Ligaments and tendons are extremely important elements of the human musculoskeletal system, holding bones together.
Under the influence of various reasons (malnutrition, injuries and hereditary diseases, severe somatic pathologies of other organs), the functional state of connective tissues is disrupted, which can lead not only to a change in the quality of life, but also to disability.
There are many nutrients necessary to maintain adequate functioning of the musculoskeletal system and accelerate the regeneration of damaged connective tissue (in tendons and ligaments).
Below are 7 foods that are useful for strengthening ligaments and tendons. It is recommended to include them in the daily diet if you have diseases of the musculoskeletal system or are prone to them, as well as during periods of active physical activity.
Dairy
Milk is a valuable source of calcium, tryptophan and other amino acids for the human body.
Calcium ensures complete neuromuscular transmission, maintains tone and ensures muscle contraction, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of ligaments.
Tryptophan increases the rate of tissue synthesis of the ligament and tendon complexes, promotes the absorption of essential amino acids entered into the body with food. It has been proven that a decrease in tryptophan content in food negatively affects the functioning of the musculoskeletal system.
In addition, dairy products improve immunity.
Due to the calcium and tryptophan content, dairy products are beneficial for skeletal muscles, bones and ligaments.
Rich meat broths
Decoctions of meat products, which contain not only meat as raw materials, but bones, tendons and skin, are rich in hyaluronic acid. The combs of roosters and hens and chicken feet are especially valuable.
Hyaluronic acid is absorbed in the intestines, breaks down into individual protein metabolites, which then travel to the ligaments, tendons and joints. They are necessary for the restoration of damaged tissues.
The University of California found that hyaluronic acid helps increase the content of type III collagen in damaged ligaments, which significantly improves repair and enhances the formation of blood vessels for nutrition and oxygen supply. A decrease in the intensity of inflammatory processes was also noted.
It is recommended to add rich meat broths with the inclusion of offal to the diet to maintain the integrity and rapid restoration of ligaments and tendons when ruptured or sprained.
Recovery after surgery for Achilles tendon rupture
The Achilles tendon (lat. tendo calcaneus) or heel tendon is the most powerful and strong tendon in the human body. Despite this, it is one of the most commonly injured tendons.
The proximal part originates at the junction of the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles, the zone of its distal fixation on the posterior surface of the tubercle of the calcaneus.
An Achilles tendon rupture is usually complete. More often, ruptures occur when there is a sudden sharp load on the tendon when starting in sprinters, when the leg lifts off the ground during a jump, or when the foot is sharply dorsiflexed - a fall from a height. In case of direct trauma with a cutting object, partial damage to the tendon may occur. The patient complains of pain in the Achilles tendon area.
At the time of injury, there is a sensation of a blow to the tendon. Hemorrhage and swelling occur on the back surface of the lower third of the leg. Retraction is detected in the area of the rupture. There is no plantar flexion of the foot - the patient cannot stand on his toes
Most often, the tendon ruptures 4-5 centimeters from the point of attachment to the heel bone.
After surgical treatment
From the first days, therapeutic exercises are prescribed, aimed at improving blood circulation in the area of the operation, preventing adhesions, preventing stiffness in immobilized joints and muscle atrophy.
The classes include general tonic exercises for the upper limbs, shoulder girdle and torso (static and dynamic), exercises for the unoperated lower limb. Specific exercises include wiggling the toes, ideomotor exercises, and hip movements.
From the 3-4th day, isometric tension of the triceps surae muscle is necessary when attempting plantar flexion of the foot and extension at the knee joint. This exercise should be repeated many times throughout the day.
3 weeks after surgery, the plaster cast is replaced with a plaster boot for 3 weeks, and the foot is placed in a less flexed position.
The main objectives of therapeutic exercises at this stage are restoration of the range of motion in the knee joint, functional restoration of the thigh muscles and prevention of atrophy of the lower leg muscles.
The exercises are performed in the starting position, lying on your back, on your stomach, on your side, or sitting on a chair. In addition to general tonic exercises, special ones are performed: dynamic exercises with resistance, static efforts for the thigh muscles, isometric tension of the lower leg muscles, ideomotor exercises.
After 6 weeks the plaster cast is removed, and therapeutic exercises are aimed at restoring movements in the ankle joint, strengthening the muscles of the lower leg, and preparing for walking.
In the first days after the immobilization is removed, movements in the ankle joint are performed carefully, in easier conditions: lying down and sitting on a chair (a sliding plane is placed under the foot). The exercises are carried out independently, with self-help and the help of a rehabilitation specialist.
From weeks 6 to 12, postoperative rehabilitation is characterized by full axial loading, increased limb mobilization, and the beginning of stretching exercises. Initially, full axial weight bearing is allowed in a brace and with crutches, and then the patient is allowed to use casual shoes and dispense with crutches.
At this stage, it is advisable to place a heel pad in the shoe, which facilitates the transition from the brace (usually at this point it limits dorsiflexion to 20-30 degrees equinus) to regular shoes. The height of the heel pad is gradually reduced in accordance with the progress of the range of motion. Crutches and heel support should be stopped only after the patient has restored normal gait.
Provided that the postoperative wound is completely epithelialized, walking on an underwater treadmill is possible. The need for this simulator is due to the fact that it allows you to develop a normal gait. Walking on an underwater treadmill with the torso immersed in water to the level of the trans-mamillary line allows you to reduce the axial load on the limb by 60-75%, and when immersed in water to the level of the waist - by 40-50%.
Active range of motion is continued in all planes without restrictions, and passive motion is limited. Regular walking is sufficient to restore functional range of motion, but stretching exercises should be avoided for this purpose. As a rule, at this stage of rehabilitation, the range of motion is already at an acceptable level. Also at this stage, careful isometric inversion and eversion are started, which gradually progress to the use of elastic bands for resistance. It is advisable to restore the strength of the lower leg muscles and range of motion using a special simulator, in which the patient’s foot is fixed in a special device that allows movements in all planes.
Once an adequate range of motion of the foot has been achieved, they move on to strengthening the two main flexor muscles (mm. gastrocnemius and soleus). At 6 weeks after surgery, active plantar flexion of the foot with resistance is performed in the position of bending the limb at the knee joint at a right angle. From the 8th week, plantar flexion with resistance begins to be performed with the leg extended at the knee joint.
Plantar flexion with resistance Performed from 6 weeks after surgery. The patient sits on the edge of the couch, legs bent at the knees and hanging down. This position of the legs reduces the tension on the Achilles tendon. A loop of elastic tape is placed on the foot of the affected leg and stretched.
At this stage of rehabilitation, they are supplemented with other exercises. Perform plantar flexion with resistance on various strength machines. Continue exercise on the exercise bike, gradually increasing the load on the tarsus and shifting the point of application of the pedals on the foot closer to the toes.
Plantar flexion with resistance. Performed from 8 weeks after surgery. This exercise is performed while sitting on a couch, with the leg straightened at the knee joint lying on the couch: in this position the load on the Achilles tendon is higher. A loop of elastic tape is placed on the foot of the leg being trained and stretched.
At this stage of rehabilitation, other exercises are also used. Perform plantar flexion with resistance on various strength machines. Continue exercise on the exercise bike, gradually increasing the load on the tarsus and shifting the point of application of the pedals on the foot closer to the toes.
Exercises on weight machines
To restore plantar flexion and proprioception, it is necessary to use backward walking on a treadmill.
Walking backwards. The patient stands on the treadmill backwards, i.e., with the back of his head towards the control panel, holding the handrails with his hands. Set the speed of the treadmill to 1-2 kilometers per hour and begin walking backwards, rolling the foot from toes to heel. In this case, the patient must fully straighten the leg at the knee at the moment when the foot is fully on the treadmill.
Step-up exercises with visual guidance. The exercise begins with a low step (10 cm high). The patient stands in front of the step on the floor and takes a slow step with the healthy leg forward, rising onto the step. In this case, the body weight rests on the sore leg, which will also train balance. There should be a mirror in front of the patient, so that the patient can look at himself from the side, controlling the position of the feet and hips - it is very important to ensure that when climbing the step, the affected leg does not fall to the side. Then return to the starting position and repeat the exercise. If the exercise is performed correctly, then the height of the step is gradually increased (15 and 20 centimeters).
It is necessary to restore not only muscle strength and range of motion, but also proprioception, without which effective muscle interaction is impossible. For this purpose, exercises on moving supports such as BAPS are useful - a stand for biomechanical training of the ankle joint. The upper surface of the stand is hard and flat, and the lower surface is soft and shaped like part of a sphere.
BAPS exercises begin in a sitting position, then progress to proprioception training while standing on two legs, then standing on one leg, and gradually increase the difficulty of the exercise by throwing a ball against a wall or resistance. Proprioception and balance training on movable stands can be supplemented with strength exercises, which also begin with standing on a platform on two legs, and then gradually increase the resistance and move on to exercises standing on one leg.
From 12 to 20 weeks after surgery, there is a complete restoration of the range of active movements, strength of the flexor muscles and symmetrical balance in both lower extremities. It is believed that the normal strength of plantar flexion corresponds to the patient’s ability to rise on the toes of one leg at least 10 times. However, the patient must first demonstrate the ability to rise on the toes of both feet, and then the conditions for this exercise become more difficult.
Restoring plantar flexion strength: Start with bilateral flexion on a machine in a seated position (to eliminate the need for balancing) and gradually increase the exercises up to a unilateral calf raise at the edge of a step.
Step-down exercises (going down steps) are performed according to a progressive type, gradually increasing the height of the step (10, 15 and 20 cm). Proprioception and balance training is again done in a progressive manner (both legs - one leg). In this case, not only the already described BAPS platforms can be used, but also trampolines, swinging stands, etc.
To further restore the strength and endurance of the lower leg muscles, isokinetic exercises are used, which involve movements with accommodating resistance at a fixed speed. Consequently, thanks to this principle, the maximum possible contraction of the muscle occurs with a simultaneous full range of movements (in this case, active-passive, since in extreme positions the movements are carried out by the simulator).
Isokinetic plantar and dorsiflexion of the foot. The patient sits in a chair of a biomechanical system with an isokinetic operating mode of the HUMAC NORM type and performs dorsiflexion and plantar flexion of the foot. The exercise trains muscle strength, and the indicators allow you to evaluate the effectiveness of the rehabilitation program. It is based on the principle of adjustable and accommodating resistance to movements at a constant speed.
After gait has been restored, full range of passive movements and normal muscle strength have been achieved, they begin running on an underwater treadmill, immersing the patient in water up to chest level. Exercises on such a machine allow you to reduce the load by reducing body weight.
The volume and intensity of exercises that the patient performs at home are regulated by the rehabilitation therapist in accordance with the success achieved. The criterion for transition to the next phase is, among other things, the restoration of the ability to balance on one leg, which is compared with the contralateral one. In this case, both IMOOVE and COBS simulators in testing mode, as well as NeuroCom devices can be used.
Weeks 20 to 28 Once the strength and function of the triceps surae muscle has returned to normal, the patient begins the next phase of rehabilitation, the goal of which is to return to higher than daily physical activity. In general, all rehabilitation measures are aimed at preparing a springboard for resuming sports.
At the twentieth week after surgery, isokinetic testing is performed in comparison with the contralateral limb of plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion and eversion. Isokinetic strength assessment is preferred because it is much more accurate than manual isometric testing.
Isokinetic assessment allows the rehabilitator to obtain objective data on the strength, efficiency and endurance of the lower leg muscles, which can be used not only as a criterion for transition to the next phase of rehabilitation, but also to monitor the patient’s status. If the results of the isokinetic assessment are at least 75% of those of the contralateral limb, and the patient can rise on the toes of the injured limb at least 10 times, then they are allowed to start running forward on the treadmill. The running program should also be progressive, starting at slow speeds and short distances. The increase in load intensity is regulated by the patient’s subjective sensations; the running itself should be painless.
Continue with resistance exercises, development of range of motion and freedom of movement, as well as isokinetic exercises that strengthen the strength and endurance of the muscles responsible for plantar flexion, dorsiflexion, inversion and eversion.
In accordance with the requirements of the sport, they begin running, starting with simple straight running on a flat surface and then, according to the patient’s feelings, complicate the exercises by running sideways, running in a zigzag, in a figure 8 figure, with acceleration and braking. These exercises can be supplemented with elastic resistance.
Running with side steps with resistance. The patient places a loop of a long elastic band around his waist, the other end of which is secured to the wall. Run sideways with side steps, stretching the tape. Return to the starting position with the same extended steps.
Balance training while standing on a bolster (proprioceptive training). A loop about 1 meter long made of elastic lena is attached to the wall at a height of 15 centimeters from the floor. The patient stands facing the wall 70 centimeters from it, the loop is put on the healthy leg, and the affected leg is placed on a bolster. In this case, the affected leg is slightly bent at the knee. Begin swinging the healthy leg backwards and to the side, trying to maintain balance on the affected leg. In the starting position, the belt tension is moderate. During exercises, you should keep your back straight and your legs should be straightened at the knees.
Complex proprioceptive training (balance training while standing on a swinging platform) . The patient stands on the affected leg on a swinging platform, the healthy leg is bent at the knee. They throw the ball at the wall with their hands and catch it after pushing it off. The exercise trains the coordinated work of muscles and the ability to balance.
Working capacity is restored 2.5 months after surgery.
Sports activities are started six months after the operation.
It is most effective to carry out a recovery course in a rehabilitation center, where the entire process is supervised by specialists.
Fatty fish
Seafood contains large amounts of the valuable amino acid tryptophan. This substance is one of the main building elements for bone tissue, tendons, ligaments and skin.
The amino acid not only increases the rate of tissue restoration, but also helps normalize mood (for depressive disorders) and gives an attractive aesthetic appearance to the skin.
Scientific experiments demonstrate that tryptophan deficiency can lead to significant damage. There is a pronounced curvature of the spinal column (due to loss of functional activity of the ligamentous apparatus). Also, a lack of tryptophan increases the content of calcium, magnesium and sodium in the body, leading to multiple organ disorders.
In addition, oily fish is one of the 11 foods that are most beneficial for joints.
It is recommended to use fatty fish more often (at least 2 times a week) to maintain healthy ligaments.
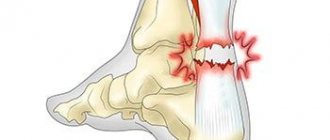
Symptoms
Pain manifests itself with active movements. Projected over the area of the affected tendon. There is no pain with passive movements. In addition, there is pain on palpation of the affected tendon, changes in the skin in the area of the affected tendon: possible redness, a local increase in temperature, local edema, swelling in the area of the affected tendon, the intensity of the pain syndrome increases over time. At first, a person is bothered by minor pain in the area of the affected tendon, which does not interfere with his daily life. But gradually the pain syndrome intensifies, the pain becomes excruciating, strong, unbearable, disrupting the normal rhythm of life.
Chicken eggs
Chicken eggs contain a wide range of vitamins (D, C, E, B), macro- and microelements, essential amino acids, which are building materials for the body’s cells.
Eggs contain a significant amount of collagen, which is broken down into valuable amino acids (proline, lysine, glycine) and used by ligaments, cartilage and muscles.
According to research, with a lack of dietary collagen, there is a decrease in bone density, decreased muscle tone, and loss of elasticity in ligaments and tendons.
To increase the absorption of collagen from eggs, you should additionally consume foods rich in vitamin C (bell peppers, citrus fruits, strawberries, pineapple).
A chicken egg is a valuable source of amino acids and vitamins necessary to maintain the anatomical and functional integrity of the musculoskeletal system.
Healthy foods for tendons
In order for a person to perform a particular movement, it is necessary that the musculoskeletal system works without misfires. And since tendons are the connecting link of this system, they must receive nutrition appropriate to their status.
Jellied meat, aspic, jelly. Rich in collagen, which is an important component of tendons. The use of these products increases the elasticity of the tendons and helps them cope with heavy loads.
Beef. Champion in essential amino acid content. It is a building material for tendon fibers.
Eggs. Due to their lecithin content, eggs are involved in normalizing the functions of the nervous system. In addition, they contain large amounts of vitamin D, which is essential for tendon health.
Dairy products. They are a reliable source of beneficial calcium, which is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses along the muscle-tendon complex.
Mackerel. Rich in fats, which are important for protecting tendon fibers from overload. In their absence, the regeneration process slows down, and the tendon may simply rupture!
Green tea. Increases the resistance of tendons to stress. Increases their resistance to stretching.
Turmeric. Due to the presence of natural antibiotics, as well as elements such as phosphorus, iron, iodine and B vitamins, turmeric promotes rapid tendon regeneration.
Almond. Contains an easily absorbed form of vitamin E. Thanks to this, almonds help tendons recover faster from injuries caused by overstretching.
Bell peppers, citrus fruits. They contain a large amount of vitamin C, which is an essential component of collagen.
Liver. Rich in vitamin D3, as well as copper and vitamin A. Thanks to these substances, the heel of the tendon is strengthened, with the help of which it is attached to the bone.
Apricot. Rich in potassium, which is responsible for the performance of the muscles that control the skeletal system.
General recommendations
For tendons, a very important nutritional requirement is the presence of calcium and collagen-forming products. In their absence (or deficiency), the necessary substances will be automatically extracted from the muscles and bones. Thus, the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system will be at risk!
If problems with tendons occur, doctors advise using ointments containing collagen.
Folk remedies for normalizing tendon function
The following compresses will relieve pain and restore the functionality of the tendons:
- shepherd's purse;
- wormwood (fresh leaves of the plant are used for a compress);
- Jerusalem artichoke.
Harmful foods for tendons
- Sugar, cakes and pastries . When they are consumed, muscle tissue is replaced by fat. As a result, the tendons are deprived of their connecting component. In addition, their overall tone decreases.
- Fats . Excessive consumption of fatty foods causes calcium blockage. As a result of this, it does not enter the tendon in sufficient quantities and it begins to extract calcium from the bones.
- Alcohol . Causes calcium blockage. In addition, under the influence of alcohol, degenerative changes occur in the transitional muscle-tendon tissue.
- Coca Cola . Contains phosphoric acid, which leaches calcium from bones.
- Oatmeal . Contains phytic acid, which blocks the absorption of calcium and its subsequent transport to tendons and bones.
Attention! The information is for informational purposes only and is not intended to make a diagnosis or prescribe treatment. Always consult a specialized doctor!
Tatyana Eliseeva chief editor of the Food+ project
Ask a Question
Rating:
10
/10
Votes: 6
Usefulness of material 10
Reliability of information 10
Formatting of Article 10
Red grapes
Grapes have a wide range of properties: they slow down aging, prevent the formation of atherosclerotic deposits on the walls of large vessels, and inhibit malignant cell proliferation.
Grapes, according to scientific research, prevent the development of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system, prevent fibrosis of the tendons of those muscle groups that, for various reasons, are not able to work properly.
An improvement in metabolic processes in the connective tissue of ligaments and tendons was also noted.
Grapes are an indispensable product for people who lead a sedentary lifestyle or have serious pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment
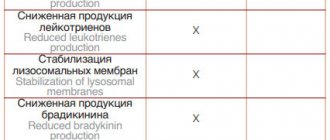
Treatment of tendinitis (tenosynovitis, tenosynovitis) should be comprehensive and include conservative therapy (rest, cold, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), as well as physiotherapeutic methods.
It must be remembered that treatment of tendonitis should include limiting physical activity, the use of physical therapy, the action of which will be aimed at speedy healing of the damaged tendon, elimination of the inflammatory process, as well as strengthening and maintaining the tone of the whole body. In addition, if you have tendonitis, your doctor may recommend wearing special orthoses that will have a positive effect on the healing of the damaged tendon. If tendonitis is characterized by a severe course, then antibiotic therapy and even surgical treatment are possible. Surgical treatment is used only when the use of conservative treatment and physiotherapeutic procedures does not bring the expected results.
An important step in the treatment of tendinitis is to determine the cause of the development of this disease. At our Clinic, doctors use modern diagnostic methods that help make a diagnosis quickly and accurately. After identifying the causes of tendinitis, our specialists will be able to prescribe you the most effective treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the symptoms, and will also allow you to forget about the pain in the shortest possible time. At the Bone Clinic, the doctor will select an individual treatment program, taking into account the stage and course of the disease and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
You will be guaranteed the best treatment for tendinitis in our Clinic. Here you can get advice from experienced traumatologists. In our Clinic, doctors are specialists, professionals in their field, working at the highest level, while achieving maximum heights and success.
What to avoid
There are many foods that negatively affect the condition of ligaments and tendons. The most harmful are:
- Sweets. The most dangerous are sugar, cakes, pastries and pastries. They promote the deposition of fat cells in muscle tissue, the development of dystrophic changes, which provokes the degradation of connective tissue.
- Fats. Inhibits the absorption of calcium by myocytes and connective tissue cells. As a result, calcium begins to be actively removed from the bones, causing osteoporosis. You should avoid animal lard, as well as long-term frying of food in oil.
- Oatmeal. Due to the presence of phytic acid in its composition, oatmeal causes a malabsorption of calcium, which negatively affects the entire musculoskeletal system.
What to do if you have a sprain
October 14, 2016
A fairly common type of injury is a sprained ligament. Remember the rules of first aid.
An ordinary walk with friends, a workout, or just everyday work can turn into a minor nuisance. Sprained ligaments are a common situation for many athletes and doctors, and it will not be difficult for them to provide first aid to others. But what if you have never encountered this problem before?
Ligaments
- These are dense connective tissue fibers that hold bones and joints together. When connective tissue is stretched, for example due to careless movement, the fibers receive varying degrees of damage, including rupture.
So, first you need to determine that you have a sprain, and not a fracture or dislocation. When a fracture occurs, deformation of the limb and severe swelling occur. If you have a dislocation, then sensitivity may disappear, the joint becomes deformed, and redness appears.
Pain with movement, bruising and swelling are the main symptoms of a sprain. But it’s still worth going to the hospital so that the diagnosis can be made as accurately and correctly as possible.
If you do have a sprain, then first aid will be as follows:
- Firstly, the injured limb must be immobilized and the victim must be kept at rest.
It is important not to rub, not to try to knead, or to disturb the injury in any way, because this can lead to more tragic consequences. - Secondly, it is important to determine the degree of stretching.
There are cases when the pain is practically not felt and there is no swelling, which means you can simply get by with a cold compress in the form of ice (it is better not to allow the ice to come into close contact with the skin and to do this, wrap the ice in a cloth), bottles or heating pads with cold water, and then, After a few days, start using warming ointment. For larger-scale injuries, it is necessary to additionally apply a fixing bandage, in the form of an elastic bandage or scarf, and in extreme cases, a splint made from improvised materials, for example, wooden planks or straight sticks, thereby fixing the affected limb on both sides. - Thirdly, give the victim any painkiller
that is available without a doctor's prescription, after asking the patient about allergies to medications. - Fourthly
, in order to reduce the swelling that appears due to damage to blood vessels (in other words, a bruise), you can draw an iodine mesh and place the affected limb on a small hill so that the blood drains from it. - Fifthly
, and this is the most important thing,
you need to see a doctor
, even if you have, at first glance, an insignificant sprain. Only a specialist will be able to determine the severity of the damage and prescribe appropriate treatment.
After the doctor confirms the suspected diagnosis and you undergo a short recovery course, you should not subject the sprained ligaments to heavy loads. It is best to wear a bandage until you are completely sure of your recovery.
Usually, if the assistance is provided competently and all the doctor’s advice is followed, no consequences arise. But if you experience an increase in body temperature, increased pain and limited mobility over the next two days after the injury, then you should urgently go to the hospital.
Tags:
- Stretching
To leave a comment you must be an authorized user