Humeral periarthritis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system, the cause of which is the pathology of the tissues located in the area of the shoulder joint - tendons, ligaments, muscles, etc., developing with injuries to the spine, some chronic diseases and as a result of degenerative processes in the joints themselves. Treatment of the spine, joints, and adjacent soft tissues should begin immediately as soon as symptoms of their damage appear. However, people often ignore the first signs of the disease until severe pain and the associated limitation of movement force them to consult a neurologist or surgeon. Therefore, it is important to know what manifestations of discomfort may indicate the onset of a serious illness and require urgent medical intervention.
There are the following forms:
- simple;
- acute;
- chronic.
In addition, the lesion can be unilateral or bilateral. The first is more common.
Inflammation of the shoulder joint
Inflammation of the shoulder joint
Inflammation of the tissues of the shoulder joint area is a common pathology that can occur equally often in men and women, regardless of age.
It develops due to the influence of a significant number of different causes. If inflammation of the shoulder joints has been established, treatment is prescribed by a medical specialist taking into account an integrated approach. It necessarily includes measures aimed at reducing the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
Symptoms of bone and joint cancer
Symptoms of joint cancer may include the following.
General symptoms
The general symptoms of joint cancer are no different from those noted during the development of cancer in other organs and tissues. The patient's weight decreases, he has low tone, he doesn't want to eat, he regularly vomits, he recognizes the taste of food differently than when he was healthy, and from time to time he experiences an increased body temperature. Moreover, these symptoms of joint cancer are noted at advanced stages of the disease; at the initial stages, such signs are not expressed.
Local symptoms
Local symptoms of joint cancer are generally the same for any of them if a tumor has formed in it. Among the signs of joint cancer, one can note aching pain in the tumor area, and the patient experiences it both if he moves and if he remains at rest. There is a swelling at the location of the tumor; if you touch it, the person experiences pain. The joint bends and unbends worse, the shape of the bones changes.
A typical sign of oncology is pain in the joints at night, but analgesics do not relieve it. As the disease worsens, such sensations may intensify. In the later stages of cancer, joint pain can become very painful.
Also, with this type of neoplasm, the bone is destroyed. As a result, calcium enters the blood, causing hypercalcemia (oversaturation of the blood with released calcium), which causes stomach pain and vomiting as calcium enters the digestive system.
For example, the symptoms of cancer of the shoulder joint are similar to those characteristic of a tumor in the knee.
Symptoms of metastatic cancer
Other symptoms occur in joint cancer of metastatic origin. The reason is that the initial symptoms arise due to the tumor affecting the organ in which it initially developed. As a result, the immediate signs of joint cancer are blurred, since it is secondary in nature. In this case, metastases can spread to a number of joints, since the process of metastasis in a typical case is multiple.
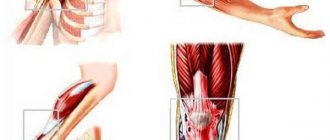
Structural features
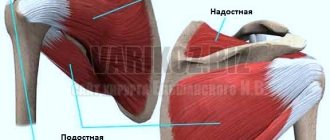
The shoulder joint has a round shape. The structure makes it possible to achieve a significant range of hand movements performed in 3 planes. The joint is strengthened by the ligaments and tendons of the muscles that form the cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, rotator cuff).
The articular surfaces of the bones contain a cartilaginous canal that provides sufficient gliding, and the joint itself is covered with a connective tissue capsule. The complex structure is a factor that often provokes the development of inflammatory reactions in various structures.
Treatment of joint cancer
The treatment of joint cancer falls under the purview of orthopedic oncology, and accordingly it is dealt with by orthopedists. Therapy for this disease is complex. Among other things, treatment of joint cancer involves radiation therapy and chemotherapy, and surgery is also possible.
In total, the process consists of three stages.
- The first stage of treatment for joint cancer consists of radiation therapy or chemotherapy sessions. At the same time, doctors strive to reduce the size of the tumor and eliminate small metastases.
- In the second stage, surgery is performed to remove the tumor and lymph nodes, followed by reconstruction to restore those parts of the body that were affected by surgery. In the treatment of joint cancer, surgery becomes the central event. Doctors strive to perform it as gently as possible, so that the least possible damage is caused to the joint with cancer, as well as to the surrounding tissues. If resection turns out to be necessary, then an implant is subsequently placed in the place from which certain tissues were removed.
- At the third stage of treatment for joint cancer, postoperative chemotherapy or radiation therapy is performed. Its purpose is to suppress tumor cells in the place where the tumor was previously excised, as well as in areas where metastases have penetrated.
Physical exercise also becomes an integral element of the treatment process for joint oncology. Since joint cancer affects the body’s motor ability, you should consult a specialist before exercising.
Etiology
The trigger for the inflammatory response is damage to the tissues of the shoulder, which develops as a result of several common causes:
- An infectious process that often develops in soft tissues and is caused by the activity of pathogenic (disease-causing) or opportunistic microorganisms.
- Suffered injuries, which include dislocation of the joint with complete or partial release of the head of the humerus, rupture or sprain of ligaments, tendons, capsules, fracture of the bone base, damage to cartilage.
- Systematic long-term and significant physical activity, leading to the appearance of small tears in connective tissue fibers.
- Autoimmune inflammation, which is the result of an impaired functional state of the immune system. It is accompanied by the production of antibodies to one’s own connective tissue with damage and inflammation of the structures of the musculoskeletal system.
- Local hypothermia of the shoulder area, leading to an aseptic inflammatory process.
- Degenerative-dystrophic processes, primarily associated with impaired nutrition of cartilaginous structures, their gradual destruction and the development of an inflammatory reaction.
Often, under the influence of etiological factors, inflammation develops not only in the joint, but also in the surrounding nearby tissues. This disease is called periarteritis.
How does the technique work?
During the exposure of the organ to nuclear magnetic radiation, degenerative processes are stopped and the restoration of cartilage tissue begins, which will last for one year after treatment. Bone structures, ligaments and tendons are also strengthened. Besides:
- inflammatory processes stop;
- cells and tissues become more resilient;
- hypoxia is suppressed;
- organs gradually return to full function.
MBST therapy not only allows you to cure the shoulder joint, it is also effective in treating diseases such as:
- arthrosis of any degree (including osteoarthritis);
- glenohumeral periarthritis (periarthritis - inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder);
- osteoporosis;
- osteochondrosis;
- meositis, tendinitis, synovitis, subacromial bursitis and other tissue inflammations;
- some types of intervertebral disc damage;
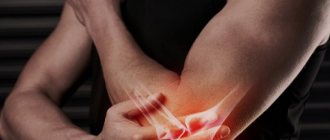
- epicondylitis (inflammation of the tendons of the forearm at the junction with the muscles, typical during some sports activities - the so-called “tennis hand” and “golfer’s elbow” syndromes);
- sports and other injuries with damage to muscles, tendons and ligaments.
In addition, MBST therapy allows you to avoid injuries and fractures by strengthening organs, which is especially important for athletes who experience enormous stress on their musculoskeletal system every day.
Signs and diagnosis
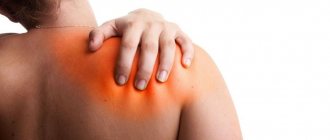
The main clinical manifestation of the inflammatory process is shoulder pain. It can hurt for quite a long time. The intensity of discomfort sensations can vary, usually higher during active movements. With significant inflammation affecting a large volume of tissue, redness of the skin (hyperemia) and swelling appear.
Determining the cause of the disease is carried out using various diagnostic methods, which include visualization of structures, various laboratory and functional studies. Based on the results, the doctor determines that the shoulder joint is inflamed. Treatment is selected in accordance with the causes of development and severity of the inflammatory reaction.
When is it necessary to visit a doctor?
Many people often have a question: when should you seek help from a specialist? In some cases, if the pain is short-lived and occurs as a result of banal overwork, it is quite possible to do without various kinds of preventive actions. In all other situations, it is worthwhile to contact specialists for help without wasting time. This is especially true in the following cases:
- The cause of pain is injury or bruises;
- Pain is accompanied by a rash and fever;
- Taking painkillers does not help relieve pain;
- Painful sensations last for a long period of time and do not have a clearly defined root cause. It is important to remember that successful treatment of the shoulder joint begins with timely diagnosis.
Diagnostics and therapy
Diagnosis and therapy
Treatment of inflammation of the shoulder joint is complex. It includes several areas, the choice of which depends on the cause, nature, localization and severity of the inflammatory process:
- Inflammation of the joint capsule of the shoulder joint - treatment is aimed at drug reduction of the severity of the inflammatory reaction, as well as eliminating the impact of the cause, for which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory, antibacterial agents, and immunosuppressants are used.
- Inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint - treatment includes resting the shoulder, anti-inflammatory drugs, and surgical manipulation if necessary.
- Inflammation of the shoulder joint ligaments - treatment includes achieving goals in terms of reducing the severity of inflammation, as well as restoring fiber strength using modern techniques for performing plastic invasive manipulations.
The main therapeutic areas include conservative tactics, surgery and rehabilitation measures.
Diagnosis of shoulder tendonitis
If tendinitis of the shoulder joint occurs, the success of treatment largely depends on the accuracy and timeliness of diagnosis of this pathological process. At the same time, in order to establish the specific form of the disease, it is imperative to undergo laboratory tests and perform a thorough examination of the patient. The disease can also be detected using the following diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the shoulder joint;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- X-ray.
A prerequisite for identifying metabolic pathologies and rapid recovery of the patient is a biochemical blood test.
All the above studies are carried out in honey. In this case, innovative technology is used, and highly qualified specialists are involved in deciphering the test results. This allows you to quickly diagnose the disease, correctly draw up a treatment plan and eliminate the occurrence of complications.
Non-surgical tactics
Non-surgical treatment for inflammation in the tissues of the shoulder is prescribed in most cases. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and glucocorticosteroids (hormonal agents with a pronounced anti-inflammatory therapeutic effect) are used as medications. For chronic inflammation, physiotherapy is used, the essence of which is the therapeutic effect of certain physical factors.
An alternative treatment option is intra-articular administration of platelet mass (a concentrated suspension of platelets), which has a stimulating effect on regeneration processes. Some folk remedies in the form of medicinal plants also have an anti-inflammatory effect, but their use is possible only after consultation with a doctor.
Causes of joint and bone cancer
Joint cancer can have a number of causes. Among other things, it can occur due to injuries that damage the joints. Chronic diseases are also a prerequisite for cancer.
The disease can also develop on the joint for which endoprosthetics was performed. In addition, heredity and the presence of ancestors who had a malignant neoplasm can also lead to the appearance of a tumor.
Cancer can also be caused by low levels of immunity. In addition, if this part of the body is exposed to ionizing radiation, it can lead to joint cancer.
It is also worth keeping in mind that joint cancer is divided into primary and metastatic.
- Primary cancer is a disease in which cells inside the joints initially degenerate into cancer; all of the above-mentioned causes of joint cancer are related specifically to this type.
- Metastatic cancer suggests that the original tumor originated in another tissue or organ. Subsequently, the metastases moved to the joint. Of course, the cause of joint cancer in this case will have to do with that very organ (intestines, prostate, mammary glands, lungs). It is worth noting that this type is more common, in other words, a tumor in a joint in most cases becomes a consequence of a tumor in another part of the body.