Stubbed toes are one of the most common injuries. The foot is vulnerable to various injuries. But such injuries are usually harmless, and limb function is restored within a few days. But often a severe bruise is accompanied by a fracture of the metatarsal or phalangeal bones. Without proper treatment, such damage can lead to complications and disruption of the supporting functions of the foot.
But sometimes victims do not see a doctor. They do not feel much pain and cannot understand whether the finger is broken or not. Therefore, it is important for everyone to know how to distinguish a fracture from a bruised toe. The signs of these injuries, at first glance, are similar; even a doctor without examination cannot always determine whether a bone is broken. But a fracture has certain distinctive signs that will help make a preliminary diagnosis.
Foot structure
The human foot consists of 26 bones and includes three sections:
- Phalanges of fingers (14 bones).
- Each finger consists of three phalanges, only the thumb has 2 wide tubular bones.
- All toe bones are connected to the rest of the foot by the joints of the proximal phalanges.
- On the little finger, the upper two phalanges can often be fused, but this does not affect movement in any way.
- Tarsus (7 bones that form the heel and the connection to the shin).
The department includes the following bones:
- cuboid;
- wedge-shaped;
- scaphoid;
- talus (high bone);
- calcaneus (large bone).
Calcaneus
takes on the entire load, maintains balance, distributes weight. The bone is attached by many ligaments and tendons and has 6 joints. The talus connects the lower leg and foot, has 5 articulations, without muscles. This bone allows a person to turn the leg up to 90 degrees, raise it and lower it.
Scaphoid
is located next to the talus and forms the upward instep of the foot. The joint is formed by 3 sphenoid and cuboid bones, connected by tendons to the scaphoid.
Some people experience slight deviations in the structure of their feet. For example: another navicular bone, which causes shoe rubbing due to high arches. Or an additional bone behind the talus, which puts an end to ballroom dancing or ballet classes, due to the impossibility of standing on your toes.
Metatarsus
consists of 5 tubular bones that make up the middle part of the foot and form its arch. The first metatarsal bone is thickened, the second bone is longer than all the others. The entire department is responsible for finger movement.
The metatarsal bones are shaped like a pyramid, their front parts are rounded. The rounded heads of the bones are connected by joints to the phalanges, and at the base - to the tarsal bones.
The proximal parts of the bones are connected to fragments of the hindfoot.
The cause of the development of hallux valgus is a dysfunction of the first metatarsus. Valgus occurs due to salt deposits on the head of the first phalanx.
The coordinated functioning of the entire ankle is ensured not only by tendons, ligaments and joints, but also by muscles, nerve endings, and blood vessels.
The muscles are responsible for the extension and flexion of the fingers, except for the big one, and are located in the rear of the metatarsus. There are other muscles on the sole of the foot that are responsible for adduction and abduction of the toes and flexion of the foot.
Characteristics
The main indications for wearing a plaster splint on the hand, forearm, and wrist joint are fractures of tubular bones, ruptures of ligaments and tendons, dislocations of the hand and other joints, including habitual ones. Bandages are made from special bandages of various lengths and widths. In addition to the fabric base, the dressing material contains gypsum.
Plaster bandage.
After wetting the bandage in water and applying it to the injured arm, it hardens and takes the shape of the limb, fixing it in the correct position. This promotes the healing of bone fragments, torn ligaments or muscles, and the relief of inflammatory or destructive-degenerative processes.
In pharmacies or medical equipment stores you can purchase more modern versions of plaster splints - plastic devices with metal and fabric inserts. They are sold under different names:
- hard bandages;
- tires;
- orthoses;
- retainers.
Wrist orthosis with forearm grip.
Traumatologists usually apply a plaster splint for a fracture of a tubular bone, such as the radius. The joints are usually secured with rigid or semi-rigid orthoses. When wearing such devices, a certain range of movements is maintained. There is no displacement of articular structures that impedes healing, but muscle atrophy and tissue ischemia are completely excluded. The likelihood of developing irreversible post-traumatic changes in hyaline cartilage is also reduced.
Arrests of doctors: rheumatologists deprived patients of the most effective remedy for joint pain!
Bubnovsky Sergey Mikhailovich
leading rheumatologist of the country, deputy. Chairman, 1st Deputy Director of the Federal State Budgetary Institution NIIR named after. V. A. Nasonova
Find out more...
What is happening is what our law enforcement agencies should have done a long time ago - arrest this entire mafia. Just think about these numbers - more than 1 million crippled lives in 12 years! People, most of them pensioners, turned to doctors for help. And instead of treating, they profited from people’s suffering, knowing in advance that the remedies they prescribed would not help. And this practice was widespread not only in commercial ones, but also, worst of all, in public clinics.
The use of plaster or plastic retainers reduces the stress on damaged tissues, and, if necessary, completely eliminates them. The severity of pain decreases, inflammatory processes slow down and stop, and swelling resolves. This allows traumatologists and rheumatologists to reduce doses of NSAIDs, analgesics, muscle relaxants and glucocorticosteroids that damage the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract.
| Type of splint for fixing the arm | Design features and scope |
| Soft | They have a cotton or elastic synthetic base. Some models are equipped with rigid inserts to prevent excessive stress on injured joints. One of the types of bandages (elbow pads, wrist joint fixators), used for treatment and preventive purposes |
| Medium hardness | The design of the splints contains metal or plastic inserts (plates, knitting needles, rings) for more reliable immobilization. Medium-hard models are usually used for dislocations, subluxations, partial ruptures of muscles, ligaments, tendons, exacerbations of arthrosis or arthritis, lateral and medial epicondylitis |
| Hard | This group includes plaster splints and complex, durable plastic orthoses. Finished products are equipped with a fastening system - hooks, metal snaps, buttons. As the tissue is restored, the degree of fixation decreases, which makes it possible to strengthen the muscular frame of the arm at this stage. Rigid orthoses are often used for long bone fractures |
Ligamentous apparatus
The entire joint system provides the necessary functionality of the foot.
- Tarometatarsal - Small, flat joints with limited mobility. They form the base of the foot, with the help of ligaments in the tarsus.
- Interphalangeal - Provides immobility of the phalangeal bones.
- Subtalar - Inactive, located in the hindfoot, providing the arch of the talus and calcaneus.
- Metatarsophalangeal - A ball-and-socket joint that allows the fingers to flex and extend.
- Talocaleonavicular - Connects three bones to the axis of rotation. The foot can be rotated outward and inward.
- Ankle - A large joint connecting three bones. Forms a block between the tibia and the talus. The joint is attached to cartilage and forms ligaments on the side.
- All rotational and flexion movements of the leg occur at the expense of the ankle. The entire load while walking or running falls on the ankle joint.
The foot performs 3 functions:
- Supportive
- the ability to prevent pressure from the supporting surface. If the function is impaired, the person experiences severe pain when running or jumping. When walking, the foot performs a pushing function - accelerating movement. - Cushioning
- smoothes out shocks when walking and running. It protects joints from damage. If the arch of the foot is low, then the function is reduced, diseases of the bones, joints, and sometimes internal organs develop. - Balancing
– provides full coverage of the support surface and maintains the position of the human body when moving.
Signs of a broken finger
Symptoms vary depending on the severity of the injury and its location. When the first phalanx is fractured, the victim feels severe pain in the finger, but when the phalanx of the little finger is fractured, no pain is felt. A person may not even know about the crack; the bone heals itself without fixation or plaster.
General symptoms of toe fractures:
- Inflammation: swelling and redness of soft tissues, increased temperature at the fracture site;
- Sharp and severe pain in the finger when trying to move or when touched;
- Incorrect position of the finger bones;
- Inability to put weight on the leg, limited finger movement or immobility;
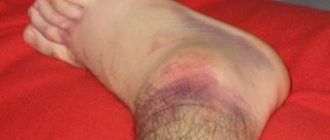
- Hematoma in the area of the damaged bone, hemorrhage, bluish skin color;
- Unnatural finger mobility;
- Positive Jacobson's sign: increased pain on palpation of the head of the metatarsal bone;
- Shortening of a finger due to a splinter fracture;
- Pronounced pulsation or twitching of the sore spot;
- An open wound with bone fragments due to an open fracture.
If little time has passed since the injury, upon physical examination of the injured foot, crunching of bone fragments is observed. This happens due to friction between the edges of the broken bones. Fractures of the finger are combined with dislocations of the phalangeal joints, sprain or damage to the ligamentous apparatus.
Ankle fixation
An ankle fracture or injury is a fairly common injury, which is manifested by a visible change in the normal shape of the ankle and the occurrence of acute unbearable pain. If a limb is damaged and the described symptoms appear, you must immediately seek medical help and undergo an x-ray examination. It is the x-ray that will help confirm or refute the likelihood of a fracture and indicate to the doctor the location of the dislocation or displacement.
If there is no fracture, the doctor places a special splint in the ankle area and securely ties it to the ankle using an elastic bandage.
An elastic bow has a number of advantages over a regular gauze bandage - it can be used repeatedly, has increased plasticity, due to which it allows you to securely fix the limb and prevent squeezing.
The elastic bandage is easily removed for additional treatment procedures - treatment of swollen areas on the leg, antiseptic treatment of the wound, application of medicinal ointments.
Sometimes a splint is applied to the ankle after a fracture - when there is no longer a need for a cast, but the joint still needs to be fixed in a certain position. The bandage fits securely to the leg, does not loosen and fixes the joint.
How to distinguish a fracture from a bruise
You can determine whether it is a finger fracture or a bruise using several parameters:
- movement;
- phalanx shape;
- hemorrhage;
- features of pain syndrome;
- skin coloring at the site of injury, swelling.
When a finger is bruised, the clinical picture is as follows:
- Severe pain occurs, which gradually subsides. At first it becomes aching, then disappears. Applying a cool compress or ice speeds up this process.
- The finger remains in its natural anatomical form, without deformation.
- At first it is impossible to move a finger; the slightest movement intensifies the pain. As the pain disappears, motor activity is restored.
- The skin color on the sore spot becomes pink or dark red, depending on the bruise. Swelling does not always appear immediately; sometimes swelling may appear after a day.
- At the site of the injury, the blood spreads diffusely, forming a bruise.
How to recognize a broken finger
The pain in the toe is severe and often radiates to nearby parts of the foot. Upon palpation, the pain intensifies and does not go away even after an hour or two.
Unnatural position of the finger, deformation of the finger phalanges.
The victim feels strong pulsation and swelling of the finger.
The patient cannot move his finger and experiences severe pain when trying to lean on his leg. To relieve symptoms, the victim fixes the finger in one position.
Swelling and hematoma appear at the fracture site, the skin becomes bluish, and hemorrhages are visible under the nail. The swelling does not subside for several weeks.
Physiotherapy
During the rehabilitation period, the following procedures are indicated:
- UHF. Used to warm tissues and enhance microcirculation. Improves metabolic and reparative processes, accelerates the formation of callus.
- Magnetotherapy. Sessions begin a few days after the injury, and the plaster cast and metal rods are not an obstacle to their implementation. The procedure enhances bone mineralization, improves calcium and phosphorus metabolism, and relieves swelling. The course consists of 10-15 sessions.
- Interference currents. Electrodes are applied to the affected area, which deliver rhythmic impulses of various frequencies (from 0 to 100 Hz). After exposure to electric current, blood circulation and tissue trophism improve, pain syndrome decreases, and lymph movement accelerates.
- Paraffin or ozokerite applications. The thermal procedure improves blood flow and accelerates bone tissue recovery. In addition, there are more than 70 nerve endings on the skin of the feet. Their irritation has a positive effect on the cardiovascular and endocrine systems.
Classification of finger fractures
The classification presents a large number of types of fractures, but only a few are important for the clinical picture.
Depending on the causes of the fault, there are:
- Traumatic (due to injury).
- Pathological (as a result of decreased bone strength).
Depending on the location of the bone fracture on the phalanx, there are:
- basic;
- average;
- nail;
- combined.
Based on the number of bone fragments, the following types of fractures are distinguished:
- Single-fragmented and double-fragmented (after a strong blow to a blunt object).
- Multi-fragmentation (the result of a strong blow to a blunt object with a bumpy surface).
- Shatterproof (as a result of excessive load on the phalanx during a fall).
There is a separate classification according to the fracture line of the phalanx:
- transverse;
- longitudinal;
- oblique;
- helical;
- S - shaped and T - shaped.
According to the nature of skin damage from debris:
- open;
- closed.
They, in turn, are divided into fractures with displacement and without displacement. Open fractures are always displaced, this is confirmed by wounds on the skin, which cannot occur without the presence of bone fragments.
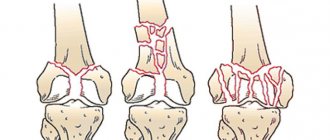
Displaced fractures are divided into the following subtypes:
Angular misalignment - More common in young children due to soft growing periosteum. The bone is damaged only on one side, the second part remains intact due to its retention by the periosteum. The fragments of the phalanx are displaced in the direction opposite to the fracture.
Longitudinal divergence of fragments - This pathology is rare; this is facilitated by problems with the ligamentous apparatus in humans.
Longitudinal entry of debris - Entry of phalanx debris is common. Nearby muscles and ligaments tighten the fragments and move them so that the broken finger becomes shorter.
Debris impaction —This type of injury accounts for one-third of all toe fractures. This is due to the fact that the pressure force during an injury coincides with the natural axis of the finger, and the neighboring joints take the entire load on themselves.
In this case, the joints of neighboring phalanges are severely injured, cracks form, and the cartilage is deformed. This type of injury is often confused with a closed fracture, without any displacement.
Rehabilitation procedures
After a toe fracture and prolonged immobilization in a cast, the foot cannot immediately fully perform all functions. The fact is that muscles become less elastic due to inactivity, and joints also cannot move as before. It takes a few days for the foot to look the same as before.
Procedures that promote a speedy recovery are as follows:
- Physiotherapy – electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, ozokerite, etc.
- Massage – tones muscles and develops joints. It can also be done at home if you have the appropriate skills.
- Physiotherapy.
Urgent Care
Help consists of relieving severe pain and treating the wound, and, if necessary, ensuring the leg remains immobile.
Procedure for providing assistance to the victim:
- Give an anesthetic (Ketorol, Ketanov, Dexalgin, Nise, Meloxicam).
- Treat the wound with any antiseptic and apply a cool compress to your finger. The compress will relieve inflammation and “freeze” the nerve endings.
- Fix the finger motionless, place cotton wool between the injured and neighboring fingers. If you are not confident in your abilities, or the injury is too serious, it is better to wait for the doctors.
- Place your foot so that it does not come into contact with the floor or objects, and do not wear any shoes.
- Ideal position: rest your foot on your heel in an elevated position - on a pillow, for example. This way the blood will not flow to the foot, the swelling will gradually subside and the pain will decrease.
- The person must be taken to the emergency room or hospital.
Treating a fracture yourself is not recommended!
Making a splint with your own hands
This fixing device can be made by hand. To do this, you need to have gauze cloth soaked in plaster and dry plaster itself. Gypsum is mixed with water in equal proportions, then after a few minutes it is checked how hard it has hardened. To do this, squeeze the material in your hands. The plaster must remain intact, not break or crumble - in this case, everything is done correctly. If the material is unstable, breaks and crumbles in your hands, and also has an unpleasant odor, then mistakes were made in its preparation.
After the solution has been made, take a bandage three meters long and cut off its edge. Such bandages are better modeled because they are more elastic. The prepared mixture is applied to a certain area of the bandage, several layers are made (4-7) and the ends are folded towards the middle. Then, using water, vigorously smooth them out with your hands. The resulting bandage is applied to the damaged limb, and small incisions are made on the protruding areas (on the heel).
Use of additional materials
When spraining ligaments and dislocating a joint, use not gauze with a bandage, but an elastic bandage with plaster. The use of an elastic bandage has a number of advantages, since it is more flexible and reusable. These characteristics contribute to the rapid healing and restoration of injuries, since the device is easily removable and allows you to treat swelling with the help of special creams and ointments. Doctors advise using a removable device with an elastic bandage only a week after the injury. If there is such a possibility, then it is better to use synthetic polymer gypsum, which does not break or crumble when hardened.
Diagnostics
Deformation of the phalanx is easy to detect during external examination of the foot. Other types of cracks and fractures cannot be detected without the help of technical means. The patient must see a traumatologist or surgeon, who will determine the exact type of injury and its statute of limitations.
To clarify the type of finger fracture, the victim will need to have a fluoroscopy of the foot in two projections. After receiving reliable examination results, the doctor will determine the type of fracture and prescribe treatment.
Prevention
To prevent a fracture, you need to follow these recommendations:
- Shoes should be comfortable and fit your feet;
- The diet should contain foods containing calcium. It is useful to eat fermented milk products, cabbage, beans, apples, etc. They will ensure normal functioning of the body;
- In addition to proper nutrition, take vitamins C, B12, D;
- Follow safety precautions in areas where there is a high risk of injury. These include sports grounds, hazardous industries;
- Regularly undergo medical examinations. They help detect chronic pathologies that can cause weakening of bones and sudden injuries.
Now you know what to do if you break your toe. If you receive a serious injury, you need to call an ambulance and subsequently follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Thanks to this, it will be possible to prevent dangerous complications and achieve rapid healing.
Treatment
After receiving the examination data and external examination, treatment is prescribed. The method and treatment regimen are selected individually, depending on the type of fracture and its location.
Plaster application
Plaster immobilization is required to maintain immobility of the phalanx. The cast is applied not only to the broken toe, but also to the entire foot. The bandage secures the top of the foot, forming a “boot.” This bandage ensures rapid fusion of bones and recovery. In some cases, plaster is not required.
For example, if a crack was discovered that can go away on its own, without any treatment. Or operations were performed on the leg that were not related to the fracture.
The main disadvantage of gypsum is loss of shape when wet, hypothermia in winter. All these factors slow down the growth of callus.
The duration of wearing a cast depends on the severity of the fracture, its type and the presence of complications. For a closed, uncomplicated fracture, plaster is applied for 2-3 weeks. Complete fusion of the bones occurs a month after the injury.
If the fracture of the finger was with numerous fragments, with displacement, then plaster immobilization lasts a month, and complete healing and recovery occurs after 2 months.
With open fractures, open reduction of the bones is required, so the person will be in a cast for about 8 weeks, and the final recovery will occur after two and a half months.
Recovery slows down if complications arise. For example, osteomyelitis. The patient will need to undergo surgery, the recovery from which will take another 30 days. This is only provided that osteomyelitis has been eliminated completely.
Another complication may be improper bone fusion. To do this, the bones are “broken” and the phalanx is re-formed. After such a reposition, recovery will take another 3-4 weeks.
Is it possible to walk “in a cast”?
During the entire period of treatment, the patient must walk on crutches or use a cane.
Based on the results of fluoroscopy and assessment of the condition of the bones of the foot, the doctor decides whether it is possible to rely on the broken limb or not.
Algorithm for applying a splint
For quick and correct restoration, this fixation device must be of the correct size. Measurements (length and width) are taken from the healthy leg. The splint should be equal to half the circumference of the limb.
In this case, the following rules should be adhered to:
- You should prepare a container for water, a bandage, and scissors in advance;
- the best immobilization occurs when 2-3 joints are captured;
- Before applying the bandage, the leg is given a comfortable position;
- during the fixation process, the leg must be motionless;
- to create comfort for the affected limb, the fixator must repeat its shape;
- in order to control the condition of the damaged area, the fingers are left open, that is, they are not bandaged;
- the bandage must harden, so it must be handled with care until it dries;
- The retainer should not be excessively tight or loose.
If lower limb injuries are not treated promptly, they can lead to serious complications. In some cases, surgical treatment is performed because manual repositioning of the bones is necessary.
Operative methods
The operation is necessary in the following cases:
- open fracture;
- comminuted fracture;
- closed with offset;
- osteomyelitis;
- incorrect fusion of fragments.
The following therapeutic methods are used:
Skeletal traction - Performed if closed reduction is not possible. Under local anesthesia, nylon threads are passed through the skin and bone fragments, which pull the fragments into the correct position. The ends of the threads form a ring that is held on a plaster hook. The patient remains in this state for 3 weeks, after which the threads are removed and the plaster is reapplied for another three weeks.
Open reduction - This is a full-fledged operation, during which bones and fragments are connected using screws and screws, plates, knitting needles, and wire. After the operation, the patient walks in a cast for another 4 weeks.
Closed one-stage reduction - Used for finger fractures without displacement of the nail phalanx. This is the setting of bones to their natural position, before injury. It is performed under anesthesia, as the procedure is painful. It is often possible to successfully set the bones only the third time. Traction devices are used for reposition. After the operation, the position and mobility of the bones are checked; if everything is in order, the foot is immobilized with a splint until complete recovery.
Removable bandage
A polymer bandage is used for fractures of the thumb, middle, finger or little finger. It keeps the finger stationary and does not interfere with everyday life. An adhesive bandage is especially indispensable for a fracture of the little toe, when there is no point in attaching a cast to the entire foot.
The bandage does not restrict a person’s movement and protects the phalanx from external influences.
What is a splint and what is it for?
The splint is a plaster-based bandage, which is secured on top with a regular bandage. Using this device, the damaged area of the leg is fixed in an anatomically correct position. It reliably protects and covers the injured segment of the leg. It is used not only for healing fractures, but also for correcting congenital pathologies of bones and joints of the legs. Correction of congenital leg pathologies is carried out in early childhood, when bone structures are just forming and can be corrected.
The splint is a removable structure, which, unlike a simple plaster cast, is very convenient because it makes it easy to carry out sanitary and hygienic procedures. People call a splint a splint.
An elastic bandage is placed on top of the plaster splint, covering the completely damaged area. For pathologies or damage to the joint, only elastic bandages are used. The bone structures are fixed with other splints.
These structures are made from different materials. There are devices called clamps that are made of plastic. It better immobilizes the limb and keeps it in the required position.
Drug therapy
Three types of medications are used in the treatment of fractures:
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- chondroprotective.
They are taken orally and topically on the painful area.
The action of the drugs provides:
- stimulation of the processes of restoration of damaged tissues;
- improvement of salt metabolism in bones (calcium-phosphorus);
- replenishment of calcium deficiency;
- elimination of inflammation.
The patient is prescribed: Chondroitin, Teraflex, Calcemin, Vitamin D3, Calcium Gluconate, Nise, Nurofen, Dexalgin. For local impact on the inflamed area: Traumeel-gel, Nise-gel, Voltaren.
The gel is applied three times a day.
Treatment depending on the type of fracture
Marginal fracture of the first phalanx of the thumb
Occurs as a result of a strong blow to the foot on a blunt object.
Treatment:
- the nail is cleaned of blood clots;
- fix the debris;
- attach the broken finger to the adjacent phalanx;
- remove the nail (if there is extensive hemorrhage).
Displaced fracture.
Therapy:
- skeletal traction;
- reposition (if several phalanges are displaced);
- plaster “boot” for 4 weeks.
Multiple fracture.
If several fingers are broken at once, a plaster plate and splint are applied.
Compression fracture of the thumb.
The joint is immobilized with knitting needles and plaster is applied for 4-8 weeks.
Fracture of the anterior phalanges without displacement.
A patch bandage is required for 2-3 weeks.
Open fracture.
Treatment:
- wound disinfection;
- tetanus vaccination;
- reposition of bone fragments;
- application of plaster.
Closed fracture with displacement.
All bone fragments are repositioned and the foot is cast.
Recovery
The rehabilitation period lasts up to two months. For the entire period, the patient must observe restrictions on exercise and movement, avoid long walks and sports.
Recommendations during the recovery period:
- exclude from the diet foods that wash calcium out of the body (coffee, carbonated and alcoholic drinks);
- eat foods rich in calcium (fish, cottage cheese, eggs, vegetables);
Visit a physiotherapy office:
- UHF lamps - to accelerate regenerative processes and metabolism - up to 15 sessions;
- Soda and salt baths - to eliminate callus after casting - up to 15 procedures;
- Applications with ozokerite or hot salt - to improve blood circulation;
- Therapeutic gymnastics for all fingers except the broken one - to prevent contracture - up to 20 sessions;
- Mechanical therapy (after casting) - to restore motility of the phalanges - 30 minutes a day, 25 sessions.
Causes
A common cause of a fracture of the little toe is a traumatic impact on the toe. Since the bone of the little finger is small and fragile, a weak impact is enough to cause a fracture.
A heavy object falling on the little toe or hitting a finger against a hard corner is quite enough to cause a fracture of the little toe.
Another common reason leading to a fracture of the phalanx of the little finger is a pathological factor. This happens when there is insufficient bone strength due to a disease, for example:
- tuberculosis;
- osteoporosis;
- the presence of tumors in the body;
- osteomyelitis, etc.
Players of team sports such as football, field hockey, and rugby often suffer a fracture of the little toe. Despite the fact that the little finger bone is small and fragile, the process of fusion takes a long period of time and requires maximum effort and patience.
Complications
Unfavorable outcomes of even minor fractures occur when assistance is not given in a timely manner, or when the patient ignores the injury (when the person did not know about the fracture, or simply left everything to chance).
Consequences of long-term nonunion or improper fusion:
- Hematoma formation;
- Deformation of the finger with impaired mobility;
- The appearance of callus;
- Deformation of the joints, their immobility, ankylosis - improper fusion of bone fragments into one fragment;
- Osteomyelitis, sepsis - after insufficient wound disinfection;
- False joints, mobility of phalanx fragments.
Gangrene is a dangerous consequence in which tissues die due to lack of blood circulation, as a result of improper fusion.
All these factors delay the rehabilitation of a person; the only way out is the destruction of incorrectly fused fragments and their new reposition. For osteomyelitis, sepsis and gangrene, therapy is tailored individually, depending on the person’s condition.
Salt baths
A moderate concentration of saline solution will help cure a foot injury. To prepare it, dissolve 1 tbsp in a liter of hot water. a spoonful of salt, it is better to take sea salt for these purposes. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and has a beneficial effect on bone tissue. The optimal water temperature is 37-38 degrees. A warm bath will warm the sore spot well and speed up recovery. After it, a positive effect occurs - the muscles relax, the sensitivity of the nerve endings decreases.
Take the salt bath for 10-15 minutes, after which you do not need to wash your feet. Pat them dry with a dry cloth and let your feet rest. To enhance the effect, decoctions of medicinal plants and fir branches are added to the water.
During the procedure, the limb must be freely located in the basin so that the person has the opportunity to move it.
Note! Salt baths are not used for open wounds, diabetes, hypertension and a tendency to blood clots.