Treatment of joints » Knees » Article publication date: 03/16/2013 Article update date: 01/27/2020
The knee joint is one of the largest and most complex joints in our body. Unfortunately, he is prone to injury. A sprained or torn ligament can occur as a result of a fall, blow, overuse, or unnatural movements. How dangerous is this and what can it mean? Injuries, of course, are best avoided, but if a knee sprain occurs, treatment started in a timely manner will avoid unpleasant consequences.
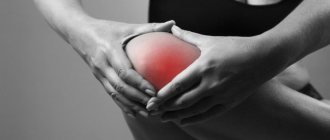
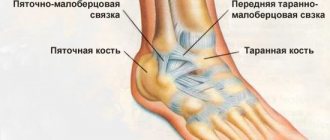
The photo shows the structure of the knee joint
What causes knee sprains?
Knee sprains are a common type of injury. This is especially true for athletes; in the past, such damage could lead to the end of their sports career. However, in most cases such consequences can now be avoided. Knee injuries most often occur in sports such as:
- hockey,
- football,
- skis,
- basketball,
- run,
- figure skating,
- body-building,
- powerlifting.
However, injury does not only occur due to sports activities. Bending your legs suddenly, stopping and changing direction while running, lifting heavy objects, and jumping can all cause sprains. In this case, the cause will be a strong and sharp muscle contraction.
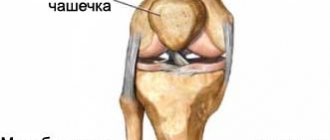
The knee ligaments connect four bones: the femur, tibia and fibula, and the patella - the kneecap (see picture above). They maintain the integrity of the joint structure and protect it from excessive stress.
- Collateral ligaments connect the femur and tibia of the lower leg on the sides. Their sprain occurs from a lateral blow to the knee - due to excessive displacement of the bones to the right or left.
- Cruciate ligaments - anterior and posterior. They are located deep in the articular cavity. Injured by excessive flexion or extension of the knee. And also when falling on it or being hit from the front or back.
- The patellar ligament connects it to the tibia of the leg. Damaged when falling on your knee or landing during a jump.
Tests and diagnostics
To recognize a rupture of the internal ligaments, it is necessary to conduct an examination and, using the method of palpation/light pressure on the area of the outer surface of the knee, damaged ligaments, retract the lower leg to identify an increase in the valgus position of the knee joint. This symptom of shin deviation can be visualized using radiography. In case of a stretch - an incomplete rupture, a gap of approximately 2-3 mm is visible on the film between the femoral condyle and the tibia, while the rupture will allow the tibia to be retracted much more easily, and the void recorded on the radiograph will be much wider.
In case of incomplete rupture of the cruciate ligaments - anterior or posterior, which are less common - the internal collateral ligaments and/or the internal meniscus may be damaged. Rupture of the anterior cruciate ligaments leads to subluxation in the front, and posterior cruciate ligaments, respectively, in the back, and is characterized by an anterior or posterior “drawer” symptom.
To determine the extent of change in knee instability, you may also need to:
- conducting electromyography, rheovasography, podography and other functional and biomechanical examinations;
- biopsy and arthroscopy to detect damage to specific anatomical structures.
Symptoms and degrees of sprain
Common signs of a knee sprain include:
- pain that arose at the time of injury and does not go away over time, especially severe when pressing on the knee, flexion and extension, as well as when supporting the injured leg;
- swelling and bruising, which often does not appear immediately;
- stiffness and a feeling of instability in the knee, difficulty moving in it, and in severe cases - complete inability to bend and straighten the leg;
- crunching and clicking in the joint, accompanied by pain.
During the course of the injury, three degrees of severity are distinguished.
- Mild or grade 1 sprain. Occurs with minor damage, the symptoms are mild and disappear quickly (within 1 – 3 weeks).
- Moderate or 2nd degree sprain. The structure of the ligaments is more damaged than in a mild form of injury: they are no longer able to maintain the integrity of the joint due to overextension and tears. There is significant difficulty in moving the knee.
- Severe or third degree sprain. There is an almost complete or complete rupture of one or more ligaments of the knee joint. Characterized by severe pain, up to a state of shock. The knee loses stability: either complete stiffness or looseness appears - the possibility of movements beyond the normal amplitude.
Simultaneous damage to several ligaments is common. The most commonly injured are the internal collateral ligament and the anterior cruciate ligament. In the case of a sprain of the external collateral ligament, as a rule, other anatomical structures of the knee (tendons, menisci) also suffer, since the external lateral section is “structured” more complexly than the internal one.
- Fluid under the skin on the knee after a bruise or injury: symptoms, first aid and treatment
Severe sprains are often combined with rupture of blood vessels and nerve fibers, and are therefore accompanied by bleeding into the joint cavity and disruption of nerve conduction in the leg. Also, a severe sprain may be accompanied by rupture of muscle tendons or their complete separation from the bones.
Displacement of bones relative to each other can occur in different directions
Symptoms of sprained ligaments
When a knee sprain occurs, you need to pay attention to the symptoms; they will not only help identify the injury, but will also help determine its severity. Moreover, each type of ligament is characterized by certain manifestations.
Isolated ligament damage without bone injury is typical for the area in the knee and ankle joint. But if the injury occurs in other areas, an additional dislocation or fracture occurs along with the sprain. Moreover, in each case, the signs of sprain of the knee joint can be very different and have different severity.
If there is a sprain of one or more ligaments, joint instability may occur - support functions are impaired, subluxations and an unstable gait may occur.
Collateral ligaments
A sprain of the lateral ligaments of the knee joint occurs when the tibia is excessively deviated outward or toward the inward side. As a rule, injury occurs on the side opposite to the deviation. During a sprain of the lateral ligaments of the knee joint, the patient may have the following symptoms:
- painful feelings appear in the knee;
- the knee joint may be unstable;
- the lower leg may deviate in the direction opposite to the tear;
- limited joint mobility, often caused by pain.
When diagnosed, swelling is detected in the damaged area. In this case, the swelling has smoothed contours. After about 2-3 days, a hematoma forms in this place, which often descends to the lower leg. And fluid, often blood, may be found in the knee joint.
Cruciate ligaments
The anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments provide protection to the lower leg from anterior and posterior displacement. It is for this reason that if a strong deviation of the tibia is detected in the indicated directions, a sprain or rupture of the ligament may occur.
During a sprained cruciate ligament of the knee, a number of symptoms may occur:
- unpleasant painful feelings in the knee area;
- instability of the joint when walking, which manifests itself immediately after injury;
- There may be limited movement of the joint. This condition is observed due to severe pain.
The severity of pain depends on the amount of free fluid in the joint. The more it is, the more intense the pain will be. This occurs due to the application of strong pressure on the nerve endings. An examination may reveal an enlarged joint. This usually occurs due to hemarthrosis and traumatic synovitis.
In any case, it is necessary to carefully study the symptoms and treatment of a sprained cruciate ligament of the knee. These factors are closely interrelated; it is based on the intensity of the symptoms that appropriate treatment therapy is selected.
Patella
When the muscles of the knee joint and patella are strained, symptoms of different types may occur. Partial and complete ruptures are also common.
If a ligament injury occurs in the knee and patella, the victim may experience the following symptoms:
- severe pain may occur;
- instability of the knee joint;
- limitation of motor functions of the knee joint, this occurs due to pronounced pain.
During an examination, a doctor may detect the following symptoms during a sprain of the knee joint and patella:
- swelling in the area of injury;
- a hematoma and bruises below the patella may be detected on the surface;
- knee pads can be located quite high when the ligaments of the knee joint are sprained;
- lack of tension on the patellar ligament when the quadriceps (quadriceps) muscle is pulled;
- There may be a sign of a “stuck heel.”
Diagnostics
First of all, of course, the doctor will ask the victim about the nature of the injury and perform a visual examination to determine the severity and which joint structures are damaged. Of the additional methods, the following studies help obtain the most complete information about the joint:
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) - takes a series of layer-by-layer images in different projections, in which all structures are clearly visible, including cartilage, ligaments and tendons.
- Computed tomography (CT), a method similar in information content, is often considered as an alternative to MRI.
- An ultrasound of the knee (ultrasound) will allow the doctor to examine the joint area in detail. This is one of the most accessible methods, but requires professional training of a doctor in the field of ultrasound diagnostics, otherwise unreliable results are possible.
- Arthroscopy is an endoscopic method for examining the joint cavity from the inside. It is classified as minor surgical operations. They are used for the purpose of both diagnosis and treatment - for example, when other methods cannot determine the nature of the injury and the degree of damage. With the help of arthroscopy, ligaments are sutured, bleeding is stopped and other therapeutic procedures are performed.
- X-ray in several projections in case of damage to the ligamentous apparatus of the knee is used as an auxiliary method, since it does not allow us to see the ligaments and soft periarticular tissues. Looking at X-rays, the doctor can judge the nature of the damage only by indirect signs.
Treatment
Restoring full leg function is very important, especially for an athlete. But, unfortunately, this is not always possible. Modern methods of low-traumatic operations make it possible to restore the joint in case of many injuries, but sometimes this takes quite a long time - it may require not one, but several consecutive operations, followed by stage-by-stage rehabilitation. It all depends on the severity and nature of the injury.
Treatment for mild sprains is often limited to the following:
- Immobilization - tightly bandaging the knee with an elastic bandage or using a special bandage (brace). This provides immobility and rest to the joint.
- Cooling - applying an ice pack or a special cooling pack to the affected area. This reduces pain and tissue swelling.
- Providing the injured limb with rest, that is, excluding any movements in the joint and support on the sore leg for the first time after the injury. Crutches should be used to walk.
- By placing the knee in an elevated position in bed. The victim should spend most of the time lying down, raising the sore leg above the level of the heart - this helps reduce swelling.
For mild sprains, other than these measures, nothing more is usually required. Although sometimes the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory and painkillers, as well as thermal physiotherapeutic procedures.
Moderate severity of injury requires more serious measures. Immobilization is carried out using a plaster cast or bandage for a period of 3 to 4 weeks. Drug therapy is prescribed using anti-inflammatory and restorative agents, thermal physiotherapy, and after removing the bandage, massage and therapeutic exercises.
Treatment for a severe sprain usually begins with surgery to restore the structure of the joint. After the operation, a plaster cast is applied for a period of 2 months or more, depending on the severity of the injury. A patient in the acute stage of injury is in a traumatology or orthopedic hospital, after which he is transferred to a dispensary register with an orthopedic doctor at his place of residence.
- Dislocation of the knee joint: symptoms, first aid, treatment
After discharge from the hospital, a set of rehabilitation measures is required to develop the knee and restore the full range of movements in it. Rehabilitation includes a course of massage, physical exercise, swimming in the pool, exercise equipment, and thermal treatments.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of re-injury or initially reduce the chance of a knee sprain when playing sports, adhere to the following rules:
- Use knee protection: wear special equipment designed for your specific sport.
- Always wear comfortable sports shoes with spring soles when training.
- Strengthen your leg muscles by performing special exercises.
- When doing strength training, increase the load gradually. Use recommendations only from experienced instructors.
Now, knowing about the causes and consequences of knee sprains, you will learn to avoid traumatic situations, and if something happens, you will be able to provide first aid to yourself and others.
Owner and responsible for the site and content: Alexey Afinogenov.
How is diagnostics performed?
If the first symptoms of a knee sprain appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. A specialized institution will be able to conduct a full examination and identify the presence of injury, its complexity, as well as associated injuries.
So what to do if you sprain the knee joint, where and who to contact? First of all, you should undergo an examination by a doctor - an orthopedist-traumatologist. He will be able to make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment. First of all, he will examine the sore knee and become familiar with the disturbing symptoms.
During examination, the patient should describe how the sprain in the knee area hurts. He should tell you where the discomfort occurs, the nature of the pain and accompanying symptoms.
After this, the doctor prescribes an instrumental examination, which includes the following diagnostic methods:
- X-ray. This examination method is used quite often. This procedure allows you to distinguish a sprain from a rupture or fracture;
- Magnetic resonance imaging. It is an additional diagnostic method, but it is highly accurate. It is recommended to perform in cases where radiography could not determine the exact clinical picture. An MRI also reveals damage to nerve endings, stretching of muscle tissue and tendons;
- arthroscopy. This examination method is carried out in situations where there is a suspicion of bone or ligament separation.
Anatomy of the knee joint and ligaments
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles .
To understand how a knee sprain occurs, you need to understand the structure of the ligamentous apparatus and find out how many ligaments are in the knee joint.
The articulation of the bones (femur and tibia) in the knee joint is fixed by paired cords: two cruciate (posterior and anterior) and two lateral collateral (external and internal). The ligamentous apparatus also includes the oblique, popliteal, medial and lateral cords. The ligamentous apparatus holds the bones in the correct position and regulates the movement of the joint. It consists of collagen fibers, has high strength and relative elasticity, which allows you to smoothly bend and unbend the leg.
With a sudden movement or impact, strong tension occurs on the ligamentous fibers, which leads to their damage.
Features of the structure of the knee joint
The knee joint has the most complex structure of bone articulation in the body. It is formed by three large bones - the tubular (femur), sesamoid (patella) and tibia. The location of all surfaces and their connection is ensured thanks to cartilaginous layers - menisci.
And between the muscle tendons there are special synovial bursae and fatty bodies. Fixation of this complex structure is carried out not only by strong and durable muscles, but also by a well-developed ligamentous apparatus, namely the following types of ligaments:
- collateral or lateral. It is due to them that the tibia and femur are connected on both sides;
- cruciform. They are localized in the synovial cavity and cross the menisci;
- own ligament of the patellar region. It connects the patella with the tibia.
Signs of a Knee Sprain
The term knee ligaments refers to four main components, including the paired cruciate ligaments and lateral counterparts. Together, this system maintains the stability of the knee as a whole and ensures its amplitude and rotational-circular motion.
- What to do and how to treat sudden acute pain in the knee: first aid for injuries
Signs of stretching of the described components are not specific and depend on a number of factors, in particular the severity of the injury, its nature, as well as the localization affected by the pathological process. In general, the main signs of a knee sprain include:
- The appearance of pain. When stretched, the pain syndrome is of an unstable, temporary nature, intensifying during palpation. In a state of complete rest, it disappears after a while;
- Swelling. A swelling forms in the joint area, usually small or medium in size. In rare cases, it is accompanied by partial hematomas and internal bruising due to disruption of the integrity of peripheral vessels;
- The appearance of unpleasant sensations when moving. In particular, this is crunching and clicking while walking or running;
- Limitation of joint mobility. When the ligaments of the knee joint are severely sprained, the range of motion of the joint is limited.
General information
One of the most common types of injuries is sprained ligaments , most often of the ankle or knee joint.
The main cause of sprains is sudden movements in the joints that exceed their normal amplitude. It is important to distinguish between sprains of ligaments and tendons, because the latter are connections between muscles and bones, while ligaments are the elastic connecting link of bone formations. Moreover, they are capable of regeneration, therefore, when restored, they are given time to grow on their own, even if they are completely torn.
The structure of the ligamentous-capsular apparatus
Most often, simple sprains, tears of the lateral (medal), cruciate ligaments, and damage to the meniscus , and complex injuries are also possible, combining damage to the internal ligaments and the meniscus, including the cruciate ligaments. For example, a sprained tibia is a severe injury to all or almost all the ligaments of the knee joint.
What to do if you sprain your ankle: first aid for injury
In the event that an ankle sprain does occur, it is necessary to provide first aid correctly. Only following certain recommendations will prevent the development of unwanted complications.
The most complete first aid guidelines for sprained ankles include the following:
- Place the victim in a supine position. Using the means at hand, roll up a roller and place it under your shin so that your foot is slightly higher than your body. Remove your shoes and socks. The listed actions will help to significantly slow down the progression of edema.
- Pain relief. Various anti-inflammatory or painkillers in tablet (Analgin, Paracetamol), powder (Nimesil) or injectable (Kaver, Dexalgin) forms are suitable for this.
- Treat wounds and abrasions. In some cases, there is a violation of the integrity of the skin. Wash the wound with 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Next, treat the edges of the skin with alcohol or iodine solution. Cover with a sterile bandage.
- Immobilize the injured ankle. To do this, apply a figure-of-eight bandage with an elastic bandage. The absence of a bandage can be compensated for by using any durable fabric.
- Apply ice to the injured ankle. Cooling soft tissues simultaneously produces several necessary effects: swelling is reduced, hematoma formation is prevented, and pain intensity is reduced.
- Contact the emergency room for qualified medical assistance to carry out the necessary diagnostic measures and treatment.
When providing first aid after a sprained ankle, the use of painkillers and cooling ointments is allowed. This should be done immediately before applying the bandage.
Causes of ligament damage
According to statistics, sprains account for 20% of all ankle injuries.
- Impacts to the foot or shin area.
- Rolling of the leg backwards, which can occur while jogging or walking quickly on stairs or uneven terrain.
- Tucking of the foot to the outside or inside, possible when moving on a flat surface or performing physical exercises.
Doctors identify a set of factors that make ankle ligaments more defenseless to external influences and prone to rupture.
- physical inactivity, which makes the ligaments inelastic;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- excess body weight;
- degenerative changes in bones and joints caused by a person’s advanced age;
- congenital or acquired disorders of the anatomically correct position of the foot;
- intense sports training;
- wrong choice of shoes: uncomfortable models, 12-centimeter heels, etc.
Regardless of the reasons that led to the rupture of the ankle ligaments, the problem is treated within 2-5 weeks, depending on the severity of the case. During this period, the person is forced to abandon the load on the lower limbs or move with the help of crutches.
Standard recovery times
Sprains have several degrees of varying severity. The greater the severity, the longer the patient will have to be immobilized and treat his own ankle.
There are three degrees of stretching:
- minor injury;
- moderate injury;
- serious injury.
The mild degree can be treated at home, but the next two stages cannot be cured at home.
It is important to understand that self-medication for serious injuries will only lead to negative consequences, and in the long term – to disability. And the rehabilitation period in the absence of medical assistance also increases.
anonymousGood afternoon! My name is Natasha, I'm 33 years old. 2 years ago in February, I fell and injured my right knee and there was very severe swelling. In the evening at the hospital they said it was a sprain, they prescribed me gel, injections and tablets and to tie my knee with an elastic bandage, and told me to go to the clinic in the afternoon. At the clinic, the doctor sent me for an x-ray, then he looked and said that there was a crack and put me in a cast from my hip to my heel. My leg didn’t stop hurting, and within a day the cast looked as if it had been put on 10 minutes ago. And I went to the doctor again. hospital and there the 3rd doctor on the 3rd day said that there was no crack but a sprain and take what was prescribed on the 1st day. Before the New Year it hurt but not significantly, and after the New Year it started as soon as I slipped (I didn’t fall) or did not successfully step over the threshold how a strong and sharp pain appeared in the knee, that it cost me a lot of strength to stay on my feet because the stability in the knee disappeared and after an hour severe swelling appeared. I didn’t go to the hospital. After each time I applied gel, bandaged it and lay for a while for 2 weeks and the pain went away and so I could even sit down. And on May 1 (this was already the 4th time since the New Year) I just stood there as my knee hurt badly and my leg began to swell, I couldn’t rest because it’s spring and I live in the village and I again I smeared the gel and bandaged my leg. Because I didn’t lie for a week above the knee and up to the toes, my leg swelled twice and I went to the hospital. I was sent for an ultrasound of the knee, ultrasound CONCLUSION: Deforming osteoarthritis of the knee joint, 2 degrees. Suprapatellar bursitis with signs of synovitis. I was prescribed 5 injections of DICLOBERL, SERRATA tablets, 40 pieces of CARTIGEN tablets, 2 per day for 2 months. After 2 weeks of treatment, my leg did not stop hurting, only the swelling went down a little, although I was lying more. The most severe pain was in the middle of the knee on the inside and outside, it’s hard to bend. Then I went to another hospital. The doctor there put the ligaments in place and prescribed 3 injections of KETOROLAC and 3 injections of REUMOXICS and told me to pour cold water on my knee and come to him again in a week. He corrected me again. bundles and said to lie down. I lay in bed for 2 weeks, did nothing, only went out a couple of times a day when necessary, and then with a stick, the pain disappeared, mild swelling still remained in the knee. And 2 days ago I walked 150 meters in one direction and back (I walked slowly and with a stick) and my leg swelled again and started to hurt, and I can’t completely straighten it, it’s not bent much. Please help me, how to treat it correctly, and how long will it take? Thank you in advance. Artak Matsakovich Matsakyan, traumatologist-orthopedist answers. Hello! I don’t know what techniques can be used to put the ligaments in place and what did the doctor do with you? You most likely have instability in the joint; you may have a torn meniscus or anterior cruciate ligament. You need to do an MRI of the joint and seek an in-person consultation with a qualified orthopedist.
A knee sprain is one of the types of injuries that occurs when sudden movements of the joints exceed the normal amplitude. In this case, a characteristic sign is a feeling of severe and sharp pain. The injury requires treatment, otherwise serious complications develop.
Do you think that joint diseases can be cured without visiting a doctor? Contents
Degrees of stretch
When a knee sprain occurs, the lateral or cruciate fibers are affected. Doctors distinguish three stages of injury depending on its severity:
- First. It is characterized by small tears of the ligaments, while the mobility of the knee is preserved. A person feels pain only during active movements. At rest the knee does not bother me.
- Second. Damage to individual fibers of the knee joint is observed due to tearing of its ligaments. The injury is accompanied by the appearance of bruises. An inflammatory process begins in the knee joint, severe pain and swelling appear. It is difficult for a person to control a limb.
- Third. At this stage, a complete tear of all the fibers of the knee joint occurs, severe pain, bruising and swelling appear. The victim cannot stand up or lean on the affected leg.
It is worth noting that any stage of the disease requires medical attention.
Pathogenesis
Usually the lateral ligaments of the knee are susceptible to injury - the rupture occurs in the area of the joint space or at the place of their attachment, causing pain on the part of the damaged ligament. This is caused by a violation of their physiological elasticity, when the tension in the ligament is too strong, this leads to tearing, rupture or separation of the ligament from its place of attachment. Pathologically and anatomically, the sprain is close to a bruise , but is supplemented by disintegration and rupture of individual fibers.
Damage to the ligaments, menisci and other structures of the knee joint causes rapid atrophy of the thigh muscles, a decrease in their tone, strength and ability to voluntarily contract the quadriceps muscle, therefore it is extremely important to carry out the correct treatment to restore full extension of the joint, as well as to ensure that it stays in this position sustainability.
Important! Despite the good regenerative properties of ligament tissue, no replacement tissue formed during restoration can fully provide the same strength and function of the natural ligament, and it will differ both in structure and size. This can lead to stiffness, stiffness, instability and a high likelihood of re-injury, therefore, to obtain the best result, it is necessary to carry out adequate treatment and restoration of the anatomical integrity of the ligaments under the supervision of a qualified physician.
Causes of injury
The main factor causing knee ligament injury is awkward movements and increased stress on the joints. A sprain can happen at home or during exercise. The following situations also provoke injury:
- sharp bending of the knee;
- lifting weights;
- injury;
- knee strike;
- sudden squat.
Doctors believe that knee sprains are most often diagnosed in people who play sports professionally, for example, figure skaters, hockey players, gymnasts, and boxers. But such injuries in the hospital are also encountered by people who lead an inactive lifestyle, due to which the ligaments and muscles become weak and are easily injured.
Causes
Sprained knee ligaments often occur when performing active movements and placing a high load on the limb. This type of damage to the ligamentous apparatus can occur at home and during professional sports. This means that no one is immune from this injury; it can occur in adults and children with the same frequency.
To understand how to cure a knee sprain, you should first understand the reasons that caused the injury. Children can get severe sprains of ligamentous fibers during active games, with incorrect and sudden movements of the leg, as well as during professional sports training.
The main factors causing sprain of the knee ligament include:
- performing unnatural movements for the knee. These moments often arise during training and competitions;
- Ligament sprains can occur during rapid changes in direction while running;
- partial rupture of muscles and tendons can occur in athletes during basketball, football, and hockey;
- A knee sprain can occur from a direct blow to the back, side, or front of the knee. This injury often occurs when falling from a ladder or on a slippery surface;
- Often the injury occurs during a sharp collision between athletes and each other.
Athletes whose activities involve lifting heavy objects and running with frequent changes of direction are at high risk of severe knee sprains.
Sprains under the knee often occur at home. The following reasons may lead to this:
- sprain of the ligamentous tissue can occur when the leg is sharply bent at the knee;
- sudden stop while running;
- quick change in running direction;
- stumbling;
- sharp swings of the legs (often while making a turn);
- carrying heavy objects;
- jumping on a hard surface;
- sudden falls;
- severe bruise of the ligaments on the knee as a result of a blow from behind, from the side or directly from the front;
- twisting in the longitudinal axis (sharp turn of the leg, dislocation).
A sprained knee joint often occurs when a heavy load is applied or as a result of a sudden movement. For this reason, anyone can experience this injury, regardless of age or type of activity.
Symptoms
It is quite difficult not to recognize an injury, since its symptoms manifest themselves quite clearly:
- A person feels sharp pain in the knee area. It is almost impossible to tolerate it; you need to take a painkiller.
- The damaged area becomes swollen, redness appears, as internal hemorrhage occurs and a hematoma forms.
- The injured area becomes warmer than the rest of the body, and pain occurs when you touch it.
- The victim feels pain even at rest; the discomfort intensifies when trying to bend the leg or lift it up.
- The person feels weak and breaks into a cold sweat from the pain.
- Rare symptoms include nausea and vomiting.
- In the first hours after injury, some patients can move the affected limb, as the pain is not pronounced. This condition is considered dangerous, since additional loads on the damaged joint worsen the condition of the connective tissue.
A knee sprain can be distinguished from a muscle sprain by the fact that pain and discomfort with the first type of injury occurs no later than two hours after it was received. The second type of injury is characterized by the fact that the victim can only feel pain the next day.
How to distinguish between a tear and a stretch?
A knee sprain cannot completely limit the movement of the affected area. Partial or complete rupture of the ligaments renders the injured area completely immobile.
Doctors note that healing a knee that has suffered a sprain is much easier and faster than restoring a limb after a rupture of one of the elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Main symptoms
Rupture of the collateral ligaments of the knee
Symptomatic signs of sprains may appear:
- Severe pain at the time of injury, which does not go away for a long time. When a person puts pressure on the sore lower limb or leans, bends or straightens it, the pain becomes unbearable.
- The appearance of swelling and bruising after some time.
- The movements of the knee become stiff and unstable, it is difficult to move; in severe cases, it is impossible to fully bend or straighten the leg.
- In the damaged area, you can hear crunching and clicking sounds accompanied by painful sensations.
If you have symptoms that do not go away for some time, you should immediately go to the hospital for consultation with a doctor.
First aid
First aid for a knee sprain is provided as follows:
- The victim is seated or positioned in such a way as to remove the load on the injured limb. This will help reduce pain and swelling.
- The sore leg should be placed on a hill (a stack of books, a cushion, etc.). This reduces blood flow to the injured area.
- Cold should be applied to the sore area for no more than 20 minutes (a heating pad with ice, ice wrapped in a cloth, a cool bottle of liquid, etc.). This will help reduce swelling.
- The mobility of the injured limb must be limited. To do this, a splint is placed on it. The leg must be bandaged with an elastic bandage or knitted material.
- The victim is given a painkiller (Solpadeine, Ketanov or Ibuprofen).
- The patient must be taken to the emergency room or an ambulance must be called.
Possible complications and consequences
If, after receiving an injury, you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, the treatment of your sore knee may take a long time. In addition, ligament damage significantly limits motor activity.
Some patients who do not see a doctor in time, after an injury, forever lose the opportunity to play their favorite sport. On the contrary, timely and adequate therapy will allow the patient to return to physical activity after some time.
Preventive actions
Comfortable shoes with springy soles
To reduce secondary injury or initially reduce the possibility of injury, you should adhere to some recommendations:
- The use of means that protect the knee areas in the form of special equipment for sports activities.
- Wearing comfortable shoes for sports activities with springy soles.
- Before the main classes, you should carry out special exercises aimed at strengthening the leg muscles.
- It is necessary to gradually increase the degree of load during strength exercises. Classes must be carried out under the supervision of an experienced leader so as not to harm your limbs.
If a ligament rupture occurs, you should contact a medical facility. The specialist makes a diagnosis based on symptomatic signs and the results of studies.
Diagnosis of knee sprains
If a knee injury occurs, the patient should show the damaged area to an orthopedic traumatologist. To clarify the diagnosis, doctors use the following examination methods:
- X-ray. This method is used to prevent bone fractures. The ligaments themselves are not visible on x-rays.
- MRI and CT. The studies allow us to see the entire structure of the knee joints, that is, its ligaments, cartilage and tendons.
- Athroscopy. The examination method is endoscopic and is considered a surgical intervention, since it examines the joint cavity from the inside. It is used not only for diagnostics, but also for medicinal purposes.
- Ultrasound. Using this method, the doctor will be able to obtain the most reliable information about the condition of the knee and its ligaments.
If necessary, the doctor advises the patient to do a general clinical analysis of synovial fluid, which is taken from the damaged joint.
Treatment for knee sprains
The doctor decides which treatment method is best for damaged ligaments, depending on the severity of the injury. As a rule, the patient is prescribed painkillers and wearing a special bandage that relieves swelling.
After the pain disappears, the patient may be prescribed special physical exercises that strengthen muscle tissue. The orthopedist also recommends physiotherapy for knee sprains. Sometimes surgery is necessary.
This video uses a live example to describe the signs and methods of treating knee sprains:
Drugs
An orthopedist-traumatologist prescribes the following medications for sprains of the knee joint:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These include Ortofen, Indomethacin, Diclofenac, Movalis and Voltaren.
- Products in the form of gels and ointments to eliminate swelling and normalize blood circulation. For example, Lyoton, Troxegel or Troxerutin.
- Painkillers. Anesthetics are taken for painful sensations that manifest themselves not only when moving the limb, but also at rest. These include Solpadeine or Ibuprofen.
You can also eliminate pain after an injury using the Nanoplast Forte patch if it is glued to the damaged area for 3-9 days.
Physiotherapy
To treat the knee after an injury, physiotherapy with different mechanisms of action is used. To relieve pain, the doctor prescribes:
- phonophoresis with novocaine or other analgesic medication;
- ultrasound;
- pulsed magnetic therapy;
- magnetic laser influence.
In order to eliminate swelling and inflammation, the doctor prescribes:
- phonophoresis or electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory drugs;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- decimeter therapy.
To improve the recovery of knee ligaments and normalize microcirculation after injury, use:
- ultrasound;
- magnetic therapy;
- exposure to a low-energy laser.
For complete healing of ligaments, orthopedists and traumatologists recommend taking a course of laser therapy or magnetic therapy.
Exercise therapy
To strengthen damaged ligaments after eliminating the pain syndrome, the doctor prescribes the patient to perform special therapeutic physical exercises:
- Squats with a straight posture and arms extended forward.
- Flexion and extension movements of the knee joint.
- Perform pendulum movements with legs in a sitting position.
- Performing circular movements with the knee in a standing position.
After 1-2 months after the injury, depending on its severity, the patient is allowed to return to normal physical activity and sports.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is required for patients with the third stage of knee ligament damage, if the tendons are torn from the bone, several ligaments have been completely torn, the affected area is swollen, or the knee is immobilized or loose.
Folk remedies
Ointments and compresses prepared according to folk recipes can reduce pain, swelling, and relieve inflammation, but before using them you should consult your doctor.
The most commonly used treatments for sprains are:
- Potato compress. To prepare it, two raw potatoes are grated on a grater. The resulting mixture is placed in a clean cloth and attached to the sore spot. After an hour, the compress is removed and the leg is washed with water.
- Ointment made from lard and eucalyptus. Unsalted lard needs to be melted and crushed eucalyptus leaves added to it. The resulting mixture is boiled for ten minutes, then cooled. The product is applied to the damaged area every day for 20 minutes, then washed off. Store homemade ointment in a cool place.
- Clay wrap. Cosmetic blue clay in the amount of three large spoons is mixed with chamomile decoction, applied to the sore spot and wrapped in cling film. Leaves for 15 minutes, then rinses off.
Features of treatment
Treatment for a knee sprain should only be prescribed by a doctor. He selects it depending on the degree of damage and the nature of the symptoms. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as this can lead to unpleasant consequences and health complications.
So how to properly treat a knee sprain? Complex therapy is usually prescribed, which consists of several measures:
- knee fixation;
- application of cold;
- it is necessary to restrict the movements of the limb;
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures.
It is with an integrated approach that a sprain can be quickly cured. And also in the future the rehabilitation process will go well and the patient will not have any health complications.
Use of ointments
Treatment of a sprained knee ligament is often accompanied by the use of various ointments. These drugs help to greatly alleviate the condition and eliminate a number of unpleasant symptoms. Many of them have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, cooling and warming effects.
When spraining the ligaments of the knee joint, the following ointments are prescribed:
- External agents with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects - Nurofen gel, Finalgon, Fastum gel, Ketonal. They will eliminate the main causes of the inflammatory process, completely suppress pain, reduce swelling of the periarticular tissues;
- Troxevasin, ointments for knee ligaments containing menthol, essential oils that have a cooling effect and reduce discomfort. These products should never be rubbed in; they are applied to the surface of the skin in the form of a thin layer;
- ointments with a warming effect - Nicoflex, Apizartron. They contain natural substances - snake venom, essential oils, camphor, pepper extracts. The drugs accelerate blood circulation and promote rapid healing of wounds and injuries.
But before using ointments for tendon sprains, you should carefully study the instructions for use of these drugs. They have a number of contraindications and can cause side symptoms. They should only be prescribed by appropriate doctors.
How is conservative therapy carried out?
How to quickly cure a sprained knee? In some cases, conservative treatment is prescribed, which ensures complete restoration of the damaged ligament without harm to health. This therapy can use several methods that must be carried out in combination.
For conservative treatment, the following types of treatment are prescribed:
- ensuring complete peace. In the first days after injury, it is necessary to reduce, but it is better to completely eliminate, the load on the sore leg. In the subsequent period, it is better to use a cane. While the patient is lying down, his leg should be slightly elevated, this will reduce swelling and pain;
- exposure to cold. The damaged area, especially at first, needs to be cooled periodically. This will eliminate severe swelling, prevent the formation of hematoma and bruising, and will also have an analgesic effect;
- knee immobilization. It is necessary to apply a bandage made of an elastic bandage or wear a bandage. All this will help immobilize the joint and limit the likelihood of pathological movements developing in it;
- elimination of pain. If necessary, it is recommended to give the patient an anesthetic;
- carrying out anti-inflammatory therapy. In order to prevent or eliminate the incipient inflammatory process, it is necessary to carry out medical treatment using anti-inflammatory drugs. An anti-inflammatory ointment or cream is usually used;
- the use of creams that eliminate tissue swelling. Lyoton or Fastum gel has a good effect;
- using a compress with Vishnevsky ointment. When performing it, the knee area is lubricated with a thick layer of ointment, then it is well tightened with cling film. At the end, a regular bandage is applied. It is recommended to apply the compress before going to bed; it should be left overnight;
Knee sprains can be treated through physical therapy. Methods such as magnetic therapy, massage, mud therapy, and UHF have a good effect. Additionally, therapeutic exercises can be used to speed up the recovery of ligaments.
Use of medications
Treatment for knee sprains is often accompanied by the use of various medications. They help not only eliminate all unpleasant symptoms, but also ensure complete restoration of ligamentous tissue. But only the attending physician should prescribe drugs, depending on the complexity of the injury and the patient’s condition.
Treatment for a sprained knee ligament can be done using the following medications:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs. The most effective and suitable medications include Ortofen, Diclofenac, Finalgel, Voltaren, Piroxicam, Indomethacin, Movalis;
- the use of special ointments and gels for sprains. They have a positive effect on blood circulation, reduce swelling and resolve hematomas. The most effective are the following drugs - Troxevasin, Troxerutin, Lyoton, Troxegel;
- analgesic agents. Analgesic drugs are recommended for use in cases of pronounced discomfort, when severe pain occurs during movement of the limb, as well as at rest. In these cases, drugs such as Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Solpadeine, Ketanov will help.
How else can you treat a sprained knee? Often, many doctors prescribe an effective and efficient remedy - the Nanoplast Forte medical patch. It can be used for any degree of stretch. If used regularly, it will have a positive effect on the condition of the damaged area.
It is recommended to use the patch in accordance with the instructions for use. The full course of treatment lasts from 3 to 9 days.
The patch has the following positive effects:
- warming effect;
- it reduces pain;
- relieves the inflammatory process;
- improves blood circulation;
- ensures rapid resorption of hematomas.
Performing special exercises
The main treatment for sprained knee joints necessarily includes special treatment using therapeutic exercises. But it is recommended to carry out these measures only after the unpleasant symptoms have been eliminated. Under no circumstances should you start exercising if there is swelling and pain in the damaged area.
Therapeutic exercise promotes rapid restoration of ligaments, accelerates tissue healing, and restores function. But when conducting exercise therapy, the patient must follow a number of important recommendations:
- when treating knee sprains with exercise therapy, all exercises are recommended to be performed under the strict supervision of a doctor;
- physical therapy ensures rapid restoration of full physical activity;
- It is allowed to perform some exercises during the period of knee immobilization. But they must be performed under the supervision of a doctor;
- at first, you are allowed to perform light tasks at a moderate pace;
- in the subsequent period, strength exercises and training on simulators are added;
- It is recommended to perform gymnastics daily.
Carrying out physiotherapeutic methods
During the recovery period, physiotherapeutic treatment of knee sprains has a good effect. These measures are great for treating injuries with complications. They have the following positive effects:
- improve blood circulation;
- develop ligamentous tissue, muscles, tendons;
- provide active restoration of damaged tissue;
- restore full functioning of the knee joint.
Physiotherapeutic treatment of a knee sprain can be performed using the following types of treatment procedures:
- laser and magnetic therapy;
- phonophoresis;
- treatment using radio waves;
- paraffin therapy;
- cryotherapy.
Using traditional methods
Of course, treating a sprained ligament in the knee with complications using folk remedies will not be able to provide the desired positive effect. In these cases, it is worthwhile to carry out conservative therapy, which is performed under the supervision of a doctor. However, many people successfully use various natural medicines at home that help quickly cure a mild sprain.
Homemade ointments and compresses that contain natural ingredients, medicinal herbs, and natural raw materials have a positive effect on ligament damage. They eliminate swelling, have an analgesic effect and greatly alleviate the patient’s condition. Also, many of them are able to relieve large hematomas and bruises on the surface of the skin.
Before starting treatment for a sprained knee joint using folk remedies, you should consult a doctor; he will also determine the required treatment period. It is worth considering that not all natural drugs can be used; many of them may have contraindications and may cause side symptoms. Often their specialists prescribe them as an addition to the main medical therapy.
To treat sprained muscles and ligaments in the knee at home, you can use the folk remedies listed in the table below.
| Name | Description |
| Cabbage leaf compress | It is important that as much juice as possible is released from the leaf. To do this, it is recommended to frequently chop its surface with a knife. Next, the sheet is applied to the affected area, bandaged with a bandage and left for a while. All 2-3 hours will be enough. Periodically, dried leaves must be replaced with new ones. These measures can quickly eliminate severe swelling and inflammation. |
| Bodyaga for bruises | This is a natural powder that perfectly relieves tissue swelling, resolves hematomas and bruises. So how can you cure a sprained knee with bodyagi? To begin, place a small amount of powder in a small bowl and add a small amount of water. Diluted to a pulp. Next, it is recommended to apply the finished product to the surface of the affected area. It is recommended to perform these procedures every day. |
| Clay wraps | This remedy helps relieve inflammation and pain. To begin with, it is recommended to make a decoction based on chamomile. Next, a small amount of blue clay is placed in a bowl and a little broth is added to it. The finished mass must be applied to the surface of the affected area, everything is covered with cling film. After 15 minutes, everything is washed off with water. |
| Potato compress | It is a cheap and effective remedy that helps eliminate swelling and inflammation. The first step is to grate two potatoes and spread the pulp on the surface of a clean cloth. The compress needs to be fixed on the surface of the problem area. After an hour, it is recommended to completely remove the mass; the affected area should be rinsed well with clean water. |
| Burdock and honey compress | The burdock leaf needs to be immersed in hot water for 30-60 minutes. Then it cools, its surface is lubricated with a small amount of honey and aloe juice. A leaf with honey and juice is applied to the affected area; it must be secured with a bandage. The compress must be left for 45 minutes. It is better to apply it in the evening. |
| Homemade ointment | Knee sprains can be treated at home with a homemade ointment. To do this, you need to melt 200 grams of unsalted lard. Next, you need to put chopped eucalyptus leaves in it. Everything is boiled for 10 minutes. It is recommended to cool the ointment and place it in the refrigerator. Every day, the area with the sprain needs to be lubricated and the ointment left for 20 minutes, during which time it is absorbed. Residues can be washed off with warm water and soap. |
| Elderberry decoction for swelling and hematomas | This medicinal plant is highly effective and helps to quickly eliminate unpleasant symptoms of knee sprains. First you need to prepare a decoction. Hot water is poured into a glass and a handful of dry elderberry is poured in. Leave until completely cooled. Then everything is filtered. You need to moisten a gauze swab in the prepared solution and apply it to the affected area in the form of applications. After just a few uses, the swelling will become much less, and the bruises will also disappear. |
Recovery period and prognosis
The rehabilitation period for conservative treatment of injury ranges from 1 to 4 weeks. After surgery, the patient needs approximately three months to recover.
If the patient sought medical help on time and strictly followed all the recommendations of the attending doctor, then the prognosis is favorable. But the severity of the injury is also important. As a rule, after severe injuries, the knee ligaments are restored, but rehabilitation takes longer.
Carrying out restoration activities
How to treat a knee sprain using rehabilitation measures? Usually, after the swelling and pain are completely eliminated, many doctors prescribe special physical activity on the injured limb.
Carrying out exercises to restore the ligaments of the knee joint will help restore the functions of the affected limb. They will also serve as additional prevention against recurrence of damage.
When spraining the ligaments of the kneecap, which is located on the knee joint, as well as the knee, it is worth performing the following therapeutic exercises:
- you need to take a sitting position. Next, you need to alternately try to bend and straighten the knee;
- After this, you can start doing the bicycle exercise. At first, you should not perform movements vigorously, they should be careful and not intense;
- then the affected limb must be retracted to the side;
- the patient should lie on the surface of the abdomen. Then he performs flexion and extension of the limb;
- At the end, an exercise is performed to strengthen muscle tissue - tension and relaxation.
It is important to approach therapeutic exercises with maximum responsibility. The successful restoration of a limb with a sprained ligament will depend on a full rehabilitation period. It is imperative to follow all recommendations and prescriptions of the attending physician.
It is important to remember that symptoms and treatment for a knee sprain are important. These are two interrelated factors that are taken into account during diagnosis. When prescribing appropriate treatment therapy, the doctor must take into account the severity of the symptoms, their nature and severity.
Sometimes, when sprained, there may be other associated injuries - dislocations, fractures, ruptures. In this case, therapeutic therapy can be carried out with additional methods, and it can last much longer.