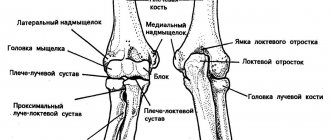
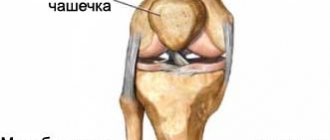
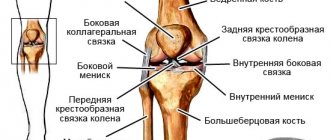
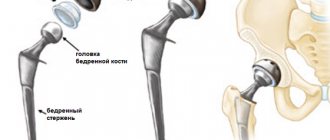
Every person has had an elbow injury at least once in their life. Any person knows the sensations when hitting the olecranon process, which are manifested by pain such as the passage of an electric current and numbness. But, as a rule, such sensations are short-lived and go away on their own. Elbow pain may appear after exercise. Weight-related elbow injuries can be minor or severe and present with symptoms such as pain, swelling, numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and decreased range of motion. But the most common cause of elbow pain is acute injury to the elbow, and the patient sometimes cannot remember the specific injury, especially if the symptoms began gradually or during daily activities. Elbow injuries most often occur during sports, professional activities, housework, and falls.
Most elbow injuries in children occur during activities such as playing sports or playing, or are the result of accidental falls. The risk of injury is higher in contact sports such as wrestling, football, or basketball, or speed sports such as cycling, skating, skiing, hockey, snowboarding, and skateboarding. The elbows, forearms, wrists, hands and fingers are most susceptible to injury when playing these sports. Any injury in a child or adolescent localized to a joint can damage the growth plates, which can disrupt normal bone growth. Older people have an increased risk of fractures in the elbow (including the elbow) due to decreased bone density and decreased muscle mass. In addition, the high risk of fractures in the elderly is due to vision problems and impaired body balance.
Main Factor
Often people decide to go to the gym before the summer beach season and think that in a month of intense training their unprepared body will acquire wonderful shape. However, excessive loads can harm the body, which is not accustomed to such frequent exercise.
Therefore, traumatic situations most often happen to beginners. Sometimes the causes of pain and the fact that the arm at the elbow does not straighten after training can be a pathology of the joints, which a person might not even suspect until they make themselves felt after increased stress.
What does this term mean?
Contracture should not be understood as a situation where the elbow does not straighten exclusively. Sometimes the arm straightens, but there are problems moving in other directions.
Contracture is any limitation in the mobility of a joint. It is often accompanied by joint deformation, swelling and pain.
If we classify pathology by type of movement restriction, we can distinguish several types:
- flexion;
- extensor;
- pronation;
- supination, etc.
The first type is the most common. It manifests itself as difficulties when trying to straighten the arm or complete inability to make this movement.
Flexion contracture is diagnosed when the arm does not fully extend
There are four degrees of joint damage:
- In the first degree, the limitation is insignificant, since a person is able to extend the arm no less than 170°.
- If it extends in the range of 130°–170°, the second degree of contracture is diagnosed.
- At the next degree, extension is possible within 90°–130°.
- With the most severe degree of pathology, the extension angle does not exceed 90°.
Next, let's look at the possible causes of the disease.
Common causes of pain
Coming to the gym for the first time, a novice athlete diligently performs all the exercises given to him by the coach, so that he would not be ashamed in front of the experienced “jocks”. Naturally, the body, not accustomed to such stress, responds with pain throughout the body. Beginners believe that if their whole body hurts, it means they did a great job. But this is completely the wrong approach.
After training, the athlete should feel pleasant fatigue in the muscles, but not severe pain. Let's look at what happens in the human body after heavy loads:
- if the muscles are poorly warmed up and stretched, and a person begins to work on weight training equipment, then painful sensations may appear due to microcracks in the muscles, which become inflamed over time and become very painful;
- a person may experience burning-type pain. This suggests that you have overworked yourself. The tissues produce a lot of lactic acid, which interferes with normal blood circulation. At this time, there is a deficiency of oxygen, and the muscles refuse to perform contractile movements, which leads to the fact that the elbow does not straighten after training. Most often, this problem appears after intense exercises on the biceps of the arms;
- Sprains occur during sudden movements of the arms, for example, when jerking while lifting a barbell. This happens when the athlete spent little time warming up and warming up the muscles and did not do exercises to stretch the ligaments;
- Dislocation of the joint also causes severe pain and loss of movement of the limb. Here you definitely need to contact a specialist for help;
- poor metabolism in muscle tissue. This is a chemical process that breaks down proteins, fats and carbohydrates to release the energy needed for training. This releases toxins, which are normally eliminated through the capillary network. This requires a lot of oxygen. If the release occurs slowly, then all these decay products accumulate in the tissues, which leads to pain and malfunction of the elbow joint.
What is the severity of pain when extending the elbow?
Depending on the individual characteristics of the patient, the severity of pain that occurs during hand movements varies widely. Discomfort when extending the arm is episodic. At rest, a person may not feel pain.
The cause of pain during joint extension is either local inflammation or compression of the nerve endings that pass in close proximity. The nature of the pain syndrome depends on the type of pathological process that causes it.
Traumatic injuries are accompanied by severe pain, which can be easily relieved with strong analgesics, incl. narcotic. Osteoarthritis or bursitis of the elbow leads to aching sensations that are constantly disturbing and only intensify when the joint is straightened. Tunnel syndrome with compression of the ulnar nerve is also accompanied by aching pain, which is combined with decreased sensitivity of the skin on the 4th-5th fingers.
Pathological factors
It may be painful to straighten your arm at the elbow after training due to diseases of the spine and joints:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine. Although mobility in the elbow is preserved, it is very painful to straighten and bend the arm.
- Epicondylitis of the elbow joint. This is an inflammatory process of the tendons after intense physical exertion. It manifests itself as pain in the elbow during grasping, rotational movements, or lifting a load. External changes are not visible, however, pain occurs on palpation.
- Arthrosis can be a consequence of a past injury or hormonal imbalances in the body. Pain occurs during flexion-extension movements, sometimes accompanied by a crunching sound. If treatment is not started in time, bone growths will form on the bone, which can subsequently lead to the fact that the elbow will no longer fully extend.
- Arthritic inflammation of the joints can lead to the arm not straightening at the elbow after training. The painful area swells and the skin color changes.
5. Bursitis can develop as a result of arthritis. Swelling appears on the back of the elbow from the accumulation of fluid in the synovial bursa of the olecranon.
What diseases can be associated with pain when extending the elbow?
The symptom that occurs with elbow extension appears due to dysfunction of the extensor muscles, which are attached inside the joint capsule. The reasons for this situation may be:
- inflammation of the epicondyles (lateral or medial epicondylitis);
- osteoarthritis;
- isolated inflammatory process;
- compression n. ulnaris (ulnar nerve) bony structures;
- nerve inflammation;
- traumatic damage to the joint;
- inflammation of the fascial bags (diffuse fasciitis);
- oncological pathology.
Based on the diagnostic information received, doctors at the Shifa clinic identify the root cause and select therapy that reliably relieves pain. Improving the quality of life is achieved through a combination of non-drug methods with medications.
Identifying the cause
You can understand the true reason why your arm does not straighten at the elbow after training after consulting a doctor. If the pain is temporary, then proper organization of loads and a good warm-up before the main activity will help. After training, it is advisable to massage the limb and rub the muscles to get rid of lactic acid in the tissues.
A hot shower will help you relax, and salt baths will help relieve stress and inflammation from your elbow. If the pain is severe and prolonged, then there is no need to hesitate; it is better to go to a therapist and check the condition of the joint.
Prevention
It is known that prevention of any disease is easier than its treatment. The same rule applies to the gym.
It is better to take precautions to reduce the risk of injury than to heroically fight this very injury later.
Methods for preventing injuries during power loads include:
- General warm-up before the main part
This includes walking, running, cycling, joint warm-up and light dynamic stretching. Duration - 5-10 minutes.
- Special warm-up
Performed before strength exercise.
Before you begin working weights, be sure to perform a warm-up approach with light weights and a high number of repetitions (40-50% of the repetition maximum).
- Maintaining the correct technique for performing the exercise
If the technique is broken and you are not able to control it, then this weight is not suitable for you. It is necessary to reduce the weight of the burden.
- Avoiding heavy weight exercises if you feel very tired or unwell
- Post-workout cool-down (light cardio and stretching of the muscles being trained)
- It is possible to carry out physical procedures on days off from training that speed up recovery - baths, massages, etc.
First aid for swelling
It may be painful for a healthy person to straighten the elbow after exercise due to the accumulation of lactic acid in the tissues. To relieve pain, reduce swelling in the elbow joint and return your arm to its former activity, you need to know how to provide first aid after training.
A fitness trainer may recommend that an athlete take a warm bath with sea salt. This will relieve muscle tension and joint inflammation. 15 minutes will be enough to complete the procedure.
Self-massage after training will restore blood circulation, remove numbness in the limbs and speed up metabolism. A steam room with a broom will help you recover well.
If the swelling is accompanied by a change in skin color or hematoma, then you need to urgently go to the doctor.
Diagnostics
If it is difficult or impossible to straighten your arm at the elbow, you should not treat with folk remedies at home. You can find a great variety of similar remedies and recipes on the Internet. However, not all of them are correct from a medical point of view. In addition, motor abnormalities in the elbow occur as a result of various factors. Therefore, each individual case requires its own approach to treatment.
A specialist must decide how to treat. Which doctors should I contact? A traumatologist, orthopedist, neurologist and rheumatologist will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment:
- Diagnosis begins with listening to the patient's complaints, examining the sore elbow and examining it with the fingers. The doctor finds out whether the person has suffered injuries or illnesses, how long it takes for the pathology to develop, what sensations it is accompanied by, etc.
- At the next stage, the patient is sent for general and biochemical blood tests. A general analysis of the level of leukocytes in the blood and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate allows us to determine the strength of the inflammatory process in the body. The second type of analysis provides information about the presence of arthritis, damage to internal organs, and metabolic disorders.
- If necessary, synovial fluid from the joint cavity can be taken for analysis.
- An x-ray of the damaged joint is required to identify its anomalies.
X-ray of the elbow joint
To clarify the diagnosis, instrumental examination methods such as magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography and ultrasound can be used.
First aid for a torn ligament
If after training you find that there is sharp pain in your elbow, swelling, a bruise, it is impossible to move your arm and elbow, and deformation of the elbow joint is visually visible, then most likely you have a ligament rupture. The first step is to apply cold to the sore spot, for example, ice wrapped in a napkin, and immobilize the arm by fixing it with a splint.
You can do a light massage around the elbow, but only where there is no pain. This will speed up blood flow and reduce pain. You should absolutely not take a hot shower or heat the rupture site. After a couple of days, when the pain subsides and the swelling subsides, you can apply warm compresses and begin working out your arm with smooth movements.
If it was not possible to cope with the problem at home, and the pain and swelling, on the contrary, only increase, you need to consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
You can figure out why the arm does not extend at the elbow joint using the following diagnostic procedures:
- The doctor collects anamnesis, examining and questioning the patient, palpates the problem area, observes how the limb is bent and at what angle it can fully straighten.
- The doctor pays attention to the described symptoms in order to exclude the infectious nature of the phenomenon in which the cartilage tissue suffers.
- Each joint disease manifests itself with certain symptoms, so it is important to listen to the patient. For example, with osteochondrosis, it is difficult or impossible to straighten the arm to the end.
- It is important to determine the nature of the pain when bending and extending the arm, as well as the moment of onset of pain.
- An x-ray is prescribed to rule out a fracture and to see the condition of the cartilage tissue.
- Tomographic examination is necessary to examine soft joint tissues.
If during the diagnostic process it is necessary to consider the general condition of the elbow joint, then arthroscopy is prescribed. The arthroscopy technique is both a diagnostic and therapeutic method.
A small incision is made in the articular cavity, through which a special device is inserted to assess the condition of the articular tissues. If necessary, during the diagnostic process, you can immediately eliminate problems and administer the necessary medications.
By inserting an arthroscope, it is possible to determine the reason why the arm does not bend in the elbow area, and at the same time restore damaged ligaments and cartilage tissue.
Help from doctors
There may be a dislocated joint or sprained ligament. X-ray will help to understand the cause of the inflammatory process, whether there are pathological changes in the joints or bones.
In any case, you cannot continue training. If your elbows do not bend after training, give your arms complete rest and immediately consult a doctor. If pain occurs only in the left elbow, this may indicate the presence of heart disease. In this case, the doctor will prescribe an ECG.
If a general blood test shows the presence of a coccal infection, the specialist will prescribe appropriate treatment. If a nerve is pinched, the athlete will be referred to a neurologist for consultation.
If the x-ray shows that there is a crack or fracture in the elbow, the surgeon will apply a plaster cast. Then special exercises will be required to develop the joint and restore its mobility.
Now you know the possible reasons for the elbow not bending after exercise and you will be able to provide first aid to yourself and your comrades in a timely manner. Be healthy!
Which doctor should you consult for pain when extending your elbow?
Pain in the elbow disrupts the patient’s general well-being and is an “alarm bell” that requires immediate consultation with a doctor. If you have discomfort in your elbow during extension, you may need help from the following specialists:
- neurologist - a specialist assesses the patient’s neurological status;
- rheumatologist - a doctor who deals with autoimmune joint diseases;
- traumatologist - a doctor who specializes in the treatment of traumatic joint injuries.
All of these doctors work at the Shifa clinic. Diagnosis of the causes of pain is carried out using innovative techniques that increase the information content of the examination. After verifying the underlying pathology that led to the appearance of pain in the joint, medical specialists select an individual therapeutic program aimed at eliminating pain, increasing the range of free movements and improving the quality of life.