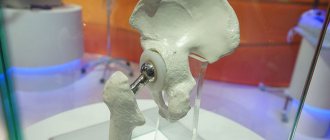
Types and signs of postoperative complications
| Problem | Symptom |
| Infectious inflammation | Increased temperature, redness in the knee area |
| Contracture | Limitation of flexion/extension, up to complete immobility |
| Synovitis | Severe pain, inability to move without assistance, swelling |
| Repeated dislocation/fracture | Crunching, decreased mobility |
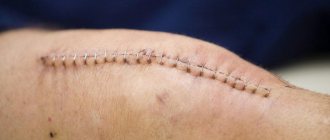
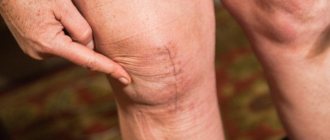
Perfectly healed suture, approximately 4-6 months after surgery.
Particularly unforeseen consequences threaten those who listened to the advice of “experienced” people not on specialized forums or on social networks, but near home. Old ladies with the best intentions (and commercials) offer ways to heal. The peculiarity of the Slavic worldview is that it will go away on its own; it does not work in the case of endoprosthetics.
Contracture
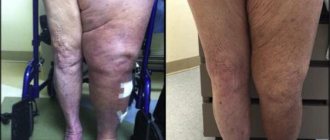
It occurs extremely rarely (0.1%), since individual prostheses are used for implantation, taking into account age, anatomical and gender characteristics, but there are precedents. Swelling in the area of the surgical field, impaired support function, joint pain are signs of the development of the disease. Ignoring the symptoms leads to shortening of the leg and lameness.
The person’s leg is in a relaxed state, but cannot straighten. Apparently there was no postoperative rehabilitation or the prosthesis is not positioned quite correctly.
Contracture can be temporary or permanent. A decrease in kinematics or complete immobility is possible. A person consciously strives to reduce discomfort, so in the postoperative period he tries to move his leg so that it does not hurt. Rehabilitation requires regular loads of a certain nature. If they lack natural blood flow and healing slows down, the pathology leads to scarring and a permanent form.
In the most difficult cases, contracture is treated surgically. It's a fairly simple procedure.
Prescribing a treatment regimen is the responsibility of a specialist. Forced flexion/extension or lack of movement will only expand the affected area.
- physical therapy and massage;
- electrophoresis, physiotherapy;
- fixation of the joint with a plaster bandage;
- absence of overvoltage, heating, hypothermia;
- control over the state of the body: proper nutrition, absence of bad habits.
There is a device that helps you independently stretch the back of your thigh.
Synovitis
Detected in 0.3% of patients. Features: the knee hurts, the leg swells, the pain does not stop even after a course of medications and physiotherapy. Inflammatory processes of the joint membrane are characteristic, as a result of which the synovial bursa fills with fluid.
In this case, the main thing is not to confuse sanovitis with infectious inflammation, because the treatment tactics are completely different.
Recovery proceeds individually for everyone, depending on the characteristics of age, gender, and general health conditions. The development of synovitis is not a medical mistake; in 95% of cases, the disease progresses due to violation of medical prescriptions. If you have been diagnosed with synovitis, a fluid puncture and a course of further rehabilitation may be prescribed.
Inflammation
After surgery, the muscles or tissue around the endoprosthesis may become inflamed. In 4-11% of cases, infectious processes lead to revision of the implant. Most often, this phenomenon is observed in patients who have undergone arthroscopy due to rheumatoid arthritis or arthrosis.
X-ray image of an infected knee joint, try to guess what is unnecessary in this image?
Also, the development of the infectious process is provoked by malnutrition or excess weight, the presence of immune diseases, alcohol consumption, diabetes and oncology. Immunosuppressants and corticoids are contraindicated as treatment, as they increase the risk of infection. Signs of inflammation:
- stable, elevated, but not too high body temperature (rises more in the evening);
- the leg does not work well, it hurts and swells;
- local redness;
- sometimes discharge of pus from a wound or joint.
If there is something wrong with your knee, the first sign is pain and increased temperature in the area of the implant.
Inflammation is an unpredictable pathology, since it can occur both in the first months after arthroplasty and 1-2 years after knee replacement. If in the long-term postoperative period you have a question: “Why is the knee hot and painful?” — most likely, we are talking about a late hematogenous infection in the implant area.
Thanks to modern equipment, the implant is installed at the site of the damaged joint with millimeter precision, and kinematics are checked in a flexed/extended position using computer visualization. 1-1.2% of cases end with repeated dislocation or fracture of the endoprosthesis. In rare situations, the problem is caused by incorrect installation or poor-quality prosthesis; 98% of patients create a problem for themselves by ignoring rehabilitation recommendations.
This happens when an injury occurs, for example a person falls. This requires revision surgery.
The main sign of a fracture is a crunching sound inside the knee joint. And if at an early stage such a symptom can be explained by a medical error or a postoperative complication, then in the future the crunching indicates the growth of scar tissue. Incorrect recovery occurs due to non-compliance with the regime and diet.
Pain after hip replacement: causes and treatment
Hip arthroplasty is the replacement of a damaged articulation element with an artificial implant.
This operation is prescribed for various reasons, these can be complex diseases of the hip joint or injuries.
After endoprosthetics, the patient must follow certain recommendations.
Most often, endoprosthesis replacement surgery is prescribed in the following situations:
- Femoral neck injuries (usually fractures).
- Severe, advanced stages of rheumatoid arthritis.
- The presence of aseptic necrosis of the head (avascular necrosis).
- Development of hip dysplasia.
- Severe stages of coxarthrosis.
The need for an implant may arise as a result of post-traumatic complications, for example, arthrosis. The patient’s life after endoprosthetics changes, as a number of recommendations appear that must be strictly followed.
There are some restrictions; the patient must perform a set of special physical therapy. At first, the patient is forced to use crutches.
The duration of the postoperative period and complete recovery depend entirely on the general condition of the patient, his age and other numerous factors. In order to avoid possible complications from hip replacement, the patient must be disciplined in following the recommendations of the attending physician.
The complex of therapeutic exercises, which is necessary to restore the hip joint, must be performed under the supervision of a medically qualified instructor. Living in a new mode will significantly bring the moment of complete recovery closer, thanks to which the patient will be able to start walking much faster without the help of crutches. It can also be noted that rehabilitation after hip replacement can continue at home.
After endoprosthetics, pain is usually pronounced. It is strictly forbidden to take any measures on your own, otherwise you may experience serious complications.
The main indications for endoprosthetics surgery are the symptoms that accompany the disease and the results of clinical and radiological studies. The symptoms indicated by the patient are the most significant factor that is an indication for surgery.
In some situations, despite the fact that coxarthrosis is in the last stage of its development (this is clearly demonstrated by x-ray examination), a person is not bothered by pain and other symptoms of the disease. This pathology does not require surgical intervention.
The endoprosthesis, which is fixed with cement, differs from the previous one in the integrity of the acetabular element.
Each component of the implant has its own parameters, so the doctor must determine the size that is ideal for a particular patient.
Endoprostheses also differ from each other in the method of fixation. Exists:
- Fixation is cement.
- Fixation is cementless.
- Combined fixation (hybrid of the first two).
The endoprosthesis can be unipolar or total. The use of one or another artificial joint depends on the number of elements requiring replacement. The interaction in the endoprosthesis is called a “friction pair”.
How long an artificial hip implant can last depends entirely on the quality of the material from which the endoprosthesis is made.
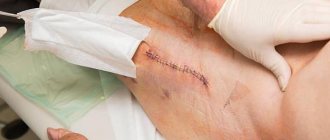
The hip replacement process is performed by two teams - anesthesiology and operating room. The operating room team is led by a highly qualified practicing surgeon. In the photo you can see where the doctor makes an incision to remove and replace the joint.
The average duration of hip replacement surgery is 1.5-2 hours. The patient is under anesthesia or spinal anesthesia at this time, so he does not feel pain. To exclude infectious complications, intravenous antibiotics are required.
After endoprosthetics, the patient remains in the intensive care unit for some time, under constant medical supervision. Over the next seven days, the patient continues to be administered drugs that prevent blood clotting and antibiotics.
In order to maintain a certain distance between the legs, a pillow is placed between them. The patient's legs should be in an abducted position.
Body temperature after hip replacement is often unstable. The patient feels pain for some time, so he is given anesthetics.
It is impossible to predict in advance how long the recovery period after endoprosthetics will take. In order for the rehabilitation process to go much faster, the patient must be disciplined and must follow all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Recommendations that must be followed for the rest of your life The patient should start moving the very next day. And this is done without getting out of bed. The patient can move and perform therapeutic exercises right on the bed.
The course of exercise therapy recommended after joint replacement surgery is as simple as possible and does not cause pain. Such exercises are done during the first month following endoprosthetics.
To fully restore mobility in the hip joint, it is necessary to constantly work on its development. In addition to a course of physical therapy, the patient is shown breathing exercises.
Most often, the patient can walk already on the third day of rehabilitation, but he must use crutches. After a few days, doctors will remove the stitches. After the operation to implant an artificial implant, the sutures are removed on the 10th, 15th day. It all depends on how quickly the patient recovers.
Many patients ask themselves: upon arrival home, how to live next? After all, in the hospital they were under the constant supervision of doctors and staff, and the entire recovery process was under control.
Indeed, life with an endoprosthesis is somewhat different from the life that preceded endoprosthesis. It has already been said above that you need to constantly work on an artificial hip joint.
The patient should move as much as possible, but avoid fatigue and hip pain. Therapeutic exercises play a huge role in the recovery process, but a set of exercises should be compiled by a doctor who keeps the patient’s medical history.
Upon discharge from the hospital, the patient is recommended to visit special centers, where physical therapy instructors will work with him.
Returning home, the patient must work hard on the new joint, otherwise the recovery period may take a long time.
If the patient does not want serious complications to arise after the operation and pain to recur after returning home, he must follow a number of recommendations.
- The artificial joint should not be allowed to bend completely.
- In the “sitting” position, the knees should not be in the same plane as the hips; they should be lower. Therefore, it is recommended to place a pillow on the chair.
- Whatever position the patient is in, he should not cross his legs.
- When getting up from a chair, your back should remain straight and you should not lean forward.
- You need to use crutches until your doctor stops them.
- Walking in the first days after endoprosthetics can only be done with the help of medical staff.
- Shoes should be as comfortable as possible, so heels are contraindicated.
- When visiting another doctor, he must be informed that the hip joint is artificial.
Hip replacement requires work not only on the joint itself, the patient must always take care of his overall health. If pain occurs in the area of the hip into which the artificial implant was implanted, accompanied by an increase in body temperature, you should immediately consult your doctor.
It is likely that many of these recommendations will eventually be abandoned. This will depend on how long it takes the patient to fully recover. Usually seven to eight months are enough for rehabilitation.
The patient should be informed that an artificial hip implant, like any mechanism, has its own service life. Therefore, over time, the endoprosthesis wears out. On average, its validity period lasts 10-15 years and depends on certain conditions and features.
If the endoprosthesis quickly fails, most likely it was not used correctly. Any active sports are contraindicated for a patient with an artificial hip prosthesis.
When doing physical therapy at home, the patient should be aware that ignoring the doctor’s recommendations can cause serious complications. Exercise therapy exercises should not be difficult or cause pain. Large loads should not be placed on the artificial joint.
Comprehensive therapy for such a phenomenon as crunching when going down or up stairs, walking and other leg movements is necessary in the presence of diseases that have provoked changes in the articular and adjacent tissues.
For degenerative changes caused by arthritis and arthrosis, it consists of taking medications whose action is based on restoring cartilage and maintaining its structure in a healthy state.
Equally important is taking anti-inflammatory drugs, hormonal medications and painkillers. These medications are also suitable when there is a crunch in the knee after a limb injury.
Recommended medications:
- tablets, capsules or ointments with chondroitin;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments and tablets;
- joint fluid substitutes in the form of injections;
- painkillers in the form of ointments, gels, tablets and injections;
- warming preparations for local action with pepper, camphor and peppermint.
- Separately, it is worth highlighting ointments containing viper venom, for example, Salvisar. The peculiarity of such ointments is that they do not contain NSAIDs, which means they do not cause side effects characteristic of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory ointments, while they have an analgesic effect for arthritis, myalgia and neuralgia.
Development of thrombosis
Internal venous thrombosis is found in half of patients undergoing knee replacement. In 2% of cases, thromboembolism develops, which can be fatal. The high likelihood of complications has forced specialists to develop effective preventive measures that are included in the surgical protocol. The risk group includes:
- patients over 75 years of age;
- obese people
- diabetes mellitus;
- oncological diseases;
- patients taking hormonal drugs.
During surgery, enzymes begin to enter the blood, increasing its coagulability. This means that the formation of blood clots begins at this time. In half of the cases, thrombosis is detected on the first day, in 75% - in the next 2 days after prosthetics.
To prevent this complication, medication and orthopedic methods are used. The latter include:
- compression underwear;
- physiotherapy;
- electrical stimulation.
Oral anticoagulants are considered the most effective medications. They are taken within 14–35 days.
Types and signs of postoperative complications
Knee replacement is performed to relieve chronic pain and improve a person's quality of life. After surgery, people are able to move normally and stop taking pain medications (unless they have severe osteoporosis in other joints). However, sometimes, after endoprosthetics, the patient develops alarming symptoms. His temperature rises, severe pain, swelling, crunching in the knee and other unpleasant phenomena appear.
Painful sensations may indicate the development of infectious complications, contractures, synovitis, joint instability or other dangerous consequences.
With purulent-inflammatory complications, fever, chills, headache and general weakness appear. His knee also hurts unbearably, and the surrounding skin becomes red and hot to the touch. The pain is bursting, and pain relief with ointments and tablets has no effect. Why is the knee hot? This is explained by the accumulation of pus inside the joint and the development of an acute inflammatory process.
With thrombophlebitis of the veins of the lower extremities, the leg swells and a feeling of fullness appears in the lower extremities.
What to do if pain in the knee appears after endoprosthetics? You need to go to the doctor immediately. In the worst case, he will recommend repeated surgery and revision of the joint cavity; at best, he will advise what ointment or medications to use. It is possible that knee pain is caused by nerve irritation and will go away within 2-3 months.
Inflammation
Postoperative pain syndrome
Knee replacement is performed to eliminate discomfort and restore joint mobility. After prosthetics, the patient is able to move independently and stop taking medications. However, it also happens that after surgery there is pain in the knee, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature, swelling and crunching.
Pain after knee replacement may indicate:
- the addition of a bacterial infection;
- development of synovitis;
- contractures;
- joint instability;
- other dangerous complications.
The type of pathology is determined based on the nature of the discomfort. Purulent inflammation is accompanied by fever, headache, and general weakness. A person’s leg hurts a lot, the skin turns red and becomes hot. The pain is pressing, ointments and tablets do not help in this case.
Increased local temperature and swelling of the knee are explained by the accumulation of purulent contents and the development of acute inflammation.
In the presence of contractures, the mobility of the knee joint is impaired. The pain has a mild aching character, it intensifies when walking.
With thrombophlebitis, the discomfort is bursting in nature. If a person after endoprosthetics notices that the knee is hot, severe pain and cramps appear, he should immediately consult a doctor.
In some cases, repeated surgery is prescribed to eliminate the cause of the discomfort, or drug therapy. The pain may be associated with irritation of the nerve roots, in which case it disappears after a few months.
Is a disability group given to people who have undergone endoprosthetics? In fact, the operation is not grounds for receiving benefits. People don't do it to become disabled. Surgery helps them improve their quality of life and enable them to move normally.
Inflammation
Complications after hip replacement surgery
Negative consequences and complications after hip arthroplasty (HJ) occur infrequently, but they are not excluded. In the postoperative period, the patient may experience inflammation accompanied by a bacterial infection. Due to non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations, dislocations and fractures of the prosthesis, blood clots and other disorders occur.
Hip replacement is a complex and traumatic operation, so it cannot always be completed without negative consequences. To reduce the risk of complications, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period after endoprosthetics. The following are at risk for postoperative disorders:
- elderly people over 60 years of age;
- those suffering from systemic pathologies, such as diabetes, arthritis, psoriasis or lupus erythematosus;
- patients with a history of fractures or dislocations of the hip joint;
- patients suffering from chronic inflammatory diseases;
- violating the advice and recommendations of the surgeon.
In older people, complications after knee or hip replacement develop due to physiological characteristics. Due to the fact that as the body ages, joint structures become thinner and destroyed, older people are at greater risk of experiencing negative consequences.
If a person has a fever after hip replacement, swelling, a purulent fistula has formed and is experiencing severe pain in the thigh, most likely an infection was introduced into the wound during the operation. For such symptoms, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and auxiliary products that can help relieve inflammation.
They often develop in late rehabilitation periods, when the patient ignores physical limitations and early refuses to move on crutches. Due to the increased load, the femoral component is displaced in relation to the acetabulum, as a result of which the head of the endoprosthesis does not coincide with the cup. The damaged area swells and hurts, the person cannot take some familiar positions, the leg loses its functionality, and lameness is observed.
If discomfort has just begun to appear, it is better to immediately visit a doctor; the sooner you begin to eliminate the problems, the less consequences there will be.
If nerve fibers are damaged during surgery on the hip joint, neuropathic syndrome develops. This complication may be a consequence of lengthening the leg after installation of the implant or pressure on the nerve endings of the resulting hematoma. The main symptom of neuropathy is acute pain that spreads to the entire lower limb.
Sometimes it feels as if the foot is numb or there is a burning sensation and a feeling of goosebumps running across the skin. With such symptoms, it is dangerous to endure pain and self-medicate. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, you will be able to normalize your health with the help of physical exercises, otherwise you cannot do without surgery.
After replacing the hip joint, the integrity of the bone structures of the hip may be damaged in the place where the endoprosthesis leg is fixed. This is often a consequence of decreased pelvic bone density or poorly performed endoprosthetic surgery. If a fracture occurs, the person experiences severe pain, swelling and hematoma form at the site of the injury, and the functionality of the joint is impaired.
The first days after endoprosthetics, the patient will be partially immobilized, as a result of which the blood flow in the veins and arteries will be disrupted. This leads to critical blockage of blood vessels with a thrombus. Often the condition does not have pronounced symptoms, so it is important to control blood circulation and not violate the doctor’s recommendations during the postoperative recovery stages. Sometimes, with thrombosis, the patient notices that the limb hurts and is swollen; shortness of breath, general weakness, and loss of consciousness may also bother.
Complications during endoprosthetics can be very diverse. One of the most common is the body’s rejection of the implant. After prosthetic surgery, the body may react inadequately to foreign material, resulting in inflammatory and allergic reactions. Swelling, suppuration and fistulas form at the implantation site. In addition, a person may experience:
- blood loss;
- loosening of the prosthesis structure;
- lameness;
- groin pain;
- edema, due to which the legs swell so that the function of the joint is completely impaired.
If in the first days after the operation symptoms of infection begin to appear and a fistula has formed at the resection site, the doctor prescribes antibiotics, NSAIDs and painkillers. If dislocations, subluxations or fractures are suspected, an MRI examination is prescribed. When the diagnosis is confirmed, revision endoprosthetics is performed, replacing the destroyed structure with a new one.
To prevent complications after hip replacement, in the initial stages and in the long-term periods after surgery, it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations and monitor your health. On the 2-3rd day after endoprosthetics, you are allowed to sit on the bed, then on a chair, but you should not immediately load the sore joint.
An important factor influencing the patient’s condition in the postoperative period is proper nutrition. The diet should include products of plant origin, red meat and fish, dairy and fermented milk products, nuts, seafood, cereals, jellied meat. Proper and balanced nutrition, in addition to recovery, will help control body weight, which is especially important in the first months of rehabilitation, when the patient’s activity will be limited and the risk of gaining extra pounds will increase.
Sources
- Malysheva, Inna The most important thing about salt deposits and gout / Inna Malysheva. – M.: Vector, 2014. – 133 p.
- Romanovskaya, N.V. How to defeat osteochondrosis / N.V. Romanovskaya, A.A. Romanovsky. – M.: Modern writer, 2001. – 224 p.
- E. V. Solovyova Joints hurt: what to do? Arthritis, arthrosis, radiculitis, salt deposition / E. V. Solovyova. – M.: St. Petersburg: Nevsky Prospekt, 2006. – 160 p.
Author of the article: Vasily Chirkov
Good afternoon My name is Vasily, I have been working as a therapist in a municipal clinic for just under 11 years. Considering myself a professional, I want to teach all website visitors how to solve complex problems. All data for the site has been collected and carefully processed in order to convey all the necessary information in a convenient form. However, in order to apply everything described on the site, mandatory consultation with professionals is always necessary.
✔
About me
✉
Feedback
Types and signs of postoperative complications
The frequency of infectious complications after surgery is 0.2-4.5% for primary prosthetics and 4.5-12% for revision (repeated) prosthetics.
The development of purulent-inflammatory complications in the first 12 months is due to microbial contamination during surgery. Pathogenic microorganisms can penetrate the knee joint aerogenously or by contact. They are carried into the wound with dirty air, the surgeon's hands or surgical instruments.
The risk of postoperative complications is especially high in elderly patients with diabetes mellitus, obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, immunodeficiency conditions and in patients taking corticosteroids. The prognosis is also worsened by the limited experience of the operating surgeon, large blood loss, the duration of the operation over 3 hours and the use of bone cement without an antibiotic in the composition.
In a later period (a year or more after surgery), inflammatory complications are a consequence of the hematogenous spread of microorganisms. Pathogenic microbes penetrate into the joint cavity through the bloodstream from foci of chronic infection.
Possible sources of hematogenous dissemination:
- skin;
- organs of the genitourinary system;
- Airways;
- oropharynx;
- lower parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
The severity of clinical manifestations in a patient depends on the source of infection, the virulence of the pathogen and the time of development of the pathology. The classic bright picture of purulent inflammation (fever, swelling and hyperemia of the knee, fistula formation) is observed in less than half of the patients. Others may be bothered by constant pain in the knee joint, which intensifies with movement.
To successfully combat paraprosthetic infection, an integrated approach is required. The most effective is open sanitation of the joint cavity with complete removal of all components of the prosthesis (preservation of any of the components of the implant may ultimately lead to repeated surgery). At the same time, the patient is prescribed local antibiotic therapy by creating a depot in the inflammatory focus.
Conservative treatment of infectious complications is possible only with early diagnosis, low virulence of the pathogen and the presence of contraindications to surgery.
Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities develops in 40-60% of patients who have undergone major orthopedic surgery. An analysis of a number of clinical studies has shown that after knee replacement, this complication occurs in 85% of patients. In 0.1-2% of cases, thrombosis leads to fatal pulmonary embolism (PE).
Risk factors for thromboembolic complications:
- obesity ІІ-ІІІ degree;
- age over 75 years;
- chronic heart failure;
- varicose veins;
- diabetes;
- oncopathology;
- previous heart attack;
- long-term immobilization;
- taking steroids and hormonal contraceptives;
- chronic nonspecific lung diseases (CNLD).
During the operation, the human body begins to release substances that increase blood clotting. Thrombosis begins during surgery, so they occur in the early postoperative period. In 50% of cases they appear on the first day, in 75% - in the first 48 hours after surgery.
In orthopedics, mechanical and medicinal methods are used to prevent postoperative thrombosis. The first include compression, electrical neurostimulation and physical therapy. As for medications, unfractionated and low molecular weight heparins, vitamin K antagonists, and coagulation factor X inhibitors are used for prophylactic purposes. In recent years, doctors increasingly prefer oral anticoagulants (Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Dabigatran etexilate).
In the first 5-6 days after, the patient is in the hospital, where he receives all the necessary medications and procedures. To prevent thromboembolic complications, the patient is given anticoagulants to avoid infection - antibiotics. In the early stages after surgery, the patient is recommended to wear compression stockings.
The day after endoprosthetics, doctors remove drainage from the wound, which served to drain fluid. Afterwards, walking with elbow crutches or walkers is allowed. The medical staff helps the patient get up and explains how best to walk and what exercises to do. Early physical activity and exercises help avoid the development of contracture.
If the patient does not experience any complications, he is soon discharged from the hospital. Working people are given sick leave. The length of sick leave can range from 1.5 to 3 months. Upon discharge, doctors give the patient a number of recommendations for caring for the postoperative wound. After two weeks, the patient will need to come to the hospital to have the stitches removed.
For 5-6 weeks the patient is forced to walk with crutches. After this period ends, he will no longer need them. However, you can return to long walks, swimming and other vigorous activities in 5-6 months. The question of playing sports is decided together with the attending physician. Orthopedists prohibit heavy physical activity.
A follow-up examination of the patient is usually carried out 2-3 months after surgery. If, during the examination, doctors identify signs of instability, infection, thromboembolic or other complications, the patient is given the necessary assistance. After the first scheduled examination, a person visits a doctor once every 2-3 years.
At the end of the rehabilitation period, it is worth continuing to do the exercises for several more years. Therapeutic exercise is necessary to maintain normal muscle tone and functional muscle activity. Exercise helps a person maintain weight. Since obesity accelerates the development of osteoporosis, preventing it helps prevent loosening and instability of the knee joint.
Endoprosthetics are often performed on older people prone to osteoporosis. Surgery further traumatizes the bones, which contributes to their further destruction. Therefore, to prevent osteolysis, the patient needs to take drugs that normalize metabolic processes. Medicines must be taken daily.
Drugs used for preventive purposes:
- Alendronate;
- Recostin;
- Fosamax;
- Alendronic acid;
- Bonviva;
- Rizendros;
- Zolerix.
The listed drugs inhibit proteolysis, that is, they slow down the destruction of bone tissue. Along with them, doctors recommend that patients take calcium, phosphorus and vitamin D supplements. They saturate bone tissue with essential minerals, thereby strengthening them. Particularly effective in this regard are medications containing hydroxyapatite (Calcimax, Ossein-Hydroxyapatite). This substance is very well absorbed and acts much more effectively than calcium carbonate or calcium citrate.
20 years after primary endoprosthetics, the patient must consult a doctor to monitor the need for revision surgery. The specialist must carefully examine and examine the person. If the patient shows signs of instability of the knee joint, re-endoprosthetics may be necessary. After revision surgery, the incidence of complications is higher than after primary surgery.
Inflammation
Joint replacement surgery is not a whim, but an opportunity to maintain independence and avoid disability. Implantation is recommended if it is impossible to restore the natural mobility of the limb using conservative methods. Surgical intervention is performed for:
- severe damage to the ligaments, when therapy and compression are not effective;
- osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, to stabilize the pathology and remove damaged elements;
- bone dysplasia, when bone growth is impaired;
- progressive aseptic necrosis. Tissue death begins, subsequently natural blood flow stops, and the joint ceases to function completely;
- gout.
The surgeon is the person on whom it depends whether your problem will be solved or worsened, so choose a doctor very responsibly.
Modern doctors prefer gentle techniques; interventions on an open surgical field are carried out only if it is impossible to carry out the procedure in a minimally invasive way. With computer-guided arthroscopy, healthy tissue is practically not damaged, and the risk of bleeding and infection is reduced.
Measures after surgery
To remove excess fluid and blood clots from the wound, drainage is initially installed. Vital signs are taken daily during inpatient observation to make the recovery process as effective as possible.
If knee replacement is successful, a course of antibiotics and rehabilitation measures is prescribed:
- Exercise therapy under the supervision of a methodologist. You should not count on a miracle immediately after the operation; at first you will even have to bend and straighten your leg with the help of a doctor;
- massotherapy;
- procedures in the physiotherapy room depending on health conditions;
It’s really better to get up as early as possible, ideally get out of bed on the second day after surgery and take your first steps.
Why does a knee or hip joint endoprosthesis crunch and click?
Date of last update: 02/25/2019
The appearance of clicks in the first months after endoprosthetics is caused by movements of the periarticular ligaments, muscles, and muscle tendons. When moving, they “rub” against each other or come into contact with bones, which is accompanied by characteristic sounds. Such clicks cause irritation for patients, but in no way harm their health.
Curious! Clicking in the knee joint is most often caused by the “crow’s foot” structures, and in the hip joint – by the tendon of the rectus femoris muscle.
At a later date, clicks may occur due to changes in the spatial orientation of the endoprosthesis components. As you know, over the years, the implant wears out a little, and its articular surfaces lose congruence. As a result, a discrepancy occurs between the parts of the prosthesis, causing them to collide with each other during movements. This leads to the appearance of sounds. In some cases, a person may have the feeling that the hard parts of the endoprosthesis are in contact with each other.
Note that normally, clicking should not be accompanied by pain or other alarming symptoms.
Signs of pathological clicking:
- pain in the joint area;
- the appearance of severe discomfort in the knee or hip;
- limitation of movements in the lower limb;
- fever, skin hyperemia, swelling in the area of the operated joint.
The appearance of these symptoms may indicate late postoperative complications. The most common of these include periprosthetic infection, loosening and instability of endoprosthetic components.
If you do not have alarming symptoms, there is no point in worrying. Most likely your joint clicking is of a physiological nature. To make sure there are no complications, you should see a doctor regularly.
If you experience pain, a fever, or have difficulty walking, you should seek medical help without delay.
Table 1. Diagnostic methods that help identify the cause of clicking sounds.
Some people complain of a characteristic clicking sound in the operated joint after hip or knee replacement. They may occur months or years after surgery. As a rule, such clicks are painless and do not cause physical discomfort to the person.
| Video (click to play). |
What sports and physical activities will I have to give up after endoprosthetics?
Any exercises with axial load on the operated joint should be avoided. These sports include basketball and tennis and other sports that involve jumping and running.
What sports and physical activities are acceptable after endoprosthetics?
Patients are allowed and, moreover, recommended after total endoprosthetics to do aerobic exercise such as walking up to 3 km per day, swimming, exercise bike and moderate strength training. If you are involved in any sport and would like to continue to do so after surgery, you should discuss this with us prior to surgery.
When can I start swimming after endoprosthetics?
After knee replacement after 8-12 weeks
After hip replacement - 8-12 weeks
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xCRpngDOinY
Important! The pool must be equipped with steps since you cannot use a vertical ladder to go down and up.
When can I drive?
Typically, you will be able to drive within 6 weeks after surgery. This issue will be resolved after your first follow-up visit to us after surgery.
How long should I take precautions after total hip replacement?
You should be limited to 90 degrees of hip flexion. Your leash doctor will show you how to pick up objects from the floor and put on socks. You should not cross your legs during the postoperative period. You should not carry more than 12 kg after surgery. You should not rotate through the operated joint.
I noticed that the incision site on the knee or hip joint is warmer than the opposite one. Should I worry about this?
If you feel warmth in the surgical area, but there is no redness, no discharge from the wound and you do not have a fever, then there is no need to worry. Such heat in the wound area can remain for 4 months, and this is associated with increased blood flow in the area of the operation, which indicates wound healing.
Can I take a knee?
Yes, you can stand on your operated knee 6 weeks after surgery as long as you do not experience any discomfort.
What does it mean if I feel or hear a clicking sound in my knee after knee replacement?
How long after surgery can I visit the dentist?
If you have an acute toothache, you can immediately visit a dentist. But we must remember that after the operation, for the rest of your life, before any dental manipulations at the dentist, you must take antibiotics. It is best to schedule a routine visit to the dentist 12 weeks after surgery.
Who prescribes antibiotics before visiting the dentist?
Our recommendations will include antibiotics in case of an emergency visit to the dentist. After this, you will take antibiotics prescribed by your dentist.
What infections should I be afraid of after endoprosthetics?
An ordinary runny nose does not pose a threat, but if the runny nose is complicated by bronchitis or sinusitis, you need to visit a physician to prescribe antibiotics.
Antibiotics recommended for toothache may not be suitable for other infections. Consultation with a therapist is necessary.
- Infections requiring attention:
- Dental abscess
- Urinary tract infections
- Wound infections
! If you have any doubts, it is better to call and consult with the operating surgeon.
Before what procedures and manipulations there is no need to take antibiotics?
Before routine smears, tests, blood donations, eye surgery (if the cause is not infection) and mole removal.
Will there be any problems going through a metal detector at the airport?
There are chances that the metal detector will respond to your prosthesis. It may take a few extra minutes to check, since joint replacement is quite common, airport security will sort out this situation quite quickly. If you are planning a trip, you must have a photocopy of your discharge summary with you.
Can I be examined using an MRI machine?
Yes. The metal that is currently used in the production of prostheses allows for MRI examinations.
What is the success rate of endoprosthetics surgery?
More than 95% of patients are satisfied with the results of the operation, and they have returned to their normal lifestyle. The service life of the hip joint endoprosthesis is more than 20 years, the knee joint is more than 15 years, provided that the recommendations are strictly followed in the postoperative period.
How long will it take me to recover after such an operation?
The recovery period depends on many factors, gender, your age and your state of health. Typically, a walker or crutches are used for the first month, followed by a transition to a cane. Patients use a cane until they feel confident walking. On average, after 3 months you will be able to return to your normal lifestyle.
When can I return to work?
If you spend most of your work time at a desk, you can start working in 6 weeks. This is usually resolved after the first follow-up visit to the doctor after surgery. If you need to move a lot at work (walking, standing, bending), then most likely you will be able to return to work in 3 months; this issue will be resolved by your surgeon before the end of your sick leave.
Billy, Everything seems to be behind us, but I am worried about a strong crunching and clicking sound in the joint, even without bending the joint, i.e. sitting while moving your knee from side to side. The doctor explained that when walking, a clicking sound in the joint seems to be in the order of things, like this is how the prosthesis gets used to. And how are you ??
Good day! I highlighted it in bold about the movement of the knee from side to side. Do you mean that you move your leg at the hip from side to side, but your leg is on the floor? Or is your foot not on the floor, but as if you are swinging your knee in weight from left to right? If the latter, then I would advise you to stop doing this, because... Doctors and a rehabilitation specialist told me that this should under no circumstances be done. Some kind of backlash is generated, which is good.
In general, in theory the joint shouldn’t click, but it doesn’t seem to be a big deal. For most people it clicks.