Problems with the tendons of the foot and ankle
The exact incidence of ankle tendinitis is unknown, but available evidence suggests that tibialis posterior and peroneal tendonitis are fairly common conditions. The tibialis anterior tendon is less commonly affected, except in younger athletes who are increasing their training programs or starting to run on inclines.
Risk factors for developing peroneal tendon problems include high arches, which can occur at any age. Lesions of the tibialis posterior tendon are associated with flat feet and are more common between the ages of 40 and 50 years.
Pathology of the tibialis anterior tendon.
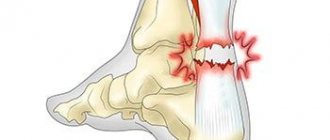
Tibialis anterior tendinitis is characterized by pain and swelling on the front of the ankle. The disease usually occurs in middle and old age. The cause is often physical activity or injury to the ankle joint, and may be due to changes in the nature of physical activity or the type of shoes used. Symptoms are worse with prolonged standing and walking and relieved with rest. Upon examination, local pain and sometimes swelling in the area of the anterior surface of the ankle joint is revealed. Resisted dorsiflexion of the ankle often increases symptoms.
In Fig. Localization of pain and swelling with tendinitis of the tibialis anterior tendon.
Risk factors for tibialis anterior tendonitis include excessive tightness of the calf muscle, obesity, flat feet and exercise.
Pathology of the posterior tibialis tendon.
Tibialis posterior tendinitis is characterized by pain in the area of the inner surface of the ankle joint and arch of the foot, which intensifies with prolonged standing and is often accompanied by collapse (dropping) of the arch of the foot and visible protrusion of the navicular bone. The main objective signs of the disease are local pain along the tendon and in the area of its attachment to the scaphoid bone. If there is only local tenderness at the tendon insertion, it may not be tendonitis, but accessory navicular bone. This latter diagnosis can be confirmed radiographically.
Rheumatoid diseases lead to a decrease in the strength of the joint capsule and a gradual thinning of the tendons, and can cause, in particular, dysfunction of the tibialis posterior tendon.
The integrity of the tibialis posterior tendon can be confirmed by asking the patient to rise onto his toes on one leg. Some patients with severe tendinopathy simply will not be able to raise themselves onto the toes of one leg. This may be due to muscle pain or weakness, or both.
Pathology of the peroneal muscle tendons.
Patients with peroneal tendonitis complain of pain and sometimes swelling along the posterolateral aspect of the ankle joint. Concomitant involvement of the sural nerve (due to inflammation or damage to nearby tendons) may lead to decreased sensation or a burning sensation along the outer surface of the foot. The pain may be localized to the insertion of the peroneus brevis tendon on the metatarsal bone and, if preceded by recent trauma, radiography is necessary to rule out a fracture.
Rice. Localization of pain and swelling with tendinitis of the peroneal tendons.
If the retinaculum of the peroneal tendons is damaged, they can slip out of the groove of the lateral malleolus at the level of the ankle joint. This condition is called chronic peroneal tendon subluxation. Patients with this condition may describe a clicking sensation in the affected area during physical activity, and sometimes subluxation can be provoked by physical examination.
Achilles tendinopathy
Causes of tendinopathy | Risk groups | Signs | How to treat
Achilles tendinopathy is a disease that makes simple movements difficult: walking, running, climbing stairs. All that is required of the patient is to promptly contact a specialist at the first symptoms. Tendinitis can only be effectively treated under the supervision of a doctor. Orthopedists and neurologists at Doctor Ost MC eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the cause of tendinopathy.
Sign up
The Achilles tendon, which connects the lower leg and foot, is very strong and reliable. But just as water wears away a stone, daily heavy loads on the Achilles gradually destroy it. Achilles tendinopathy is one of the common ailments. The discomfort in the heel can be so severe that it becomes impossible to walk. You should not endure this pain - tendinopathy is treated using effective techniques.
Doctor Ost MC does not waste time on symptomatic treatment of tendinopathy. It is known: in order to get rid of pain, you need to look for and eliminate its cause. This is not difficult if the clinic is well equipped and does not use modern treatment methods. These are the conditions created at the Doctor Ost MC.
CAUSES OF TENDINOPATHY
The Achilles tendon is a dense bundle of collagen fibers. With regular exercise, the fibers do not receive sufficient nutrition and begin to break down. The more damaged fibers, the greater the discomfort. If the patient makes no attempt to stop the process, acute tendinopathy becomes chronic. In this condition, even a minor injury is dangerous: the already damaged tendon can rupture.
To prevent the condition from becoming critical, tendonitis must be treated on time, immediately after the first symptoms appear. Treatment will be quick and truly effective if you entrust it to a neurologist or orthopedist at Doctor Ost MC and do not self-medicate.
ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY: GROUPS AT RISK
Achilles tendinopathy is an inflammatory process that occurs in response to excessive stress. Most often they suffer from:
- Women who prefer high-heeled shoes;
- Athletes (especially track and field athletes);
- Patients with systemic connective tissue diseases or hormonal insufficiency;
- Patients with flat feet and pathologies of the structure of the lower extremities.
Tendinopathy can also occur due to a sudden injury: for example, after an unsuccessful fall. But more often this disease is not accidental and is associated with serious stress on the Achilles.
Ask a Question
SIGNS OF TENDINOPATHY
The tendons that connect the tibia and heel bone provide the ability to jump, run, and rise on the tiptoes. We make these movements every day. Therefore, even a slight inflammation is felt immediately. Symptoms of Achilles tendinopathy:
- Pain along the back of the lower leg closer to the heel bone during movement. Passes at rest;
- Decreased foot mobility;
- Swelling over the Achilles injury;
- Redness, local increase in temperature over the injured area.
In the chronic form of tendinopathy, the pain becomes constant, bothers you even without load, a crunching sensation is felt with any movement (calm walking, climbing stairs), and a noticeable mass formation appears above the Achilles.
HOW TO TREAT ACHILLES TENDINOPATHY
As soon as pain in the heels and legs begins to seriously bother you, you should immediately contact a specialist! You should not expect that the discomfort will go away and the fibers in the Achilles tendons will recover on their own. What is most likely to happen with acute tendinopathy is that it will become chronic and will regularly remind itself, reducing the quality of life. Don't risk your health and don't wait for a tendon to rupture! It is always easier and faster to cure diseases of the musculoskeletal system in the initial stages!
At Doctor Ost MC you can get rid of pain from Achilles tendonitis in one visit. The therapy does not require much time; basic treatment can be done at home. Even in advanced cases, treatment of tendinopathy will not require hospitalization if performed using the unique methods of the Doctor Ost MC.
how much does it cost? Achilles tendinopathy is treated by a neurologist and an orthopedic traumatologist.
The cost of consulting a specialist is indicated in the “consultative appointment” section of our price list. Follow the promotions, don't miss out on the best price! What our center’s specialists can do when treating tendinopathy:
- Relieve tendon inflammation with high-intensity HILT laser;
- Start the process of restoring collagen fibers with alloplant injections or PRP therapy;
To prevent tendinopathy from returning, the orthopedist at Doctor Ost MC will help correct flat feet, create an individual exercise therapy complex, and refer you for massage or taping.
What to do if your foot ligaments are inflamed
The first thing to do when the foot ligaments are inflamed is to immobilize the affected limb. No physical activity is allowed. Inflamed ligament fibers can tear quite easily. In this case, surgical treatment will be necessary.
At home, you need to ensure complete rest for the limbs. It is advisable to place your leg on an elevation so that the shin and thigh are parallel to the floor. In this way, it is possible to reduce the degree of increase in infiltrative edema and partially relieve pain.
Ointments and other medications cannot be used without a doctor’s prescription. The only indication is an increase in body temperature above 38 °C. In this case, it is allowed to take 1 tablet of acetylsalicylic acid.
Consult a doctor immediately, since it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis at home for this condition. You may have a compression fracture of a small bone in the foot due to latent osteoporosis. And this injury can only be identified using an x-ray.
Motrin® for tenosynovitis
Motrin® is a modern non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that helps relieve pain and inflammation, including tenosynovitis. Motrin® is clinically proven to provide pain relief for up to 12 hours1. At the same time, the active substance of the drug (naproxen) helps to cope with inflammation, reducing the activity of cyclooxygenase and blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins, which is important in the treatment of diseases such as tenosynovitis.
Before use, read the instructions.
Up to contents
Causes of foot tendonitis
Damage to the tendons of the foot with plantar tendonitis develops due to the influence of the following factors:
- Excessive physical activity;
- Mechanical impact of damaging factors (bruise, bone fracture, dislocation, damage to the ligamentous apparatus);
- Metabolic disorders in the human body;
- Infectious processes in tendons;
- Excess body weight.
Plantar tendonitis occurs when there are bone abnormalities that occur during fetal development or due to injury. Some medications can affect the condition of the tendons.
Treatment of foot tendonitis
Drug therapy for tendinitis is aimed at eliminating the source of inflammation and reducing pain. For this purpose, rheumatologists prescribe the following medications:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (orally, intramuscularly or locally);
- Glucocorticoids (locally or at the site of localization of the focus of the inflammatory-degenerative process);
- Ointments that have an irritating effect on the skin of the foot.
You can improve your condition and reduce the severity of pain using traditional medicine methods. Patients use them if pain occurs during weather changes. In this case, healers recommend taking one teaspoon of sarsaparilla infusion and ground ginger root 3 times a day. Walnuts have an anti-inflammatory effect. You can use the partitions of walnuts infused with vodka. Herbalists recommend taking one teaspoon of the tincture 2 times a day.
If the patient prefers to resort to homeopathy, he is recommended to take Arnica Montana 9 CH. This homeopathic remedy should be taken 3 tablets under the tongue three times a day, an hour after meals or drinks. Do not use menthol-flavored toothpaste or chewing gum while using this drug.
If tendonitis occurs after an injury and does not respond to drug therapy, patients are offered surgery. Severe cases of plantar tendinitis are discussed at a meeting of the Expert Council with the participation of professors and associate professors, doctors of the highest category. Leading specialists in the field of bone and tendon diseases collectively decide on the need for surgical treatment. The operations are performed by experienced orthopedic traumatologists. Surgeons are fluent in the techniques of modern surgical interventions on tendons.
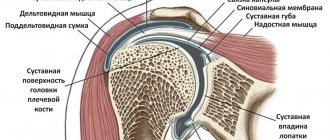
Which joints are most often affected?
A tendon connects bones or bones and muscles. It is covered on top with connective tissue, and on the inside with a synovial membrane that secretes lubricant for better gliding and movement of the limbs. The inflammatory process leads to disruption of this process. Sliding slows down and pain occurs.
Most often, inflammation affects the tendons of the forearm, hand, wrist, ankle and foot. Tenosynovitis can be acute or chronic. If, when the first signs of the disease appear, a person does not carry out effective treatment, does not fight inflammation and pain, and after the clinical manifestations subside, he continues to load the tendon, then the disease begins to recur frequently. Dystrophy of the tendon sheaths occurs, and motor activity drops sharply.
Up to contents
What triggers the development of tenosynovitis?
Experts include the following provoking factors:
- microtrauma of tendons;
- heavy physical work associated with joint overload;
- bruises from an accidental fall on a sharply bent or straightened limb;
- spread of infection to the tendons and their sheaths with osteomyelitis, infectious arthritis, phlegmon;
- toxic reactive inflammation of tendons with rheumatic joint damage;
- entry of pathogens into joint structures through the bloodstream during tuberculosis, gonorrhea or other infectious diseases.
Up to contents
Types of damage
Tendon injuries are tendon stretching or rupture. A sprain occurs as a result of excessive effort, for example, when playing sports or doing physical work. Pathological sprains are distinguished. They arise as a result of arthrosis, arthritis, when the tendon loses strength. A stretch of more than half the thickness of the tendon is called a tear.
From the point of view of orthopedics, it is ruptures that are dangerous. They are:
- complete - the tendon is completely torn from the bone;
- partial – incomplete tear.
Also distinguished:
- open gap. Occurs as a result of an open injury - fracture, cut, etc. In addition to the tendon, nerves and blood vessels are damaged;
- closed. When damaged, the skin remains intact.
Depending on the location, there are:
- tendon rupture in the leg;
- tendon rupture in the arm;
- shoulder tendon rupture
and other injuries.