoking the development of a small tumor that is constantly growing.
The general symptomatic picture has the following manifestations:
- The patient feels severe discomfort in the intergluteal folds. It begins to seem to him that a foreign object has appeared in this place, interfering with sitting, walking, and playing sports. Lying on your back, you feel constant discomfort.
- A small hole appears in the intergluteal folds. When this hole begins to become clogged, swelling develops. The resulting swelling may move away from the line of the buttocks.
- The hole between the buttocks may enlarge and ooze. This period is characteristic of the active phase of the pilonidal cyst.
- During the development of the acute form, several holes may appear. Through them, the pilonidal cyst pushes out purulent, mucous fluid. In places where the development of the disease is particularly active, channels open. In the passive zone, the channels and openings close, forming scars.
- During the passive stage, internal processes do not stop, a cyst with an abscess is formed, a high temperature and severe pain appear.
If such manifestations and signs are not paid attention to in time, serious consequences may occur and the treatment process will be quite lengthy and not always successful.
Classification according to ICD 10
Pilonidal cyst in the international classification of diseases ICD 10 is coded:
- L00-L99 class 12 - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
- L05- Pilonidal cyst.
- L05.0 – Pilonidal cyst with abscess.
- L05.9 - Pilonidal cyst without abscess.
- L00-L08 - Infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue.
Drug treatment
The process of treating cysts with medications is usually carried out in conjunction with surgery. Without this, treatment is symptomatic, unless the disease is in its infancy.
Efficiency
This type of treatment should be carried out after consultation with a doctor. You need to carefully look at the composition of the drugs and strictly adhere to the dosage to avoid negative consequences. All the necessary information about taking medications is in the instructions for them, and you must also follow the doctor’s instructions. Also, under no circumstances should you use the following drugs in a mixture with alcohol.
Indications and contraindications
The indication for treatment of a coccyx cyst at home is a weak degree of progression of the cyst, in which the primary and secondary openings have not formed. This type of treatment is also effective in alleviating the symptoms of the disease.
We advise you to study - A set of exercise therapy exercises for scoliosis
It is necessary to follow the correct order of taking medications and do not forget to drink bifidobacteria to normalize intestinal function after taking antibiotics. So what needs to be done to treat a coccyx cyst? Below are the remedies by category that correspond to the order in which you take your medications.
Antibiotics for coccyx cyst
- Summed is an antibiotic based on azithromycin. Dosages must be carefully observed due to the strong effect.
- Augmentin - this drug is an antibacterial agent of the penicillin series. Another name is Amoxicillin.
- Pefloxacin is an antibacterial medication in the form of film-coated tablets.
Anti-inflammatory
- Civilin - this medicine is an extract of burdock root in combination with bean leaves. Has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect.
- Ibuprofen gel is also a powerful remedy that helps against inflammation. In addition, it also has analgesic and antipyretic properties, which is good for cysts.
- Voltaren Emulgel – has pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Like ibuprofen, it reduces fever, although it is not as effective.
Regenerating
- Bepanten is an excellent remedy that helps in healing the skin. Can be found in the form of cream, gel or tablets.
- Artra - this drug is aimed at regenerating cartilage, which suffers when a coccyx cyst develops.
- Aloe vera extract, a well-known natural remedy, is absorbed into the deep layers of the epidermis, helping to heal cyst marks.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine cannot cure the disease, but it can significantly help reduce symptoms. Folk recipes, like pharmacy ones, can cause similar effects. Let's look at a few effective recipes:
Propolis. To make it you will need propolis tincture (6 parts alcohol to 1 part propolis) and a napkin (necessarily sterile). Soak, press to the sore spot and leave for 2-3 hours.
St. John's wort. Dried St. John's wort is crushed, three tablespoons are measured and poured into the pan. Pour in 0.5 liters of hot water and boil for 15 minutes.
Plantain. Fresh plantain leaves are rinsed with boiling water and crushed until juice is formed. A gauze pad is soaked in this juice and applied to the swelling for 15-20 minutes.
Calendula. You will need a pharmacy tincture of calendula (alcohol) and a soft napkin. You need to keep it for at least 4 hours, and preferably all night.
There is an effect from these prescriptions, but it is temporary; in any case, you should not delay visiting a doctor.
Drug treatment
Treatment with medications is most often used to relieve pain and reduce or stop inflammation. Drugs are prescribed to the patient before and after surgery. Analgin is often prescribed for pain relief, and Ibuprofen and its analogues are a good anti-inflammatory drug.
The dosage of drugs is determined exclusively by the attending physician in accordance with the patient’s condition. The doctor prescribes antibiotics at the time of severe suppuration to prevent the infection from spreading.
Many antibiotics have serious side effects, which is why it is very important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescription so as not to harm your body even more seriously.
Folk remedies in the treatment of coccyx cysts
To alleviate the course of the disease, traditional medicine can help, but consultation with a doctor is required. If the doctor does not object, you can use the following recipes:
- Tar compress. The mixture is prepared from 2 tbsp. spoons of butter and 1 tbsp. fly in the ointment. It is applied to the area of the cyst and secured with a bandage. It is better to do the procedure before bed, leaving it overnight.
- Propolis tincture. You can use a tincture made from 1 part propolis and six parts alcohol. Moisten a sterile napkin with the infusion and apply for 2-3 hours. Repeat this procedure for a week.
- Tincture of calendula. This tincture can be bought at a pharmacy. A napkin is moistened with it and applied to the sore area. The napkin is covered with compress paper and secured with a bandage. Keep the compress for 3-4 hours. Usually it is enough to do 7 procedures.
- Plantain compress. Fresh plantain leaves are ground to release the juice. Soak gauze in juice and apply a compress to the wound for a few minutes.
Causes of suppuration of the epithelial coccygeal tract
The defect in question is of a congenital nature, representing a narrow canal located under the skin in the area of the intergluteal fold, very close to the coccyx.
Each embryo develops a tail at the 10th week of intrauterine development. During the normal course of pregnancy, this tail should eliminate itself - however, in some cases, there is a relapse of the muscle tissue of the tail, which leads to the formation of this defect.
The specified pathological tube is lined with epithelium from the inside. Therefore, as on the skin, sweating occurs here, as well as hair growth. The waste products of the intravenous epithelium are discharged out through one or more pinholes.
In the absence of any exacerbations, the pilonidal sinus does not cause discomfort in a person, and it can be detected by chance during a medical examination of the intergluteal area.
The epithelial coccygeal duct is formed in the embryonic period due to a failure in fetal development. As a result, a hole lined with epithelium remains in the area of the gluteal fold (approximately 4–7 cm from the edge of the anus). It can be almost invisible, in the form of a point, or, conversely, quite wide, resembling a funnel. This hole is the beginning of the coccygeal passage. The latter is not connected with the coccyx and sacrum; it ends blindly in the subcutaneous tissue.
There is an assumption that ECC is formed due to improper hair growth in the anus and its ingrowth into the skin. For this reason, foreign medical experts call this pathology a pilar cyst.
The coccygeal passage is a congenital pathology caused by a defect in intrauterine (embryonic) growth. Experts cannot say exactly what exactly provokes such a failure in development, but it is known that the risk of the formation of an epithelial canal in the coccyx is higher if a woman suffers from endocrine disorders, pathologies of the heart, or the musculoskeletal system.
- pathologies of the mucous uterine lining (endometriosis, endometritis, endometrial hyperplasia of the glandular type);
- uterine fibroids;
- fibroadenoma of the mammary glands;
- insufficiency of the adrenal cortex or pituitary gland;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism, diffuse goiter, hypothyroidism).
We advise you to study - Pain in the back of the neck and radiates to the head
What is EKH
The epithelial tract is a narrow tube in the midline in the fold between the buttocks, not connected to the coccyx or sacrum, the end of which is located in the subcutaneous tissue. The tube opens with pinholes (1 or several) on the skin - the primary epithelial tract.
Through pinholes (entry gates for infection), waste products of the epithelium that lines this passage are periodically released to the outside.
When these openings become blocked or mechanical injuries occur, the contents accumulate in the lumen of the passage and inflammation occurs. During inflammation, the ECX expands, its wall is destroyed, and fatty tissue is involved in the inflammatory process. The abscess often reaches a large size, then breaks through, forming an opening of a purulent fistula, which is called a secondary opening.
Diagnosis of the epithelial coccygeal tract
Diagnosis of a coccyx cyst is quite simple; the diagnosis is made according to the localization of the process characteristic of this disease. Patients complain of aching or twitching pain, discomfort in the presence of a tumor in the intergluteal fold, purulent discharge from the orifices.
An important diagnostic sign of a coccyx cyst is the primary fistula openings in the form of depressions of various sizes, located one above the other along the midline of the intergluteal fold, 2-3 cm above the anus. There is no connection between the fistula and the rectum. In some cases, the primary openings are located low above the anus, and they resemble perirectal fistulas.
Diagnosis of purulent complications of ECX is much more difficult. Often patients are sent to the hospital with an incorrect diagnosis: acute paraproctitis, pararectal fistula, coccyx osteomyelitis, coccyx abscess, which leads to ineffective treatment, prolongs the patients’ disability, and increases the number of advanced cases. ECC should be distinguished from rectal fistula, benign cystic formations, osteomyelitis of the sacrum and coccyx bones, pyoderma with fistulas. Therefore, to establish the correct diagnosis, sigmoidoscopy and probing of the tract are necessary. According to the clinical picture, ECX is divided into uncomplicated and complicated by a purulent process.
Complicated ECC can be in the stage of inflammation (acute or chronic) and remission.
When the separation of waste products from the epithelium is delayed, patients note the appearance of a small painless infiltrate with smooth contours, which creates discomfort when moving.
When the contents of the ECC become infected and there is acute inflammation, pain appears, body temperature rises, and the skin at the site of infiltration swells and becomes hyperemic.
With chronic inflammation, scanty purulent discharge from the bursa is observed, without swelling or hyperemia. Near the secondary holes, scar tissue changes appear. Some secondary openings become scarred, and discharge is observed through others.
When inflammation is in remission for several months or years, the secondary openings of the ECC become scarred; when pressure is applied, no discharge appears from the primary openings.
A developed abscess can open on its own or with the help of a surgeon. If an independent autopsy occurs, the pain disappears, the wound closes, and a deceptive period of well-being begins. In this case, complete recovery does not occur, since the patient is left with a temporarily attenuated focus of chronic infection, which often leads to a secondary exacerbation after several months or years with the formation of fistulas, abscesses, and phlegmon.
During the lull between exacerbations, patients are bothered by dull aching pain or discomfort in the coccyx area, often in a sitting position, and discharge from the primary orifices.
Diagnostics
A coccygeal cyst is easy to diagnose: it is detected during a routine examination and palpation. The doctor makes a diagnosis based on the main sign of pathology - the presence of a primary fistula opening.
Sometimes it is necessary to exclude anomalies in the form of a pararectal fistula, proctitis, sacral osteomyelitis, or rectal fistula. Then, as an additional study, the following are prescribed:
- Sigmoidoscopy.
- Probing of fistula passages.
- X-ray of the pelvic area.
- Biopsy with histology (if cancerous degeneration is suspected).
If a person notices inflammation of the coccygeal tract, the presence of a fistula, or pain in the intergluteal area, then he should consult a proctologist. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis and, if necessary, refer you to other specialists for consultation.
Establishing diagnosis
The coccygeal cyst progresses quite quickly, then the inflammatory process covers an increasingly larger area of soft tissue, and complications develop. Therefore, it is recommended to start treatment as early as possible. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a proctologist.
Important. It is not difficult to identify a coccyx cyst; the main thing is to accurately determine its location. After all, often abnormal holes do not coincide with the source of formation.
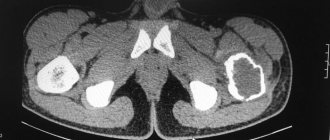
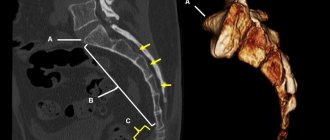
At an advanced stage, when the formation has already festered and accumulations come out of the canal, it is quite simple to make a diagnosis. However, sometimes a doctor may prescribe an x-ray to distinguish a coccygeal cyst from similar diseases, for example, coccyx osteomyelitis, paraproctitis (formation of pathological canals between the rectum and skin due to suppuration).
In the early stages, the following instrumental diagnostic methods are used to detect a tumor:
- X-ray of the pelvis.
- Computer or magnetic resonance imaging.
After making a diagnosis, the doctor draws up a treatment strategy.
No ads 2
Suppuration of coccyx cyst: treatment
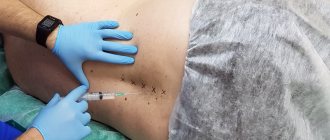
Inflammation of the epithelial coccygeal duct is treated in the Yusupov multidisciplinary hospital, in the coloproctology department. Diagnosis of the disease begins with examination and interview of the patient. The proctologist listens to the patient’s complaints, determines the nature and duration of the complaints, finds out whether there were injuries in the coccyx area, whether there are functional disorders in the pelvic organs. The doctor examines the condition of the skin of the buttocks, sacrococcygeal region, perineum, conducts a rectal examination for hemorrhoids, rectal prolapse, fistulas, anal fissures, tumors. The proctologist at the Yusupov Hospital can prescribe sigmoidoscopy, fistulography, and ultrasound of the sacrococcygeal area. Suppuration of a coccyx cyst is treated surgically.
The indication for sending a patient to a hospital is acute inflammation of the epithelial coccygeal duct, planned treatment of the pathology. Depending on the classification and severity of the disease, surgical treatment tactics are selected. The operation to remove the cyst is carried out as planned or emergency, depending on the patient’s condition.
There are several methods of surgical treatment of the epithelial coccygeal tract:
- The method used for a coccyx cyst complicated by an abscess is a two-stage operation. The first stage is opening the abscess and cleaning the cavity. The patient receives antibacterial therapy for seven days. Then the second stage is carried out with the removal of the affected tissues of the coccygeal tract.
- Complicated course of the disease - the abscess is opened, the purulent contents are removed, to eliminate the risk of recurrence of the fistula, the edges are sutured to the bottom of the wound. The method has the disadvantage of an extended rehabilitation period.
- Basque method. The coccyx cyst is excised under the skin. The primary coccygeal passages are sutured, and drainage is placed in the secondary passages for the outflow of secretions.
- Karydakis method. During the operation, the inflamed area with a flap of skin is removed. The wound surface recovers faster, the rehabilitation period is short.
- Sinusectomy. Removal of the cyst can be carried out in the absence of a purulent process. A substance (methylene blue) is injected into the opening of the epithelial coccygeal duct, which determines the number of openings of the coccygeal duct and location. Then, using an electrocoagulator and a probe, resection is performed. No sutures are required.
- Removal of a cyst with a laser. The operation to remove a coccyx cyst is performed using a beam of radiation. The patient can go home on the day of surgery, if there are no complications.
- If multiple coccyx cysts complicated by fistulas are diagnosed, plastic surgery is performed using a displaced flap. Not only the epithelial coccygeal duct with its branches is excised, as well as the surrounding fatty tissue. The cavities that formed after removal of the cyst are closed with displaced skin flaps.
Therapeutic measures
Cyst surgery
It is impossible to cure a cystic formation on the coccyx without surgery, since relapse will constantly occur, which will lead to the development of a chronic form and complications. Surgical intervention is prescribed by the attending physician individually for each patient. Before surgery, the doctor may prescribe medications that will ease the pain and alleviate the patient's condition. It is recommended to treat with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs:
- "Ibuprofen";
- "Aspirin";
- "Diclofenac";
- "Ketoprofen";
- "Piroxicam".
Varieties
Excision of a coccyx cyst is carried out in several ways, depending on the severity of the disease. The operation to remove the formation is carried out at the stage of remission; as an exception, emergency surgery is performed during an exacerbation. Anorectal fistula is removed under general or local anesthesia. The table shows the main methods for removing coccyx cysts.
| Method | Features of the operation | Recovery |
| Open | Opening the abscess and clearing the resulting pockets of pus | About 2 months |
| Complete section of cystic formation and lymph | ||
| Closed | Cyst excision and wound drainage | From 14 to 21 days |
| Forming a small hole to allow contents to escape | ||
| Bascom | Excision of a subcutaneous cyst from the primary formation to the fistula | |
| Cleaning the wound and installing drainage | ||
| Karydakis | Removal of the cyst and part of the skin | |
| Displacement of the wound to the central intergluteal line | ||
| Installing drainage and suturing the wound |
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient will have a long rehabilitation, during which certain rules must be followed so that the recovery process goes faster and does not become complicated:
Do not sit for 3 weeks after the cyst is removed
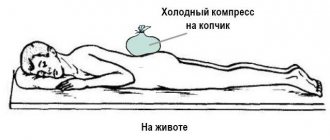
Monitor the scar carefully and see a doctor regularly. During the postoperative period, lie on your back carefully. Avoid long walks and activities. Avoid hypothermia or overheating of the body. After removing the cyst and removing the sutures, rinse the scar with warm running water. Do not lift heavy objects or perform physical activity. It is recommended to depilate the operated area for six months.
Epithelial coccygeal duct (ECC), or coccyx cyst (not to be confused with an epidermoid cyst), is a disease characterized by the presence in the coccygeal region of an elastic cord, with two or more holes, lined with the epidermis. Each stroke-cord has a depth of 2-3 cm and does not contact the tailbone itself. If you look at the frequency of the disease among men and women, the former suffer from this disease three times more often.
Surgery
Treatment of coccyx cysts is carried out with the help of surgery. During the operation, local anesthesia is used. Treatment methods vary depending on the stage and characteristics of the disease.
There are four types of coccyx cyst surgery:
- Open wound method. It is the most complex type of intervention. Postoperative recovery lasts up to 2 months. It is used to excise a coccygeal cyst that is severely advanced or accompanied by a fistula and inflammation of nearby structures. The entire formation is cut out, and the wound on the sides is sutured to the bottom. To allow pus and lymph to drain freely, drainage is used. Relapses of the disease after the recovery period are completely excluded.
- Closed wound. Having cut out the coccygeal cyst, the doctor drains the purulent accumulations. The surgeon leaves a small hole to drain fluids from the wound. Postoperative rehabilitation lasts from 2 to 3 weeks. The method significantly reduces the risk of re-formation of a coccyx cyst.
- Operation using the Bascom method. The surgeon removes the skin, starting from the abnormal canals of the primary type and ending with the area of the fistula. The area affected by the cyst falls into the fold between the buttocks.
- Karydakis method. When removing a coccyx cyst, the doctor moves the formation to the middle of the gluteal fold. The affected area and skin are then removed. Thus, the duration of the postoperative rehabilitation period is reduced.
The cost of removing a pilonidal cyst depends on the location of the operation, the method of excision, and complications of the pathology. The procedure is not considered complicated and is quite accessible. The price of the operation varies from $200 to $1000.
Manifestations
The pathology is inflammatory in nature, so it can become chronic. Then periods of exacerbation alternate with remission. If the patient continues to ignore the problem, then the likelihood of the formation of a fistula increases, through which purulent fluid, mucus and dead epithelial cells come out.
If the disease is congenital, then the cyst constantly develops in the subcutaneous fat. It has a latent course for a long time, only sometimes the patient feels slight itching and discomfort in the affected area. These are the first signs of pathology.
Under the influence of the unfavorable factors described above, the abnormal opening becomes clogged and the formation rapidly develops.
Pathological course in the fold between the buttocks
The following manifestations indicate that the cyst has festered:
- A foreign body is felt in the area between the buttocks, discomfort appears while walking and in a sitting position.
- The skin on the affected area turns red and swelling appears.
- An oval compaction appears in which cellular elements, blood, and lymph accumulate. When the patient tries to feel it, pain appears. The size of the formation may vary, some of them extend to the buttocks (to the right or to the left).
- As the purulent process develops, a sharp pain appears, which intensifies while walking or sitting.
- An abnormal opening appears in the gluteal fold through which exudate or pus comes out.
- As the disease worsens, additional holes may appear in addition to the existing one. Discharge oozes through them, and the passive passages heal.
- When the formation suppurates, the patient experiences fever, headache, and weakness.
These are the main symptoms of coccyx cysts, which appear at different stages of the pathology.
It is important to visit a doctor when the first suspicious signs appear.
Recovery after surgery to remove a herniated disc.
Restoration activities
The postoperative period for a coccyx cyst requires careful attention to the body and compliance with a number of rules.
Sutures can be removed two weeks after surgery. During this time, the patient needs to go to the dressing every day. After removing the sutures, the doctor treats the operated area with an antiseptic; later the patient should repeat the procedure independently. After another month, the patient can resume his usual lifestyle. However, for eight weeks after the operation, the patient is prohibited from exercising, carrying heavy things, sitting on hard surfaces, and sleeping on his back.
We advise you to study: Rehabilitation of the patient after removal of an intervertebral disc herniation, recovery timeYou can avoid complications after surgery using simple rules:
- You need to see your doctor regularly (at least once every seven days) and listen to his advice.
- It is allowed to wash in the shower no earlier than two days after surgery.
- Contact a doctor for help if symptoms of pathology or severe pain in the operated area return.
- After washing, change the bandage and treat the area with an ointment with a healing effect.
- You are not allowed to sit in a sitting position for three weeks after surgery.
- Do not carry heavy objects.
- Sports and exercise are prohibited.
- Once the sutures are removed, the operated area should be washed and treated daily.
- Removing hair using an epilator in the tailbone area is strictly prohibited.
- Swimming, going to the bathhouse or sauna are strictly not recommended.
Reviews
In most cases, patients manage to cure a coccyx cyst without problems. However, for this you need to decide on surgery. Those patients who are afraid of surgical intervention only increase their chances of developing complications, because conservative methods will not help cure the pathology.
Oleg, 28 years old: “I suffered from a coccygeal cyst for about 5 years. Only after it burst did I decide to see a doctor. After drainage and dressings, I was scheduled for surgery under local anesthesia. The procedure took about 40 minutes, I did not feel any discomfort. After 3 days I was discharged, at first I was a little bothered by the pain from the wound after the operation, which soon went away. I fully recovered after 3 weeks. For the first 1.5 weeks I tried not to lie on my back or sit on a chair, regularly changed bandages, treated the wound, and went to the doctor. Now I feel great, there have been no relapses, I’m very glad that I decided to have the operation.”
Sergey, 29 years old: “I struggled with the pathology for 2 years: I took medications, made lotions, compresses, ointments, but everything was useless! I decided to undergo surgery, which was performed under local anesthesia. The operation itself was successful, I did not feel any pain. The dressings did not cause pain, and when the stitches were removed, I did not feel any particular discomfort. I recovered within 2.5 weeks. Now everything is fine, the disease is not returning!”
Alexey, 30 years old: “I delayed the operation for a long time, I still couldn’t make up my mind. But when I realized that drugs and folk remedies wouldn’t help, I went to the hospital. A drainage tube was installed in the wound, which remained there for 5 days. During the operation, it turned out that there were already 2 cysts. Naturally, the treatment process was delayed. Therefore, I recommend that if a cyst appears on the tailbone, everyone should not be afraid of surgery. If you wait too long (like me), it will only get worse!”
Symptoms
A teratoma on the coccyx may not manifest itself in any way for many years until inflammation begins in the area of the coccygeal canal. The initial symptoms of a cyst will be discomfort while sitting and the presence of an abnormal bulge between the gluteal muscles, which periodically becomes moist due to secretion. From time to time the patient may experience back pain.
When the sebaceous ducts inside the epithelial canal become clogged, they are filled with exudate, which causes suppuration and inflammatory processes. The same symptoms appear when pathogenic microorganisms enter the body from the outside. With the development of suppuration, the coccygeal neoplasm increases in size, and the inflammatory process begins to spread to nearby areas.
A festering cyst may manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- the teratoma increases in size and causes severe pain, difficulty bending and difficulty sitting;
- increasing pain appears in the coccyx area, especially after a long stay in a sitting position;
- the swelling grows, asymmetrical swelling occurs, redness spreads laterally from the intergluteal fold;
- if there is suppuration, a painful pulsation is felt in the tailbone;
- due to poisoning of the body by products of the inflammatory process, general symptoms of poisoning of the body appear - fever, pain in the head and muscles, weakness, nausea, vomiting;
- additional holes open, which expand the coccygeal passage, and pus begins to flow through them;
- when the volume of purulent masses increases greatly and neighboring tissues are affected, an abscess appears in the lower part of the spine;
- when the additional outlet of the coccygeal passage breaks through, a purulent fistula is formed.
If you treat a festering cyst at home, the matter will end with the abscess breaking through and the formation of a scar in its place. For some time, the pain will decrease, but the internal cavity of the formation will remain, which after a while will again cause suppuration. In addition, acute inflammation can become chronic, in which case discharge will periodically emerge from the coccygeal passage, accompanied by pain and redness. New passages will form, and old ones will scar, forming seals. Such a sluggish process can drag on for several years. To permanently eliminate the disease, you need to immediately consult a doctor.
Predisposing factors
Sacrococcygeal tumor most often occurs due to congenital defects of the fetus. For a long time, the pathology does not manifest itself in any way. Its suppuration occurs under the influence of negative factors, for example, after injuries to the coccyx or hypothermia.
Pilonidal formation develops when there is abundant hair between the buttocks. If the hair begins to grow rapidly, then over time the bulbs grow into the skin, provoking the formation of a cyst.
In addition, there are the following causes of pathological formation:
Pain in the coccyx area in men
- Passive lifestyle, sedentary work.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Decreased immunity, development of infectious processes that provoke the formation of cysts.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Coccyx injuries.
- Insufficient care, non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
These are the main factors that provoke the manifestation of epithelial formation.
No ads 1