Orthopedics
Inflammation of ligaments and tendons is a pathology that causes discomfort and discomfort in the hand area. As the disease progresses, the pain becomes constant and its intensity increases.
Tendinitis needs to be treated on time! In advanced cases, a person may completely lose the functionality of the hand.
Causes of pathology:
- sprains sustained while doing work or playing sports
- weakening of tendons with age, improper formation
- associated diseases: arthritis, osteoarthritis, scleroderma, lupus erythematosus
Main complaints:
- pain during active movements or palpation
- swelling
- redness, warmth in the inflamed area
- crunching sound when performing rotational movements with the brush
- limited movement
- the appearance of nodules under the skin, compactions
Treatment methods for tendinitis
Treatment is prescribed taking into account the causes of the pathology. During this time, it will be necessary to exclude physical activity and ensure rest of the affected hand. For this purpose, wearing flexors, splints or bandages is prescribed.
- Drug treatment Medicines are prescribed to reduce pain, relieve swelling, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Exercise therapy and massage Exercises are allowed to be performed after acute pain has been eliminated.
- Physiotherapy The following may be prescribed: ultrasound, electrophoresis, magnetic and laser therapy, ultraviolet irradiation. The course consists of 10-12 procedures.
- Surgical treatment Surgery is indicated when drug treatment is ineffective. Goal: remove scar tissue and lumps that have appeared in the inflamed joint.
An integrated approach is possible. There are contraindications, consultation with an orthopedist is necessary.
HOW CAN FLEXORS BE INJURED?
The presenting bundle of finger tendons is injured more often. To damage these (external) flexors, it is enough:
- deep cut on the side of the palm;
- laceration;
- a sharp jerk (in an attempt to lift weights or hold a slipping load).
As a rule, such a separation of the tendons of the finger may not be initially noticed. In approximately 25% of cases, patients with injury cannot explain (precisely state) during which operation they received the injury. This makes treatment difficult, but with the capabilities of modern medicine in the practice of treating damage, it is not a death sentence.
Injury to the deep digital flexors is a much more serious problem. It can also be invisible against the background of a state of shock and severe pain in the fingers. But restoring internal flexors is much more difficult.
The causes of damage to the internal buried flexor tendons are most often:
- severe pressure injuries (crushed fingers, heavy objects falling from above);
- fingers getting caught in moving blades of instruments and devices;
- deep cuts;
- gunshot wounds;
- damage in the form of chopped injuries.
Postoperative period
Recommendations will depend on the treatment method. If there was an operation:
For 1-2 weeks, you need to wear a special bandage on your wrist. After 1 month, you need to do therapeutic exercises and massage. After 3-4 months, you will be able to return to sports activities.
For prevention purposes:
- avoid overloading, take breaks in work (10-15 minutes per hour is enough)
- choose the optimal working position
- do massage and hand exercises
- Always warm up before starting a workout
- athletes use wrist protection
Damage to the extensor tendons of the fingers and hand
Damage to the extensor tendons is a rather complex problem in hand surgery due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the extensor apparatus of the fingers. Damage to the extensor tendon leads to impaired finger extension.
Anatomically, there are 8 zones of damage to the extensor tendons:
Fig.1. Zones (levels) of damage to the extensor tendons of the hand and fingers
The symptoms and treatment method depend on the area of tendon damage.
There are open and closed extensor injuries. Even a small wound on the dorsum of the fingers, hand or forearm can be complicated by tendon damage. There are frequent cases of closed, that is, subcutaneous damage to the extensor tendons. They can be the result of either a high-energy injury (falling, lifting a heavy object, etc.) or occur during everyday work (putting on clothes, making a bed, etc.). In some cases, the extensor tendons can be torn off with a piece of bone at the site of their attachment, and can also be combined with damage to other anatomical structures (vessels, nerves, ligaments, etc.). Fresh and old damage are also distinguished.
Fig.2. Damage to the extensor tendon of the finger in 1 zone
Symptoms:
The most important symptom of damage to the extensor tendon of the finger is a violation of its function: the impossibility or limitation of its extension. The finger “hangs” and it is impossible to straighten it independently, without the help of the other hand. Depending on the area of damage, extension may be impaired in different joints.
Fig.3. Incised wound of the hand with damage to the extensor tendon of the 3rd finger (the patient cannot independently straighten the finger)
Diagnostics:
Most often, to make a diagnosis, a thorough study of the patient’s medical history and disease, and an examination of the patient is sufficient. With open wounds of the hand and forearm or with chronic injuries, tendon damage can be combined with damage to nerves, blood vessels and other anatomical structures, which requires a thorough knowledge of anatomy and specialized training from the doctor.
Also, to clarify the diagnosis and differential diagnosis, in some cases additional studies are required, such as radiography, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging.
Treatment for extensor tendon injuries:
Treatment tactics for damage to the extensor tendons depend on the area of the tendon damage, the nature of the damage (open or closed), the individual characteristics of the patient, as well as some other factors.
Conservative treatment:
For some types of damage to the extensor tendons (for example, with closed damage in zone 1), conservative treatment is possible, which consists of applying a special splint to the finger. The splint keeps the finger in the correct position while the tendon heals. After removing the splint, it is important to properly “wean off” it, otherwise the treatment result may be incomplete.
Conservative treatment:
For some types of damage to the extensor tendons (for example, with closed damage in zone 1), conservative treatment is possible, which consists of applying a special splint to the finger. The splint keeps the finger in the correct position while the tendon heals. After removing the splint, it is important to properly “wean off” it, otherwise the treatment result may be incomplete.
Surgery:
The vast majority of extensor tendon injuries require surgery to restore function. The choice of the type of operation lies with the surgeon and depends on many factors (area of damage, nature, duration of injury, individual characteristics). In general, the complexity of the anatomical structure of the extensor apparatus of the fingers and hand requires the surgeon to have a thorough knowledge of anatomy and special training in the field of hand surgery.
Primary surgical treatment of the wound:
For acute open injuries, the first stage of treatment is primary surgical treatment of the wound, which includes washing the wound with mechanical removal of mechanical impurities and foreign bodies, excision of crushed and non-viable tissue, stopping bleeding, revision of the wound, in order to accurately identify all damaged structures and install the final diagnosis, as well as suturing the skin. In some cases, if appropriate conditions and qualified personnel are available, and there are no contraindications, primary surgical treatment of the wound can be supplemented with primary tendon repair.
Tendon suture – there are many different types of tendon sutures; the choice of a specific type depends on the area of tendon damage and the skills of the surgeon. The main requirement for a tendon suture is to ensure strong, sufficiently long-term fixation and good adaptation of the ends of the tendon, even with multiple injuries.
Any surgery on the wrist flexor tendons is extremely difficult and must be performed by a qualified hand surgeon.
The intervention, if necessary, can be supplemented by intervention on nerves, blood vessels, ligaments and bones.
After the operation, a rigid plaster or plastic bandage is applied for a period of 4 weeks and rehabilitation treatment is prescribed, which should begin 1-2 days after the operation and includes physical therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, paraffin therapy, and massage.
What are tendons
Visually, the tendon is a bundle of threads. This is the part of the muscle with which it is attached to the bone. Often ordinary people confuse tendons and ligaments, the first of them are located between the muscles and bones, and the second fix the bones in the joint.
Ligaments provide mobility to the joint. The function of tendons, or hamstrings, is to transmit forces from muscles to bones.
Tendons are made up of connective tissue made up of different types of collagen fibers. They come in various shapes and have a specific structure, due to which they have high strength, but have little stretch.
With age, there is a weakening of the tendons, which can even with minor loads lead to tears - that is, partial disruption of the integrity of the tendon bundles. This can occur in both the central and peripheral areas of the tendon.
Treatment of tendon injuries is carried out by a traumatologist, surgeon, or osteopath.
Prevention
To avoid tendon rupture, follow safety precautions when working in production or when preparing food.
In more than 80% of cases, injury occurs due to carelessness and haste. When doing intense sports, pay special attention to warming up. Use warming ointments and do warm-up sets before performing the exercise to avoid serious injury. If you are overweight, you need to normalize your diet and add moderate physical activity. Often, increased body weight places high stress on the joints, increasing the likelihood of injury.
We do not recommend self-medication, as it can lead to serious consequences.
Partial tendon rupture: causes
If we talk about people who engage in intense training or professional sports, the cause of such damage most often lies in insufficiently warmed muscles. Every athlete knows that before exercise it is necessary to warm up their muscles. However, it is not always possible to complete this fully, and as a result, the tendons may suffer.
Muscles that are not ready for increased loads and sudden movements contract irregularly and too strongly. As a result, during a particular exercise, such muscle tension leads to tendon damage.
Also, athletes and workers of heavy physical labor constantly experience microtraumas of the tendons from overexertion. Bundles of collagen fibers “wear out” and partially break. The situation gets worse if treatment is not carried out immediately and fully. Over time, the muscle whose tendon has been damaged shortens, and each repeated injury worsens its physical and functional condition. In such cases, it is difficult to restore the anatomical integrity of the tendon using therapeutic methods.
There is a high probability that a complete rupture of the tendon will occur; treatment will then be carried out surgically.
In addition to the above negative factors, tendon fibers can tear for the following reasons:
- ·impacts with a blunt object (direct mechanical damage);
jumping and unsuccessful landing;
falling on an outstretched arm;
sudden movements, jerks;
lifting loads;
weakening of tendons due to general aging of the body.
Partial tendon ruptures also occur due to the individual characteristics of the body. These may be pathologies such as, for example, congenital abnormalities of connective tissue or other degenerative processes in tendon bundles, muscles and joints.
The condition, degree of strength and functionality of the tendons is influenced by nutrition, the level of immunity, and the use of alcohol and tobacco.
Separately, mention should be made of the open type of damage, in which the tendons are torn due to open wounds. For example, workplace injuries often occur in which the hands are partially or completely damaged.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues, lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 2 300 |
| MRI of soft tissues (one anatomical region) | 6 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Signs and methods for diagnosing partial tendon rupture
Regardless of the location of the damage, with injuries of this type, patients complain of the same symptoms:
- pain of an acute, sharp nature;
weakening of the joint;
redness of the skin;
·limitation of mobility of the injured limb;
tumor, edema, hematoma;
· in some cases – a local increase in temperature.
Since similar signs are observed with sprained ligaments, various dislocations and subluxations, only a qualified specialist should diagnose the damaged tendon and treat it.
The doctor must examine the site of injury, ask the patient about the nature of the injury and sensations, and examine the area using palpation. In most cases, with a partial rupture of the hamstring, the victim can move the injured limb, so the specialist can conduct something like testing: he will ask you to perform some exercises and evaluate the result.
In addition, an x-ray will be taken, the results of which will refute or confirm the presence of a tendon rupture.
Other examinations if such injuries are suspected:
- ·angiography;
MRI;
· Ultrasound;
Ultrasonography
When is surgery needed for extensor avulsion?
Despite the fact that even conservative treatment delayed for months gives good results, sometimes surgery is still performed for such an injury. The indications are as follows:
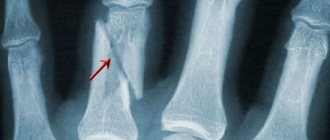
- Avulsion of a bone fragment greater than 30% of the width of the articular surface.
- Subluxation of the distal phalanx towards the palmar side.
- The patient has no hope for a good result of conservative treatment (bad experience, lack of persuasiveness of the doctor, reluctance to wear a retainer for a long time).
- The injury is more than 3 months old, although Medscape gives six months.
Surgical treatment (tendon repair)
Cut tendons do not heal on their own; tension in the tendon causes the cut ends to separate, sometimes by several centimeters. Without surgery, there is no prospect of regaining the movements that have been lost. Recovery can be done under general or local anesthesia (injection of local anesthetic into the shoulder). The wound is widened so that the cut ends of the tendon can be found and connected with sutures. At the end of the operation, the arm and forearm are immobilized in a plaster cast over the bandages, with the wrist and fingers in a slightly flexed position to protect the surgical site.