Tendonitis is a process of inflammation that occurs where a muscle connects to a bone. This disease belongs to fatigue diseases of the musculoskeletal system of the body, since its development occurs against the background of deteriorating tissue condition. Standard medications that relieve pain and inflammation are ineffective for this problem. They help relieve discomfort and eliminate symptoms, but cannot cure the disease.
Knee tendonitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the tendon above the knee. It connects the thigh muscle to the tibia. Hip tendonitis is an inflammation of the tissues and ligaments that surround the joint. There is also tendinitis of the tendons that are located in the area of the ischial tuberosity. This process is considered the most dangerous to human health, so its treatment must be started immediately after the diagnosis has been made. If this is not done, the tendonitis will develop into a pinched sciatic nerve.
Elbow joints may also suffer from a similar condition, but it may have different names depending on the specific location of the problem. It is popularly called “baseball elbow.”
Many people confuse tendinosis with stretched or torn tendons. But they have a significant difference. When tendons are mechanically injured, some fibers are torn and soon begin to grow together and heal. The affected area brings discomfort and acute pain to the person, so he is forced to reduce the load on it. With tendonitis, tissue rupture occurs constantly, and their healing is always at different stages. The load on the affected area is not reduced. It is for this reason that treatment may be delayed, and the disease becomes chronic.
Stages of tendinitis
Modern medicine distinguishes several stages of this disease. These include:
- Acute phase. The damaged area of the body causes severe pain. If a person feels discomfort in a calm state, then with physical activity it develops into unbearable acute pain;
- Subacute phase. The pain persists and is accompanied by swelling. Movements become difficult and limited;
- Chronic phase. Tissue degeneration occurs. Pain becomes a constant “guest”, as does stiffness.
Stages of osteoarthritis of small joints of the hands
As a rule, treatment of osteoarthritis of small joints of the hands is delayed due to the slow progression of the disease. Symptoms increase gradually, which makes it difficult for the patient to objectively perceive their intensification. However, experts distinguish 3-4 stages of the disease, which make it possible to adjust therapy and make predictions about the course of the process with considerable reliability.
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands of the 1st degree is characterized by mild, barely noticeable pain, joint mobility is preserved and the patient may not suffer any restrictions in daily activities. The tissue around the affected joints begins to harden.
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands, grade 2, involves the presence of constant, but not too severe pain. The range of motion in the joint is reduced, and osteophytes, clearly visible on x-rays, appear, which prevent full movement. Towards the end of the stage, the fingers may become thinner because the muscles responsible for normal hand activity are no longer used and begin to atrophy. Against the background of this process, the joint nodes become especially noticeable and begin to crunch audibly when bending the fingers due to the narrowing of the lumen in the joint.
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands of the 3rd degree is expressed by severe pain and extreme difficulty in flexion movements. The number of osteophytes increases, almost completely limiting the mobility of the joint. The photographs show an extremely small amount of cartilage tissue. The atrophy of the muscles responsible for fine motor skills of the fingers is completed. Bone density increases, severe deformation and signs of osteosclerotic changes are noticeable.
Modern classification of the disease
Tendonitis can be different. There is a certain classification, which is based on the characteristics of inflammation and methods of its treatment. Today, doctors distinguish between serous, purulent, and fibrous inflammatory processes.
Tendinosis is also divided according to the place of its occurrence. There are such tendinitis:
- Temporal.
It causes difficulty chewing food. When the jaw opens, a clicking sound may occur. Often the process is accompanied by discomfort or pain;
- Tendonitis of the shoulder joint.
The disease affects the capsule, which serves as the connection of the tendon with the supraspinatus and biceps muscles. Only an experienced specialist can help solve this problem. With tendinosis of the shoulder joint, the patient cannot fully raise his arm up or move it behind his head;
- Biceps tendonitis
leads to impairment and stiffness of hand movements;
- The disease that affected elbow joint
, does not allow full flexion and extension of the limb in this place. Accompanied by severe pain during physical activity and movement;
- Wrists.
It makes itself felt after physical activity. The patient feels stiffness in his hands, and is also unable to bend and straighten his fingers;
- Hip joint.
It is difficult for a person with this disease to move, let alone run or perform other more intense physical activities. After some time, the joint becomes permanently dysfunctional;
- Knee joint.
With this disease, the tendon in this area is affected. Damage can lead to partial or complete degeneration. The reason is the constant wearing of uncomfortable high-heeled shoes, as well as physical training to the limit. If adequate treatment is not provided, the patient may remain crippled for life;
- Achilles tendon
. Most often, professional athletes and heavy physical labor workers suffer from this problem. The disease is characterized by the presence of painful sensations even at rest. The pain intensifies when walking up stairs, and there is a feeling of stiffness in the joint;
- Feet.
In this case, the pain extends not only to the lesion, but also “radiates” to the lower leg. If you do not undergo treatment, then over time nodules appear in the foot, which make it difficult to move the leg;
Whatever type of tendonitis bothers you, it is important to consult a doctor in time so that he can conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary medications. Self-medication is not only ineffective, but also unsafe for health.
Osteoarthritis of the hands: what is it?
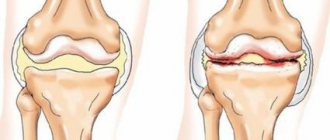
Osteoarthritis of the interphalangeal joints of the hands refers to a whole range of pathological conditions in which the joints of the fingers suffer. The dystrophic process leads to thinning and cracking of the cartilage, gradual destruction of connective tissue and, in later stages, to deformation of the joint. At the same time, the load on the ligaments and muscles of the hands increases - they are in chronic overstrain, which is expressed by pain, swelling, a reduction in the range of motion, as well as rapid fatigue and decreased performance. The shock-absorbing function of the joint capsule deteriorates, the cartilage ceases to retain the amount of moisture that it needs to maintain elasticity. In an effort to prevent further destruction of the joints, the body triggers the production of osteophytes - spine-like and other bone growths that limit mobility and injure adjacent tissues. This leads to chronic pain and inflammation. The metacarpophalangeal joint is poorly involved or not involved at all (unless there are generalized joint diseases or wrist injuries). In the early stages, the process is considered conditionally reversible, but in the absence of treatment, the changes become permanent, and the condition of patients can only be alleviated and maintained.
Osteoarthritis of the hands without treatment quickly spreads to all tissues of the hand - bone, cartilage and muscle. Undesirable, physically noticeable friction appears in the joints, their destabilization is observed, and the capillary supply of the hands deteriorates significantly. Fine motor skills are steadily deteriorating. For patients, performing the simplest household and professional duties becomes painful, grasping movements cause discomfort, handwriting changes, and irritability appears. In the early stages, irregularities and damage to the joint capsule, clearly visible on x-rays, appear. The last stages are characterized by loss of ability to work and complete disappearance of cartilage.
Causes of joint tendonitis
Many people are interested in the question, where does this disease come from? Most often it occurs in two categories of people. The first is professional athletes who train often, for a long time and for wear and tear. This excessive stress on the body leads to damage to tendons and joints. The second is the age category of people who have “passed” forty. In this case, the cause of tendonitis is age-related disorders in the body.
Damage due to excessive physical activity can be caused by a variety of factors:
- If you start doing exercises without the necessary warm-up and warm-up, and also if you systematically violate the technique of performing them;
- Problems in the hip joint appear when running technique is violated. The foot does not land on the ground correctly, the joint suffers from an impact on a hard surface, since the foot is at the wrong angle;
- Exercises that involve sudden jumps, bends, and turns can also provoke the appearance of a similar problem;
- Using incorrect and uncomfortable shoes when we are talking about outdoor activities and not in the gym;
- Problems with the elbow joint are caused by sudden movements of the hands, accompanied by a violation of the technique of performing exercises. As well as constantly performing the same movement with frequent intervals;
- If you apply too much weight during exercise, tendinitis of the shoulder joint may occur.
The anatomical features of the human skeleton can also cause this disease. For example, problems in the hip joint may be caused by unequal leg lengths. Custom-made shoes with soles of different heights can help the situation. Problems in the knee joints often cause bowed legs or dislocated joints.
The older a person gets, the less elastin fibers he contains in his body. They are responsible for the mobility and elasticity of tendons. At the same time, the number of collagen fibers increases. They are responsible for the strength of fabrics. Therefore, this leads to the development of tendinosis.
In rare cases it may be caused by:
- infectious diseases that are sexually transmitted;
- metabolic disorders;
- mechanical injuries in the place where the tendons are located;
- autoimmune diseases.
How do joints help movement?
In order for the skeleton to move at the joints, the bones must be connected to each other. This joint must be both flexible and rigid to allow the bones to move freely within a strictly limited range. To meet these conditions, the bones in the joint area are connected by ligaments
.
In addition, in the area of the joint, muscles are also attached to the bone using tendons
. Ligaments and tendons are strong enough to hold the joint in place, but also flexible enough to not tear during normal movement. The placement of ligaments and tendons determines how the various joints will move. For example, the knee can only bend forward and not backward.
Symptoms of tendinitis
This disease comes with several different symptoms. But the most obvious of them is pain. At the initial stage, discomfort may be noticeable only after physical exertion or hard work. Over time, they visit a person with enviable regularity. The sensation can be described as a dull pain, which is concentrated at the site of tissue inflammation. At the same time, it appears only during the movement. When the joint is at rest, the discomfort disappears. If you press on the area of the body where the disease has begun to develop, the pain becomes stronger.
If the inflammation is in an advanced state, then a symptom of tendonitis is redness of the skin around the affected tendon, as well as a local increase in temperature. The joint loses mobility, in some cases a characteristic crunch appears when the body moves.
Elastic nodules in the tissue that can be palpated are also a symptom of tendinitis. They occur after prolonged treatment. There may be one or several nodules. They are an accumulation of fibrous tissue that appears in place of inflammation.
A symptom of shoulder tendonitis may be the appearance of calcifications. These are denser nodules that represent an accumulation of salt deposits. Very often, tendinosis ends in tissue rupture, which leads to longer treatment and rehabilitation.
Joint diseases: diagnosis
Diagnosis of these diseases begins with an external examination of the patient and his questioning (collecting an anamnesis). Particular attention is paid to: the state of the patient’s immune system (information is collected about past or existing diseases, and, first of all, of an infectious nature), the nature of the work, food preferences, bad habits, and the social conditions of the patient’s life. After this, the patient’s blood and urine are examined to detect infectious agents, determine the level of cholesterol, magnesium, phosphorus, vitamins D and Ca. Tendon reflexes must be examined. Instrumental methods for diagnosing joint diseases include: - radiography of problem areas; - computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the same places; - angiography and Dopplerography (determining the degree of vascular patency).
Tendonitis in pregnant women and its features
This disease is a frequent “guest” of women who are expecting a child. If there are suspicions, then it is preferable not to do an x-ray or computed tomography during the examination. Any medications that a pregnant woman will take must be prescribed by the attending physician and also agreed with the gynecologist. In this case, self-medication will be dangerous not only for the patient, but also for her unborn child.
When the first symptoms of tendinitis appear, doctors advise limiting yourself to physical therapy, rest, and applying cold compresses to the affected area. If you need to relieve inflammation and reduce pain, ointments based on painkillers are prescribed.
If the problem enters an acute phase, the doctor may resort to immobilization of the joint. Antibiotics may be prescribed, but only if a bacterial infection is found and other treatments have been ineffective. In the most extreme cases, surgery is performed on the joint.
Features of the development of tendinitis in children
This disease does not occur as often in children as in adults. The most “popular” place where tendinosis occurs is the knee joint. At the first symptoms of tendonitis in a child, you need to contact a pediatric traumatologist. He will conduct an examination and make an accurate diagnosis. After this, the little patient will be prescribed the necessary medications. Most often, the list includes muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, both for oral administration and in the form of ointments.
For a certain period of time, you will have to limit your mobility and remove all physical activity. If the pain is very severe, the joint is immobilized. Treatment includes a variety of physical therapy, including electrophoresis. As soon as the acute phase of the disease has passed, a course of massages is carried out and physical therapy is added.
Traditional methods of treating sore joints
In medical practice, as a rule, an integrated approach is used to treat patients suffering from musculoskeletal disorders. Let's name a few popular methods:
- Drug therapy. Medications relieve pain and inflammation and improve the patient’s general condition. Intended for internal (tablets, injections) and external (gels, ointments) use.
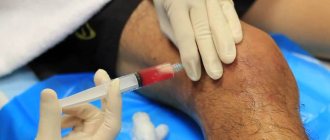
- Blockade. Direct injection of the drug into the lesion to relieve pain.
- Physiotherapy. Warming and ultrasound procedures that massage and relax damaged tissues.
- Physiotherapy. Full life of joints is possible only in constant movement. The therapeutic set of exercises must be selected individually, in consultation with a doctor.
- Manual method. Effectively affects the restoration of damaged periarticular tissues. Has no side effects.
- Surgical intervention. An emergency measure used in the most difficult and dangerous cases for the patient’s health.
Timely consultation with a doctor will ensure your joints have a long and fulfilling life. Medical specialists will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. A high level of service and complete confidentiality are guaranteed.
Complications after tendinitis
Like any other disease, tendon tendinitis can have complications. It is not difficult to avoid them if you start the right treatment on time. However, it may happen:
- tissue ruptures;
- chronic course of the disease, which is accompanied by constant pain;
- processes of bone tissue proliferation, which lead to inflammation of various types.
Timely examination by a doctor and compliance with all his instructions will minimize the likelihood of complications.
Joint diseases: prevention
It is a well-known truth that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. On top of that, it's much cheaper. Prevention of joint diseases consists of a healthy lifestyle, compliance with certain rules: 1. To maintain the normal functioning of the immune system, restore the optimal flow of all metabolic processes, and, therefore, to prevent joint disease, it is necessary, first of all, to eat right. Eat more often (up to 5-6 times a day, but in small portions), minimize the consumption of animal fats, canned and “dead” food (sausages), increase the consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables, and fiber. 2. A sedentary lifestyle is a direct path to joint disease. Start moving more: jog in the mornings or evenings, walk for at least 45 minutes a day, if possible, sign up for swimming. 3. Start consuming probiotics on a regular basis (preserving the microflora of the stomach - the most important part of the immune system is of great importance in the prevention of joint diseases), vitamin and mineral complexes. 4. Temper your body (a bath and a contrast shower are the best means for this). 5. And the last thing - be optimistic, know that everything is in your hands and “there are no peaks in the world that cannot be taken.”
Treatment of tendinitis
It is important that treatment for this disease is prescribed by a doctor. The first step is to remove excess stress on the joint whose tendons are inflamed. It is not necessary to completely immobilize an arm or leg. You can simply “take care” of your limbs and not put unnecessary strain on them physically. In order to reduce mobility, elastic bandages, bandages, and bandages are useful. Exercise therapy may be prescribed, which should be carried out by an experienced rehabilitation therapist. Properly selected exercises will not only relieve muscle tension, but also strengthen them.
To relieve the pain that always accompanies tendonitis, doctors prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They are available in the form of ointments and creams, as well as tablets for oral administration.
In some cases, treatment with glucocorticoid injections will be effective, but it should be remembered that such injections can provoke tendon rupture. Physiotherapy, which is used in combination with drug treatment, will also be useful. If a large amount of calcifications and salt deposits were found in the inflamed area, then shock wave therapy will help break them up.
If the sciatic nerve is pinched due to inflammation of the hip joint, the doctor may prescribe surgery to eliminate the underlying problem. In this case, drug treatment will be ineffective, since it can only eliminate the symptoms, but not cure the disease.
One of the most popular drugs today that helps heal inflamed joints and tendons is Artracam. It has a positive effect on the metabolism in cartilage tissues and also stimulates biosynthesis.
The main active ingredient of Artracam is glucosamine sulfate. It has a pronounced analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect, and also increases the amount of hyaluronic acid in the synovial fluid. Degenerative processes in the joints are slowed down, and joint function is restored. The pain becomes less pronounced even in the acute period.
How do joints absorb shock?
A healthy person can stomp his foot on the floor without pain. Most likely, it will not even occur to him that the force of the muscles can break the bones of the lower leg by hitting them against the bones of the thigh. This does not happen because the bones are protected from impact loads by joints
.
They work as shock absorbers, meaning they absorb energy transferred from one bone to another. The shock-absorbing properties of joints are due to the joint work of cartilage, which covers the heads of bones, and the fluid that fills the joint space. Intra-articular cartilage
is a tough and smooth tissue.
It consists of water, collagen and other substances. For better gliding, cartilage tissue is nourished and lubricated by synovial fluid, consisting of protein and sugars. It is produced by a layer of cells that line the inside of the joint. Synovial fluid
not only nourishes cartilage.
This molasses-thick liquid acts as a shock absorber, preventing the bone heads from colliding with each other. To keep the synovial fluid and bone heads in place, the joint is surrounded by a shell of tough connective tissue - the joint capsule
. It attaches to the bones in close proximity to the cartilage and forms the joint cavity.