- Tenosynovitis of the tibialis anterior muscle
- Periarthritis of the knee
- Knee massage after injury
- Massage for knee contracture
- Massage of leg joints for arthrosis
Massage is an auxiliary method of treating and restoring the knee joint. It is used for many diseases, completely different in origin. The procedure is used for injuries, inflammatory processes, and degenerative diseases. Doctors prescribe massage for synovitis of the knee joint, arthrosis, arthritis, tendovaginitis and many other pathologies. It is also used during the recovery stage after injuries and operations. Let's consider the main areas of application of the procedure.
Knee massage
Knee massage
- stimulation of blood and lymph flow;
- pain reduction;
- ensuring rapid resorption of blood clots;
- restoration of leg mobility.
First, the thigh muscles are massaged. After this, massage is performed for tendinitis of the knee joint. Next, the effect is carried out on the tibialis anterior muscle. Movements used:
- stroking;
- rubbing;
- kneading;
- vibration.
Directly the place where the source of pain is localized is massaged from the 4th-5th day of illness. Knee joint massage goes well with thermal treatments. The procedure is completed by stroking the area from the back of the foot to the knee.
Prevention.
To prevent the development of the disease, you often have to change your habits. It is recommended to unload the lower limbs by reducing weight (if it is excessive) or adjusting physical activity (make it systemic, moderate and without overload). Sports activities are not contraindicated, but those sports that allow the joint to move are effective, while those that are negative are those that are traumatic, forceful, and those that apply excessive pressure. Taking hormonal or other medications can provoke arthrosis. A lack of gelatin (collagen), vitamins, and chondroitin in the diet can also negatively affect the condition of the joints.
You may be interested in: Knee arthroscopy
Periarthritis of the knee
Therapeutic massage of the knee joint helps to cope with periarthritis. This is a group of diseases in which the soft tissues surrounding the knee become inflamed. These are usually where the tendons attach to the bone. The main symptom is pain. It develops as a result of the progression of degenerative processes and the development of reactive inflammation.
The causes of periarthritis of the knee are most often tendinitis or tendobursitis, which develops at the site of fixation of the pes anserine tendons. The inner surface of the knee hurts.
Purposes of massage:
Symptoms
It is important not to delay visiting a doctor if you experience the following symptoms:
- With a certain frequency, long-term aching pains occur, which intensify after exercise, even not intense.
- Local swelling appears and its usual shape changes.
- Stiffness is associated with pain and deterioration of gliding between articular surfaces.
- Crunching may be one of the symptoms. Appears when walking.
massage
massage
- relieve pain and inflammation;
- reduce swelling;
- ensure the outflow of lymph and prevent its accumulation in the periarticular tissue;
- relieve pain;
- ensure normal trophism of soft tissue structures and their regeneration.
Massage movements are carried out in the direction from the proximal part of the limb to the distal one. First, they stroke, then vigorously rub and lightly vibrate. The strongest effect is on the places of fixation of tendon structures to bone tissue. Be sure to warm up the muscles of the thigh and lower leg. Finish the massage with stroking. After the procedure, movements are performed in the knee.
Stump care after amputation
The process of scar formation takes up to one and a half years. During this time, you need to help yourself so that lower limb prosthetics
was successful. In this case, you can get back on your feet faster and regain mobility.
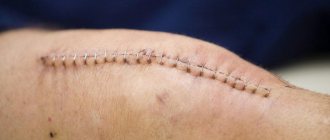
The postoperative suture is monitored in the hospital. If the patient has concomitant diseases that prevent the rapid healing of sutures (diabetes, vascular pathologies), he must follow the special recommendations of doctors. The wound heals in 3–4 weeks, after which a scar forms. It must be kept clean and moisturized with a cream or ointment recommended by a doctor. When the scabs fall off, you need to carefully massage the scar to prevent adhesion to the tissues underneath it. A doctor or nurse should show you how to do this in the hospital.
Massage
The stump should be massaged during the entire period of scar formation, but provided that there are no signs of an inflammatory process. The basic massage movements will be shown by a rehabilitation specialist in the hospital. As a rule, these are light and deep stroking of the stump in the direction from the end to the groin, kneading. The scar area is massaged with fingertips in a spiral, acting carefully and without stretching the tissue. It is important to relax the muscles during the massage in order to work them out. To glide, use massage cream. Complete the massage with vibration pats. It is necessary to massage the stump daily, preferably twice a day; the procedure takes 10–15 minutes.
Decongestant therapy
After surgery, swelling occurs, which can last up to a month or longer. But even after this, the stump will decrease in volume. To remove swelling after amputation and restore normal blood and lymph flow, you need to regularly place the truncated limb in an elevated position for 20 to 30 minutes. To improve circulation, you need to tense and relax the muscles of the stump in this position every 5 to 7 seconds.
Compression therapy is also necessary. It is carried out using bandaging with an elastic bandage and compression hosiery. A prosthetist should select the size of the compression sheath and give recommendations for wearing it while preparing the leg stump for prosthetics.
Compression therapy rules:
- You can bandage strictly after the doctor’s permission;
- compression cannot be performed if you have diabetes, problems with blood pressure and blood vessels, a non-healing wound and some other diseases;
- Under no circumstances should bandages be performed at night;
- the bandage is wound without tension: compression is achieved not by tension, but by increasing the number of layers - there are more at the bottom, fewer at the top;
- the bandage is applied diagonally, for each type of amputation there is a winding diagram;
- the bandage should not cause discomfort or pain, should not be too tight or loose, and the skin should not be purple or bluish.
To assess how correctly decongestant therapy is being administered, you need to regularly measure the circumference of the stump at the same points at the same time.
Knee massage after injury
Knee injury is a flexible concept. As a result of mechanical impact on the joint, a wide variety of pathological changes can occur: rupture of the cruciate or collateral ligaments, menisci, damage to the synovial bursa, intra-articular bone fractures, damage to hyaline cartilage, etc.
For severe injuries, massage does not play a major role in the healing process. Patients often require long-term limb immobilization or surgery. Therefore, we will consider situations when a knee joint is massaged after an injury that did not lead to significant tissue damage. This procedure is most effective when:
- bruise;
- traumatic bursitis;
- minor damage to the ligamentous apparatus.
As an auxiliary procedure, knee massage is also used for other pathologies, including bone fractures, complete rupture of ligaments, and significant damage to the menisci.
Traumatic bursitis
Which contracture is more dangerous: immobilization or post-traumatic?
Immobilization contracture most often occurs as a consequence of post-traumatic contracture. A simple example: when any part of the body (arm, leg, finger) is damaged, severe pain inevitably occurs, and a person unconsciously chooses a position for the injured limb in which the pain will be less. Most often this is an unnatural, incorrect position. But the damaged joint gradually gets used to it, and after a while it becomes very difficult, if not completely impossible, to change the position. This is immobilization contracture resulting from injury.
After two to three weeks, leaving the limb in the wrong position can lead to irreversible changes that can only be cured with joint replacement surgery.
Traumatic bursitis
Traumatic bursitis
Often observed in the area of the patella (prepatellar bursitis). It is an inflammation of the synovial bursa. Pathology can occur in acute or chronic form. Chronic bursitis is characterized by pain only with maximum flexion of the limb, as well as with palpation.
The massage begins with impact on the thigh muscles. Next, the anterolateral surface of the knee is stroked and rubbed. To do this, use the base of the palm and four fingers gathered in a bun. Massage the area above and below the patella. Finish with flexion and extension of the knee and stroking the entire injured leg.
Injury
With a bruise, hemarthrosis and synovitis can develop. Hemarthrosis is a consequence of vascular rupture. As a result, blood accumulates inside the joint. Inflammation after injury is reactive and leads to the accumulation of exudate in the knee.
Treatment requires joint puncture. A mobilization bandage is often applied. Massage is performed to resolve effusion, prevent atrophy of the quadriceps femoris muscle, and eliminate pain.
Ligament damage
Complete ligament rupture is treated surgically. Long-term immobilization of the knee is then required. Massage is used only for incomplete rupture, as part of conservative treatment, or at the rehabilitation stage. It helps relieve pain and restore joint function. They only affect the thigh muscles, and the knee joint itself is only stroked.
Meniscal damage
Meniscal tears are treated surgically in most cases. Occasionally, such injuries are treated conservatively (in case of minor injuries in the paracapsular zone of the meniscus).
During the acute period of injury, massage is done to reduce pain and speed up the resorption of effusion. It can reduce recovery time. Only the thigh muscles are massaged, stroked and kneaded. Massage of the knee itself can be done from the second or third day.
Massage after a knee fracture
A joint is made up of many components. When patients talk about a knee fracture, they usually mean a fracture of the patella, the most protruding part of the joint.
Most often, this injury is the result of a blow to the straight leg or a fall. Conservative therapy involves puncture of the joint and its immobilization for up to 4 weeks. If the fragments diverge, surgery is performed.
Reasons for the development of contracture
The appearance of contracture may be due to unsuccessful operation, prolonged immobilization of the knee joint, or improper behavior of the patient in the postoperative period. Note that a slight limitation of knee mobility in the first days after surgery is quite normal.
Table 1. Types of contractures.
| By development time | |
| Temporary | Appears immediately after surgery and usually disappears without any consequences. Its cause is a reflex contraction of the leg muscles in response to painful sensations in the knee. |
| Persistent | Characterized by impaired mobility of the knee joint for more than three weeks. The reason may be a poorly performed operation or poor rehabilitation. |
| For reasons and mechanism of development | |
| Functional | It develops due to prolonged immobilization of the knee joint and is not accompanied by changes in the periarticular tissues. It responds well to conservative treatment. |
| Organic | It occurs due to incorrect installation of the endoprosthesis, intraoperative damage to the joint capsule, ligaments, and tendons. The reason may be the formation of adhesions in the periarticular tissues or prolonged inactivity of the muscles of the lower limb in the postoperative period. |
A device for increasing the range of motion.
Functional temporary contracture is the least dangerous. With timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, you can quickly get rid of it. If the limitation of knee mobility is persistent and is accompanied by organic changes in the joint or periarticular tissues, it will be much more difficult to recover. Most likely, the only way to get rid of such contracture is through surgery.
Curious! Without active movement, muscles can gradually atrophy and become unable to contract normally. This can be avoided through early mobilization. That is why doctors make sure that the patient gets out of bed as early as possible with the help of crutches, begins to walk and perform special exercises.
Massage after a knee fracture
Massage after a knee fracture
Massage is done for the following purposes:
- prevention of hip muscle atrophy during the period of immobilization;
- strengthening regenerative processes;
- reducing pain and eliminating swelling.
If a plaster splint is applied, massage begins on the third or fourth day. It helps to quickly get rid of hematoma and swelling. After removing the plaster, a gentle massage of the knee is indicated. The main attention should be paid to the quadriceps femoris, as it is most susceptible to atrophic changes.
Stages of arthrosis
Arthrosis stage 1
The structure of healthy cartilage tissue and osteoarthritis.
Signs are mild and inconsistent. Painful symptoms occur after overloading the limb and may persist for some time. Imaging diagnostic methods can detect cartilage deformations. During periods of exacerbation, anti-inflammatory therapy is recommended. Then you need to find out what factors that provoke degenerative processes can be eliminated. To prevent further development, non-surgical treatment methods, intra-articular injections, are prescribed.
Arthrosis stage 2
The pain becomes more severe and lasts longer. Swelling and stiffness appear periodically. X-rays show a narrowing of the joint space, changes in the structure of the cartilage and menisci. In this case, conservative treatment and observation by a specialist are also necessary. The question of the need for arthroscopic surgery is being decided.
Stage 3 arthrosis
Movements are difficult. The pain syndrome persists for a long time. In addition to decreased mobility, sometimes there is a crunch in the knee, “jamming” of the joint. MRI or X-ray examination shows a decrease in the thickness of the articular cartilage, a violation of its integrity, and the presence of inflammatory processes. The effect of taking anesthetics is significantly reduced. Treatment should be comprehensive, with continuous monitoring of the patient. If arthroscopic correction is possible, surgery is prescribed.
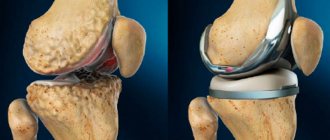
Arthrosis stage 4
This stage leads to disability. There is no cartilage tissue, osteophytes appear on the bone tissue. Pain and limited mobility are constant; conservative therapy can only bring relief for a short time. In this situation, surgical intervention with endoprosthetics is recommended.
Massage for knee contracture
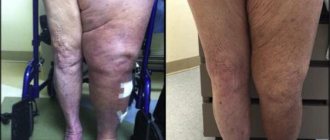
Contracture is stiffness. It is mainly the result of injury or surgery. Contracture is also a complication of long-term immobilization of the leg.
The problem with this disease is associated with anatomical changes in the soft tissues. Scars appear in it. The purpose of the massage is to loosen the scar, increase its mobility and develop the joint.
A massage effect is performed on the antagonist muscles. At the same time, muscle stretching exercises are performed. Often, after removal of the cast, patients experience atrophic processes in muscle tissue. The more pronounced they are, the softer the massage effect should be. Mainly muscles are massaged. This excludes techniques such as tapping, chopping or squeezing.
Massage accelerates blood flow in the muscles. It has a positive effect on metabolism, normalizes muscle tissue trophism, and improves joint mobility. But sometimes massage and exercises do not work, and then contractures have to be treated surgically.
General recommendations
In addition to exercises aimed at forming a stump, the patient himself must be prepared for prosthetics. You need to start preparing immediately after discharge from the hospital. While still in the hospital, the patient is referred to a rehabilitation specialist, exercise therapy instructor, and prosthetist to receive general recommendations and supervision.
What you need to do to maintain maximum mobility and activity:
- Perform the recommended set of general physical exercises to keep yourself in good shape. Therapeutic exercises begin under the supervision of a doctor on the first or second day after surgery.
- Do not forget about training the muscles of the remaining limb.
- It is important to ensure verticalization. On days 5–6, you should try to stand on crutches. Walking on crutches helps to overcome problems associated with poor coordination and loss of balance.
- It is important to train your back muscles. When limbs are amputated, they receive increased stress. Without appropriate training, the lumbar spine arches, which leads to problems with both the back and walking on a prosthesis. It’s good for your back to do pull-ups on the horizontal bar, do push-ups, and hang on a wall bars.
- Be under the supervision of a doctor in order to promptly notice the development of negative consequences of amputation - tissue infiltration, osteoporosis, swelling, etc.
If there are concomitant diseases, it is important to achieve their compensation and stabilize the general condition.
3. Treatment of the disease
Treatment of contracture can be conservative, requiring physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage, plaster casts and other procedures. In this case, it is unacceptable to immediately straighten the joint forcibly. Therapeutic gymnastics is also introduced gradually, moving from gentle movements to more active ones that develop ligaments.
If treatment of contracture with conservative methods fails, then surgery is resorted to. For surgical treatment of contracture, osteotomy, tendon transfer, resection of muscles and tendons, and removal of skin scars can be used.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!