Basically, an orbital fracture is a unilateral injury, only in approximately 5% of cases are bilateral “blowout” fractures of the lower wall of the orbit.
Orbital fractures are divided into 6 main types, but some of them contain subtypes:
- Classical. The weakest inner half of the lower wall medial to the infraorbital canal is damaged.
- With the inclusion of the infraorbital canal.
- Fracture of the lower and medial walls, the so-called inferomedial fracture.
- Total fracture of the lower wall of the orbit. This injury is usually associated with high velocity of the piercing object, resulting in complete fracture of the bone.
- Atypical types of burst fractures include rectangular, triangular, and stellate.
- Linear fractures of the lower wall without displacement of parts of the bone: Y-shaped and lateral linear.
The doctor may suspect a fracture of the orbit of the eye even when examining the patient. An accurate diagnosis is made only after receiving an x-ray.
In addition, orbital fractures are divided into grades, depending on the severity of the injury:
- A fracture with displacement of the fragments, in this case, surgery is necessary to return the bones to their original position.
- Fractures without displacement. In this case there is no facial deformation.
- Presence of cracks, without fracture or displacement of fragments.
The last type of injury is considered the easiest; it does not require surgical intervention. Conservative methods are used for treatment.
Fractures are divided into closed and open. In the first case, the injury is internal, the soft tissues are not broken and there is no contact of the bones with the environment. With an open fracture, soft tissues are damaged, such injuries are accompanied by bleeding of varying intensity.
Main symptoms of an orbital fracture
An orbital fracture is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms. First of all, this is severe swelling around the eye and hemorrhage. In addition, symptoms of injury include:
- The swelling spreads to the nose and upper cheeks, the eyelids, as well as the teeth and gums of the upper jaw are affected.
- Decreased sensitivity of different parts of the face.
- Difficulty moving the eyeballs.
- Visual impairment, which is manifested by doubling of objects. This occurs due to internal hemorrhage between the soft tissues and the periosteum.
- Enophthalmos often occurs, in which case the eyeball seems to fall inward.
- Crepitation sounds occur due to the development of subcutaneous emphysema.
In addition to these symptoms, there may be a disturbance in facial configuration. Sometimes strong asymmetry is visible.
A fracture of the upper wall of the orbit is considered less traumatic than the lower one. This is due to the fact that there is no risk of damage to the nasal bones and mucus getting into the pathological focus.
Structure
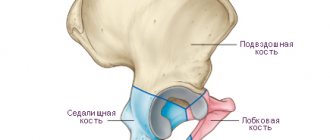
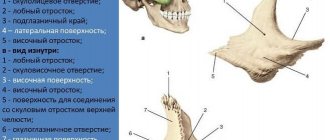
The orbit is 2 depressions in the human skull. They contain the eyes and appendage organs. The cavity is also called the orbit. Outwardly, it resembles a pyramid, which has rounded edges. Its base faces forward, and its apex is adjacent to the optic canal. The cavity contains a human eye with muscles and a salivary gland, which performs an important cleansing function. The orbital cavity consists of 4 walls. These are the upper, medial, lower, lateral: they are all saturated with numerous vessels, as well as nerve endings.
The orbit and bony orbit perform a protective function in the human body. In particular, it protects the eyes from negative external factors. The eye socket is connected to the skull. In its cavity there are many inclusions and branches: the inflammatory process occurring in it poses a danger to the brain. The cause of the pathology is usually a broken bone.
When to urgently call an ambulance
There are cases when you should not delay seeing a doctor. Delay can have serious consequences. It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance in the following cases:
- If visual functions are severely impaired.
- If there is complete or partial prolapse of the eyeball from the orbit.
- if there is swelling and hematoma of the eyelids, the palpebral fissure is greatly narrowed, and the mobility of the eyeball is too limited.
- If there is severe retraction or prolapse of the eyeball.
In addition, emergency medical care is necessary if there is a crunching sensation in the orbital area upon palpation.
Treatment
Treatment for orbital injuries depends on the severity of the fracture. For a successful recovery, the patient will need to be observed not only by a surgeon, but also by an ophthalmologist and an ENT specialist.
The goal of all medical procedures is to restore the integrity of bone tissue and return displaced fragments to their places. Treatment should correct existing vision problems, such as squinting and double vision.
For simple fractures and cracks, it is possible to do without surgery using medication and fixation of the fracture. In this case, the patient must remain completely calm and should not sneeze or blow his nose.
If the fractures are complex, displaced, and there is also a risk of vision loss and the spread of pathogenic microflora from the nasomaxillary sinuses, the victim must be operated on immediately.
Additionally, it may be necessary to correct the incorrect position of the eyeball.
If eye pressure is high, surgeons delay surgery. This choice of doctors is fraught with risks, if hemorrhage occurs, the pressure in the eye will reach a critical level. You will need to use a drainage device.
In the absence of treatment, within 2-3 weeks after the accident, the bones begin to heal incorrectly, and the wandering fragments of the lower wall are destroyed. Instead, scar tissue forms.
Diagnostics
An orbital fracture is diagnosed based on an examination of the patient, as well as on the results of an x-ray. To determine the disease, the following diagnostic techniques can be used:
- The degree and volume of mobility of the muscles of the eyeball is determined.
- An external examination of the patient is carried out to determine chemosis and soft tissue edema.
- Detection of crepitus during palpation in areas of development of internal emphysema. The degree of displacement of bone fragments, if any, is also determined.
- Neurological examination to determine the degree of sensitivity of the optic nerves.
- Determining the degree of prolapse or retraction of the eyeball.
- Biomicroscopic research method.
- Assessing the extent of traumatic injury.
When examining the orbit of the eye, foreign bodies of various types are often observed. In a third of cases, orbital injuries are combined with the development of erosion of the corneal layer.
Against the background of such fractures, there are often ruptures of the eyeball, disruption of the retina, hemorrhages and its detachment.
Causes of damage
Fractures always occur as a result of physical impact; violation of the integrity of the orbit is no exception:
- According to statistics, the majority of such injuries occur among the male part of the population, since representatives of the stronger sex receive similar injuries as a result of fights if the blow falls in the area of the eye or bridge of the nose.
- Another common source of orbital fractures is car accidents, where the impact is often on the face.
- Injuries while playing sports.
- Accidents, falls and impacts with blunt, hard objects.
First aid
In case of orbital fractures, it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible. But it also happens that the victim’s condition is very serious, and therefore it is important to be able to provide first aid:
- Quite often, with injuries of this kind, blood vessels are damaged, which leads to profuse nosebleeds. In this case, you need to make sure that the victim does not throw his head back. He should be seated comfortably or laid on his side. Turundas soaked in peroxide are inserted into the nose.
- If the injury is of a closed type, then you can apply something cold to the eye area to reduce swelling and pain. It is important to apply cold through a cotton napkin or thin towel. You can hold it for no more than 10-15 minutes.
- If the fracture is open, then before the doctor arrives, you can wash the wound with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. In this case, it is better not to use hydrogen peroxide, since this disinfectant solution will only add to the suffering of the victim.
Before doctors arrive, it is important to ensure that the patient is completely at rest. if the pain is severe, you can give painkillers, for example, Ibuprofen or Nimesulide. Afterwards, doctors must be told what exactly the sick person took.
Symptoms
Any fracture causes pain, bruising and swelling. Most of the symptoms depend on the location of the fracture.
With a fracture of the lower jaw the following are observed:
- excessive salivation;
- problems with swallowing;
- change in bite;
- change in skin color;
- jaw displacement.
With a fracture of the upper jaw, the following are possible:
- nose bleed;
- swelling under the eyes and on the eyelids;
- face stretching.
Symptoms of a broken nose may include:
- discoloration under the eyes;
- blockage of one or both nostrils or a displaced septum;
- curvature of the nose.
Symptoms of an orbital fracture:
- blurred, impaired or double vision (diplopia);
- difficulty moving your eyes left, right, up or down;
- swollen forehead or cheek or swelling under the eyes;
- sunken or bulging eyeballs;
- redness of the whites of the eyes.
Therapy
Orbital fractures require complex treatment. In each case, the treatment regimen is determined individually, taking into account the condition and age of the patient. Can be assigned:
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Symptomatic treatment to eliminate pain, bruises and swelling.
- Surgical treatment is necessary to restore the symmetry of the skull, as well as eliminate intraocular hematomas.
Injuries of this nature differ markedly in the location of the damage and their severity. At the first examination of the patient, the doctor cannot always determine whether surgical intervention is necessary or not.
Indications for surgery
There are a number of indications for the operation. The need for surgical intervention in a particular case is determined by the doctor. The main indications are:
- Visual impairment. Often, due to a fracture of the orbit, the visual organ is slightly displaced, which leads to double vision. A significant hematoma can lead to severe compression of the optic nerve and loss of vision. Bone fragments can block muscle contraction, which will ultimately lead to impaired eye movements.
- Severe disturbance of facial features. Surgery is necessary if the eye has moved lower and there is asymmetry of facial features.
- If the infraorbital nerve is compressed by a bone fragment and this causes numbness in the cheeks, lips or nose.
In addition, surgery is also necessary if the injury causes severe bleeding or the face is severely damaged.
It is advisable to perform surgery immediately after the fracture, before swelling develops. If swelling has already appeared, it is recommended to wait a few days.
Operations are divided into early ones, which are performed in the acute period, within two weeks after injury. At this time, the most optimal conditions for restoring the integrity of the damaged organ.
But the operation can also be delayed. In this case, surgery is performed two weeks after the injury, but no later than four months after the injury. Doctors call this period the gray period.
Finally, the operation may be late, several months after the injury. In this case, an osteotomy is required and the risk of complications is quite high.
The most effective treatment method is surgery. In this case, several methods are used to correct the bone tissue of the orbits and zygomatic arch. All operations are performed through small incisions, which then heal and leave no scars. This operation can be performed from one of the walls of the orbit. During the surgical intervention, extensive access to the fracture site is provided, and it is also possible to implant different types of prostheses.
If there is a foreign body in the orbit and its removal will not damage the eye, then surgery is prescribed.
Postoperative period
During the first few days after surgery, patients complain of pain. Swelling and subcutaneous bleeding appear in the operated area. Eye movements remain limited for several days, and objects may appear in two. All these symptoms disappear without a trace within a few days, but sometimes it takes a couple of weeks for complete restoration of visual functions. Sensitivity may be impaired for several months, but then everything is restored.
It is worth considering that there are contraindications for surgery to restore the bones of the orbit. This includes severe traumatic brain injury and pathologies for which any operations are strictly prohibited.
Is this injury a serious problem?
Some types of facial fractures are relatively minor, but others can cause serious harm and even be life-threatening. This is why it is important to get proper diagnosis and treatment before serious complications can arise.
The facial nerves and muscles responsible for sensation, facial expressions, and eye movements are located near the bones of the face. In close proximity is the brain and central nervous system (CNS). Facial fractures can cause damage to cranial nerves, depending on the specific type and location of the fracture. Fractures of the orbital bone (eye socket) can cause vision problems. Nasal fractures can make it difficult to breathe or smell. In addition, jaw bone fractures can cause breathing problems or make it difficult to eat and speak.
If a facial bone injury occurs, the victim should immediately seek medical help.
Rehabilitation
After the operation, a computed tomography is performed to evaluate the control of the result of the operation. For several months, the patient is registered with a surgeon and an ophthalmologist; these doctors examine the patient several times a month.
With a timely operation and a smooth course of the postoperative period, swelling begins to subside within 3-4 days. And after a week, only small traces of hematomas will remain.
Rehabilitation is entirely aimed at restoring visual function. Patients are advised to make special eye movements and also avoid nasal congestion. During the recovery period, you should carefully blow your nose and sneeze. It is important to avoid increased pressure in the nasal area.
Risks
Treatment for a facial bone fracture may result in swelling, pain, bruising, bleeding, and infection. Scars may remain after surgery. Treatment may damage nearby tissue and nerves, causing numbness. During the operation, the sinuses may be damaged. Even with surgical intervention, it is possible to maintain facial asymmetry and vision changes. The bone and tissue grafts may move out of place, requiring another operation. The plates and screws used to secure bones may become infected or need to be replaced. There is also a risk of blood clots.
The consequences of facial bone fractures without treatment can be facial asymmetry, pain in the face, eyes, or blindness. Bleeding can block the airway, making breathing difficult. Bleeding in the brain is also possible, which can lead to seizures and be life-threatening.
Advantages of Ikhilov Complex
- The clinic's doctors are traditionally highly qualified. Each specialist has undergone long-term specialization and has unique experience in surgical reconstruction of ocular orbital structures.
- Accelerated diagnostics using modern tomographs.
- A wide range of methods for surgical reconstruction of damaged bone tissue of the orbit, including using minimally invasive access, natural and artificial implants.
- A personal translator-curator for each patient, a comfortable atmosphere in the ward, an invariably attentive and friendly attitude from the medical staff.
Enter your contact information, we will call you back and sign you up at the Ikhilov Complex!
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)