Why surgery is needed
The use of various fixing elements (wires, plates, pins, screws) can reduce recovery time and improve the outcome of fracture treatment. The braces provide the patient with mobility and maintain activity during the treatment period. In some cases, such structures are not removed even after complete healing, for example, if their removal will lead to bone deformation or re-fracture. But in most cases, after the clamps have served their purpose, they need to be removed. This can only be done surgically.
3. Disadvantages and contraindications
Many sources indicate that a common disadvantage of all metal osteosynthetic methods, including those involving the use of perpendicular wires, is the need to remove them, i.e. repeated intervention with all the ensuing risks. However, this can only be called a disadvantage with a certain stretch. The fact is that in terms of technical complexity and invasiveness (the volume of intervention, its traumatic nature), removal of a wire cannot be compared with the initial operation of bone reposition, restoration of normal anatomy and installation of implants (whether wires, intraosseous pins or bone plates). Moreover, fixatives made from biocompatible materials do not need to be removed at all - such a procedure is mandatory only for young and mature patients in order to completely eliminate even the hypothetical possibility of complications and side effects in the future. In some cases, the edges of the fixing needle are not outside, but under the skin; the question of removing it or leaving it in place is, generally speaking, debatable, and in each case is decided according to strictly individual indications, taking into account many existing circumstances and factors.
Finally, it should be noted that sufficiently durable self-resorbable (biosoluble, biodegradable) materials are already being successfully used today, which, probably in the future, will completely replace metals in osteosynthesis. Ultrasonic osteosynthesis is also considered a promising alternative.
Contraindications to metal osteosynthesis, incl. transosseous compression-distraction, relatively few: severe somatic condition of the patient, lesions of the central nervous system with convulsive syndrome, severe circulatory disorders in the extremities, osteoporosis (confirmed by a special diagnostic study, a tendency to thinning, structural changes and progressive fragility of bone tissue), as well as a large wound area with open fractures, especially with intense contamination and/or infection.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Benefits of Retainer Removal at GMS Clinic
The Center for Surgical Traumatology/Orthopedics at GMS Hospital specializes in such operations. Removal of fixators after osteosynthesis in our clinic is performed by experienced orthopedic traumatologists with extensive practical experience. The use of the latest approaches to the procedure provides the following advantages:
- minimal surgical trauma;
- mild pain syndrome;
- no complications;
- short rehabilitation period;
- complete restoration of functionality of the injured area.
The decision to operate is made by a specialist based on a comprehensive examination. Before deciding to remove the fixation elements, the orthopedic surgeon analyzes the risks and the likelihood of possible complications.
Make an appointment with a traumatologist-orthopedist at the GMS clinic. Experienced specialists will quickly carry out the necessary diagnostics, analyze the situation and prescribe surgical intervention. Thanks to the use of modern equipment and microsurgical techniques, the removal of any pins will take place without complications, and rehabilitation will be short.
Cost of removing retainers (wires, plates, pins, screws)
The prices indicated in the price list may differ from the actual prices. Please check the current cost by calling +7 495 104 8605 (24 hours a day) or at the GMS Hospital clinic at the address: Moscow, st. Kalanchevskaya, 45.
| Name | Price |
| Removal of single pins and screws from the upper limb - from large segments | RUB 29,820 |
| Removal of the intramedullary telescopic rod | RUB 158,928 |
| Removal of metal clamps from the upper limb - from large segments | RUR 79,464 |
| Removal of metal clamps from the upper limb - from small segments (wrist joint, hand) | RUR 79,464 |
| Removal of metal clamps from the lower limb - from large segments | RUR 79,464 |
| Removal of metal clamps from the lower limb - from small segments (foot, ankle) | RUR 79,464 |
Dear Clients! Each case is individual and the final cost of your treatment can only be found out after an in-person visit to a GMS Hospital doctor. Prices for the most popular services are indicated with a 30% discount, which is valid when paying in cash or by credit card. You can be served under a VHI policy, pay separately for each visit, sign an agreement for an annual medical program, or make a deposit and receive services at a discount. On weekends and holidays, the clinic reserves the right to charge additional payments according to the current price list. Services are provided on the basis of a concluded contract.
Plastic cards MasterCard, VISA, Maestro, MIR are accepted for payment. Contactless payment with Apple Pay, Google Pay and Android Pay cards is also available.
100% sterile
Fast healing and short rehabilitation period
Minimal trauma to surrounding tissues
Modern medical equipment and advanced diagnostic and treatment methods
Make an appointment We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Oksana
What indications to use
There are absolute and relative indications for the removal of fixing structures. The absolute ones are:
- planned removal of fixators after complete and correct bone fusion;
- infection of the fracture area - in these cases, the structure is removed, since it will only interfere with the fight against infection and will not allow the wound to heal quickly;
- individual intolerance to any component of the alloy from which the fixing elements are made;
- loosening of the structure or breakage of an element;
- unstable fixation of the bone with the formation of a false joint;
- the fixing element is the cause of a complication or development of a concomitant disease;
- surgical intervention is required in the area of the fracture, and the metal structure interferes with this;
- the retainer interferes with normal bone growth (in children and adolescents);
- the metal structure can cause injury, since the patient’s life is associated with high mobility (athlete, stuntman, circus performer, etc.);
- questionable quality of implants.
Relative indications for such manipulation as removal of fixing pins and other structures include psychological and physical discomfort caused by the metal structure.
Fixing elements are not removed in elderly, weakened patients, especially those suffering from various chronic pathologies (hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, etc.). It is impossible to remove structures in the pelvic area, on the anterior side of the spine and in the area of the shoulder joint if the radial nerve was isolated when installing the fixator. If there are pustular rashes or inflammatory processes on the skin in the area of the fracture, surgery is performed only after preliminary treatment.
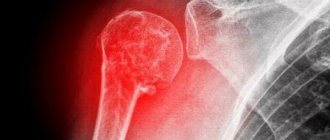
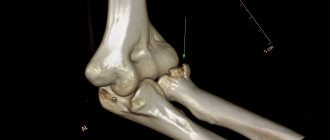
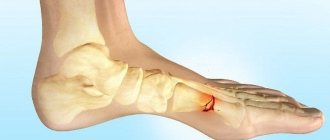
Osteosynthesis for ankle fracture
An ankle fracture is a very common leg injury.
It occurs more often than others because the bone in the ankle area is thinner and more often subject to mechanical stress. In case of such damage, contact a traumatologist to perform osteosynthesis surgery. Osteosynthesis is a surgical procedure in which a broken bone is fixed with a titanium plate or screws for an ankle fracture . It is performed for displaced fractures. When starting treatment, fixation is attempted using the method of closed reduction (in the case of a closed fracture). Surgical intervention is indicated in the presence of an open fracture, after two unsuccessful attempts at closed reduction, secondary displacement of bone fragments, ingrowth of soft tissue into the space between the fragments, in case of improper bone fusion or complete absence of fusion. These are the main reasons why plates are placed on the bones after an ankle fracture .
Preparation, diagnostics
Before the operation, you will need to undergo a comprehensive examination, the purpose of which is to identify contraindications to the procedure and check your general health. The examination includes:
- examination by a traumatologist-orthopedist;
- radiography of the fracture area in different projections;
- blood tests (general, biochemical, hospital infections, coagulation, blood group and Rh factor), urine;
- electrocardiogram;
- fluorography;
- consultation with an anesthesiologist.
In some cases, additional research may be required. A week before the intervention, you must give up alcohol and limit smoking. On the day of surgery, do not eat, drink or chew gum.
How is the operation performed?
As a rule, fixators are removed 8–12 months after osteosynthesis. The operation is performed under local, regional or general anesthesia. In most cases, removal of fixing screws is less traumatic than bone osteosynthesis and can be performed without long-term hospitalization of the patient. Access, surgical tactics and volume of intervention are determined by the location and type of structure. The surgeon excises the surgical scar, separates the underlying tissue, releases the fixatives from the scar adhesions and removes them.
The doctor sutures and drains the wound layer by layer and applies a sterile bandage. The sutures are removed at 10-12 days. When the needles are located externally, they are mechanically removed with special instruments, without deep dissection of the skin and soft tissues. To prevent the development of infectious complications, a short course of antibiotic therapy is prescribed. The duration of the operation is on average 30 minutes. The Department of Surgical Traumatology/Orthopedics of the GMS Clinic performs removal of all types of metal structures.
You have questions? We will be happy to answer any questions Coordinator Tatyana
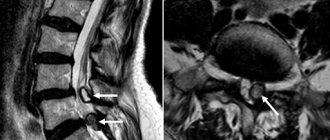
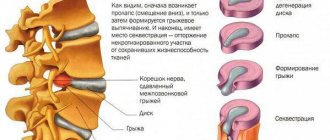
2. Indications and essence of the operation
PCDO is used for double fractures of paired bones, in the presence of fragments (and corresponding reposition, i.e. “reassembling the bone”), for fractures of the patella, clavicle, olecranon, and in other cases when plaster immobilization is not effective and reliable enough. Compression-distraction osteosynthesis makes it possible to fix fractures not only in “conventional” orthopedic traumatology (limb fractures), but also in such a complex and responsible area as, say, maxillofacial surgery.
The essence of the method is that one or more metal knitting needles are inserted into the bone, perpendicular to its longitudinal axis, tensioned and secured with a threaded connection from the outside. The foundations of the methodology were not laid by academician G.A. Ilizarov, as many people think, but by the German surgeon M. Kirchner, who at the beginning of the twentieth century developed the tactics of passing the bone with a drill, and the design of the external bracket, and the tension system. The implant used still bears his name (“Kirchner wire”) and has many advantages over a slightly earlier Swiss invention (“Steinmann nail”). As for the legendary Ilizarov dynamic compression-distraction apparatus, universal and applicable in a wide variety of situations and modifications, this idea was truly brilliant (and far from the only one of this outstanding specialist).
It received worldwide recognition and provided a revolutionary breakthrough not only in domestic but also in world orthopedics.
Visit our General Surgery page