Today, such an injury can be called quite rare, since people now practically do not walk barefoot.
It is important to recognize the injury as early as possible and make an accurate diagnosis in order to take the necessary measures in time, because the person’s future life and the possibility of normal movement will depend on the correct treatment.
The rehabilitation process after such an injury usually requires quite a long time.
In this article you will learn what to do if your toe is dislocated and how to provide first aid to the victim.
Common causes of a dislocated toe
Most often, a dislocated toe occurs as a result of a blow to the fingers or foot, and in most cases, athletes face this type of injury. Dislocations of the big toe are more common than others, but according to medical statistics, they account for only about 2% of the total number of patient visits to traumatologists with any kind of dislocation.
The big toe is injured more often than others because its location is somewhat specific, it is much larger than the others, it always protrudes forward, and therefore is the first to take any blow.
In isolated cases, a dislocation of the little finger is observed, which occurs when there is a side impact with an object.
In addition, in some cases, dislocations of the bones of the metatarsus and tarsus are observed, which occur due to a sharp unnatural turn of the foot or a strong blow. Such a dislocation causes visible deformation of the foot and requires urgent action.
Symptoms of a sprained toe
When a dislocation occurs, the first thing to do is limit the functionality of the damaged joint, and sometimes even part of the foot. A person experiences acute pain almost immediately after the blow, but it intensifies significantly when trying to step on his foot or move his fingers.
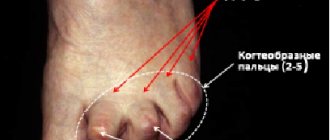
Movements are immediately limited. Any movement of the finger during a dislocation causes unbearable pain. In this case, the damaged toe is always deformed, which gives the foot an unnatural appearance.
Gradually, a hematoma appears at the site of injury, which can cover the entire surface of the finger and surrounding tissues. But swelling, like swelling, appears very quickly if measures are not taken immediately. When a finger is dislocated, swelling can spread to the entire surface of the foot, which will significantly complicate the injury's reduction and treatment.
Surgery
If the finger dislocation occurred more than a month ago, surgical intervention is necessary. The damaged joint is restored 2–3 weeks after surgery.
If the dislocation occurred a very long time ago, then open surgery does not always give a positive result. Then the patient is indicated for resection of the base of the proximal phalanx of the injured finger.
After the above procedure, in order to restore the correct position of the dislocated finger, the patient is shown skeletal traction using a splint.
But the most effective and common method of treating dislocations is the conservative method. After realigning the injured toe and applying a special bandage, the patient can lead a normal life.
But if closed reduction is unsuccessful or the dislocation is old, surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
Diagnostics
When a finger is dislocated, it becomes severely deformed and often takes on an unnatural position, so a doctor can easily diagnose an injury only by the presence of external signs and a study of the medical history.
But to determine the characteristics of the damage, an x-ray examination will be required. When the phalanx of the thumb is dislocated, the distal part is most often damaged, since it is here that the joint has the greatest mobility and the maximum level of load also occurs here.
In second place among toe dislocations in terms of frequency of diagnosis is damage to the fourth toe, or more precisely its phalanx.
The middle toe is extremely rarely dislocated, even when seriously injured, because due to its central position it is quite well protected.
When carrying out diagnostics, a displacement of the damaged fingers to the outside or back is often detected. Dislocations towards the sole occur only in isolated cases, since their occurrence is possible only with the special structure of the foot and ligamentous apparatus.
Symptoms
There are some features that distinguish finger dislocations from other deviations of this type. Common symptoms include:
- visible deformation;
- limited mobility;
- unnatural finger position;
- pain;
- swelling and swelling of the dislocated phalanx;
- bleeding (rare).
Due to the severity of the above symptoms, patients may experience dizziness, and the weaker sex may experience loss of consciousness, nausea, and increased heart rate.
Consider in more detail the specific areas of injury that occur most often.
First aid and self-reduction
It is important to remember that you are only allowed to correct an injury yourself in an emergency, when it is not possible to get help from a qualified specialist within the next 2 hours after receiving the injury.
In all other cases, self-reduction is strictly prohibited, since with any careless or incorrect movement a person may remain disabled and forever lose the ability to move normally.
It is very important to take the patient to the hospital within the first hour after the injury, before swelling begins to form at the site of injury, which will significantly complicate reduction.
To prevent the formation of edema and swelling, it is necessary to apply ice to the site of dislocation immediately after injury. Cold will not only reduce the likelihood of swelling, but also ease the pain, because such a dislocation is always accompanied by very sharp and severe pain. It is important that the victim's leg is elevated to reduce blood flow to the injured limb.
Under no circumstances should you wrap your leg or apply warming agents . Such measures will not bring any benefit, but will only significantly worsen the condition and increase the size of the tumor. It is also important to remember that ice compresses should not be used in cases where the victim has diabetes. This measure reduces the level of blood flow to the affected leg, but in case of diabetes mellitus this can lead to many complications.
How can you distinguish a possible bruise from a fracture?
A bruise or fracture can be determined by several parameters:
- Features of the pain syndrome.
- Finger movement.
- Skin color at the site of swelling (bruise).
- Presence of hemorrhage.
- Phalanx shape.
The clinical picture of a bruised finger is as follows:
- The victim experiences sharp pain, which begins to subside over time. The nature of the pain is “aching.” Using a cold compress can speed up the process of relieving pain symptoms.
- When bruised, the finger is not deformed. Immediately after a bruise, all movements are accompanied by sharp pain (pulsation is possible); as the pain subsides, the motor activity of the finger is gradually restored.
- Depending on the nature of the bruise, the color of the skin at the site of the injury may be dark red, pink, or pale pink. Swelling may appear immediately, after a day, or not appear at all. The blood at the site of the injury spreads diffusely (scattered), a bruise may appear.
Treatment and methods for reversing a dislocated toe
A closed type of dislocation, as a rule, can be eliminated in a regular emergency room or clinic, where further treatment will be provided, as well as observation and measures taken to restore motor function in the area of damage.
A closed dislocated toe is reduced according to a specific pattern. The first step is an x-ray examination, which allows the doctor to see all the features of the injury and the resulting displacement. After this, the damaged finger is treated with iodine and anesthetized with an injection of novocaine injected into the area of the distal phalanx and the damaged finger.
You will be interested...
First aid and treatment of an ankle dislocation If the dislocation is classified as difficult to reduce, the doctor can insert a special thin needle through the distal phalanx, which is fixed in a special arch. In addition, the doctor can use a claw. You should not be afraid of the needle insertion procedure; it is not particularly difficult and is absolutely safe.
After this, the doctor performs traction on the injured finger, while a second doctor (nurse or other assistant) holds the patient by the area of the lower leg of the injured leg, providing countertraction. When the required traction is achieved, without weakening it, the doctor realigns the displaced phalanx by pressing in the desired direction with the thumbs.
After the reduction has been carried out, it is necessary to carefully check the presence of flexion and extension function of the joint , as well as take a control x-ray, after which the doctor will apply a special adhesive bandage to further fix the finger.
In some cases, a small splint is required to ensure complete immobilization of the finger, for example, if the thumb or little finger is dislocated and cannot be fixed with the adjacent fingers.
The duration of wearing a fixing bandage will be different in each case , but on average it is about 3 weeks, during which special exercises should be performed to ensure movement of the joints of the injured finger and contribute to a faster recovery.
Rehabilitation and possible complications
The duration of rehabilitation after such a dislocation largely depends on the timeliness of the reduction, the complexity of the injury, as well as on compliance with all doctor’s instructions during treatment. On average, recovery time can range from 3–4 weeks to several months, if surgery was required to reduce a dislocation (for example, an old one).
Possible complications of such an injury include:
- Rupture of muscle tissue, tendons and joint ligaments.
- There is a possibility that the dislocation will occur again in this area in the future.
- The likelihood of habitual dislocation occurring due to improper or insufficient treatment.
- Damage to blood vessels or nerve fibers at the site of injury.
- Arthritis is at risk of developing over time, usually several years after the injury.
To prevent possible complications, it is important not to try to treat a dislocation on your own without the help of a qualified specialist.
Sprained big toe
The structure of the thumb has its own characteristics. The head of the metatarsal bone, shaped like a hemisphere, faces the finger itself, towards the base of its phalanx, in which there are voids. Thanks to these voids, the head of the bone is precisely connected to the digital phalanx, forming a joint that has fairly free mobility of the bones between them.
The joint is held in place by 3 ligaments, two of which are located on the sides, and the third on the plantar part. It is the part on the side of the sole that is the most vulnerable place of the joint, since during injury this ligament is torn most often, which leads to dislocation.
When a dislocation occurs, the phalanx is separated from the metatarsal bone, and the finger moves upward . In most cases, the ligaments located on the sides of the joint remain intact when the thumb is dislocated. When receiving such an injury, it is important to accurately determine the dislocation and distinguish it from a possible fracture or severe bruise.
Very important!
This massage is contraindicated for people with diabetes, since the cold slows down the movement of blood through the vessels, and this will have a bad effect on the body of a person with diabetes. In such a situation, you can simply raise your leg to a higher place. This will also reduce blood flow and pressure.
There are situations in which a person who has suffered a dislocation, without discomfort or pain, refuses treatment. Or the dislocation was not corrected after the injury. In these positions, one thing is clear - in both of them an “old dislocation” is formed, which will be more difficult to correct; here the doctor will have to apply splints.
Tissue swelling and stretching occurs due to displacement of the articular bone. With timely reduction and correct fixation until healing, swelling disappears and the finger regains its previous appearance.
It happens that the finger “gets along” in its new place - this situation cannot be corrected without the intervention of a surgeon. You should not self-medicate; the best option would be to consult a doctor in a timely manner, which helps reduce the risk of complications.