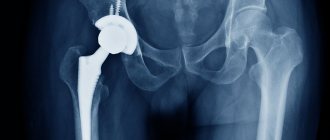
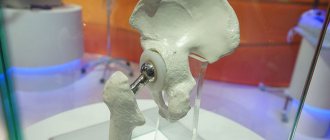
Today, endoprosthetics of large and small joints is one of the most popular types of surgical intervention in the field of traumatology and orthopedics. In Western clinics, the volume of such operations totals more than 1 million per year. Domestic endoprosthetics clinics are still several times behind, providing prosthetic services to only 40-50 thousand patients, although the need for implants is much higher.
The technique has proven its effectiveness in practice, however, even the most advanced technologies can lead to complications in the long term. Instability of parts of the endoprosthesis is the most common pathology, which can cause undesirable consequences and lead to the need for reoperation.
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Symptoms of hip replacement instability
Even during the consultation with the attending physician, the patient should be explained possible side effects and complications after surgery. The surgeon himself must foresee such negative consequences based on diagnostic data during the examination of the patient. Incorrect selection of an individual prosthesis can lead to its failure within five years after installation. Repeated endoprosthesis surgery can be avoided if all precautions are followed and actions that could damage the stability of the implant are not performed.
The following signs of instability of the hip joint endoprosthesis can be identified:
- The occurrence of permanent aching pain in the joint both during walking and at rest. Often the pain intensifies closer to night (during sleep).
- Loss of support for the artificial joint.
- General weakness in the lower extremities, fatigue when walking.
Most patients are mistaken in believing that the symptoms listed above are the result of the effects of surgery, which will go away on their own within a short time. in fact, everything is much more complicated. It is advisable to consult a specialist as soon as possible and undergo diagnostic procedures that will show whether repeated surgery is required.
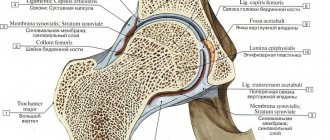
The thing is that the installed implant affects the movements of the hip joint, both during total endoprosthetics and when replacing only part of the damaged joint. As a result, the process of bone tissue restoration may slow down. Loosening of the prosthetic leg in most cases leads to the development of local osteoporosis. Thus, the mobility of the endoprosthesis itself is limited.
Unfortunately, modern scientific and laboratory research has not been able to identify a material for prostheses that would cause absolutely no harm to human health. As a result of friction of the implant components against each other, tiny particles settle in the surrounding tissues, causing infectious processes and tissue death. Local blood circulation may also be impaired. Therefore, when the first signs of loosening of the hip joint endoprosthesis appear, you should immediately seek help from your doctor.
Before treating hip subluxation
It is very important to conduct a high-quality differential diagnosis before treating hip subluxation. During this procedure, the doctor must determine the plane of displacement of the femoral head and the degree of its instability. It is also very important to establish the exact cause of this condition. If the cause is not eliminated, then any, even the most effective treatment, will not give a positive and lasting result.
Diagnosis begins with an examination by a doctor. The orthopedic surgeon performs a manual examination and a series of diagnostic functional tests. This allows you to understand how unstable the articulation of the bones is. Then a dynamic x-ray is prescribed. It is very important to carry out radiographic examination with changes in the position of the lower limb. As mentioned above, a subluxation can be unstable, so displacement of the femoral head can only be detected dynamically.
An MRI examination may be required to establish the exact condition of all tissues of the hip joint. Ultrasound, electromyography, and a number of blood tests may also be indicated. A precise plan for a diagnostic examination is drawn up by a doctor based on data obtained during the initial examination of the patient.
Consequences of instability
Prosthesis displacement
As a result of this phenomenon, the implanted implant not only loses its fixation and becomes loose, but also leads to a gradual or sudden change in the length of the legs. In this case, immediate consultation with a doctor and repeated surgery on the limb are required. The main reasons include the following:
- incorrect installation of the implant;
- insufficient contact between the surfaces of the joint and the prosthesis;
- heavy loads on the implant;
- weak connection of product components.
Dislocation - dislocation.
Osteolysis
The formation of this process can result from partial or complete destruction of the bone, which occurs as a result of the interaction of the components of the prosthesis with living tissue.
Endoprosthesis fracture
Diagnosis of prosthetic fractures, which periodically occur, suggests the following reasons for such consequences. These include:
- incorrect selection of an individual implant;
- excessive or premature high physical activity of the patient;
- overweight patient.
To prevent the onset of such consequences, you must strictly follow the recommendations given by your doctor and not engage in excessive physical activity.
Special cases include loosening and damage to individual components of the prosthesis. In a fairly short period of time, the structure of the polyethylene liner or femoral stem may collapse. Dislocation or fracture of the endoprosthesis also occurs quite often. Therefore, it is imperative to follow the recommendations of specialists, as well as carry out diagnostic and preventive measures. This is guaranteed to help prevent the occurrence of negative consequences of the operation.
Formation of blood clots
Such clots form in the vessels of the lower extremities. This complication does not require repeated surgery. It is enough to complete a therapeutic course prescribed by a doctor. It may include various physical exercises for the legs or taking medications.
Inflammation
To prevent the development of infectious processes, experts recommend taking antibiotics in the first two years after installation of the prosthesis. The prescription of medications in each case is considered individually, based on the general condition of the patient’s body.
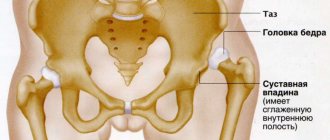
Hip diseases can develop at any age. As a result of the disease, there is a restriction in the function of the hip joint, which is accompanied by pain, lameness, limited mobility, muscle degradation and deformation of the affected leg.
Causes of joint disease
The causes of this disease are varied. They may have:
- degenerative;
- inflammatory;
- congenital;
- traumatic nature.
The most common disease of the hip joint is coxarthrosis, in which gradual degeneration of the articular cartilage occurs.
As a result of this disease, the function of the joint is impaired, which manifests itself in the occurrence of pain and a decrease in joint mobility and the ability to move independently. Symptoms that constantly increase over time can be temporarily mitigated with the help of medications, physical therapy and spa treatment. However, in this case we are talking about a progressive disease, and in an advanced stage of the disease, the only treatment option is surgery to implant an artificial hip joint.
We would like to give you a more detailed description of the diseases listed below. To do this, follow the appropriate links. If you would like to receive more information about the method and process of the operation, as well as about the hip joint prostheses we use, please follow the link Endoprosthetics.
Coxarthrosis
Wear and tear of the cartilage of the hip joint occurs in many people over 30 years of age. The reason for this is a continuous decrease in the elasticity of the articular cartilage. However, the course of the disease is very individual, since other factors also play an integral role in the progression of the disease, such as:
- overweight;
- playing sports;
- “genes” are the individual properties of cartilage.
Some people do not experience significant wear and tear of the cartilage of the hip joint even into old age. Due to the reduction of articular cartilage, friction between the femoral head and the acetabulum increases, which in turn leads to additional damage to the cartilage. At the same time, this process may be accompanied by inflammation of the hip joint capsule and synovial membrane. The consequence of this is pain and limited mobility of the affected hip joint. If the cartilage wears down completely, bone-on-bone friction occurs (femoral head and acetabulum), which can lead to complete immobility of the joint if left untreated.
A fairly common disease of the hip joint is also “death of the head of the femur,” the so-called necrosis of the femoral head. In this case, a violation of blood flow develops in the area of the femoral head, which leads to the destruction of the bone tissue of the femoral head with damage to the surface of the joint.
Causes of coxarthrosis
The causes of this disease are complex, some of them are still not fully understood. The following factors may be the key reasons for the development of the disease:
- long-term use of drugs containing corticosteroids;
- excessive alcohol consumption;
- kidney diseases for which dialysis is indicated;
- viral or bacterial infection of the joint or trauma accompanied by femoral neck fractures
- bone or the femoral head itself.
This disease can be diagnosed using a special layer-by-layer study, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study helps to more accurately determine the severity of the disease and is the basis for choosing a treatment method - naturally taking into account the age and individual situation of the patient.
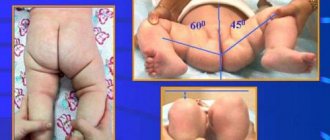
Hip dysplasia
Much less common than “normal” wear and tear of the hip joint is congenital deformation of the acetabulum, the so-called “hip dysplasia.” Without appropriate treatment, already in infancy, the head of the femur becomes displaced and extends beyond the acetabulum. As a result, already at this early age, improper distribution of the load on the head of the femur occurs, which leads to premature abrasion of the cartilage and, ultimately, to the development of premature arthrosis.
With the help of regular ultrasound examinations in early infancy, it is possible to identify acetabular dysplasia and carry out appropriate treatment in order to prevent the development of long-term consequences.
Incorrect position of the femoral neck axis
Another relatively rare cause of improper loading of the femoral head is the incorrect position of the axis of the femoral neck in relation to the femur. Typically, the angle between the axis of the femoral neck and the femur is between 120° and 130°. If the angle goes beyond these limits, the load is unevenly distributed in the area of the femoral head, which leads to increased abrasion of the cartilage and, ultimately, to the development of arthrosis.
This process can be prevented by performing correction surgery (corrective displacement surgery), especially in young patients (under 60 years of age). During this operation, the bone wedge of the femur is removed, which allows the femoral neck and femoral head to be brought into a more correct position in relation to the acetabulum. This changes the angle between the femoral neck and the femur, thereby eliminating the uneven load on the femoral head.
However, a necessary condition for this operation is that the stage of the disease is not too advanced.
Contact us
The Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology at the University Hospital of Solingen specializes in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Led by Professor Sascha Floe, you can receive high-quality assistance on all issues. You can make an appointment for a consultation, diagnosis or treatment at the clinic with Professor Floya through the international department.
You can contact the Russian-speaking staff of the international office by leaving a request on the website or writing to us by email: Email: [email protected] Tel.: +49 212 5476913 Viber | WhatsApp: +49 173-2034066 | +49 177-5404270 For your convenience, please save the phone number in your phone book and call or write to us for free on WhatsApp, Viber or Telegram. Applications made on weekends or holidays will be processed on the first business day. In urgent cases, request processing is carried out on weekends and holidays.
Diagnosis of prosthesis instability
When the first symptoms of instability of the hip joint endoprosthesis occur or before they appear, it will not be superfluous to undergo a course of diagnostic measures. The doctor will prescribe the following types of examination:
- X-ray examination of the hip joint;
- analysis of the state of bone tissue and its density using the densitometry method;
- analysis of metabolic processes in bone tissue.
In some cases, the appointment of the above measures occurs immediately after surgery. Of particular danger is the initial presence of osteoporosis in the patient, since it is this feature of the bone tissue that can provoke instability of the prosthesis after installation.
Minimally invasive endoprosthetics in the Czech Republic: doctors, rehabilitation, terms and prices.
Find out more
Methods for treating joint implant instability
Timely diagnosis and treatment will help to avoid serious consequences. In this case, it will be possible to quickly normalize and stabilize the process of bone tissue restoration. This will also have a positive effect on the process of integration of the prosthesis into the human body.
Temporary walking with crutches may be prescribed as a preventative measure. At the same time, a course of taking appropriate medications is prescribed. In some cases, the patient will be recommended certain physical exercises for the lower extremities.