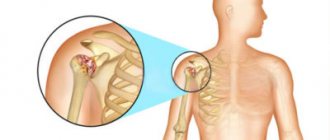
Tendinitis is a disease that causes inflammation in the tendons and connective tissues. Localized in places where the bone and tendon come into contact. May spread along the muscle tissue. Absolutely all individuals are susceptible to pathology. Most often, shoulder tendonitis occurs in the following places:
- Biceps tendons;
- Shoulder joint capsule;
- Supraspinatus muscle.
Patients complain of limited movement, severe pain of unknown etymology.
Description of the disease
Shoulder tendonitis is a pathological condition associated with inflammatory processes in the shoulder. The tendons and soft structures surrounding the shoulder joint are affected. The disease is widespread. Athletes and people who have previously suffered injuries in the shoulder area are susceptible to it. Sometimes it can manifest itself in young people in adolescence or later.
Inflammation of the shoulder joint – tendonitis – more often affects the female body, which is associated with hormonal changes in the body. Men are characterized by a menopausal form of the disease.
Recently, scientists have begun to devote more time to the spread of the disease. This is due to the impact on the patient’s quality of life, the ability to move, and independently care. If the diagnosis is confirmed, long-term treatment with mandatory rehabilitation is required.
Features of the course of the disease
Pathology begins to appear after damage to the capsule of the shoulder joint, which includes five different muscles. Tendon tissue under the influence of prolonged intense stress leads to exhaustion. If the rights of work and rest are respected, the tissue is capable of independent restoration and active cell regeneration. However, in the absence of a break in physical labor, microcracks of the ligamentous apparatus occur, where the inflammatory process gradually develops.
The first signs appear at the site of attachment of the ligaments to the bone tissue, then spread to healthy tissue. In severe cases of tendinitis of the shoulder joint, code according to ICD 10, adhesions occur, and with prolonged intensive work, the tendon ruptures and finally thins. As a result, the muscle capsule ruptures.
Shoulder tendonitis develops in three stages, namely:
- Stage 1 – there is swelling and damage to the bursa and tendon;
- Stage 2 – connective tissue grows with the appearance of scars. Inflammation actively spreads along the bursa and tendon;
- Stage 3 – the patient experiences tendon ruptures and pathological changes in bone matter.
It is impossible to restore the shoulder joint after complete destruction. Pathology leads to loss of ability to work and disability.
Reasons for formation
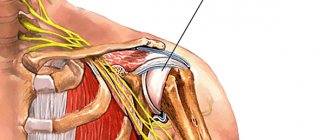
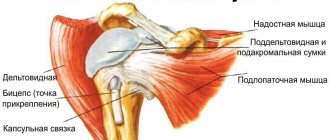
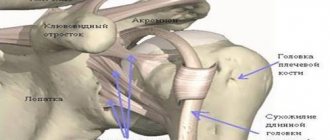
The shoulder joint consists of the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus. The spherical head is only partially directed into the cavity. It is held in place by tendons and ligaments that make up the rotator cuff. The cuff consists of the tendons of the teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus, and subscapularis muscles. Intense physical activity and injury often cause damage to the rotator cuff and ligaments.
Inflammation forms in the supraspinatus tendon and gradually spreads to healthy tissues: muscles, joint capsule, subacromial bursa. Next comes degeneration and thinning of the tendons. Micro-fractures occur.
Also, one of the main causes of pathology is improper treatment after operations and injuries, the presence of cervical osteochondrosis at any stage.
Other causes that can cause shoulder tendinitis include:
- Infections, especially sexually transmitted diseases;
- Injuries in the area of tendon weaving;
- Diseases that cause metabolic disorders.
At-risk groups
Certain categories of people are more likely to get tendonitis. The following population groups are affected by the disease:
- Persons who regularly perform work with increased load on the shoulder girdle;
- Athletes: tennis players, swimmers, weightlifters;
- Loaders;
- Gardeners;
- Women during menopause, after hormonal changes;
- Men aged 50-60 years
In the older age group, tendinitis of the shoulder joint ICD 10 occurs due to loss of elasticity of the tendons. Regular excessive loads on the shoulder can provoke pathology. No break during intensive work with active work with hands, shoulder movements, frequent lifting of weights. Athletes are susceptible to tendonitis without long-term rehabilitation due to injury. The disease is also provoked by:
- Infections such as gonorrhea;
- Early history of joint diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Allergy to potent drugs;
- Problems with the functioning of the thyroid gland;
- Congenital pathologies and genetic predisposition.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it for a long time. In addition, even timely started therapy does not always give the desired results. Prevention of tendinitis comes down to simple rules:
- It is necessary to exercise regularly. This will help strengthen the muscular-ligamentous system. It is not at all necessary to go to the gym and subject your body to grueling workouts. It is enough to walk more often and do basic exercise therapy at home. Yoga and Pilates, and classes in the pool will also be useful.
- If possible, it is better to avoid monotonous load on your shoulders. Otherwise, it is necessary to give quality rest to this part of the body.
- Before any physical activity, it is useful to do the simplest exercises.
- It is better to increase the intensity of all exercises performed gradually. At one time this figure should not exceed 10%.
- If primary symptoms of the disease appear, you need to remove the load and consult a doctor again.
Also, prevention of the disease and possible complications is compliance with all medical recommendations during the recovery period, especially after surgery. The appearance of any discomfort in the shoulder is a reason to consult a specialist. Otherwise, you may not notice the onset of the pathological process.
Symptoms
Patients consult a doctor complaining of severe shoulder pain. Discomfort occurs with certain movements: when reaching out and raising an arm, lifting a light or heavy object. In the case of throwing movements, the pain intensifies and has an acute form. Often patients indicate discomfort at night, for example, when turning towards the affected area during sleep.
As the disease actively spreads, the pain becomes intense and manifests itself even with light movements without the active participation of the shoulder joint. For example, during a handshake, trying to take a small object.
Gradually, stiffness in movement and limited joint mobility appear. Depending on the form of tendinitis of the shoulder joint, the symptom is defined as a crunch.
In the later stages, the patient regularly experiences regular pain, even at rest. Irradiation is observed along the anterior and outer surface of the shoulder. On palpation, pain occurs in the area of the intertubercular groove, the anterior edge of the acromion. Movements are constrained.
Shoulder tendonitis symptoms and treatment are as follows:
- Localized pain. However, unlike osteochondrosis, it manifests itself when performing certain movements. It can be aching, dull, sharp, depending on the stage of its progression;
- On palpation, the pain and inflammatory reaction intensify due to the penetration of bacteria. The density of tendon tissue decreases, which is determined by the thickening of the joint capsule;
- The affected area has swelling with redness of the skin;
- The presence of purulent masses in severe forms of the disease;
- Stiffness of movements.
You can suspect problems with the shoulder joint by the presence of a characteristic creaking sound in the shoulder. Gradually, the patient cannot lift even a small load. The arm does not rise above 90 degrees and does not go behind the back. Depending on the form of the disease, symptoms may vary.
Prognosis for recovery
At the initial stage of development of the disease, the prognosis is always favorable. Timely initiation of therapy can stop inflammation and prevent further degeneration of the joint. In advanced cases, the patient may periodically experience pain in the affected area. Sometimes there is a restriction in joint mobility, and the risk of injury increases significantly. After surgery, the prognosis is also positive. Most patients experience complete restoration of range of motion.
Advertising:
Calcific tendonitis of the shoulder joint
Calcific tendinitis of the shoulder is a condition in which calcium deposits in the tendons of the rotator cuff muscles. The muscles along with the tendons of the rotator cuff are responsible for movement in the shoulder joint. With the disease, there is a deposition of calcium salts in the thickness of the tendons of the rotator cuff. The process may be accompanied by severe pain due to the inflammatory process. This form of tendonitis affects people over 40 years of age.
The disease most often affects middle-aged women 30-60 years old. In the process of calcium deposition, pressure on the tendon increases, which causes chemical irritation and inflammation. Pain syndrome also develops in the shoulder joint. The pain gradually increases as the disease worsens.
Sometimes calcific tendinitis is painless. Together with chemical irritation, causing intratendinous pressure, narrowing of the subacromial space, causing pinching of the tendon and disruption of its functions. As a result of such processes, the patient is practically unable to raise his arm.
This form of tendonitis can be identified by the following signs:
- Pain when moving the arm, especially with vigorous activity in the upper and outer part of the shoulder, may radiate to the forearm;
- Limited mobility;
- Frequent night pain due to uncomfortable sleeping position.
There are two types of calcific tendinitis: degenerative and reactive. The first type is typical for older people. This is due to decreased blood flow to the rotator cuff tendons. As a result, the strength of the tendon decreases and fibers rupture during loading. To keep the tendon intact, the body tries to heal the affected parts with scar tissue, which is done by depositing calcium salts.
The exact cause of reactive tendinitis has not been established. This type is divided into three stages. During the first, recalcification, conditions for salt deposition are formed. during the second period, the process of deposition of calcium salt crystals on the tendons begins. Deposition can sharply intensify or slow down. At the last stage of the disease, the tendons are completely exposed to pathology and are replaced by scar tissue.
As soon as the tendons heal, the pain decreases and gradually subsides.
Tendonitis: 6 Exercises to Help You Relieve Pain
What is shoulder tendonitis?
When the tendons become inflamed, this is usually accompanied by the appearance of microcracks that prevent normal movement of the arms or legs. If we are talking about shoulder tendonitis, it affects the biceps and 4 other muscles. They are called the “rotator cuff”: these are the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and teres minor muscles.
Subscribe to our INSTAGRAM account!
The three main factors in the development of shoulder or glenohumeral tendinitis are:
1. Age
Tendinitis is more likely to occur in people over 40 years of age and in older adults over 65 years of age. However, the disease is “getting younger”; it is increasingly being diagnosed in young people aged 25-35 years.
Mechanical factors
Elevation of the shoulder as a result of certain work or physical activity implies an increase in the friction force of the tendons and their “wear and tear”. As a result, microtraumas and, as a result, tendinitis may appear.
Vascular factors
Here the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles are affected. Both are the most vulnerable to degenerative processes.
Among the main symptoms of shoulder tendonitis, pain should be noted:
- when there is pressure
- when performing certain movements (especially raising the arm)
- when doing stretching exercises in the cold
- during night sleep and rest
With tendonitis in the rotator cuff muscles, the symptoms will be more specific:
- pain in the side or back of the shoulder
- pain arc symptom (increased shoulder abduction to 120 degrees)
- immobility or constant desire to raise an arm or “crank” a shoulder.
Useful Exercises for Shoulder Tendonitis
The goal of a set of exercises for shoulder tendonitis is to reduce pain and increase joint mobility. Then everyday activities will not cause physical discomfort.
Moreover, these exercises will also be useful for strengthening the muscles around the shoulder joint and stretching them. With their help, for example, you can return to professional sports much earlier. It all depends on the life circumstances of each individual person.
Before starting these exercises, it is advisable to consult an orthopedist and physiotherapist. Then you can be sure of their effectiveness and learn how to do them correctly.
Gradually, this set of exercises will restore flexibility and mobility to your shoulder, increase muscle strength and generally improve your posture.
- It is very important to start with a warm-up to “warm up the muscles” a little. The pace should be slow. After completing your workout, you should stretch to improve blood circulation.
- The second stage of exercise involves the use of additional weight.
With shoulder tendonitis, pain most often occurs at night (when the arm is at rest). However, it can be felt throughout the day (and simply intensify at night).
Here are some exercises that will help you relieve pain.
Initial stretch
- Starting position: standing, opposite a table or chair. Place your healthy hand on the edge and lean your torso forward.
- Your back should be parallel to the floor and your legs straight.
- Let the sore arm hang down like a pendulum. In this position, make small circular movements clockwise.
- After 20 repetitions, start making circular movements in the opposite direction. Gradually increase the amplitude of the circles.
2. Stretching
- Starting position: standing, back straight. Raise your affected arm to the opposite shoulder. If your right shoulder is affected by tendonitis, then your right hand should be placed on your left shoulder.
- With the palm of your healthy hand, grab the patient’s elbow and press lightly from bottom to top. Your shoulder should rise as much as possible without causing pain.
- Hold this position for a few seconds, lower your arms and repeat again.
Supported stretching
For this exercise you will need support in the form of a wall or a window frame or doorway.
- First, stand up and lean your painful arm against the wall.
- Bend your body forward to stretch your shoulder. The healthy hand should be behind your back.
- Stay in this position for at least 10 seconds, lower your arms and repeat again.
Tendinitis of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint
Tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint ICD 10 is formed in the tendons of the muscles of the shoulder joint, then affects the supraspinatus muscle fibers. Lack of proper treatment leads to the rapid spread of the disease. Causes of tendonitis of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint include:
- Professional sports;
- Work requiring heavy physical labor;
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- Presence of shoulder dysplasia;
- Frequent colds;
- Long-term rehabilitation after suffering fractures of the upper limbs;
- Endocrine diseases.
With this disease, there is a high risk of further rapid deterioration of the physiological capabilities of the articular complex, the rapid formation of an inflammatory process, and thinning of the tendon. Such pathologies lead to complete degradation of the shoulder joint.
Supraspinatus tendinitis most often develops after injury to the muscle capsule of the acromioclavicular joint, the acromiococlavicular ligament, or the acromion itself. The inflammatory process can be weak, sluggish, asymptomatic, and rapid. Tendinitis of the supraspinatus muscle of the shoulder joint requires long-term treatment with a mandatory long rehabilitation period.
Causes of the disease
Professional sports that require stress on the shoulder joint (tennis, volleyball, basketball, gymnastics, shot throwing and javelin) are the main cause of pathology in young people. Painters, plasterers and masons are also at risk. Contribute to the manifestation of pathology:
- shoulder injuries;
- immobilization for more than 3 weeks;
- bone and joint pathology (arthrosis and osteochondrosis);
- congenital pathology of the shoulder;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Secondary tendonitis occurs with autoimmune, infectious, parasitic pathologies and endocrine diseases.
Biceps tendonitis
Biceps tendonitis is a type of inflammation that affects the shoulder joint. The disease affects tendons and muscles that connect bones.
This form manifests itself in the form of severe pain and limited hand mobility. If biceps tendonitis is left untreated, a chronic process occurs in which the tendons completely lose functionality. The inflammation primarily affects the upper anterior sections of the shoulder. Actively progresses with physical activity and overexertion. On palpation, pain is felt in the intertubercular groove. The pain can be mild or pronounced. Acute pain occurs at night.
Biceps tendonitis also occurs due to a tear of the rotator cuff. Leads to weakening of the tendon and severe inflammation. Impingement and shoulder instability can cause biceps tendonitis. In the first case, the pathology develops due to pinching of the soft tissue between the head of the humerus and the upper part of the scapula. Such processes occur due to systematic, specific movements.
Shoulder instability occurs due to regular frequent movements of the humeral head, as well as repeated excessive loads, for example, when throwing a ball, swimming. The labrum gradually moves away from the place of attachment to the articular surface and forms a pathology. Such processes also form after dislocation. When the labrum is torn, which causes the head of the humerus to produce sudden excessive movements in the socket. As a result, the tendons are damaged, the injured area becomes inflamed, and tendonitis of the long head of the biceps tendon is formed.
For the Achilles tendon
Causes of Achilles tendonitis:
- constant overstrain of the calf muscle;
- unusual loads on the tendon at the age of 40-60 years, which are caused by running and walking;
- violation of the training regime in professional athletes.
In the conservative treatment of tendonitis, special importance is attached to exercises aimed at stretching and working out the muscular balance of the lower leg muscles.
Exercise therapy for Achilles tendonitis:
- Stretching the calf muscles and Achilles tendon. The starting position is to stand opposite the wall and lean against it with straight arms. One of the legs must be placed in front and the other behind the body. Do squats. Make sure that your feet do not leave the floor. Crouch down as much as possible and hold in this position for a few seconds. Repeat 20 times a day.
- Eccentric muscle training is a series of exercises that involves tensing a muscle while lengthening it. If performed incorrectly, you can harm the Achilles tendon. Therefore, it must be carried out with extreme caution, accompanied by an instructor. A ladder is required to perform the exercise. Place the toes of your feet on two adjacent steps. In this case, the heels can move freely up and down. Lower your heels as far as possible and stay in this position for 10 seconds. Repeat 15 to 20 times.
- You can complicate the task by performing the same exercise, only while standing either on one leg or with weights.
When treating tendinitis, it is important to choose the right shoes. It should have a soft back and a small heel. This will reduce the tension, thereby reducing the load. For acute pain, you may need to wear a special support orthosis.
Rotator cuff tendonitis
With tendinitis of the rotator cuff, pain and inflammation develop in the outer upper part of the shoulder joint, which can radiate to the elbow. They arise due to sudden and unusual loads, especially during prolonged work, for example, with arms raised up.
Sometimes the disease affects a specific structure of the rotator cuff. This shape can be determined by pressing the tendon between the head of the humerus and the acromial arch. Pain occurs in the middle of the upper part of the joint. The disease also affects the infraspinatus and teres minor muscles. The patient complains of difficulty raising his arm or doing any work.
For the knee joint
Causes of tendinitis:
- significant loads on the knee joints;
- presence of damage;
- hereditary factor;
- incorrect posture;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- decreased protective properties of the body;
- infection by bacteria and fungi.
Exercise therapy for knee tendonitis is aimed at stimulating and stretching the quadriceps muscle.
The duration of treatment is 2-3 months. After this period has expired, you can move on to exercises and do workouts.
The following exercises must be performed:
- Quadriceps strain. The person lunges with one leg forward. The second leg is in a kneeling position on the bolster. Do light springy squats.
- Stretching the hamstring muscles. Sit on the floor, place a cushion under both legs slightly above the knee. Place your hands on the floor. Spend a few minutes in this position.
- Lie on your side and lift your leg up as high as possible. If you feel pain, hold the position for a few seconds.
- Lying on your back, alternately lift your sore leg up.
- To perform the next exercise you will need a ball. Starting position: standing against the wall, with your back tightly pressed to the surface. Hold the ball with your feet near your knees. Make squeezing and unclenching movements.
- To perform the following exercise, you will need a special stand at an angle of 45 degrees. Stand with both feet on the stand. In this case, the heels should be located on a hill. Do slow squats.
Diagnostics
In the treatment of tendonitis, it is important to timely and correctly diagnose the pathology. To confirm one form or another, a number of tests are prescribed after examining the patient. The disease can be determined through the following examination options:
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- Ultrasound of the joint;
- X-rays.
To detect metabolic disorders in the body, as well as determine other negative effects, a biochemical blood test is performed. Such tests are carried out at the Yusupov Hospital clinic. After visiting the consultation, the patient can immediately carry out all the necessary tests on site using the new equipment. Quick diagnosis allows you to immediately apply a treatment method and prevent the spread of pathology throughout the body.
Physiotherapy
Biceps tendonitis or another form of pathology requires physical therapy treatment, which helps improve blood flow and speed up metabolism in the tendon tissue and surrounding area. Ultraviolet irradiation and electromagnetic radiation are especially often prescribed - a course of procedures will relieve shoulder pain and increase the rate of regeneration of inflamed areas. Magnetic therapy has a similar effect on the body, which can be carried out even in a subacute form (other physical treatment is indicated only for chronic pathology).
A modern type of therapy is laser irradiation. The medical laser beam quickly accelerates metabolism, so after just a couple of sessions the discomfort in the hand decreases.
Electrophoresis and phonophoresis are usually used to enhance the intensity of the drug effect; they are carried out with:
- anesthetics;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- angioprotectors;
- analgesics;
- corticosteroids.
Shock wave therapy relieves swelling, helps resolve fibrous nodules, scars and adhesions; it is especially indicated in the presence of calcifications in the tendons. Usually 2-3 procedures are prescribed per week in a course of 10 procedures, which is enough to achieve stable remission. Other types of physiotherapy that are suitable for the inflammatory process in the shoulder joint are ozokerite, therapeutic baths, paraffin therapy, microcurrents.
Treatment
Treatment for tendonitis of the shoulder joint is provided in the form of a complex effect on the pathology. In therapy, it is important not only the medicinal effect, but also the patient’s desire to recover quickly and understand the essence of the disease. The following treatment methods are used:
- Drug therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- The use of therapeutic exercises;
- Visiting massages;
- Surgical intervention in late stages of diagnosis.
The method of treating shoulder tendonitis is selected individually for each patient, based on his test results. Great care is taken to ensure that the affected shoulder remains at rest. The factors that provoked inflammation must be eliminated.
Drug therapy
The doctor determines how to treat shoulder tendonitis in each specific case. Medicines are prescribed to eliminate swelling, pain, and relieve muscle tension. In the presence of destructive processes, drugs are prescribed to resume metabolic processes. Conventionally, all medications are divided into the following types:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The most effective include Naklofen, Movalis, Ketorol, Indomethacin, Revmoxib, Ortofen. Used orally with great caution due to the large number of side effects;
- Additionally, compresses with Dimexide are prescribed. The active components of the drugs quickly relieve the first signs of the disease;
- Analgesics. Prescribed to relieve pain. Paracetamol, Ibuprofen are suitable;
- Gels and ointments to normalize blood circulation, accelerate tissue restoration, and improve metabolic processes. These include: Voltaren-Emulgel, Deep Relief, Fastum-gel;
- Steroid hormones are rarely used. This could be Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone. Assigned in neglected forms.
Treatment is carried out strictly under the supervision of the attending physician.
Physiotherapy
An important criterion for how to treat shoulder tendinitis is the use of physical therapy. It has a good positive effect in rehabilitation therapy. The following procedure options are prescribed:
- Electro- and phonophoresis of novocaine;
- UHF therapy;
- Laser treatment;
- Wave therapy;
- Mud and paraffin therapy;
- Magnetotherapy.
The course consists of 7-10 procedures, which must be carried out strictly as prescribed by the doctor. This way you can get a quick and lasting positive result.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is required during the recovery period. With its help, it is possible to restore the functions of the joint to its full extent. Therapeutic exercises contribute to the proper functioning of the muscular-ligamentous system. It is carried out under the supervision of a specialist and only during the absence of acute signs of the disease. It is carried out gradually, without sudden movements. Efficiency depends on the patient’s persistence and desire to get results.
Restorative massage
Used to relieve pain. Leads to muscle relaxation and improved metabolic processes. Conducted in 10-15 sessions.
Surgery
Prescribed in cases where conservative therapy has failed or in case of tendon rupture. Basically, arthroscopic surgery is performed with minimal trauma. With its help, the affected areas of tissue are removed, plastic surgery is performed and the tendon is properly fixed. After surgery, rehabilitation treatment is required.
Before the procedure, it is necessary to determine which area of the shoulder joint is affected. Based on the diagnostic results, a form of therapy is prescribed. Calcific tendinitis of the shoulder joint requires surgical treatment.
Prevention methods
To prevent the development of pathology during training, all muscles must be warmed up. The load increases gradually in accordance with the strengths and capabilities of the person. When pain occurs, it is important to immediately respond by reducing activity and ensuring adequate rest.
In professional activities, control over overloads is maintained. Work gives way to rest. At the first sign of injury, be sure to consult a doctor. Otherwise, there is a high risk of complete immobilization of the limb.
Help from traditional medicine
Recipes from traditional healers are considered an addition to the main course of treatment. They cannot be used as a complete alternative to therapy. In addition, you should consult your doctor in advance. Most often, folk methods involve the use of various compresses:
Advertising:
- Onions+potatoes
. To prepare the compress, you need to grate the potatoes and onions and add a small amount of clay. Apply it to the affected area, secure with a bandage and leave overnight. - Apple vinegar
. The next compress option involves a mixture of 500 ml of apple cider vinegar and 100 ml of vodka. A bandage soaked in the mixture is applied to the joint for a few minutes a day. - Saline solution
. Soak any fabric in a light saline solution, put it in a bag, and then put it in the freezer. After an hour, the compress must be separated from the cellophane and applied to the sore spot until completely dry. - Shepherd's purse solution
. As in the previous recipe, you can do it with regular gauze, but first soak it in the infusion of the shepherd’s purse.
It is worth noting once again that the use of traditional medicine recipes should always be agreed with the attending physician.
Some components may do more harm than good. For example, exposure to elevated temperature is not recommended in case of an infectious process and the presence of concomitant diseases (gout, arthritis).
Compliance with all medical recommendations allows you to relieve painful symptoms in the shortest possible time and significantly improve your quality of life. In addition, patients can fully restore the motor activity of joint structures. The doctor must tell you exactly when you can return to your normal lifestyle and prevent a relapse.
Treatment in Moscow
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital clinic specialize in determining tendonitis and establishing the form of the disease. Treatment of joint and tendon diseases is one of the main specialties of the hospital. Diagnosis is carried out by specialists of the highest category. With the help of new equipment it is possible to accurately diagnose the disease and its stage. The clinic also offers the opportunity to undergo a rehabilitation period.
If an operation is necessary, the patient stays on the territory of the institution in a comfortable patient ward, where there are all conditions for a quick and calm recovery. You can make an appointment with a doctor online or by phone.
Preventing tendonitis
To reduce the risk of developing shoulder tendonitis, you need to exercise after preliminary stretching, warming up muscle groups and tendons. Otherwise, microcracks will inevitably appear on them, which will eventually lead to an inflammatory process. If pain occurs during exercise, it is important to reduce the load and give the joint a chance to rest. In addition, for the prevention of pathology it is important:
- do not perform monotonous shoulder movements;
- do not forget about exercise therapy if you already have diseases of the shoulder joint;
- keep hormonal and metabolic pathologies under control;
- do not ignore treatment of osteochondrosis;
- eat well;
- don't get too cold.
If you play professional sports and have other risk factors, you should regularly visit a doctor and get examined in order to detect any changes in time and prevent complications.