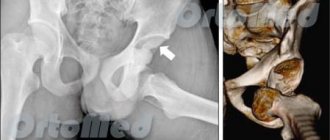
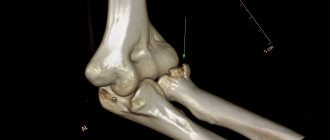
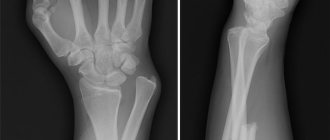
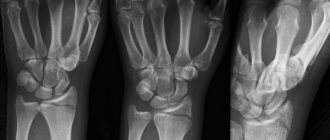
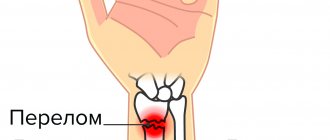
A radius fracture is one of the most common household injuries. It often occurs when falling on outstretched arms. Such an injury is a serious problem, since the period of bone fusion can be quite long due to the development of complications (in particular neurodystrophic syndrome).
Treatment of a radius fracture has 2 goals:
- fusion of fragments and restoration of bone integrity. Actually, the main outcome of the treatment will be determined by how correctly they have fused;
- preservation of arm and hand function.
The most common treatment for this type of fracture is closed manual reduction, popularly known as bone reduction. The surgeon manually positions the bone fragments in the correct position and fixes them with an immobilization bandage (for example, plaster or polymer). In the area of the fragments, repair processes are launched, and a bone callus is gradually formed, which will unite the fragments and bone into one whole.
This method is simple to perform and does not require high-tech equipment or additional special training for a traumatologist. However, an analysis of the literature shows that from 20 to 42% of such cases end in secondary displacement of fragments, which occurs already when a plaster cast is applied.
Another nuance is that any injury leads to tissue swelling, and a fracture of the radius is no exception. The possible development of edema is most likely in the first day after injury, and doctors take this aspect into account when applying a fixing bandage. In particular, preference is given to splints, which can then be replaced with circular bandages.
Closed reduction with pin fixation
This method takes place in two stages:
- Reposition of fragments
- Fixation of fragments with knitting needles
The advantages of this method are reliability, low trauma and absence of scars. The disadvantages include the following:
- risk of infection at the site where the needles are installed;
- the need for repeated surgery to remove the wires;
- the period of healing of the fracture is at least 1 month;
- high risk of developing irreversible contractures due to the long healing time and the impossibility of starting early rehabilitation.
Types of fracture
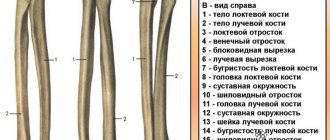
There are a large number of bones in the arm area. But, as a rule, injuries to the radius are observed - the bone located in the hand area. Fractures can be primarily:
- closed;
- open.
Fractures are differentiated depending on the zone of the upper limb in which they occurred:
- diaphyseal. In such a situation, the fracture line can be seen in the area of the bone body;
- epiphyseal. The fracture line is localized in the area of the epiphysis of the victim’s bone. In most cases, epiphyseal injuries are intra-articular;
- metaphyseal. The location of the fracture lines is the intermediate region located between the body of the bone and the end of the bone. These injuries are called periarticular.
It is worth highlighting separately the classification by type of injury. According to this criterion, damage is distinguished:
- shoulder blades;
- radius;
- elbow joint;
- collarbone;
- humerus;
- fingers
Shoulder fracture
The shoulder part of the arm accounts for approximately 7% of the total number of fractures. In this case, injuries of the shoulder neck are most often diagnosed. The most common cause of injury is a fall on one of the upper limbs. With such an injury, the joint looks swollen, and pain occurs during palpation and various movements. To clarify the diagnosis, radiography should be performed. In most cases, the patient requires conservative treatment. In this case, a closed reposition is performed with the subsequent application of a Deso bandage (or the use of an abduction splint, a Turner bandage).
Worth knowing! In the presence of a non-reducible fracture in young patients, surgical treatment is prescribed.
In this case, osteosynthesis of the surgical neck of the shoulder is performed: using knitting needles or a plate. Injuries to the shoulder shaft are not uncommon at a young age. They are diagnosed by a fall on the arm, a “police fracture” (twisting of the upper limbs), or a direct blow. With such damage, there may be a concomitant complication such as injury to the radial nerve.
Important! Injury to the shoulder diaphysis is accompanied by swelling, pain, deformation, and a sharp limitation of mobility.
With simultaneous damage to the radial nerve, sensitivity in this area deteriorates. For shoulder injuries, both surgical and conservative treatment are indicated. Conservative methods involve applying traction. After the formation of the primary callus, it is replaced with a plaster cast. Surgical intervention is necessary if attempts to compare fragments are unsuccessful (using the method of skeletal traction, interposition of soft tissues). It is also performed when there are relative indications (in order to prevent the development of post-traumatic contractures).
Provided there is a good comparison of bone fragments with concomitant nerve injury, a variety of conservative techniques are used:
- immobilization;
- physical therapy classes;
- physiotherapy sessions;
- taking medications that activate the process of nerve restoration.
If symptoms of nerve regeneration are absent over several months of conservative therapy, surgical intervention is resorted to (performing plastic surgery of the nerve trunk, neurolysis).
Injuries to the lower end of the shoulder can include:
- supracondylar;
- transcondylar.
Supracondylar injuries include flexion and extension injuries. Transcondylar fractures include T- and V-shaped trochlear fractures. During the recovery period for injuries to the middle and upper third of the shoulder, exercise therapy and attending physiotherapy sessions are recommended. In case of intra-articular injury, physiotherapy is contraindicated.
Forearm fracture
Approximately 15-30% of the total number of fractures are forearm injuries. The main causes of such damage:
- blow to the forearm;
- car accidents;
- falling from height.
Such injuries are characterized by swelling, severe pain, and deformation in the damaged area. With a diaphyseal fracture of the arm, symptoms such as pathological mobility and crepitus are diagnosed. In order to clarify the diagnosis, radiography of the affected segment is performed. For a non-displaced arm fracture, pain relief is indicated. After this, you need to put a plaster on your arm. After the immobilization period is completed:
- massage sessions;
- physiotherapy sessions;
- attending physical therapy classes.
In case of a displaced diaphyseal fracture, osteosynthesis is performed with a plate or pin. In some situations, the use of the Ilizarov apparatus is also indicated.
Fracture of the hand
Injuries to the bones of the shoulder account for more than 30% of the total number of skeletal injuries. They are the result of a fall or blow to the hand area. Damage to the bones of the wrist is diagnosed relatively rarely. Possible complications from a scaphoid injury:
- a large number of ununited fractures;
- formation of cysts and false joints.
Conservative treatment is indicated; if complications occur, surgical intervention may be necessary:
- open osteosynthesis;
- arthrodesis of the wrist joint;
- removal of a fragment deprived of nutrition.
Injuries to the metacarpal bones can be closed or open, single or multiple. Such damage is accompanied by bluish skin, swelling, and stiffness of movement. To clarify the diagnosis, an x-ray of the hand is taken. Treatment in most cases is conservative - closed reduction, plaster on the arm. If a disappointing result of reduction is obtained for an unstable arm fracture, there are indications for open osteosynthesis. In this case, skeletal traction or closed fixation with knitting needles is also performed. Finger injuries are also quite common.
They can be:
- closed or open;
- intra- or extra-articular;
- helical, oblique, splintered or transverse.
If a fracture of the fingers is suspected, the diagnosis is clarified using x-rays of the fingers. Usually they resort to conservative therapy. If it is impossible to compare the fragments, they resort to closed or open tissue fixation, and skeletal traction can be performed.
Open reduction followed by fixation with screws or plates
There are cases when severe displacement has occurred and reposition cannot be carried out using conventional methods. Then an operation is performed during which the displacement is eliminated and the fragments are fixed with titanium plates or screws. This technique is considered more durable than fixation with knitting needles. The plates firmly and rigidly hold the fragments in the desired position, therefore, firstly, it is not always necessary to wear a cast or a fixing bandage, and secondly, the wrist joint can be developed almost immediately.
Exercise therapy is the main method of restoring hand function
It is necessary to develop the arm while it is in a cast. All finger movements are done with caution. If discomfort or pain occurs, immediately stop gymnastics.
The first exercises are done at the end of the first week after applying the immobilization bandage. Gymnastics begin from the shoulder girdle and gradually move down to the wrist. Fingers should be developed especially carefully.
After the cast is removed, the patient experiences stiffness of movement, mild pain, and a feeling of fear of damaging the bone again. Limited mobility is due to the fact that the ligaments have temporarily lost their elasticity. Despite this, the movements are made more actively, involving all muscle groups of the arm, including the deep ones.
Exercises for the arm while wearing a cast
Before working out your arm for the first week after an injury, you need to assess the person’s well-being. There should be no sharp pain or high body temperature. All exercises are aimed at ensuring that the patient can simply take care of himself independently ─ hold a cup, spoon, toothbrush, change clothes, cut with a knife. When kneading the arm, sharp, circular, forceful loads are contraindicated in order to avoid repeated displacement of bone fragments.
The first set of exercises for a hand in a cast is performed in a sitting position. It is important to develop each phalanx of the fingers to avoid the formation of contractures (limitation of passive movements). At first, you can help with your healthy hand. The following types of physical activity are effective:
- place your forearm on the table with your palm up, carefully clench and unclench your fingers (6-10 times), repeat the same exercise with your palm down;
- if the fracture is without complications and the elbow is free from plaster, make flexion movements in the joint ─ the hand lies on a hard surface and slowly rises to the face with the back and inner side of the palm alternately (5-7 times);
- squeezing and unclenching a soft rubber ball or “anti-stress” toy with your fingers (10 times).
Gymnastics lasting 5 minutes is carried out 2-3 times a day. As you improve, this time is increased to 15 minutes. Criteria for successful rehabilitation at week 3: ability to dress independently with a cast on a limb, cut soft foods with a knife, and hold a filled cup.
Forearm restoration after plaster removal
Before starting the main exercises, do a light warm-up. Develop the wrist joint in a circular motion, clench your fingers into a fist, and lightly massage the hand.
Basic exercise therapy after a fracture includes the following groups of exercises:
- spreading and closing fingers;
- pressing the end phalanges onto a hard surface;
- alternately raising fingers from the table with maximum amplitude;
- rotational movements of the brush.
Effective use of available tools. It is useful to lift and hold a glass of water, knead plasticine with your fingers, toss and catch a tennis ball. To stretch the tendons and ligaments, gently rest your wrists on the table with your palms and the inside and outside of your hand.
The gymnastic complex must include movements that involve all joints and parts of the hand. At the same time, the shoulders and arms are raised and released, followed by extension to the sides. Rotate the forearm at the elbow joint clockwise and counterclockwise.
In order to restore the primary functionality of the limb, you need to use it more often in everyday life - combing your hair, dressing, preparing food.
Special forearm supination/pronation simulators help you develop your arm safely. During rehabilitation exercises, all movements are carried out anatomically and physiologically correctly (the amplitude is adjusted up to 90°C). Fast clinical results are ensured by optimizing the load in each individual case.
What is contraindicated to do during the rehabilitation period until full recovery of working capacity:
- carry a bag or package weighing more than 0.5 kg;
- lift dumbbells;
- practice with heavy medicine balls (volleyball, basketball);
- transfer the center of gravity of the body to your hands (lean);
- turn the key, open tight door locks.
With regular performance of the entire set of exercises, the functionality of the limb is restored in 1.5-3 months.
Gymnastics in warm water
Warm salt baths reduce muscle tone, relax the nervous system, relieve pain, dilate blood vessels, ensuring blood flow. For exercises, you need a container that can fit your forearm without restrictions (wide pelvis, baby bath). The optimal water temperature is 36-37°C.
Contraindications:
- infection of soft tissue at the fracture site;
- skin rashes, ulcers;
- increased body temperature;
- hypertension during exacerbation.
It is best to work out your hands in warm water in the evening, 2 hours before bedtime. Dissolve 100 g of sea salt and immerse the forearm, wrist, elbow joint, up to half the shoulder.
In the water, make bending movements with your fingers, palm, and rotate your brush in different directions. Raise and lower closed fingers, turn the palm up and down. Each type of exercise is done 6-8 times.
Therapeutic training in water is mandatory for the first 2 weeks after the removal of the cast, after which the procedure is advisory in nature.
Application of external fixation devices
External fixation devices are usually used to treat open fractures because... in this case, the integrity of the soft tissues is violated, and there is a high risk of bacteria entering the wound. Plates and screws cannot be used here due to the high risk of infectious complications.
For open fractures, the wound is first treated with an antiseptic, and only then the fragments are repositioned using an external fixation device. In medicine it is called a compression-distraction osteosynthesis device. It consists of spokes and an external fixation device that maintains the spokes in the desired condition. The needles pass through the skin and bone fragments, fixing them in the desired position and with the desired compression. Such devices allow you to cure even the most complex fenestrated fractures.
Who is at risk for a wrist fracture?
A broken wrist is an injury that affects all ages. The integrity of these fragile bones can be damaged by a fall while leaning on your hands or a strong blow. Therefore, increased risk factors include:
- playing sports, especially boxing and other martial arts, as well as football, parkour, etc.;
- skateboarding, roller skating, skating, scootering, cycling, etc.;
- ice;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes (with slippery soles, large platforms, high heels, etc.).
In the older generation, the risk of wrist fracture is aggravated by age-related bone loss - osteoporosis. The loss of bone calcium and, accordingly, strength is associated with a deficiency of sex hormones. Women face a shortage of the latter earlier than men. Therefore, after 45–50 years, with the onset of menopause, they are especially susceptible to fractures.
Rehabilitation
Treatment of bone fractures involves not only the fusion of bone fragments, but also the complete restoration of hand function. During the healing period, the fracture site must be immobilized so that the fragments are in contact with each other and a callus can form. This immobilization leads to impaired muscle function and the formation of contractures in the joint. To eliminate these consequences, a set of special exercises is prescribed. And if the correct healing of a fracture is primarily determined by the actions of the doctor, then restoration of hand function depends entirely on the efforts of the patient.
Our emergency room operates without breaks and holidays. To treat a fracture of the radius, the Medical Center uses modern techniques; consultations are conducted by orthopedic traumatologists with many years of experience.
Principles of rehabilitation for a fracture of the radius
After the bone is anatomically restored, it is necessary to resume the functionality of the entire limb. During your stay at rest, muscles and joints lose mobility. To achieve your previous physical shape requires time, diligence, patience and constant physical therapy work.
Important! In most cases, rehabilitation after a fracture takes the same amount of time as the person was wearing a cast. The exceptions are complex injuries with tendon ruptures, joint damage, and multiple fragments of bone tissue.
Comprehensive restoration includes the following activities:
- physical therapy, use of special exercise equipment (mechanotherapy);
- water procedures ─ warm salt baths, gymnastics in water (hydrokinesitherapy);
- paraffin applications;
- physiotherapy ─ UHF, magnet, electrophoresis, laser;
- massage;
- a diet rich in calcium, taking vitamins to regenerate and strengthen bone tissue.
How to speed up healing
Comprehensive restoration includes:
- use of special simulators;
- physical therapy classes;
- carrying out water procedures;
- use of paraffin applications;
- conducting physiotherapy sessions;
- following a diet that includes calcium-fortified foods;
- taking vitamin and mineral preparations that help strengthen bone tissue.
A person walking in a cast due to a broken arm should avoid eating the following foods:
- semi-finished products;
- strong brewed coffee;
- foods containing large amounts of fat;
- alcoholic drinks;
- sweet sparkling water;
- salty and spicy foods;
- smoked meats.
The products listed below help slow down the process of calcium absorption and stimulate its active excretion from the body. If a strict diet is not followed, fluid is retained in the body, which leads to edema and prolongation of the recovery period.
During the period of treatment and rehabilitation, it is recommended to prepare a fruit salad from the following ingredients:
- bananas;
- apples;
- citrus fruits.
It is recommended to dress the salad with yogurt with a low fat content. Such dishes are useful for both children and adult patients. You can diversify your diet with steamed meat. In this case, preference is given to rabbit, beef, and chicken. In addition, sea fish baked in the oven or steamed is useful. An excellent side dish for it can be pasta or dishes made from legumes. The patient’s diet must certainly include fermented milk products. A patient who has suffered a hand injury should not forget about vegetable salads. In the preparation of such dishes, the following ingredients are used:
- tomatoes;
- fresh herbs;
- apples;
- cucumbers;
- olives;
- cabbage.
Vegetable salads should be seasoned with vegetable oil. As a result, the vitamins contained in such dishes are much easier to absorb. To speed up the recovery process after a hand injury, it is worth enriching your menu with foods that contain a lot of vitamin C. This vitamin has an antioxidant effect and activates the healing process of bone tissue. Sources of antioxidants are legumes, nuts, vegetable dishes, and fruits. Moreover, the largest amount of such substances is found in berries and fruits of bright colors.
First aid measures
Timely first aid for a hand injury helps to avoid adverse complications. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Call an ambulance.
- Immobilization of the injured limb. In this case, an improvised tire is made from scrap materials. Then the limb is securely fixed with a cloth or bandage. Place gauze or clothing under your arm.
- Cold is applied to the area of injury.
In the case of an open fracture, an exclusively sterile bandage is applied to the wound surface, which is pre-impregnated with an antiseptic. If there is bleeding, the limb is tied with a belt before the ambulance arrives. If the victim experiences severe pain, it is permissible to use tablets from the group of analgesics with an analgesic effect. These medications include Ketorol and Baralgin. Worth knowing! Before the ambulance arrives, it is forbidden to independently remove fragments from the wound or set the bone using your own efforts.
Complications of long-term wear
When wearing a plaster cast for a long time, the following complications may occur:
- formation of a false joint. This complication occurs when the plaster is not fixed well enough, and a callus forms with a gap between the bone;
- formation of callus of abnormal size. In this case, a violation of the motor function of the wrist joint may be observed;
- the occurrence of Volkmann's ischemic contracture. This complication is a consequence of incorrect (too strong) fixation of the limb with a plaster splint. Due to deterioration of arterial blood flow, deformation of the wrist and fingers occurs.