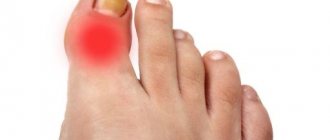
How does joint polyarthritis occur?
With polyarthritis, several joints become inflamed simultaneously or one after another.
Inflammation occurs in the synovium, or joint tissue, which contains many nerve endings and blood vessels. Because of this, they quickly respond with inflammation to external or internal influences. Inflammation spreads to other parts of the joint: cartilage, joint capsule, tendon ligaments and bursa. Polyarthritis leads to changes in the articular cartilage, ligaments and joint capsule. In severe cases, the joints become deformed.
Polyarthritis most often occurs as a result of viral and infectious diseases: acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, rubella, viral hepatitis, STDs, herpes viruses, cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus. The disease can be caused by injuries, metabolic and immune disorders, diseases of the nervous system and hereditary predisposition. The appearance of the disease is provoked by physical overload, hypothermia, allergies (including medications), excess weight and chronic infections.
Lifestyle and nutrition
With polyarthritis, as with other diseases, it is necessary to approach your health as responsibly as possible: maintain a daily routine, alternating periods of activity with periods of rest, sleep at least 8 hours a day, and practice moderate physical activity that your health condition allows. It is also necessary to tune in to a positive mood, because with depression there is a constant synthesis of adrenaline, and the body spends a lot of energy on neutralizing it and other manifestations of stress, and not on fighting the disease.
For arthritis of the fingers, it is recommended to follow a diet. The diet should be varied, not overloaded with fatty foods and salt. The diet should include apples, cranberries, lingonberries, pumpkin, onions, and seafood. Strictly exclude canned food, smoked meats, alcohol-containing drinks, strong tea and coffee.
Particular attention should be paid to proper nutrition
In case of gouty polyarthritis, it is necessary to exclude foods rich in purines from the diet; in general, one should maintain a diet close to vegetarian.
It is recommended to use products containing agar-agar, which is very beneficial for cartilage tissue. And also maintain a water regime, drinking at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
You should also ensure that the body mass index is in the optimal value, because excess weight will complicate the treatment of the disease due to deterioration of blood supply and tissue nutrition, and its deficiency can lead to exhaustion, prolapse of organs and other additional health problems.
Kinds
| Name of polyarthritis | Symptoms | Description of the disease |
| Rheumatoid | Intense pain in the joints, they swell and become deformed. The skin around the joint turns red and the temperature rises. As the disease progresses, the pain intensifies and stiffness in movements appears. | It usually affects the small joints of the hands and feet. Then the disease affects the internal organs: heart, blood vessels, kidneys. In rheumatoid arthritis, the synovium and blood vessels grow. Over time, the disease destroys cartilage and deforms joints. |
| Infectious | The skin over the joint becomes swollen and red, and the joint does not move well. | Occurs against the background of the diseases listed above. Polyarthritis goes away faster when the underlying disease is treated. In the chronic form of polyarthritis, the joints lose mobility. |
| Crystalline (exchange), gouty | Initially, pain in the joints is felt in a certain position. As the crystals grow, the pain intensifies. | Appears due to metabolic disorders and salt deposition in the joints. Salt crystals cause joint irritation and inflammation. |
| Psoriatic | The joints hurt and are difficult to bend, especially in the morning and after a long rest. | It develops 6-8 months after a person becomes ill with psoriasis. The disease most often affects the joints in the feet. Mostly people under 40 years of age are affected. |
| Reactive | Leg joints hurt and swell. The urethra and prostate become inflamed in men, and the uterus and vagina in women. | Reactive polyarthritis occurs due to an infection that enters the genitourinary system or lungs. As a result of polyarthritis, diseases of internal organs appear. |
| Post-traumatic | Aching pain in the joints, muscles, crunching in the joints when moving. | Occurs after a contusion, fracture, crack in the joint, microtrauma inside the joint, if metabolic disorders or osteoporosis are present. |
Stages and manifestations
Polyarthritis of the fingers develops gradually, sometimes the process takes many years. There are four stages of disease development, each of which is characterized by different signs and symptoms:
- At the initial stage of the disease, symptoms are not clearly expressed. Morning stiffness appears, the pain is not strong and occurs only when there is a load on the hand. In general, there is discomfort in the hands and fingers. At this stage, patients rarely go to the doctor, attributing these manifestations to bad weather or too much stress.
- Signs of polyarthritis of the hands at the second stage of the disease are increased pain, the formation of nodules in the joint area, their swelling and difficulty moving. The pain is no longer dependent on the load and can occur even at night. A cracking sound appears in the joints of the fingers.
- During the third stage of the disease, symmetrical deformation of the joints occurs. Severe pain appears during exercise, and joint mobility decreases sharply. The patient can no longer take good care of himself. The presence of a disease with such manifestations is an indication for assigning disability to the patient.
- At the fourth stage, polyarthritis of the fingers leads to complete destruction of cartilage, fusion of the phalangeal bones and loss of mobility.
Deformation of the hands in the last stage of the disease
Conservative treatment of polyarthritis of the fingers can only be done if the diagnosis is made at the first and second stages. At the third, and even more so at the fourth stage, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Lifestyle with polyarthritis
Those suffering from polyarthritis of the hands, first of all, must follow a special diet. A number of foods contain substances that can alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
These include:
Diet will help relieve symptoms of polyarthritis
- fatty sea fish;
- vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables, such as citrus fruits;
- apples;
- nuts and seeds, only unsalted;
- turmeric, ginger;
- garlic;
- buckwheat, oat and millet groats.
The main condition of the diet is the exclusion of these foods from the diet:
- pumpkin, tomatoes, eggplants, hot peppers (especially for gout);
- fatty meat, offal, margarine;
- alcohol;
- chocolate, gingerbread, cookies, condensed milk;
- spinach, sorrel, rhubarb, green onions.
Meals should be three times a day. Neither overeating nor fasting should be allowed. The patient needs to drink a sufficient amount of water per day, which should be calculated by the doctor, depending on the patient’s weight. It is necessary to control body weight. However, you can only lose weight under the supervision of a doctor.
In general, you should lead a healthy lifestyle, get enough sleep, walk, do physical therapy, and get rid of bad habits. It is necessary to strictly avoid physical exertion on the affected arm.
Treatment methods
Treatment of polyarthritis is a complex therapy that has three areas:
- treatment of the main disease, the consequence of which is polyarthritis;
- relief of acute manifestations of arthritis, pain and swelling;
- measures aimed at restoring joint tissue.
Drug treatment
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Designed to relieve inflammation and joint pain. The drugs help to quickly relieve pain and inflammation in the affected joint, but do not affect the course of the disease and are an auxiliary remedy. NSAIDs inhibit a special enzyme in the body that is responsible for the inflammatory response. According to the mechanism of action on this enzyme, they are divided into 2 groups: COX-1 and COX-2.
COX-1:
- Aspirin. A traditional remedy discovered in the 19th century. In terms of action - weak. Nowadays, it is usually replaced with stronger drugs.
- Diclofenac. The most popular of the NSAIDs. Used as tablets or ointment. Quite a strong analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent.
- Ibuprofen. Not very strong, but well tolerated by the body. Available in tablet form.
- Ketoprofen. Medium strength NSAID. Available as: tablets, aerosol, rectal suppositories, cream, gel, solution for external use or injection.
- Indomethacin. Strong NSAIDs, however, have many side effects.
Diclofenac in injection form Ketoprofen in gel form Ibuprofen in tablets Indomethacin in suppository form
COX-2:
- Meloxicam. The most famous medicine containing this substance
- Movalis. Suitable for long-term use, even for several years. Available as: tablets, ointments, rectal suppositories, injection solutions.
- Celecoxib. Quite a strong remedy. It is gentle on the stomach.
- Nimesulide. It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant effects, slows down the destruction of joint tissue. Available as: tablets, granules for solution, gels for external use.
Movalis is the latest generation drug Nimesulide tablets Celecoxib capsules Meloxicam tablets
Corticosteroids
They relieve the inflammatory process by suppressing the immune response.
This type of medication is usually prescribed for the treatment of polyarthritis caused by autoimmune diseases - rheumatoid or reactive.
Examples of drugs:
- Hydrocortisone. Synthetic glucosteroid drug. It is used in the form of ointments, tablets, intramuscular and intravenous injections.
- Dexamethasone. A synthetic analogue of the adrenal cortex hormone. Has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Long-term treatment with this drug can cause osteoporosis and disorders of the entire body, so it is prescribed with great caution. Medication form: tablets and injections.
- Prednisolone. Another synthetic analogue of the adrenal hormone. The drug is very powerful and is prescribed only for the most severe forms of polyarthritis. Available in the form of tablets, ointments, intravenous and intramuscular injections.
- Betamethasone (diprospan) . An effective injection drug. Injected directly into the affected joint or periarticularly. After one administration, the effect of the medicine lasts up to 10 days.
Betamethasone gel Dexamethasone in ampoules Hydrocortisone for external use Prednisolone in the form of ointment
Chondroprotectors
Medicines whose action is aimed at restoring cartilage and preventing its damage. They contain chondroitin and glucosamines - structural elements of cartilage tissue or hyaluronic acid.
Types of chondroprotectors:
- The first group is based on extracts from animal cartilage and bone marrow . Currently, only a medicine called Alflutop is available. May cause allergies.
- Mono-drugs . They contain only one of the active ingredients - chondroitin or glucosamine. With chondroitin: Chondroitin, Chondrolone, Structum, etc. With glucosamine: Flexamine glucosamine, Artron flex, Dona.
- Complex drugs. Contains a balanced complex of both substances. (Chondroitin complex, Arthron complex, Teraflex). Or they consist of glucosamine and/or chondroitin + diclofenac/ibuprfen. (Triaktiv, Movex, Artron, etc.).
- Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid are also used to treat arthritis (Fermatron, Viskosil, Suplazin, etc.).
Structum in capsules Aflutop in injection form Fermatron Glucosamine with chondroitin
Antibiotics
Typically used to treat infectious polyarthritis.
Such medications are prescribed depending on the specifics of the underlying disease:
- Tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones help with penetration of urogenital infection into the joint (Tetracycline, Metacycline, Ofloxacin, Roxithromycin).
- Penicillins, cephalosporins and macrolides are suitable for the treatment of arthritis caused by respiratory tract infections (Ampicillin, Cefatoxime).
- Fluorohydroxyquinolones act against bacteria of the gastrointestinal tract (Ofloxacin, Sparfloxacin).
Tetracycline tablets Ampicillin solution Ofloxacin solution
Antimetabolites (Methotrexate)
It is used to treat the most severe forms of psoriatic and rheumatoid polyarthritis, if standard therapy does not have an effect.
Methotrexate is an effective antitumor and immunosuppressive agent. The main area of application is various forms of cancer.
Painkillers
To relieve pain in polyarthritis, NSAIDs are prescribed - Diclofenac, Ketoprofen, Meloxicam, Movalis and others. In addition to the anti-inflammatory effect, these drugs also have an analgesic effect.
Vitamins
First of all, the patient needs calcium. Complex calcium preparations are prescribed in combination with D3. (eg Calcium D Nycomed). As well as zinc, brewer's yeast and fish oil.
Physiotherapy
Includes:
Physiotherapy for hand treatment
- treatment with massage and manual therapy (special techniques of physical influence on muscles to relieve pain);
- therapeutic exercises;
- treatment with various heating;
- ultrasound therapy;
- Magnetic therapy, a relatively new method, is a treatment with magnetic fields that has an analgesic and decongestant effect;
Endoprosthetics
It is performed in the later stages of polyarthritis, if the phalanges of the fingers have already fused. Goal: restoration of motor activity of the hands. The essence: replacement of damaged joints with artificial prostheses.
Folk remedies for polyarthritis
To achieve a long-term effect of treatment in combination with drug treatment, it is good to use traditional methods.
The folk method of treatment is a light auxiliary one and in no case should replace the drug method or the main therapy.
Popular recipes for decoctions and infusions for treatment at home:
- 3 tbsp. linden blossom spoons, 2 tbsp. spoons of elderberry, 1 tbsp. l. Pour chestnut seeds into 2 cups of boiling water. Keep in a water bath for 15 minutes. Drink half a glass 2 times a day.
- Drink homemade tea made from rose hips and currants instead of regular tea.
- Pour 300 g of pine/Christmas needles into 0.5 liters of water and, stirring, bring to a boil. Cool slightly, squeeze out the needles. Keep your hands in the broth for 15-20 minutes.
- Mix 150 ml of 70% alcohol, turpentine and oil of Provence, add 3 g of camphor. Use the resulting mixture to lubricate joints for pain.
- Decoction of bay leaf. Bay leaves are brewed and boiled for 6 minutes in 0.5 liters of water, infused for an hour. It should be taken orally in several sips throughout the day.
Methods for preparing and using compresses and baths:
- A compress of iodine, lemon juice and two aspirin tablets is made into an ointment-like consistency and used as a compress at night for 6 days.
- A compress of honey and alcohol is prepared by mixing 1:3 diluted alcohol with honey in equal proportions, warming up in a water bath for no more than 10 minutes. The composition is applied to a cloth and applied to sore joints at night.
- Sea salt is a good folk remedy for treating joints; it should be dissolved in hot water and soaked in your hands.
Clinical picture of the disease
The history of hand pathology is individual and depends on the etiology of the disease.
Standard features:
- Pain syndrome;
- Swelling of the phalangeal joints;
- Increased temperature in the affected area;
- Poor circulation in the fingers;
- Feeling of tightness.
For early diagnosis, every detail of the patient’s condition is important. First of all, the epicenter of the disease, symmetry, constant or modified inflammation, and the presence of typical diseases with complications such as polyarthritis are determined. Laboratory tests complement the clinical picture. Together with an external examination, they provide the basis for making a diagnosis.
The presence of rheumatoid index, uric acid, antibodies in double-stranded DNA, and antinuclear factor in analyzes determines the causes of the disease.
In some cases, a biopsy of synovial fluid is necessary. Studying the biochemical composition is an important stage in accurate diagnosis. The picture of the disease may vary depending on the causes of the pathology. Each type of disease has its own characteristics and characteristics. Type determination is the initial goal of early diagnosis.
Which doctor should I contact?
If your city has a small clinic, if you suspect polyarthritis, you should contact a therapist. He must conduct the first examination, write out directions for tests and send to a rheumatologist or orthopedist. A traumatologist, immunologist, infectious disease specialist or surgeon is also involved in the examination and treatment, depending on the type of polyarthritis.
ADVICE! In large cities, you can find a special arthrologist and immediately begin treating the disease with him.
Diagnostic methods
The purpose of diagnosis is to determine the type of arthritis. The treatment program depends on the underlying disease against which polyarthritis developed. A comprehensive examination is being carried out. Much attention is paid to collecting anamnesis, complaints and features of the clinical picture.
- A biochemical blood test is carried out, first of all, to identify the rheumatoid type of disease. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, createnine level, spartate aminotransferase, rheumatoid factor are examined.
- To assess the degree of joint damage, the patient undergoes scintigraphy; Ultrasound of joints; magnetic resonance (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan.
- If metabolic polyarthritis is suspected, intra-articular fluid is examined by biopsy.
- Additional studies of various organs are also possible, depending on the picture of the disease. And for the infectious type: bacterioscopy, PCR diagnostics, enzyme immunoassay, etc.
Physiotherapy
It is carried out in combination with drug treatment. Procedures are performed on the hands using special equipment or manual methods:
- Ultrasound therapy;
- Magnetotherapy;
- Electrophoresis;
- Paraffin applications;
- Manual therapy;
- Massages;
- Mud baths;
- Low temperature treatment – dry ice and nitrogen;
- Laser correction of cartilage tissue.
All methods are united by one goal - relieving pain and restoring mobility to the fingers.
Prevention
The disease can deprive a person of his main function. The inability to carry out the movements inherent in nature puts the patient in a dependent position on others. Simple preventive measures can prevent the development of the disease itself or prevent progression to a chronic form:
- Avoid hypothermia, use gloves in winter;
- If pain occurs, take warm baths with the addition of medicinal herbal mixtures;
- Massage your hands periodically, this improves blood circulation;
- If possible, visit the pool; a kind of hydrotherapy has a positive effect on the functionality of the finger joints;
- Do not hover your hands under any circumstances. Warming procedures should only be prescribed by a doctor. Otherwise, you can create a favorable environment for inflammation;
- Completely treat all infectious diseases;
- Do not refuse a preventive examination, even if there are no obvious symptoms.
It should be remembered that the disease in its advanced form is incurable. A timely visit to a rheumatologist will help maintain full mobility of the limbs into old age.
Polyarthritis of the hands - what is it?
A complex form of arthritis. It is a multiple inflammation of the finger joints. May be acute, subacute or chronic (slowly progressive). It is accompanied by pain and swelling in the affected joints, leading to irreversible deformation and immobilization of the hand.
It occurs both as an independent disease and as part of a systemic dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system. Polyarthritis most often occurs after 40 years of age, but it can also develop in young people, and in rare cases even in childhood.
In children, polyarthritis is usually temporary and goes away on its own, but there is also an unfavorable course of the disease, which leads to lifelong disability.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| MRI of the wrist joint (1 joint) | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions