According to statistics, after 30 years, every fourth person experiences pain in the knee joint. After 50 years, approximately 70% of Russian citizens turn to the doctor with similar complaints. The disease occurs in both young and old people. At first, unexpressed painful sensations do not cause much discomfort, but later the pain syndrome intensifies, and not only long walks are difficult, but it is difficult for a patient with sore joints to even get out of bed. How to treat osteochondrosis of the knee joint (OCS) while the disease is not yet bedridden?
Features of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Osteochondrosis of the knee joint is a fairly common pathology, occurring in 60-70% of all known cases of the lesion.
The vast majority of patients diagnosed with gonarthrosis achieve a successful result, however, there are cases of pathology becoming chronic.
The clinical picture of the disease is quite variable and depends on the existing form of pathology. Symptoms may not appear immediately, which makes it difficult to identify pathology at the initial stages of development.
An interesting fact is that with the development of pathologies during puberty, the disease can recede on its own, without the use of additional therapeutic agents, which is due to the completion of the stage of bone tissue formation.
Exercise therapy
For osteochondrosis, physical therapy can be used. It is important to remember that exercise therapy for osteochondrosis of the knee joint has its own characteristics. Classes must be prescribed by a specialist. He is also obliged to ensure that the patient performs exercises for osteochondrosis of the knee joint correctly.
Exercises
Exercises for osteochondrosis of the knee joint help strengthen muscle fibers. At the same time, physical stress on the knee joints should be moderate.
Important: Physical activity during this period should be light. Exercises should not be painful. The load and number of exercises must be increased gradually. Exercises are performed when the knee is affected in a squat or in a horizontal position of the body.
It is advisable to exclude outdoor games and exercises involving heavy weights. Eliminate rapid movement in space from life.
Think
You also need to think about reducing the use of uncomfortable body positions for a long time. Uncomfortable postures disrupt blood circulation in the affected joint. This means that the tendon will not receive enough nutrients. Doctors recommend doing exercises for 30–40 minutes during treatment of osteochondrosis. per day. It is recommended to divide exercises for osteochondrosis of the knee joint into several approaches, so that each session lasts 10–15 minutes.
Pathological forms
Today, it is customary to distinguish three forms of pathology, differing not only in symptoms, but also in the course of pathological changes:
- Koenig's disease
– inflammation of the cartilage tissue with subsequent detachment from the bone, which leads to difficulty in moving the knee. The form is most often found among adolescent and elderly patients.
- Osgood-Schlatter disease
– damage to the tibial tuberosity with subsequent thickening of the cartilaginous tissue of the knee, as well as the formation of a painful formation that limits the mobility of the leg. The pathology is most often diagnosed in adolescents who are actively involved in various sports (athletics, figure skating, etc.).
- Larens-Johansson disease
– characterized by a structural disorder of the patella, expressed in ossification. The damaged area is visible visually due to the appearance of edema. On palpation the patient experiences severe pain.
Probable causes
Among the likely causes of the development of pathological processes in the knee, it is worth highlighting:
- age characteristics
– mechanical wear and natural aging of tissues causes the destruction of cartilage in patients over 60 years of age;
- increased body weight
– the more weight, the faster the joints wear out. The risks of pathology with excess body weight are several times higher;
- hereditary factor
– causes the development of pathological processes mainly for young people;
- increased physical stresslanguages
– the main reason for the development of pathology in people whose work involves increased stress on the lower extremities.
It is also worth noting the existence of increased risks of musculoskeletal diseases after operations and injuries.
Operation
In some cases, due to destruction of the joint, only endoprosthesis replacement is possible. In order for the new joint to work like the original one, you should carefully prepare for the operation. You need to strengthen your muscles. The postoperative period is also important. At this time, you should also perform exercises on simulators under the supervision of a specialist.
Surgical treatment has advantages and disadvantages. Improvement is observed faster, but there is still a certain risk.
Most often, operations are performed using the following methods:
- Arthroscopy. The procedure is considered minimally invasive endoscopic. Restoration of intra-articular structures usually occurs quickly, without complications.
- Osteotomy. Involves cutting the bone, correcting the axis of the limb, and fusing the bones. It takes a long time for bones to heal. The advantage of the procedure is the postponement of endoprosthetics for the future.
- Prosthetics. The operation is considered major. The ends of the articular bones are cut out, and the metal parts of the prosthesis are placed on top of them. The procedure eliminates pain and restores greater mobility of the joint.
Symptoms of the disease
Among the general clinical symptoms of osteochondrosis of the knee joint, it is worth highlighting:
- painful sensations
– a classic sign, the intensity of manifestation of which is determined by the degree of development of pathological processes;
- local manifestations
– slight swelling;
- limited mobility
– initially there is a limitation of active movements (walking and running), and then passive ones (bending/extending a limb with outside help);
- characteristic crunching sound when performing movements
– mainly in the first hours after waking up, disappearing as daytime activity increases;
- transient lameness
, turning into a permanent one.
Classification
Research by American rheumatologists has made it possible to develop a classification of existing types of lesions, which takes into account not only the causes of the pathology, but also the features of its localization.
1. Primary/idiopathic
- local;
- generalized (involving several areas of the musculoskeletal system).
2. Secondary knee
Because of:
- post-traumatic;
- congenital;
- caused by damage to the bone tissue system.
By localization:
- local;
- generalized.
3. Tertiary
- caused by endocrine pathologies;
- caused by neurogenic arthropathy.
It is important to note that the variability of forms and the similarity of the clinical picture necessitate a diagnostic consultation with several specialists, including: a rheumatologist, a traumatologist, and an orthopedist.
Degree of development of pathology
The intensity of the lesion is determined by three degrees of osteochondrosis of the knee joint, each of which is characterized by a specific set of symptoms.
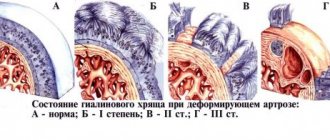
Osteochondrosis of the knee joint 1st degree
The initial stage of development of the disease. Symptoms at this stage are practically absent.
Physical activity provokes minor painful sensations.
Due to the fact that the tissues are just beginning to deform, it is quite difficult to visually identify abnormalities on an x-ray image.
Osteochondrosis of the knee joint 2nd degree
Due to the progression of tissue destruction, pain intensifies, muscles weaken, and spasms occur.
When the deformation becomes visually noticeable, the patient experiences quite severe pain and crunching when walking.
Osteochondrosis of the knee joint 3rd degree
Pathological processes progress, accompanied by pronounced pain, which is caused by the almost complete destruction of cartilage tissue and exposure of bone.
The progress of the pathology forces the patient to place the lower limb in a certain way, which impairs motor activity.
Painful sensations do not leave the patient even at rest.
Diagnostics
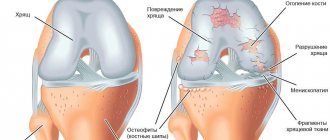
To exclude arthritis, tendonitis, tendovaginitis, in which symptoms are similar to arthrosis, differential diagnosis is carried out. Using an instrumental examination, the condition of the knee joint and its functional activity are determined. An X-ray is performed. The image shows all the changes: osteophytes, narrowing of the joint space, deformation of bone structures.
You can learn more about the level of cartilage damage after CT, ultrasound, and MRI. Research will help to find out about the location of inflammation in soft tissues, muscles, ligaments and tendons.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Regardless of the degree of the disease, measures to eradicate pathological processes must be comprehensive.
Only a specialist can determine the optimal treatment plan, taking into account the patient’s medical history and the characteristics of the pathological processes.
IMPORTANT! Self-medication can cause the situation to worsen and lead to irreversible consequences.
Drug therapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
determined taking into account an individual plan developed by a specialist.
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), including the drug Artradol, are considered to be particularly important and effective in drug therapy.
In addition, the following drugs may be prescribed in combination:
- analgesics;
- chondroprotectors;
- muscle relaxants.
Physical therapy (physical therapy) as a method of complex treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Physical education classes occupy a special place in complex therapy.
The use of gymnastic exercises helps improve blood circulation and activate metabolic processes, relieving spasms and strengthening the ligamentous and muscular apparatus.
Physiotherapy
It comes in handy in the subacute period, when pain subsides.
An important point in the use of physical therapy is strict adherence to the recommendations of the attending physician and limitation of sudden movements, as well as monotonous loads.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Physiotherapy helps relieve pain and also improves blood circulation.
Among the most effective physiotherapeutic procedures, it is customary to highlight the following:
- electrotherapy
– electric shock, which provides a warming effect and improves blood flow;
- shock wave therapy
– targeted impact with acoustic waves, which helps to activate metabolic processes and reduce swelling;
- vibration therapy
– exposure to vibration on affected tissues, the use of which is possible only for grades 1 and 2 osteochondrosis of the knee joint;
- laser exposure
– improves blood flow, relieving inflammatory processes.
It is important to note that physiotherapeutic procedures are only an integral part of complex treatment, and also help speed up the healing process and shorten the period of drug exposure.
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis of the knee joint
Can the last degree of osteochondrosis of the knee joint be corrected? Definitely.
In a situation where conservative methods do not give the desired results, surgical intervention comes to the rescue, the key task of which is to preserve functionality.
The choice of surgical technique is based on the degree of development of pathological processes and is determined taking into account the individual characteristics of a specific clinical picture:
- Drilling out affected tissues
– used in the absence of inflammatory processes. The method has a particularly high percentage of efficiency.
- Fixation of bone tissue with screws
– is implemented in the presence of semi-mobile fragments, however, it has a fairly high risk of complications.
- Securing large pieces using accessible methods
– tissue plastic surgery, using your own cartilage tissue, which allows you to restore the functionality of the limb.
Physiotherapy
To relieve the exacerbation, physiotherapy for osteoarthritis is recommended. Its goal is to reduce muscle spasms, reduce pain, relieve joint stiffness, and eliminate contractures. Depending on the type of effect of physiotherapy for osteochondrosis, they are divided into the following procedures:
- General action. The group included acupuncture, electrosleep;
- local. Involves an impact on the joint area. This group includes electrophoresis with medications, laser therapy, thermotherapeutic method of influencing the joint, diadynamic therapy, magnetic therapy, administration of anti-inflammatory drugs under the influence of ultrasound;
- helping to get rid of reactive synovitis. The group includes the impact on the patient’s body of a high-frequency electromagnetic field, the method of electrotherapy, which consists of exposing the body to galvanization and medications, as well as ultraviolet exposure;
- eliminating joint stiffness. The group includes the following procedures: ultraphonophoresis, electromyostimulation, medicinal electrophoresis, traction therapy.
- Massage also plays an important role. It has an analgesic effect, relieves inflammation, and helps restore joint function. Also, thanks to massage, muscle tension decreases, their trophism improves, strength and tone increase.