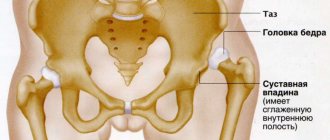
The hip joint is the largest and most powerful joint in the human body, responsible for functions such as moving the hips, lifting and lowering, bending and extending the legs, and also takes part in bending the body. A femoral dislocation at the hip joint is an injury in which the head of the femur is displaced beyond the acetabulum. These dislocations account for no more than 5% of all dislocations. Dislocations can be divided into 2 types: anterior and posterior dislocations. Anterior dislocations are extremely rare and represent a downward displacement of the femoral head with rupture of the joint capsule. Posterior dislocation occurs more often, as a result of which the head of the hip joint pops back.
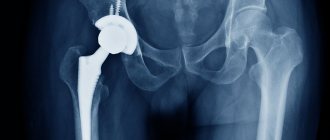
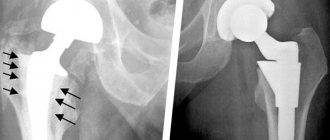
In cases where the hip joint loses its functions (the smooth cartilage that allows the femoral head to glide easily in the acetabulum is worn away) and any movements cause unbearable pain, patients undergo endoprosthetic surgery. An endoprosthesis is an artificial substitute for a human organ (performing its function), which is located inside the human body. Hip replacement is an operation to replace the affected components of the joint with an endoprosthesis that has the anatomical shape of a healthy joint and allows for a full range of movements. Dislocations during such an operation occur very rarely, but they do occur, and these are mainly dislocations of the head of the endoprosthesis.
Signs of dislocation.
The symptoms of dislocation of a healthy joint and an endoprosthesis are the same.
- Acute pain in the thigh area
- Standing on an injured leg is unbearable
- Inability to move the hip joint.
- Obvious deformation of the hip joint (depending on the type of dislocation)
- Forced position of the leg (depending on the type of dislocation)
- Increased pain when trying to make any movements with the injured leg
- Swelling and bleeding in the buttock, groin and thigh area
Hip joint: dislocation in adults
If a person experiences pain in the pelvic area, the joint has moved out of the hole. In other words, a dislocation has occurred. It comes in front and back. The latter is most common in those who have survived a road traffic accident.
What does a person feel when they are dislocated?
The following are the symptoms of the disease:
- Pain at rest;
- Pain on movement;
- Deformation;
- Lameness, it hurts to stand on your leg;
- The legs are of different lengths;
- Swelling of the legs.
The reasons for this problem are:
- Injury during sports;
- Consequences of an accident;
- Wrong movement;
- Consequences of beating;
- A fall;
- Birth difficulties, after which a person suffers from subluxation for the rest of his life.
Two different dislocations
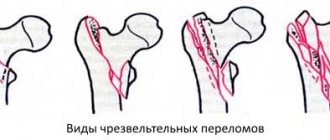
With the anterior type of dislocation, which occurs as a result of a fall with the leg abducted to the side, the head of the joint moves down, tearing the capsule. To treat anterosuperior and suprapubic dislocation, a cast is applied.
In the posterior type of dislocation—the most common—the femur moves inward. There are several types. We are talking about central, posterior superior, posterior inferior, congenital. Most often the problem occurs after a strong impact. As a result, the leg moves poorly and the person experiences severe pain.
Most often, elderly people suffer from hip dislocation. To eliminate the consequences, a plaster cast is applied to the leg. The injury can also be caused by the surgeon's intervention during joint replacement.
Dysplasia in adults
Often the cause of dislocation is hip dysplasia, which is congenital. Therefore, you need to use a tight bandage to avoid constant release of the bone from the capsule.
There are two types: minor and subluxation. The first appears more often in children. If left untreated, it becomes chronic, the person will limp all his life, he will have a duck's gait. The second is due to the displacement of the head of the bone, and not just the cartilage, which moves up or down. Treatment is possible only under anesthesia, when the doctor sets the leg and applies a plaster cast or a tight bandage.
Symptoms of injury
It is necessary to detect that a problem has occurred immediately in order to avoid irreversible consequences when a person remains lame for life. Arthrosis may develop and the joint becomes unstable, leading to permanent deformities. To do this, at the first sign you should go to the doctor.
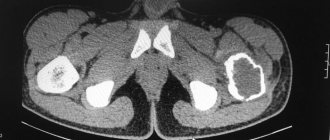
Only a rheumatologist can make an accurate diagnosis. First you need to undergo a full examination and take an x-ray. The photo will clearly show the problem. When diagnosing an injury, the doctor will pay attention to where the joint is directed, whether there is pain, and where it is located.
Adults experience limited movement and severe pain in the joints
. If subluxation occurs, then the ligaments can recover faster, which reduces the rehabilitation period. Often the pain is so severe that it seems like a fracture has occurred. But the picture shows whether this is really so. Adjusting the joint yourself is dangerous. When delivering the patient to the emergency room, you need to fix the leg in the same way as for a hip fracture.
Symptoms in adults vary. The patient may complain of pain in the hip joint and that it is difficult for him to move his leg. In any case, it is necessary to reduce the load on this part of the body, and also to fix the tibia so that it does not dislocate again after reduction.
If you miss the signs of a problem, then it becomes old, becoming chronic. In any case, the shape of the joint changes, pain is felt, and the affected leg becomes shorter than the healthy one. Movement activity is disrupted.
How to diagnose correctly
Before a diagnosis can be made, the patient must be anesthetized. Since otherwise his problem will not give him peace, he will not be able to work with his leg. After anesthesia, the doctor makes passive movements to determine what exactly the problem is.
Unlike childhood disease, adults are diagnosed differently. If a child undergoes an ultrasound, then after 16 years of age, due to the massiveness of the muscle composition, this is impossible. Therefore, adults undergo x-rays, which confirm or refute the diagnosis made by a rheumatologist surgeon.
As additional methods you can use:
- Computed tomography;
- MRI;
- Arthroscopy.
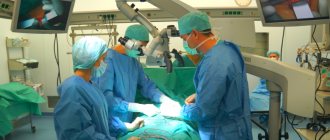
With the latter method, they not only find out whether the diagnosis is correct, but also immediately treat the joint. To do this, a camera and a tool are introduced into it. The surgeon can now adjust the bone, placing it back into place perfectly correctly. After all, the camera records everything. The doctor will notice the hematoma and, if possible, remove it using the inserted instrument.
X-rays are performed in two projections: straight and lateral. Taking into account how the head is located, the doctor makes a diagnosis, classifying it according to the type of bone displacement. If you do not understand in time what the cause of the pain is, joint dysplasia will lead to irreversible consequences even in an adult, not to mention a child who will suffer all his life.
The doctor will immediately understand that there is a problem if he conducts an external examination. For example, he will evaluate how a person stands. He will notice that one leg is shorter than the other. But still, you can’t do without an x-ray, since there are other possible causes for this symptom. As a rule, one photo will be enough. In the most extreme cases, the patient is sent for an MRI.
How to treat
First you need to numb the joint.
Then it is adjusted. Only a doctor should do this. Then a plaster cast or bandage is applied - it all depends on the complexity of the injury. The thigh area should be kept motionless for two or three months. If the bandage is removed earlier, re-dislocation is possible. In order to relieve pain, the doctor will prescribe painkillers. When the plaster is removed, you need to undergo a massage course. It is important to remember that a dislocated hip joint should not be ignored. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment.
Treatment should be carried out in the traumatology department by qualified specialists.
- A dislocated femur can be reduced without any complications under general anesthesia in a closed manner (using various reduction techniques).
- Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where fractures of the neck or femur are added to the dislocation. (If, when the hip is dislocated, the cartilage is damaged (which can lead to coxarthrosis in the long term), there is a need for hip replacement).
- Applying a plaster splint or skeletal traction for 3-4 weeks.
- After this, the patient is recommended to walk on crutches for 10 weeks and is prescribed rehabilitation procedures.
Diagnosis of prosthesis instability
When the first symptoms of instability of the hip joint endoprosthesis occur or before they appear, it will not be superfluous to undergo a course of diagnostic measures. The doctor will prescribe the following types of examination:
- X-ray examination of the hip joint;
- analysis of the state of bone tissue and its density using the densitometry method;
- analysis of metabolic processes in bone tissue.
In some cases, the appointment of the above measures occurs immediately after surgery. Of particular danger is the initial presence of osteoporosis in the patient, since it is this feature of the bone tissue that can provoke instability of the prosthesis after installation.
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Diagnosis of congenital hip dislocation in Israel
Diagnosis of this pathology is not very difficult for Israeli doctors. A complex of instrumental studies allows you to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the optimal treatment option. Diagnosis of the disease usually lasts 3 days.
First day – consultation with a doctor
Diagnosis begins with an examination of the child by the attending physician. It is noteworthy that you can get advice from an Israeli specialist remotely, without visiting Israel. To do this, it will be enough to send all medical documentation, on the basis of which an Israeli specialist from Top Ichilov will express his opinion. If in the future you decide to be treated at Top Ichilov, then the initial examination will be free for you. After the examination, the doctor sends the child for instrumental studies.
Day two – diagnostics
The standard instrumental diagnostic scheme is as follows:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- CT;
- MRI.
Third day – doctors’ conclusions
After completing all diagnostic procedures, an expert group of doctors at the Top Ichilov clinic establishes a diagnosis and determines treatment tactics.
Clinical picture of the disease
In order to begin treatment of hip dysplasia in a timely manner, you should know by what clinical signs the pathology can be recognized in the early stages.
Older children will have additional symptoms such as gait disturbance, functional weakness of the gluteal muscles, high standing greater trochanter
These include:
- shortening the length of a separate limb segment;
- asymmetry of the gluteal folds;
- unnatural outward rotation of the leg, especially during sleep;
- limitation of hip abduction (normally, the abduction angle should be 60-70 ̊, with dysplasia it decreases significantly);
- the presence of a click when spreading the legs (a symptom of slipping).
If you identify one of the above symptoms, you must contact a specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Coxarthrosis 2nd degree
The pain intensifies and lasts longer. They do not go away after completion of physical activity and remain in an immobilized state. When moving, clicking and crunching sounds are heard in the joint. Due to the shortening of the limb, slight lameness appears and joint mobility is limited. X-ray examination shows a decrease in the gap between the bones and joints, displacement of the femoral head, and the appearance of pathological growths of bone tissue in the place of destroyed cartilage - osteophytes.
We treat
- Osteoarthritis of the hip joint
For normal joint function, you need to lead an active and healthy lifestyle. The muscles, ligaments of the hip joint and its other components need to be trained. Often you just need to do gymnastics. Take time for yourself. Be healthy!
The hip joint is one of the main elements of the human musculoskeletal system. It performs several functions - it serves as a support for the spine, upper and lower parts of the body, and provides freedom of movement. This connection of bones supports the weight of the entire torso, and when walking or running, the load on it increases to a ton. Degenerative diseases (coxarthrosis, osteoporosis, chondromatosis, synovitis, bursitis), injuries reduce mobility, cause severe pain, worsen the quality of life and can lead to disability. An effective, modern approach to the treatment of such pathologies is hip arthroscopy.